What Is Chronic Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. In chronic hepatitis, liver inflammation continues for at least six months. This condition may be mild, causing relatively little damage, or more serious, causing many liver cells to be destroyed. Some cases lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis from infection is most often caused by these viruses:
- Hepatitis B and C. Often the person infected is unaware of any initial symptoms. Or the symptoms were so mild that the person did not seek medical attention. This is especially true for chronic hepatitis C. Over time, perhaps a decade or more, both types may lead to the serious complication of cirrhosis due to ongoing destruction of liver cells and resultant scarring. A minority of patients with cirrhosis develop liver cancer over time.
- Hepatitis D. Hepatitis D infects only patients already infected with hepatitis B, and it generally results in a flare of active hepatitis.
This information helps to determine the best treatment and to assess your risk of developing cirrhosis and liver failure. A liver biopsy also can help to check for other disorders, such as alcoholic liver injury or fatty liver.
Awareness Prevention And Early Diagnosis Are Essential
There’s a good reason why hepatitis C is known as a “silent killer.”
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, an estimated 3.2 million Americans live with chronic hepatitis C infection, which is transmitted through infected bodily fluids like blood and semen, and causes inflammation of the liver. Yet up to 75% of people who have hepatitis C aren’t aware they have it.
Most of those living with the virus experience only mild symptoms or don’t have any symptoms at all until they develop serious liver damage or another life-threatening liver disease. Unfortunately, that means they aren’t getting diagnosed and treatment is delayed until the later stages when irreversible liver damage has occurred.
Here, hepatologistNancy Reau, MD, associate director of the Solid Organ Transplant Program at Rush University Medical Center, explains who is at risk for hepatitis C and offers advice to help you protect yourself.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
The new hepatitis C medicines have not been tested in pregnancy.
You should not become pregnant while taking treatment as it could be harmful to unborn babies.
If you’re pregnant, you must delay treatment until after your baby is born.
Speak to your doctor before starting hepatitis C treatment if you’re planning to become pregnant in the near future.
You’ll need to wait several weeks after treatment has ended before trying to get pregnant.
Women taking ribavirin should use contraception during treatment and for another 4 months after the end of treatment.
Men taking ribavirin should use a condom during treatment and for another 7 months after the end of treatment. This is because semen can contain ribavirin.
If you become pregnant during treatment, speak to your doctor as soon as possible to discuss your treatment options.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Hepatitis A
How Does Hepatitis C Progress
When someone is first infected with hepatitis C, most likely they have no symptoms and are unaware. Occasionally people experience fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness or sometimes having a yellow color in their skin or eyes. Although having any symptoms at all is rare, if they do occur, they usually go away within a few weeks.
Around 15-25% of people who are infected will spontaneously fight off the virus on their own and they will not have a chronic hepatitis C infection and no long term damage occurs.
But around 75-85% of people will develop chronic infection. Most of the time, people with chronic hepatitis C have no symptoms at the time of infection and no symptoms for years or even decades of chronic infection. The virus will be with them until they are successfully treated with hepatitis C medications.
Around 10-20% of people with chronic infection will slowly have gradual damage in the liver over years and will eventually develop cirrhosis . This can take 20 years or more from the time of the initial infection.
Cirrhosis is the replacement of liver cells with permanent scar tissue. Cirrhosis can lead to problems such as bleeding from veins in the esophagus, fluid buildup in the belly, and damaged brain function.Approximately 15% of people with cirrhosis will develop liver cancer during their lifetime. Drinking excessively can double the chance of liver cancer in people infected with HCV.
If I Have Hepatitis C Infection Does This Mean I Am Going To Have Other Health Problems
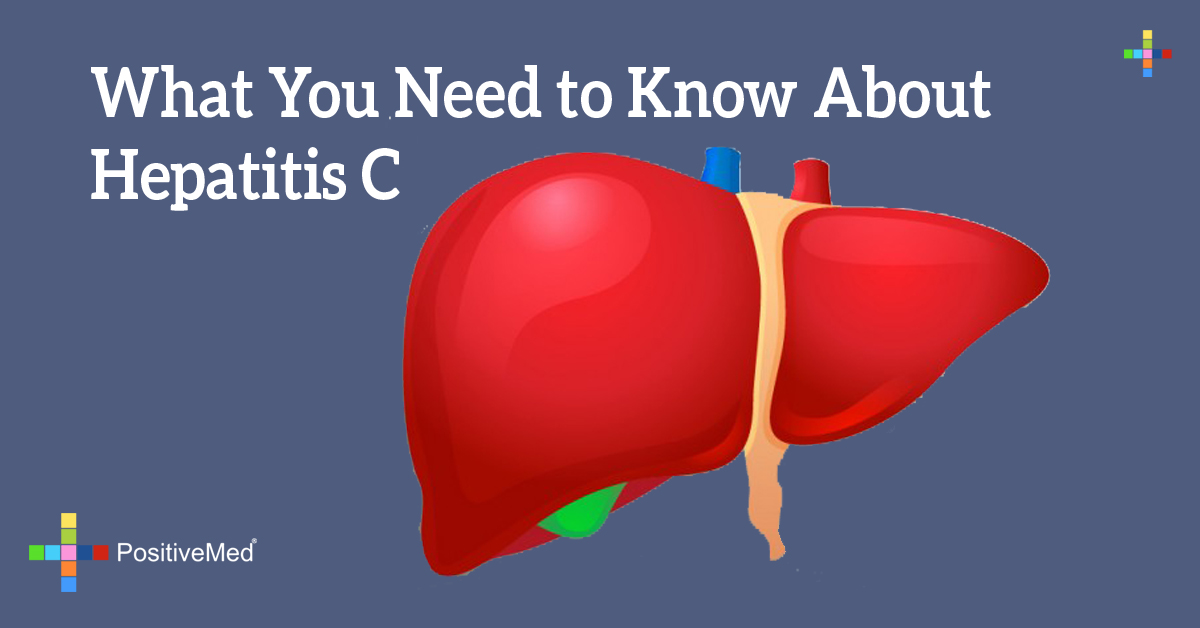
Hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Other conditions have also been linked to hepatitis C and are known as extra-hepatic manifestations of hepatitis C. They include diabetes mellitus, arthritis, hypothyroid, and aplastic anemia among other conditions. Talk to your provider for more information.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis C Now
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Can A Transplant Cure Hepatitis C
If you develop chronic hepatitis C and it leads to liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is one of the most common reasons for a liver transplant.
A liver transplant removes a damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy one. However, theres a high likelihood that the hepatitis C virus will be transmitted to the new liver in time.
The virus lives in your bloodstream, not just your liver. Removing your liver wont cure the disease.
If you have active hepatitis C, continued damage to your new liver is very likely, especially if hepatitis C remains untreated.
Read Also: Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Cured
The Path To A Cure For Hepatitis C In People With Hiv
Hepatitis C can be a chronic condition that leads to liver failure, and treatments often havent worked for patients who are also co-infected with HIV. Thanks to research led by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Gilead Sciences, new therapies are now available that can cure even complicated cases of hepatitis C without serious side effects. Read on to learn how these discoveries were made and what they mean for patients around the world.
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a liver disease that, if left untreated, can lead to liver scarring , liver cancer, and eventual liver failure. Roughly 400,000 people in the United States and 5 million globally are infected with both hepatitis C virus and HIV. People with HCV-HIV co-infection are three times more likely to develop cirrhosis or advanced liver disease than people infected with HCV alone, and hepatitis C is a leading cause of death for people with HCV-HIV co-infection.Some people who get hepatitis C virus have it for a short time and then get better on their own. This is called acute hepatitis C. But most peopleabout 75 to 85 percentwill go on to develop chronic, or long-term, hepatitis C, meaning the virus requires treatment.
Older Treatment Regimen Cured Few
First Steps toward a Viable Cure
NIH Study Aims for a Better Cure
Curing the Toughest Cases
Looking to the Future
Treatment Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is treated with antiviral medications that aim to clear the virus from your body.
New all-tablet treatments have greatly improved the outcomes for people with hepatitis C. These treatments can cure more than 95% of individuals with chronic hepatitis C. There are several new tablets that are used in combination to treat all hepatitis C strains . They are effective for people with no liver damage and those who have more advanced liver damage or cirrhosis.
These new tablet medications are available and subsidised on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme, and can be prescribed by specialists, general practitioners and specialised nurse practitioners.
There are no restrictions on accessing treatment it is available for all adults with a Medicare card. People under 18 are able to access treatment and it is recommended they are referred to a pediatrician experienced in the treatment of hepatitis C.
For more information on the new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C, see our video: Hepatitis C Cure what it means for Victorians.
If your doctor does not know about the new treatments, you can call the LiverLine on for information, and to find a GP who can help you.
Talk with your doctor about treatment options and the potential for interactions with other medications, herbal preparations and other drugs. If you take prescribed medication this will be managed so you can access treatment.
In general, if you have hepatitis C you will feel better if you:
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Mayo Clinic
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
- Do I need treatment?
- What treatment is best for me?
- What medicines should I take?
- Are there any medicines I should avoid?
- How can I cope with the side effects of treatment?
- Is there a therapist I can talk to?
- How long will my treatment last?
- Can hepatitis C be cured?
- Are organ transplants and blood transfusions safe?
- Is it safe for me to get pregnant?
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surf Ab Quant
Hepatitis C Symptoms & Treatment
FAST FACTS:
-
Hepatitis C is found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
-
Hepatitis C is mainly passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or sharing other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
-
You can prevent hepatitis C by never sharing needles and syringes, practising safer sex, and avoiding unlicensed tattoo parlours and acupuncturists.
-
Hepatitis C will often not have any noticeable symptoms, but a simple blood test carried out by a healthcare professional will show whether you have hepatitis C.
-
In the early stages, some peoples bodies can clear a hepatitis C infection on their own, others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection.
-
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can lead to permanent liver damage.
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver.
Its mainly passed on through contaminated needles, either from injecting drugs or from needle stick injuries in healthcare settings. It can also be transmitted sexually, especially during anal sex or other types of sex that may involve blood.
Some groups are more at risk of getting hepatitis C than others, including people who use drugs, people in prisons, men who have sex with men, health workers and people living with HIV.
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Is There Now A Cure For Hepatitis C
How Effective Is Treatment
Direct acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Acute Hepatitis C Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute and chronic hepatitis C are caused by the same virus.
Acute hepatitis C develops after initial infection with the HCV. This stage can last up to 6 months. Many people have no symptoms during the acute stage and never find out that they have the infection.
According to the CDC, of people with acute hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C.
The World Health Organization states that 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. This means that the virus goes away even though it hasnt been treated.
The 55 to 85 percent of people who dont clear the virus will develop a chronic HCV infection.
Chronic hepatitis C can be managed with medications and even cured, but its still a serious condition. According to the CDC,
You May Like: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
A Revolution In Hep C Treatment
More than 3 million Americans have a long-lasting hepatitis C infection. Most donât know it, because there usually aren’t symptoms.
Sofosbuvir was one of the first direct-acting antivirals to target hep C,the viru a disease spread through direct blood-to-blood contact. DAAs work in different ways to stop hep C from making copies of itself.
These drugs are kinder and gentler than the old standard of care — interferon shots and ribavirin alone. That route could take as long as a year, it only cured about half of the people, and the side effects were brutal.
âImagine taking an injection and a pill that made you feel — every day — worse than you ever felt from the infection that was being treated,â says Alexea Gaffney-Adams, MD, an infectious disease specialist in Smithtown, NY.
Side effects included flu-like symptoms, joint pain, anemia, and depression.
Limes says the old treatment felt like pouring gasoline into his system. âIt was like killing me to keep me alive.â In fact, it made his hep C worse, so his doctors took him off it.
Todayâs therapies are pills only and donât need interferon. They have very few side effects and double the cure rate — to 90% to 100%. They work in as little as 8 or 12 weeks.
âMy who had been on the older regimens — and failed, and now have the luck of being able to experience these new medications — canât believe the difference,â says Gaffney-Adams.
Hepatitis C Alcohol And Alcoholic Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver. Several things can lead to the condition one major cause is hepatitis C, which can result from a viral infection. Another is alcohol consumption, which can cause alcoholic hepatitis.
These two types of hepatitis are separate conditions. However, alcohol consumption and the hepatitis C virus also have associations with one another.
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism , HCV infection appears to be more prevalent among people with alcohol abuse disorder. Consuming alcohol also worsens HCV and can interfere with its treatment.
Keep reading to learn more about the association between hepatitis C and alcohol, as well as symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic hepatitis.
No, it is not possible to get hepatitis C from alcohol. This condition results from a viral infection, which a person can only contract if they have exposure to blood containing HCV.
However, excessive alcohol consumption may raise the risk of acquiring HCV. According to the NIAAA , research from the 1990s found that people with alcohol abuse disorder had higher rates of HCV than the control group. This was true even for individuals with no other HCV risk factors.
Scientists are not sure why HCV is more common in those who consume excess alcohol. However, some believe alcohol makes it easier for the virus to enter and remain inside the body.
Read Also: How Contagious Is Hepatitis B
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
What Is A Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical procedure. A tiny piece of liver is removed and examined to find out the extent of damage. It involves a large needle and local anesthetic, as well as some risk of bleeding. A pathologist looks at the piece of liver under microscopes to determine how much damage has occurred in the liver. This is a very useful test and used to be done very commonly. However, the procedure is done much less frequently than in the past. For most patients with hepatitis B and C, liver biopsy is not required. Today, other tests can be used to try to estimate the fibrosis in the liver.
Also Check: Vaccine Available For Hepatitis B