Lifestyle And Dietary Changes
While once considered appropriate in the management of HE, it is now understood that dietary protein restriction is not recommended. A detailed assessment of nutrition status with specific recommendations based on individual circumstances is often warranted, and should be discussed with your health care provider.
Avoidance of all alcohol, if not already achieved, is of utmost importance. All medications, including but not limited to over the counter agents that may have a sedative effect, should be reviewed by your health care provider.
An individual diagnosed with or suspected to be experiencing HE should not operate a motor vehicle or heavy machinery.
Laboratory Abnormalities In Hepatic Encephalopathy
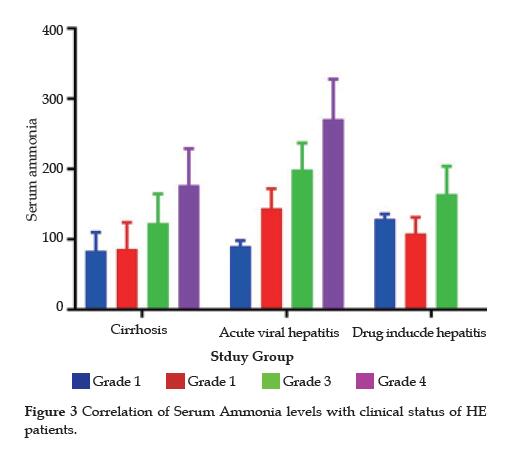
An elevated blood ammonia level is the classic laboratory abnormality reported in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. This finding may aid in correctly diagnosing patients with cirrhosis who present with altered mental status. However, serial ammonia measurements are inferior to clinical assessment in gauging improvement or deterioration in a patient under therapy for hepatic encephalopathy. Checking the ammonia level in a patient with cirrhosis who does not have hepatic encephalopathy has no utility. Only arterial or free venous blood specimens must be assayed when checking the ammonia level. Blood drawn from an extremity to which a tourniquet has been applied may provide a falsely elevated ammonia level when analyzed.
Classic EEG changes associated with hepatic encephalopathy are high-amplitude low-frequency waves and triphasic waves. However, these findings are not specific for hepatic encephalopathy. When seizure activity must be ruled out, an EEG may be helpful in the initial workup of a patient with cirrhosis and altered mental status.
Visual evoked responses also demonstrate classic patterns associated with hepatic encephalopathy. However, this test is not in common clinical use.
What Are The Long Term Effects Of Ammonia
OSHA says there are no long term effects from exposure to ammonia, but the ATSDR says that repeated exposure to ammonia may cause chronic irritation of the respiratory tract. Chronic cough, asthma and lung fibrosis have been reported. Chronic irritation of the eye membranes and dermatitis have also been reported.
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis C An Std
Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Symptoms are those of impaired brain function, especially reduced alertness and confusion. In the earliest stages, subtle changes appear in logical thinking, personality, and behavior. The person’s mood may change, and judgment may be impaired. Normal sleep patterns may be disturbed. People may become depressed, anxious, or irritable. They may have trouble concentrating.
At any stage of encephalopathy, the person’s breath may have a musty sweet odor.
As the disorder progresses, people cannot hold their hands steady when they stretch out their arms, resulting in a crude flapping motion of the hands . Their muscles may jerk involuntarily or after people are exposed to a sudden noise, light, a movement, or another stimulus. This jerking is called myoclonus Myoclonus Myoclonus refers to quick, lightning-like jerks of a muscle or a group of muscles. Myoclonus may occur normally … read more . Also, people usually become drowsy and confused, and movements and speech become sluggish. Disorientation is common. Less often, people with encephalopathy become agitated and excited. Eventually, as liver function continues to deteriorate, they may lose consciousness and lapse into a coma. Coma often leads to death, despite treatment.
What Medication Is Given To Reduce Ammonia Levels
Lactulose is also used to reduce the amount of ammonia in the blood of patients with liver disease. It works by drawing ammonia from the blood into the colon where it is removed from the body. This medication is sometimes prescribed for other uses ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B And C
Nutritional Support & Gut Access
- Intubated patients with hepatic encephalopathy should receive enteral nutrition just like any other intubated patient.
- Recent guidelines don’t recommend restricting protein intake among these patients.
empiric thiamine for Wernicke’s encephalopathy in alcoholism
- Patients with alcoholism and cirrhosis may be at risk for Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
- Differentiation of Wernicke’s encephalopathy from hepatic encephalopathy is basically impossible.
- There are no lab tests capable of doing this promptly.
- Physical examination signs of Wernicke’s encephalopathy may be absent in a comatose patient.
place a small-bore nasal feeding tube prior to extubation
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
12 November 2022
Jason B. Gibbons, Edward C. Norton, Robert D. Gibbons
29 August 2022
Alexandre Balaphas, Kyriaki Gkoufa, Christian Toso
22 September 2022
Evan Xu, Yan Xie & Ziyad Al-Aly
volume 10, Article number: 16970
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C Again
Agents Targeted To Key Pro
There might also be hypothetical benefits to utilizing agents that abrogate the augmented inflammatory state, particularly in ALF as shown for example by Chastre and colleagues in a mouse model of ALF whereby they utilized etanercept, a TNF- neutralizing antibody, to abrogate the onset of hepatic coma.63 However, the proinflammatory response which develops as a consequence of acute liver injury is vital in initiating liver repair and regeneration and it may be detrimental to use agents targeted to key proinflammatory mediators. Moreover, as functional immunoparesis is a consistent finding in patients with ALF and CLF,94,118,119 this could be detrimental rendering patients susceptible to bacterial and fungal infection. However, novel strategies that target ammonia-induced neutrophil dysfunction would be of particular interest to explore such as modulators of p38-Mitogen Activated Phosphokinase95 and TLR-9.97
Minimal Or Subclinical Encephalopathy
Patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy have a normal neurological examination however they may still be symptomatic. Symptoms relate to disturbances in sleep, memory, attention, concentration and other areas of cognition. A classic sign of HE is a sleep disturbance. On a sleep questionnaire, disturbance is seen in 47% of cirrhotics compared with 4.5% of controls. A higher frequency of sleep disturbance in cirrhotic patients with MHE has been confirmed in studies using health-related quality of life questionnaires. Sleep disturbance in cirrhosis is not associated with cognitive impairment thus it may not truly be an MHE symptom. Unsatisfactory sleep is associated with higher scores for depression and anxiety, raising the possibility that the effects of chronic disease may underlie the pathogenesis of sleep disturbance. Disturbances in cirrhotics may also be related to abnormalities of circadian rhythm.
Defective memory may be a sign of MHE. Patients with MHE have impaired short- and long-term memory. This impairment is predominantly related to deficits in attention and visual perception. Memory deficit of MHE seems to comprise short-term but not long-term memory impairment. This can be described as an encoding defect, in which memory recall is intact.
Several cognitive statements and/or complaints, have predictive value for MHE, including impaired psychomotor performance impaired sleep or rest decreased attention and poor memory .
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Acute Hepatic Porphyria
What Is Considered A High Level
When ammonia levels are equal to or higher than 55µmol/L, there is a problem. It is at this point that doctors begin to check for possible signs of H.E, as well as other possible disorders.
However, there are a few things to consider when it comes to testing for ammonia levels. Multiple factors can affect how accurate the evaluation will be. For instance, if you clench your fist while they are drawing out your blood, it could falsely raise your ammonia levels. The same happens if the technician uses a tourniquet.
Aside from that, timing is also very important. Your ammonia levels depend on what time the laboratory processes your blood sample. They may get inaccurate if they do not immediately place your blood sample on ice. More so, they must centrifuge it within fifteen minutes to get accurate results.
Now, even if they collect and process your blood sample properly, there are still concerns about how much correlation there is between H.E and ammonia levels.
A study checked out how sensitive and specific ammonia levels of 55µmol/L and above are for diagnosing H.E. The researchers found that that toxic level is only about 47 percent sensitive and about 78 percent specific.
The chance that a positive prediction from ammonia levels is indeed positive is 77.3 percent. But then, the chance that a negative prediction from ammonia levels is indeed negative is 48.6 percent. This gives ammonia levels a general diagnostic accuracy of about 59 percent.
Treatments To Increase Ammonia Clearance
Zinc. Low zinc concentrations are common in patients with cirrhosis of the liver, particularly those with HE. Even in patients who are not zinc deficient. Patients with fulminant hepatic failure and subacute hepatic failure have also been shown to have low serum zinc levels. Zinc deficiency also leads to alteration of neurotransmitters like GABA and norepinephrine. Zinc supplementation has been tried in HE. It may have a role in mild chronic HE, though further trials are necessary.
Unequivocal evidence of benefit of oral zinc therapy for treatment of acute HE is lacking. Zinc sulfate and zinc acetate have been used at a dose of 600 mg orally every day in clinical trials. HE improved in two studies there was no improvement in mental function in two other studies. However, an interesting study from Japan in 2010 showed zinc supplementation significantly improved patients’ quality of life, as it improved the physical component scale but not the mental component scale. Zinc supplementation also significantly decreased HE grade and blood ammonia levels and improved Child-Pugh score and neuropsychological tests compared with standard therapy. Interestingly this study showed as well administration of zinc in combination with L-carnosine showed to enhance intestinal barrier and improve zinc plasma levels.
Some examples for probiotics available in USA that contains same species that showed some effect for HE include :
| Drug |
|---|
Don’t Miss: How Long Can Someone Live With Hepatitis B
Brain Aqp4 And Ammonia Toxicity After Liver Failure
In addition to the above mentioned signaling pathways, increased plasma membrane AQP4 levels were observed after exposure of cultured astrocytes to ammonia or treatment of mice or rats with the liver toxin, thioacetamide .56,57,83 The authors further reported that treatment of mice with TAA that had received whole body AQP4 knock-down, exhibited a reduction in brain edema as compared to the effect of TAA alone.57 These findings strongly suggest that increased plasma membrane AQP4 also contributes to the astrocyte swelling/brain edema in AHE. However, in contrast to the findings by Rama Rao et al.,56,57,83 Jalan et al., and Butterworth et al. have shown decreased plasma membrane AQP4 post-ALF.84,85 Noteworthy, the latter research group also showed increased plasma membrane AQP4 levels in patients who subsequently died with AHE.86 The reason for these contradictory findings are unclear.
Reversibility Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Classically, hepatic encephalopathy was regarded as a reversible condition. Patients appeared to improve with either drug therapy or liver transplantation. However, a recent study assessed cirrhotic patients who had apparently recovered from an episode of overt hepatic encephalopathy. After careful psychometric testing, it was discovered that these clinically improved patients had residual cognitive impairment compared with cirrhotic patients with either minimal hepatic encephalopathy or no encephalopathy.
In 2009, Sotil et al evaluated 39 patients who had undergone liver transplantation about 1.5 years before the study. The 25 patients who had hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation, on the whole, performed worse on psychometric testing than the 14 patients with no history of overt encephalopathy prior to transplantation.
In 2011, Garcia-Martinez et al assessed the cognitive function in 52 patients who had undergone liver transplantation. Global cognitive function after transplantation was worse in patients with a history of alcohol-induced cirrhosis, patients with diabetes, and patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation. Furthermore, the brain volume after transplantation was smaller in patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation than in patients with no overt encephalopathy. These are provocative findings that require additional investigation.
You May Like: How Does Someone Get Hepatitis B
Avoid Sedating Medications Like The Plague
avoid sedating medications!
- Patients with hepatic encephalopathy are often exquisitely sensitive to sedating medications .
- For an intubated patient with hepatic encephalopathy, it is best to avoid any sedative or analgesic, except agents with extremely short half-lives .
- Even small doses of a long-acting sedative may delay extubation.
- One trick to facilitate extubation is to allow all other sedating medications to wash out of the patient.
- Patients who are comatose due to hepatic encephalopathy are usually very sensitive to sedation, so they often don’t require much propofol to achieve comfort .
History Signs And Symptoms
Patients with HE usually have advanced chronic liver disease and thus have many of the physical and laboratory stigmata associated with severe hepatic dysfunction.
| The history may reveal a precipitating cause. These include: |
|---|
| Hypovolemia |
| Infection |
| Rarely, hepatocellular carcinoma and/or vascular occlusion |
Disturbance in the diurnal sleep pattern is common, and typically precedes overt neurologic signs. More advanced neurologic features include bradykinesia, asterixis . Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes are common seizures and hallucinations and transient decerebrate posturing may also be seen occasionally.
Also Check: Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent And Without Comma
Study Design And Patient Selection
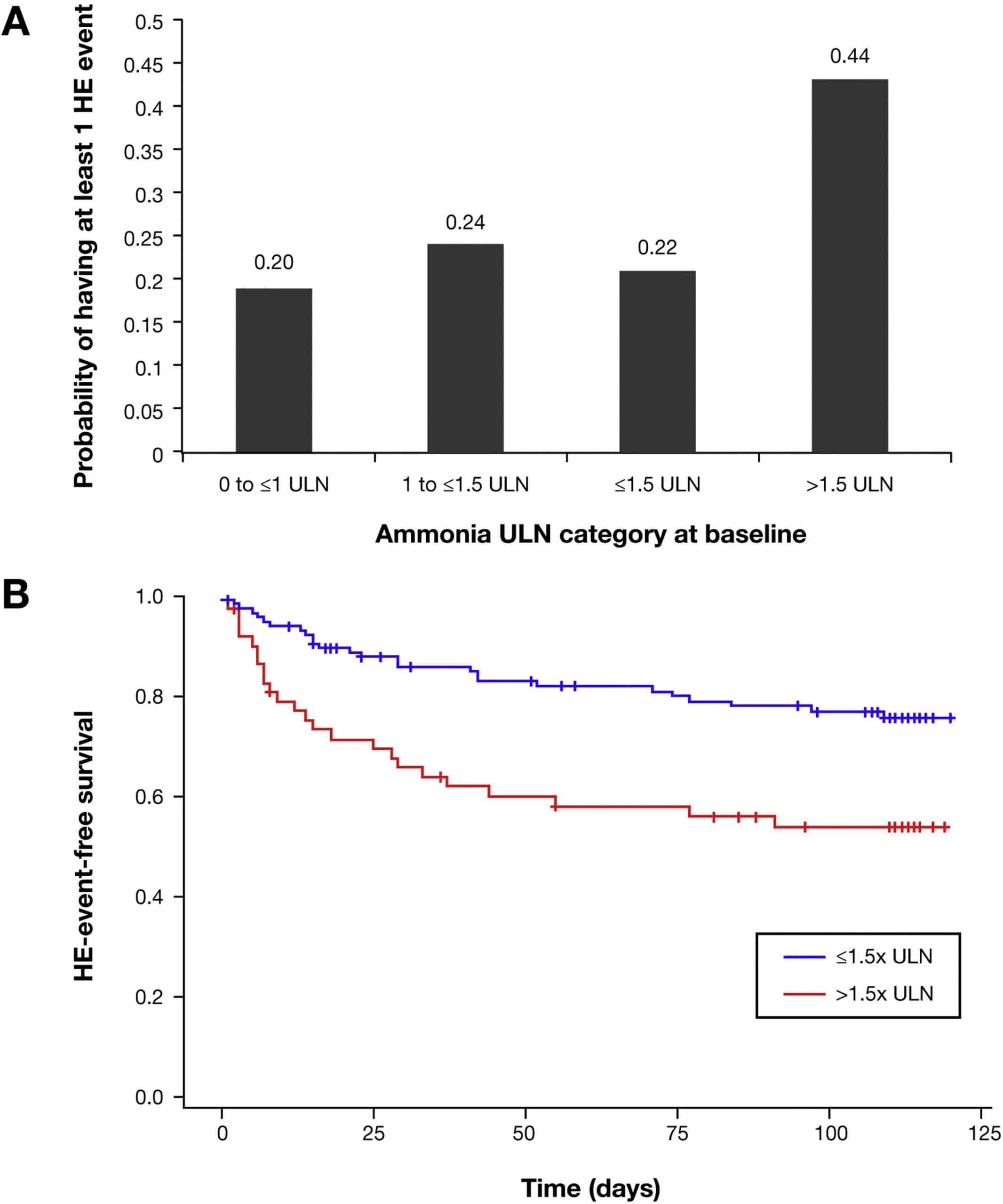
- Cohort 1 KCH, n = 447: patients sequentially assessed for liver transplantation. Arterial ammonia levels were measured.
- Cohort 2 – HCUV, n = 156: consecutive patients reviewed without previous episodes of overt HE or hepatocellular carcinoma . Venous ammonia levels were measured.
- Cohort 3 – RFH, n = 151: consecutive patients without previous episodes of overt HE or HCC, not candidates for liver transplantation. Venous ammonia levels were measured.
Associations Of Clinical Parameters And Prognostic Scoring Systems With Serum Ammonia In Hbv Reactivation
Overall, 37 patients had baseline ammonia92.5 µmol/L . In the group with ammonia92.5 µmol/L, the incidence of overt HE was higher than that in patients with ammonia92.5 µmol/L . An ammonia level92.5 µmol/L was associated with a higher frequency of organ failures coagulation 50% versus 15.7% ). In the group with ammonia92.5 µmol/L, ferritin, aspartate aminotransferase , WBC, INR, and PT levels were higher than those the group with ammonia92.5 µmol/L , while TSH, TG, and VLDL were lower than those in the group with ammonia92.5 µmol/L . The prognostic scores, including MELD, iMELD, CLIF-C OF and CLIF-C ACLF, were higher in patients with ammonia92.5 µmol/L than in those with ammonia92.5 µmol/L .
Table 5 Comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics in ACLF patients induced by HBV reactivation with and without elevated ammonia.
Patients with higher levels of ammonia had increased mortality at 28 days compared to those with normal ammonia the phenomenon can also be observed after classification of the population into HBeAg-positive subgroup and HBeAg-negative subgroup. The survival curves stratified by ammonia level are presented in Fig. .
Figure 4
You May Like: How You Contract Hepatitis B
Factors Other Than Ammonia In The Pathogenesis Of He
Factors besides ammonia have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of HE, including infections, Central Nervous System as well as systemic inflammation, inflammatory cytokines , increased cerebral blood flow, vasoparalysis and hyperemia, hyperthermia, hyponatremia, substances derived from the necrotic liver, lactic acid, TSPO and neurosteroids, glutamate/glutamine , and more recently, the accumulation of cholesterol.52 Currently, data on these factors are limited and contradictory.
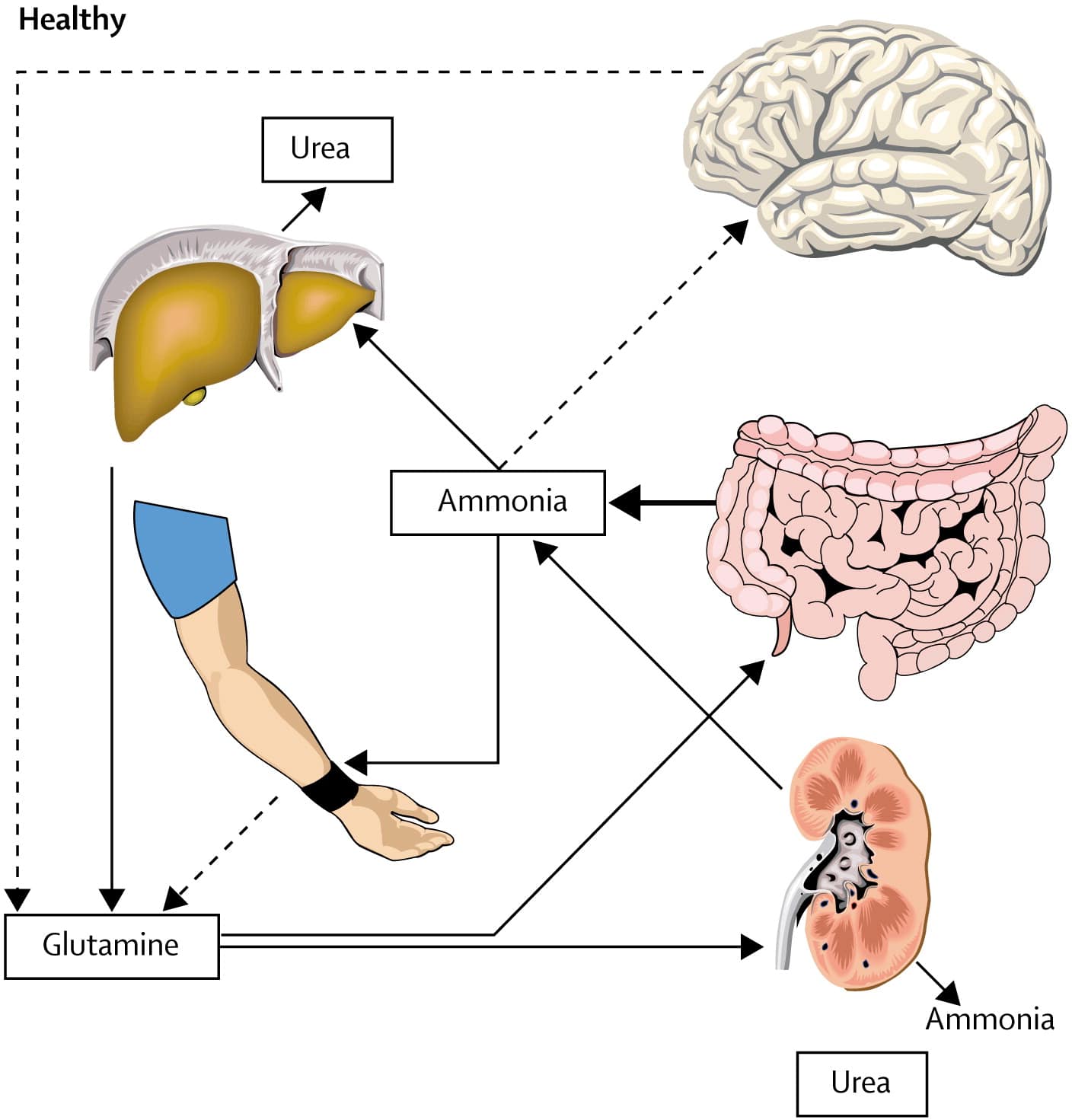
How Does Ammonia Cause Encephalopathy
Ammonia is elevated in individuals with acute and chronic liver disease and is known to affect the brain in other disorders such as Reye syndrome and certain metabolic disorders. Ammonia is normally converted to urea in the liver and cleared out of the body through the urine. Ammonia is highly toxic to the brain.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Treatment
Recent Pathological Evidence For Tdp
Hyper-phosphorylated tau has been strongly implicated in the development of neurobehavioral deficits in many neurological conditions . Recent studies have further emphasized the presence of the Transactivating DNA-Binding Protein, molecular weight 43 kDa inclusions consisting of hyperphosphorylated, ubiquitinated and aggregated forms of TDP-43 in neurons found in various neurological conditions, including Alzheimers disease , Parkinsons disease , frontotemporal lobar degeneration , amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , and chronic traumatic encephalopathy . Such inclusions have been strongly implicated in the development of the neurobehavioral defects associated with these conditions .
What Do The Results Mean
If your results show high ammonia levels in the blood, it may be a sign of one of the following conditions:
- Liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Kidney disease or kidney failure
In children and teens, it may be a sign of Reye syndrome.
In infants, high ammonia levels may be a sign of a genetic disease of the urea cycle or a condition called hemolytic disease of the newborn. This disorder happens when a mother develops antibodies to her baby’s blood cells.
If your results were not normal, your health care provider will need to order more tests to find out the reason for your high ammonia levels. Your treatment plan will depend on your specific diagnosis.
If you have questions about your results, talk to your health care provider.
Learn more about laboratory tests, reference ranges, and understanding results.
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis
Comparison Of Demographic And Clinical Characteristics In Aclf Patients With And Without Elevated Ammonia
Overall, 58 patients had baseline ammonia89 µmol/L . In the group with ammonia89 µmol/L, the incidence of overt HE did not differ from patients with ammonia89 µmol/L . An ammonia level89 µmol/L was associated with a higher frequency of organ failure coagulation 39.7% versus 16.4% ). In addition, an ammonia level89 µmol/L was associated with severe ACLF in our study . In the group with ammonia89 µmol/L, alkaline phosphatase and PT levels were higher than those with ammonia89 µmol/L , while triglyceride and very low density lipoprotein levels were lower than those with ammonia89 µmol/L . The prognostic scores, including CLIF-C OF and CLIF-C ACLF, were higher in patients with ammonia89 µmol/L than in those with ammonia89 µmol/L .
Table 2 Comparison of demographic and clinical characteristics in ACLF patients with and without elevated ammonia.