No Identifiable Source Of Infection
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, injection drug use accounts for approximately 60% of all HCV infections in the United States, while other known exposures account for 20-30%. Approximately 10% of patients in most epidemiological studies, however, have no identifiable source of infection. HCV exposure in these patients may be from a number of uncommon modes of transmission, including vertical transmission, and parenteral transmission from medical or dental procedures prior to the availability of HCV testing. There are no conclusive data to show that persons with a history of exposures such as intranasal cocaine use, tattooing or body piercing are at an increased risk for HCV infection based on these exposures solely. It is believed, however, that these are potential modes of HCV acquisition in the absence of adequate sterilization techniques.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is passed from person to person when blood from an infected persons body comes in direct contact with someone elses blood.
The most common ways people become infected with the hepatitis C virus are through:
-
Needle- or syringe-sharing
-
Exposure to contaminated razorsor instruments used for tattooing and piercings
-
Unprotected anal sex with a partner who has hepatitis C
-
Accidental exposure during surgical or medical procedures
-
Exposure during pregnancy
Since 1992, the U.S. has tested donated blood products and organs for the hepatitis C virus, so getting a blood donation or an organ transplant is an unlikely way to get hepatitis C infection.
Though much less common, it is possible to get hepatitis C from sharing personal care items, like toothbrushes or nail clippers, which can be accidentally contaminated with blood.
While the hepatitis C virus can exist in semen, breast milk, and saliva, the virus is not typically passed from person to person through contact with these fluids. Casual contact, kissing, and hugging cannot transmit the hepatitis C virus.
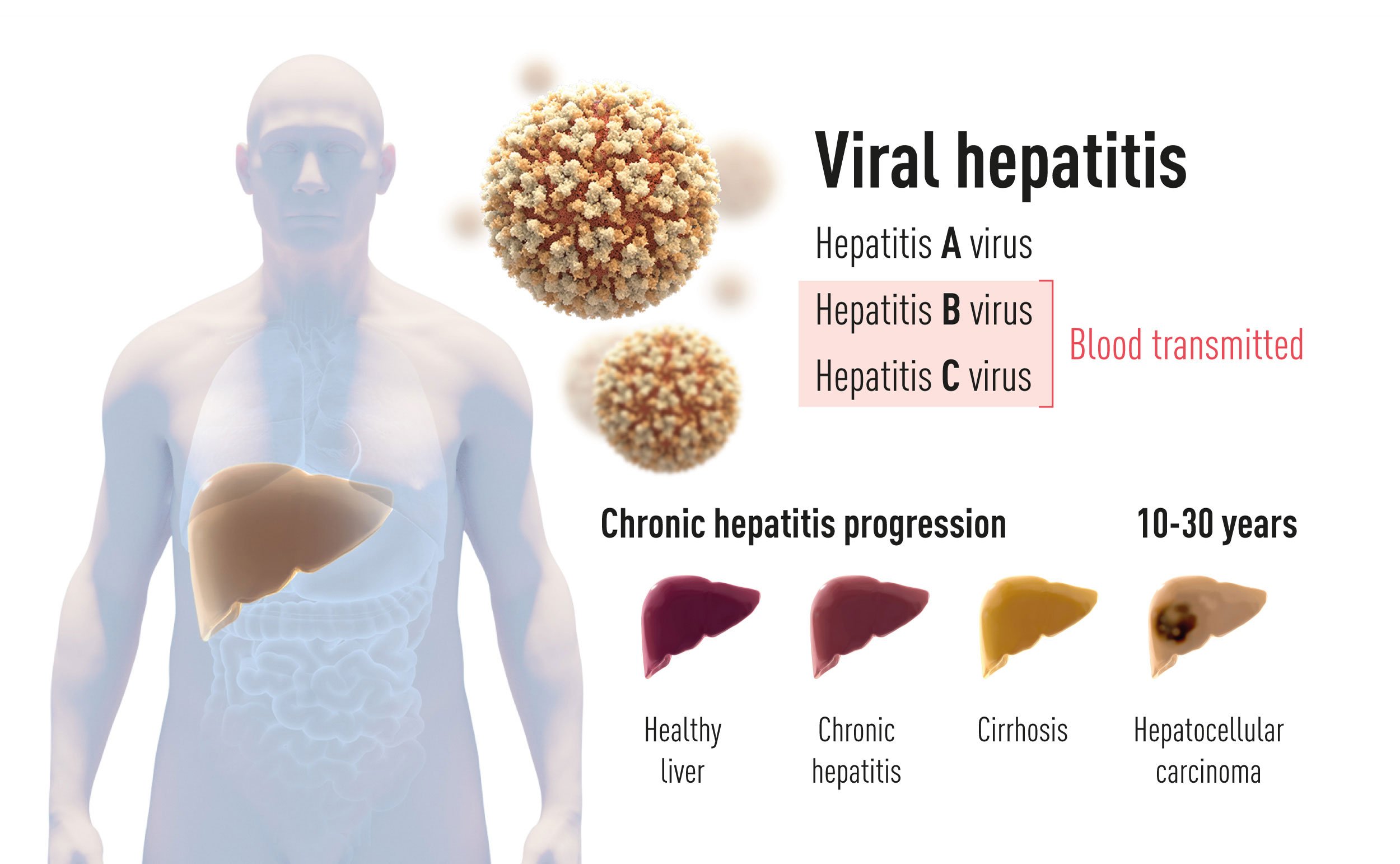
Natural Course Of Hcv
HCV infection may lead to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma in adult populations. However researches about the natural history of hepatitis C in children is little. Studies showed that perinatally-acquired HCV infection becomes chronic in approximately 80% of cases, similar to that observed in adults, but higher than that reported in children who were infected through contaminated blood products. Most studies show that HCV infected children are mostly asymptomatic. Spontaneous clearance have reported rates ranging from 21% to 75%. The European Paediatric HCV Network evaluated 266 children with vertically-acquired HCV infection and found clearance occurred in 21%-25%. Among cases of neonatal infection, 25% demonstrated spontaneous clearance by 7.3 years.
However it has not been studied clearly whether the virus is completely eliminated, and there is possibility the infants will become HCV-RNA positive again later in their life. In a study performed in United Kingdom, the overall rate of spontaneous viral clearance was 17.5% with higher clearance in the transfusion group compared to the vertically acquired group . Most children are asymptomatic with mildly abnormal hepatic transaminases. An infected infant becomes HCV-RNA positive between 0 and 3 mo after birth. Fortunately there is no case of fulminant hepatitis reported among infected infants to date.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
General Tips For Prevention
Refrain from engaging in IV drug use and be cautious with all procedures that involve needles.
For example, you shouldnt share needles used for tattooing, piercing, or acupuncture. The equipment should always be carefully sterilized for safety. If youre undergoing any of these procedures in another country, always make sure the equipment is sterilized.
Sterile equipment should also be used in a medical or dental setting.
Risk Factors For Hepatitis C
Though the risk is believed to be low, you can contract hepatitis C by having unprotected sex with an HCV-infected person. This risk increases if you have multiple sex partners, have a sexually transmitted disease, or engage in rough sex or anal sex that causes bleeding. Having sex with an HCV-infected woman who is menstruating can also increase your risk, as the virus is passed through exposure to infected blood.
Aside from unsafe sexual activity, there are several other factors that increase your risk of getting hepatitis C, including if you:
- Use intravenous drugs now or have used them in the past
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992, when better hepatitis C testing became available
- Received a clotting factor concentrate, which helps blood clot properly, made before 1987, when more advanced manufacturing methods were developed
Recommended Reading: How Long Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
But Even If Youve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease, Reau says. It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesnt completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications, Reau says. If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
You May Like: Life Insurance For Hepatitis B Carrier
Why It’s Important To Get Tested
Because hepatitis C is a highly infectious virus, the CDC recommends that adults 18 years or older get tested for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime. This is also true for pregnant people during each pregnancy.
To test whether you have a hepatitis C infection, your healthcare provider will perform a hepatitis C antibody test to determine whether you have antibodies that were created in response to the infection.
If your test is positive, your healthcare provider will also perform a hepatitis C RNA test, which accurately determines whether you have a current infection.
Once it is determined you have an HCV infection, your healthcare provider will recommend the best course of treatment. For most people, treatment with antiviral drugs will be started. There are effective treatments that can cure HCV and prevent liver damage.
How Do You Prevent Hepatitis
Both hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be prevented with a vaccine. There is currently no vaccine available to prevent hepatitis C.
To prevent spreading or getting hepatitis A:
- Wash hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds after using the bathroom, changing diapers, touching garbage or dirty clothes, and before preparing food and eating
- Follow guidelines for food safety
- Avoid unpasteurized milk or foods made with it
- Thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables before eating
- Keep the refrigerator colder than 40°F and the freezer below 0°F
- Cook meat and seafood until well done
- Cook egg yolks until firm
- Wash hands, knives, and cutting boards after contact with raw food
To prevent spreading or getting hepatitis B or hepatitis C:
- Practice safe sex and use a latex condom each time you have sex
- Dont share razors, toothbrushes, or any personal objects that might have blood on them
- Dont share needles or syringes
- Cover cuts and open sores with bandages
- Clean blood off of things with a mixture of bleach and water: use 9 parts bleach to one-part water
Read Also: How To Check For Hepatitis
Encouraging Others To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
While the odds of passing on the hepatitis C virus are low, you should still tell anyone at risk that you have hepatitis C. You should tell sexual partners, spouses, and family members. Your infection may be difficult to discuss, but anyone at potential risk must know. That way, they can get tested and treated if needed. Read more on why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Show Sources
Paul Berk, MD, professor of medicine and emeritus chief of the division of liver disease, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York City chairman of the board, American Liver Foundation.
Alan Franciscus, executive director, Hepatitis C Support Project and editor-in-chief of HCV Advocate, San Francisco.
Thelma King Thiel, chair and CEO, Hepatitis Foundation International.
David Thomas, MD, professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore.
Howard J. Worman, MD, associate professor of medicine and anatomy and cell biology, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, New York City.
The American Gastroenterological Association.
How Does Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C is spread only through exposure to an infected person’s blood.
High-risk activities include:
- Sharing drug use equipment. Anything involved with injecting street drugs, from syringes, to needles, to tourniquets, can have small amounts of blood on it that can transmit hepatitis C. Pipes and straws to smoke or snort drugs can have blood on them from cracked lips or nosebleeds. Get into a treatment program if you can. At the very least, don’t share needles or equipment with anyone else.
- Sharing tattoo or piercing tools. Nonsterile items and ink can spread contaminated blood.
- Blood transfusions in countries that donât screen blood for hepatitis C.
- Nonsterile medical equipment. Tools that arenât cleaned properly between use can spread the virus.
- Blood or cutting rituals. Sharing the tools or exchanging blood can transmit hepatitis C.
Medium-risk activities include:
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
What Are The Long
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause the liver to stop working properly. This scarring of the liver is called cirrhosis. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. But, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Prevalence Of Hcv Infection In Pregnant Women

The worldwide prevalence of HCV infection is between 1% and 8% in pregnant women and between 0.05% and 5% in children. Antenatal HCV infection rates vary worldwide, from 1% to 2.5% in the United States and Europe to more than 10% in some sub-Saharan countries. Studies have shown the prevalence to be as high as 40% in some parts of Egypt. According to the result of the maternal HCV screening project conducted in Tottori Prefecture, Japan, the prevalent rate of HCV carrier mothers who were both anti-HCV and HCV RNA positive was 0.39%, while the rate of vertical transmission was found to be 8%. However, the above maternal HCV prevalent rates may be underestimated since the current practice of HCV screening among high-risk pregnant women might miss a large number of HCV-infected patients, and besides there are no large scale HCV serosurvey studies available at present.
In a recent study performed in Taiwan, a total of 7355 healthy asymptomatic pregnant women were screened for anti-HCV during a 6-year study period, 44 were found to be HCV-infected and 22 mothers were enrolled. Half of the anti-HCV positive mothers were found to be positive for HCV RNA. All the mothers were negative for anti-HIV, 9 had invasive obstetric procedures such as amniocentesis. Of the 22 mother and baby pairs who were successfully followed up, two had eventually confirmed infected with HCV. Both of them were born to mothers with high viral load .
Read Also: What Causes The Hepatitis C Virus
Blood Spills At Home Or At The Workplace
When wiping up blood spills, it is advisable to wear gloves, use paper towels and scrub the spill with lukewarm soapy water. Cuts and abrasions should be covered.
All workplaces are legally required to apply infection control procedures, in which any blood spills are treated as potentially infectious and are dealt with in a safe manner.
These procedures should be outlined in workplace health and safety policies. If youre concerned about transmission in the workplace you can contact your health and safety officer, union, or call our LiverLine .
In all medical settings, standard precautions must be applied to all potentially infectious material.
These are precautions that have been developed to make sure that both patients and health care workers are protected from infection as much as possible.
Therefore, all bodily fluids are treated as infectious and there is NO need for anyone to disclose his or her viral status since no special precautions are required.
All medical equipment is either sterilised before use with each patient or is only for single use, while gloves and other protective gear will be used to prevent staff to patient infection.
In addition, many exposed surfaces will have protective coverings on them, which are replaced for each patient.
People concerned about transmission in a health care setting should ask the medical staff about their infection control procedures.
Remember, the best way to prevent transmission of hepatitis C is to be tested and cured.
Why Getting Tested Is Important
A blood test is one of the only ways to confirm a diagnosis of hepatitis C. Additionally, hepatitis C often has no visible symptoms for many years.
Because of this, its important to be tested if you believe youve been exposed to the virus. Getting a timely diagnosis can help ensure you receive treatment before permanent liver damage occurs.
Don’t Miss: How Much Does It Cost To Treat Hepatitis C
How Is The Virus Spread
Like hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus is spread when blood of an infected person enters the body of a person who is not infected, such as through sharing needles or “works” when shooting drugs or occupational needle stick injury. The risk of sexual transmission has not been thoroughly studied but appears to be low in long-term, monogamous relationships. There is no evidence that the hepatitis C virus can be transmitted by casual contact such as hugging or shaking hands, through foods, by sharing eating utensils or drinking glasses, or by coughing or sneezing. Hepatitis C is not spread by breastmilk.
What Is The Health Outlook For Someone With Hepatitis C
Thanks to DAAT therapy, the outlook for someone with hepatitis C is excellent. DAAT therapy cures 95% of people with hepatitis C. Even those who already have liver disease can have improved liver function after treatment. For those with advanced liver disease, DAAT treatment can lower the risk of getting liver cancer.
DAAT treatment is also available for children 3 years and older who have hepatitis C. For children younger than 3, a liver specialist will help determine when treatment should start.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Can Males Transmit Hcv To A Fetus
It is unlikely that males can transmit HCV to the fetus through sperm during conception.
A 2004 review of studies investigating assisted reproduction found that while some studies have detected HCV in sperm, the evidence suggests that ejaculated sperm is usually safe to use in fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization.
Hepatitis C Symptoms And Treatment
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver. It is commonly found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
The virus is usually passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
It often has no noticeable symptoms. Some peoples bodies can clear the infection on their own but others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection and prevent liver damage.
- The basics
Recommended Reading: What Is A Hepatic Diet For Dogs
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.
How It’s Passed On
The hepatitis C virus is found in blood and is passed on when infected blood gets into another persons bloodstream. Its seen as unlikely that it can be passed on in semen.
Most people get the virus from sharing drug injecting equipment such as needles, syringes, water cups, tourniquets, spoons, filters and swabs. Sharing things like straws and banknotes that are used for snorting drugs might pass the virus on, as can sharing pipes.
In the UK piercing and tattooing should be safe but unsterilised equipment abroad can spread the virus.
An infected person risks infecting others if they share anything that might have blood on it like a toothbrush or razor. A pregnant woman with the virus can give it to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth.
Blood transfusions in the UK are safe as blood is screened.
You can also potentially get it from medical or dental treatment abroad in countries where hepatitis C is common and infection control is inadequate.
You May Like: Can Drinking Cause Hepatitis C
Risk Factors Of Vertical Transmission
Multiple risk factors were studied to increase the risk of HCV vertical transmission, including coinfections with HIV, intravenous drug use, high maternal HCV viral load, mode of delivery, preterm labor, prolonged rupture of membranes and amniocentesis, while breastfeeding and HCV genotypes have little impact on vertical transmission. However, most of the reports are still controversial.