Potential Role Of Hcv Core Antigen In A Diagnostic Algorithm
An HCV core antigen assay can be useful in an diagnostic algorithm , but such use is even greater with a newer more sensitive assay .
Suggested algorithm for hepatitis C virus testing in anti-hepatitis C virus positive individuals. HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
As HCV RNA is still more sensitive, utility of HCV core antigen in such diagnostic algorithm will depend on potential cost saving for diagnosing HCV infection in a population setting. A big advantage is the ease to allowing reflex testing when the same testing-instrument is used for anti-HCV and HCV core antigen testing.
Thus anti-HCV positive results would be reflexed to HCV core antigen testing, and additional HCV RNA testing would only be required if HCV core antigen would be negative and potential confirmation of anti-HCV with RIBA only when both HCV core antigen and HCV RNA were negative.
In a setting where samples need to be shipped to a laboratory, HCV core antigen could prove to be more stable than HCV RNA in a setting where blood samples cannot be assessed soon after blood draw. But this would likely require some more data.
Also Check: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis C
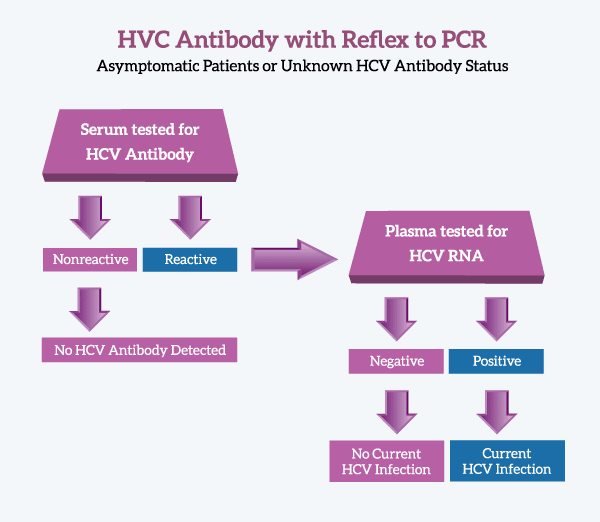
Hepatitis C Antibody With Reflex To Pcr
- Hepatitis C Ab w/RFLX PCR
- Lab Code
- Hepatitis C Antibody w/Reflex PCR
- Description
-
The Qualitative detection of Hepatitis C virus IgG and IgM antibodies in human sera by the FDA approved Abbott ARCHITECT Anti-HCV test two-step chemiluminescent immunoassay.
In the first step, sample, assay diluent, and recombinant HCV antigen coated paramagnetic microparticles are combined. Anti-HCV present in the sample binds to the rHCV coated microparticles. In the second step, anti-human IgG/IgM acridinium-labeled conjugate is added, which binds to IgG and IgM anti-HCV. Then pre-trigger and trigger solutions are added to the reaction mixture. The resulting chemiluminescent reaction is measured as relative light units .
The presence or absence of IgG/IgM anti-HCV in the sample is determined by comparing the chemiluminescent signal in the reaction to the cutoff signal determined from an ARCHITECT Anti-HCV calibration. Specimens with signal to cutoff values 1.00 are considered reactive for IgG/IgM anti-HCV. Specimens with S/CO values < 0.79 are considered nonreactive and specimens with S/CO values between 0.80 and 0.99 are Indeterminate.
Reactive anti-HCV will reflex to Hepatitis C RNA, Quantitative for confirmation with an additional charge.
For anti-HCV testing without PCR reflex for REACTIVE results, see Hepatitis C Antibody without PCR reflex on reactive samples .
- Synonyms
Question 2 Why Are Hcv Rna Results Being Reported In Iu/ml
Results are reported in international units per milliliter to facilitate comparisons between results generated by different test methods. This is important because the various methods used by different laboratories are not standardized against each other. Use of IU/mL reporting units helps to make the comparison of viral load results across different methods more reliable.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Genotype 4 Treatment
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home hepatitis C tests are available that allow patients to collect a blood sample at home and mail it to a laboratory for testing. Test samples are collected through pricking a finger with a sharp object, called a lancet, thats included in the test kit.
At-home HCV testing is a form of hepatitis C antibody testing and does not test for hepatitis C RNA or the strains genotype. Testing for hepatitis C at home is not a substitute for testing performed by a health care professional, and positive test results may need to be confirmed by laboratory-based testing.
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Contracted
Recommended Reading: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Role Of Hcv Core Antigen In Monitoring During And After Therapy
Monitoring HCV viral load with HCV core antigen during antiviral treatment might be an attractive tool for the future. Unfortunately data are too limited for strong recommendations thereof .1). Especially, there are no data with the newer antivirals available at present. For Pegylated Interferon plus Ribavirin regimens, there have been some studies suggesting that one can predict response as early as day 3, week 1 or week 2.
Meaning Of Hcv Viral Load
The number of HCV RNA international units per milliliter of blood must be measured before treatment and during the course of treatment, to assess response. Before treatment, however, the HCV viral load is not related to the patients liver disease severity or HCV prognosis. This is important for patients and providers to understand.
Note: In hepatitis B, unlike hepatitis C, a higher HBV DNA viral load does correlate with increased disease severity and increased likelihood of outcomes such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster For Healthcare Workers
Hepatitis C Is Often Asymptomatic
Offer testing to anyone with a risk factor or clinical indication.
Risk factors:
- shared drug-use equipment, even once
- received personal services , with nonsterile equipment
- exposed to blood during sexual activity
- received blood, blood products, or organ transplant before 1992
- received medical care where non-sterile equipment may have been used
- born, travelled, or lived in a region where hepatitis C is common
- born to a mother with hepatitis C
- diagnosis of HIV or hepatitis B
- clinical clues or symptoms of liver disease
- occupational exposure
Question 4 What Do These Test Results Mean: < 15 Detected And < 15 Not Detected
A < 15 Detected viral load result means the assay detected HCV RNA in the patients specimen at a very low level , but could not measure the precise level. A < 15 Not Detected viral load result means the assay did not detect HCV RNA in the patients specimen.
This test is performed using a Taqman® assay. The lowest viral load this assay can accurately quantify is 15 IU/mL, but the qualitative limit of detection is in the 10 to 13 IU/mL range. Therefore, even when the viral load is below 15 IU/mL, we can still report qualitative detection of HCV RNA consistent with active infection in some cases.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis C Transferred
Risk Of Hcv Infection In Recipients Of Blood Transfusion
Prior to 1992, blood transfusions carried a high risk of HCV infection, approximately 15-20% with each unit transfused. In 1988, 90% of cases of posttransfusion hepatitis were due to NANBH viruses which was later found out to be due to HCV. The move to all-volunteer blood donors instead of paid donors had significantly reduced the risk of posttransfusion hepatitis to 10%. Screening of blood further reduced the rate of posttransfusion hepatitis C by a factor of about 10,000 to a current rate of 1 per million transfusions. The few cases that still occur are due to newly infected people donating blood before they have developed antibodies to the virus, which can take up to 6-8 weeks.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients receiving hepatitis C testing may find it helpful to ask questions about their test results. Questions to consider include:
- What type of hepatitis C test did I receive?
- What was my test result?
- How do you interpret the results of the hepatitis C tests that I had?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my test result?
Don’t Miss: What Are The Stages Of Hepatitis B
Question 5 How Do You Interpret Hcv Antibody Reactive And Hcv Rna Not
A reactive HCV antibody test result combined with a not-detected HCV RNA result indicates no laboratory evidence of a current active HCV infection no further action is required in most cases.
If distinction between a true positive and a biologic false-positive result for HCV antibody is desired, the CDC suggests that one can consider testing with another HCV antibody assay. If there is concern regarding the handling or storage of the test specimen, obtain a new sample for repeat testing.6
How To Get Tested

Hepatitis C testing is performed by a doctor. Testing requires a blood sample, which can be collected in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Blood is often drawn from a vein in the arm or, in children, taken by pricking the skin. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Dont Miss: Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B Medication
Nat: Detection Of Hcv Rna
Molecular virological techniques play a key role in diagnosis and monitoring of treatment for HCV. Because it is difficult to cultivate the virus in cell culture, molecular techniques were instrumental in first identifying HCV, making it one of the first pathogens to be identified by purely molecular methods. NAT is considered the gold standard for detecting active HCV replication. HCV NAT is extremely useful in establishing the diagnosis of acute HCV infection, since RNA is detectable as early as 1 week after exposure via needle-stick or blood transfusion, and at least 4-6 weeks prior to seroconversion as demonstrated in a number of transmission settings. The diagnosis of HCV infection is established with antibody screening followed by NAT for HCV RNA for confirmation as well as for follow-up of patients on treatment. Viral load assessment at baseline is also critical for determining response kinetics during therapy. enumerates the role of NAT in HCV diagnosis.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A And B
Taking A Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C testing is conducted on a sample of blood. Blood samples can be collected by a doctor, nurse, technician, or other health care provider from an adult patients vein using a small needle or a skin prick on a childs heel.
For an at-home hepatitis C test, patients collect a blood sample according to the manufacturers directions. Instructions provided in the test kit detail the steps to obtain a small sample of blood and mail it for testing.
Also Check: Can Patients With Impaired Hepatic Function Be Treated With Buprenorphine
Read Also: How Can You Cure Hepatitis C
Question 3 Why Does Quest Diagnostics Also Report Results As Log Iu/ml
This makes it easier to understand whether a change in viral load is clinically meaningful.
Replicate PCR test results using the same specimen can vary analytically by as much as 0.5 log IU/mL thus, only changes greater than 0.5 log IU/mL from one measurement to the next are considered to represent true changes in viral load.3 Reporting the viral load results in log IU/mL units helps the healthcare provider accurately interpret changes in viral load and better assess a patient’s response to antiviral treatment.
Hcv Testing Without Riba
Among 43 CIApositive patients in the study group, 31 were PCR positive and 12 were PCR negative. In the group of 12 patients with negative PCR, three of four patients with S/Co ratios greater than 11 had documented diagnosis of HCV infection the fourth had no medical history available for HCV status. Two patients with S/Co ratios < 3 were likely CIA false positive. Six patients antibody S/Co ratios were between 3 and 10, with no relevant medical information available for review (Table (Table1.1. Importantly, all 31 PCR positive patients had S/Co ratios greater than 11.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Detected
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
How Is A Person Tested For Hepatitis C
A viral-load test is used to check for hepatitis C in the bloodstream. Usually, hepatitis C virus can be found in a persons bloodstream two weeks after he or she becomes infected.
*Except in case of recent risk or in people with a weakened immune system**During the first six months after HCV infection, a person may spontaneously clear the virus if there was a recent risk, repeat viral-load testing to confirm chronic hepatitis C infection
Recommended Reading: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
You May Like: What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis C testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patients health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with their insurance company. In addition to the cost of testing, there may be other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance, or for whom insurance doesnt cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis C testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
At-home hepatitis C testing starts around $49. Some at-home kits test for multiple types of viral hepatitis at once, with the cost of these panels starting around $80.
What Does The Test Measure

Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Hepatitis And How They Are Transmitted
Interpreting Hcv Rna Test Results
It is essential that the provider understands how to interpret HCV RNA test results, especially during the course of HCV treatment.
| Result of HCV RNA Test | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| A quantified viral load any exact number | Ongoing HCV infection |
| Detected | The HCV RNA is detectable but the number of international units is so low that it cannot be quantified accurately. This indicates extremely low level of virus is present. |
| < 12 IU/mL or < 15 IU/mL or < 25 IU/mL All of these are less than the LLOQ | HCV RNA is undetectable. No virus is detected at all in the patients serum specimen. |
Virus Description And Transmission
HCV is a small, single-stranded, enveloped RNA virus in the flavivirus family with a high degree of genetic heterogeneity. Seven distinct HCV genotypes have been identified. Genotype 1 is the most prevalent genotype in the United States and worldwide, accounting for approximately 75% and 46% of cases, respectively . Geographic differences in global genotype distribution are important because some treatment options are genotype specific . High rates of mutation in the HCV RNA genome are believed to play a role in the pathogens ability to evade the immune system . Prior infection with HCV does not protect against subsequent infection with the same or different genotypes.
Also Check: Which Hepatitis Is The Worst
What The Qualitative Results Mean
The qualitative results indicate that HCV is present in your blood. The test result will be either detected or undetected.
Detected means that you do have the virus in your blood. Undetected means that you dont have the virus in your blood, or you have a tiny amount that cant be detected by this test.
The qualitative test results may still be positive even if your viral load has decreased drastically due to treatment.
Read Also: Unspecified Viral Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Screening For Hcv Infection
HCV screening has several potential benefits. By detecting HCV infection early, antiviral treatment can be offered earlier in the course of the disease which is more effective than starting at a later stage. Further, early detection together with counseling and lifestyle modifications may reduce the risk of transmission of HCV infection to other people. The optimal approach to screen for HCV is to test the individuals having risk factors for exposure to the virus. The American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases recommends screening for HCV for the following individuals:
- Recipient of blood or blood components .
- Recipient of blood from a HCV-positive donor.
- Injection drug user .
- Persons with following associated conditions
- persons with HIV infection,
- persons who have ever been on hemodialysis, and
- persons with unexplained abnormal aminotransferase levels.
- Children born to HCV-infected mothers.
- Healthcare workers after a needle stick injury or mucosal exposure to HCV-positive blood.
- Current sexual partners of HCV-infected persons.
Recommended Reading: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
Also Check: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis