Chronic Hepatitis B Symptoms
Most patients with chronic hepatitis B are asymptomatic unless their disease progresses. Others might have nonspecific symptoms, such as fatigue.
Some patients experience worsening of the infection and develop signs and symptoms similar to acute hepatitis.
If patients with chronic hepatitis B progress to cirrhosis they will develop signs and symptoms of liver failure, including:
- Peripheral edema
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hbv Transmission And Infection
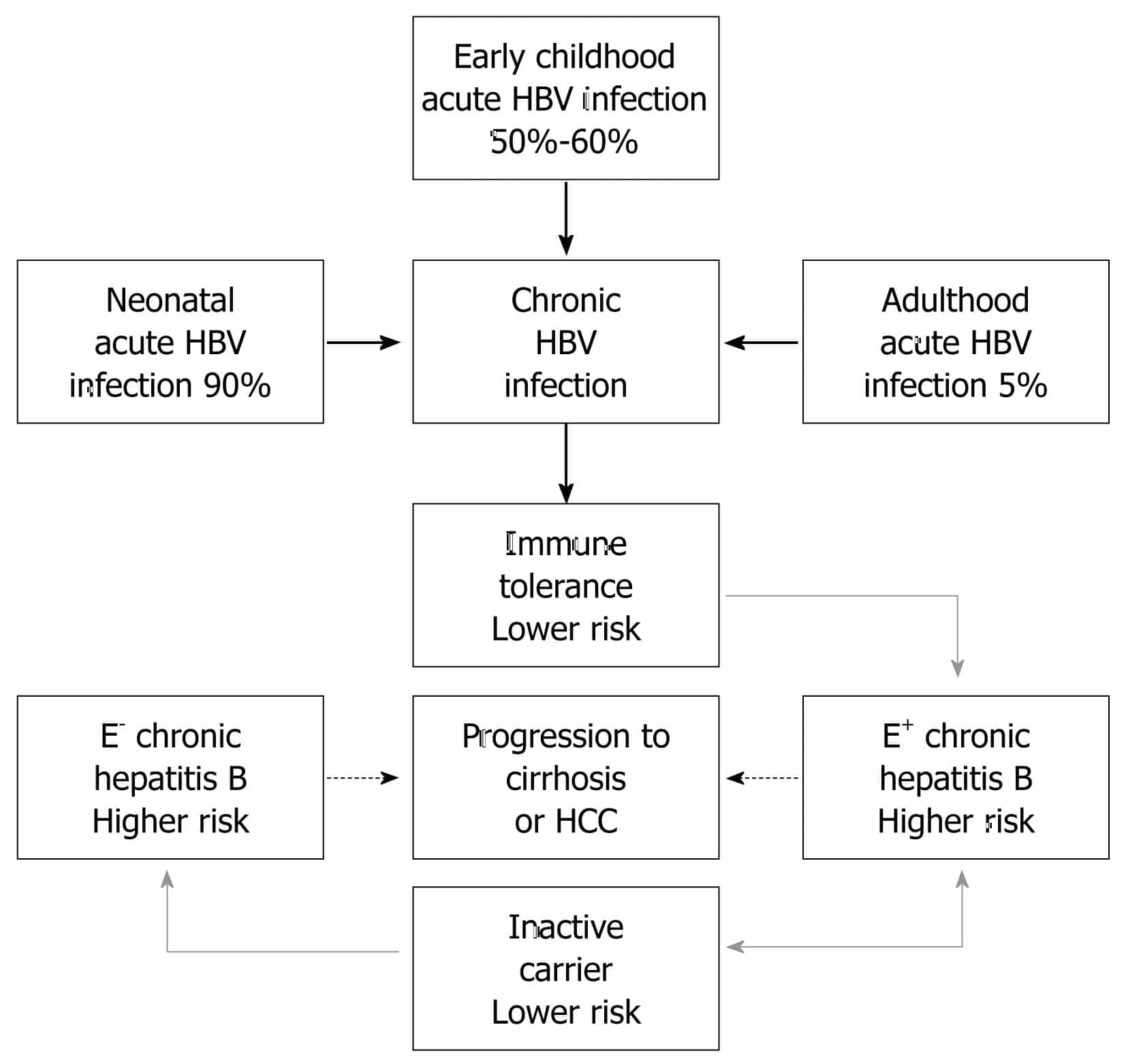
In high endemic regions, such as Asia, Africa, Pacific Islands and the Arctic, early perinatal and horizontal infection in childhood is the main route of HBV transmission with a hepatitis B surface antigen positive rate of 8%-15%, while in low endemic areas, such as Western countries, HBV is a predominant disease in adolescents and adults due to high risk sexual behaviors or drug injections, with a HBsAg positive rate of less than 2%.
The vast majority of early perinatal or horizontal infections in childhood are the main route of HBV transmission in untreated infants whose mothers are hepatitis B e antigen positive, and over 90% of them will become chronic HBV carriers. In contrast, about 90% of HBV infections may occur as acute infection and only 5%-10% may occur as chronic infection in adults. This dramatic difference in chronic rates is believed to reflect the host immunologic status and the time of infection.
There is an obvious difference between patients infected with HBV in adolescence or adulthood immediately entering immune clearance phase, and short duration and tendency quiescent after seroconversion from HBeAg to antibody against HBeAg . Such patients are termed healthy carriers. In contrast, patients with early HBV infection have a prolonged immune tolerance phase and a prolonged immune clearance phase, indicating that their diseases tend to progress after HBeAg seroconversion.
Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Among patients with chronic HBV infection, the rates of HCV co-infection vary from 9% to 30%. Hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus share a similar mode of transmission. The majority of those coinfected with HCV and HBV acquired these viruses through intravenous drug use, exposure to dirty needles, unsterilized medical equipment, and unscreened blood products. HBV and HCV co-infection can lead to severe liver disease and an increased risk for progression to liver cancer. As there is no vaccine against hepatitis C, people with hepatitis C should be vaccinated against hepatitis B to prevent co-infection.
You May Like: What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Hepatitis B
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
When permanent scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells and your liver loses the ability to function, its called cirrhosis. In this condition, your liver can no longer heal itself. This can cause a variety of health concerns, including a buildup of fluid in your abdomen and bleeding from veins in the esophagus.
When the liver fails to filter toxins, they can build up in your bloodstream and impair brain function. Cirrhosis of the liver can sometimes develop into liver cancer. This risk is greater in people who drink excess alcohol. Treatment of cirrhosis depends on the progression of the condition.
Chronic hepatitis C can cause serious long-term health consequences when it leads to liver scarring. End-stage hepatitis C occurs when the liver is severely damaged and can no longer function properly.
Symptoms may include:
- abdominal swelling
- muddled thinking
People with cirrhosis may also experience bleeding in the esophagus, as well as brain and nervous system damage.
A liver transplant is the only treatment for end-stage liver disease. Those whove had hepatitis C and received a liver transplant almost always see a return of the infection. Because the disease recurs, treatment of the viral infection usually follows transplant surgery.
Because alcohol is processed in the liver, consumption of excess alcohol can hasten liver damage, so its important to not drink it. Damage also progresses faster in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV.
Diagnosis Of Hepatitis B
Jeong Eun Song, Do Young Kim
Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Contributions: Conception and design: DY Kim Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: None Data analysis and interpretation: None Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Hepatitis B virus infection is a major global health problems leading to severe liver disease such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma . HBV is a circular, partly double-stranded DNA virus with various serological markers: hepatitis B surface antigen and anti-HBs, anti-HBc IgM and IgG, and hepatitis B e antigen and anti-HBe. It is transmitted by sexual, parenteral and vertical route. One significant method to diminish the burden of this disease is timely diagnosis of acute, chronic and occult cases of HBV. First step of HBV diagnosis is achieved by using serological markers for detecting antigens and antibodies. In order to verify first step of diagnosis, to quantify viral load and to identify genotypes, quantitative or qualitative molecular tests are used. In this article, the serological and molecular tests for diagnosis of HBV infection will be reviewed.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus serology molecular diagnosis
Submitted Aug 01, 2016. Accepted for publication Aug 28, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.09.11
Read Also: How Did I Get Hepatitis C
Acute Vs Chronic Hepatitis B
A hepatitis B infection can result in either an acute infection or a chronic infection. When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an “acute infection” . Most healthy adults that are infected do not have any symptoms and are able to get rid of the virus without any problems. Some adults are unable to get rid of the virus after six months and they are diagnosed as having a “chronic infection.” A simple blood test can diagnose an acute or chronic hepatitis B infection.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is directly related to the age at which a person is first exposed to the hepatitis B virus. The younger a person is when they are first infected, the greater the risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection:
- More than 90% of infants that are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of young children between 1 and 5 years who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of healthy adults 19 years and older who are infected will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
The recommendation for hepatitis B vaccination of babies and children is so important because they are at the greatest risk of developing a chronic infection if they are not protected against the hepatitis B virus as soon as possible.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B usually does not cause any symptoms. If there are symptoms, they can range from mild to serious. However, in chronic cases, symptoms may not develop until many years later.
In the case of acute hepatitis B, symptoms may include:
- Low-grade fever
For chronic hepatitis B, symptoms that may develop include the above-mentioned symptoms, as well as:
- Severe cases of nausea and/or vomiting.
- Bloated/swollen stomach.
- Liver complications, such as liver failure or liver cancer.
Because of similar transmission methods, HBV/HIV co-infection is another complication that may arise.
WHO estimates show that about one per cent of persons with HBV infection are also infected with HIV.
The reduction of the immune system’s capabilities caused by HIV seems to exacerbate the effects of hepatitis B, especially in chronic cases, but further studies are needed to determine if this is the case.
Also Check: Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hiv
What Exactly Is Hepatitis B
However, it cannot be spread to others by sneezing or coughing. Hepatitis B causes liver inflammation that can if it persists cause lasting liver damage.
For many people, hepatitis B is a short-term illness that goes away on its own after some time. For others, however, it can become a chronic condition.
Younger people, especially infants and children below the age of five, who are infected by HBV have a much higher risk of developing chronic hepatitis B.
People from certain regions in the world also carry a higher risk of developing chronic hepatitis B, including persons from Sub-Saharan Africa, the Pacific islands, the Middle East, as well as parts of Northeast and Southeast Asia.
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months are diagnosed as having a chronic infection. This means their immune system was not able to get rid of the hepatitis B virus and it still remains in their blood and liver.
The risk of developing a chronic hepatitis B infection is also directly related to the age at which one first becomes exposed to the hepatitis B virus:
- 90% of infected newborns and babies will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- Up to 50% of infected children will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
- 5-10% of infected adults will develop a chronic hepatitis B infection
Learning that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection can be very upsetting. Because most people do not have symptoms and can be diagnosed decades after their initial exposure to the hepatitis B virus, it can be a shock and a surprise to be diagnosed with a chronic hepatitis B infection. The good news is that most people with chronic hepatitis B should expect to live a long and healthy life.
There are effective drug therapies that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging a liver. There are also promising new drugs in the research pipeline that could provide a cure in the very near future. Although the risk of developing a serious liver disease or liver cancer is higher for those living with chronic hepatitis B than those who are not infected, there are still many simple things a person can do to help reduce their risks.
Also Check: How Did You Get Hepatitis B
How Long Does It Last
According to the World Health Organization , the complete vaccine series induces protective antibody levels in of the infants, children, and adolescents who receive it.
Immune memory induced by the HBV vaccine can last for in healthy people. That said, studies into the duration of the protection that the vaccine offers are ongoing.
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Reactive Espaol
What Is The Outlook For People With Hepatitis B
The outlook for people with HBV is better now than ever before. You are certainly able to live a full life and help yourself stay healthy. You should make sure to have regular check-ups with a healthcare provider who is qualified to treat hepatitis B, possibly a liver doctor.
Make sure you are vaccinated against hepatitis A. Check with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before taking other medications or over-the-counter products, including supplements and natural products. These could interfere with your medication or damage your liver. For instance, taking acetaminophen in large doses may harm your liver.
Follow the usual guidelines for living a healthy life:
- Eat nutritious foods, choosing from a variety of vegetables, fruits and healthy proteins. It is said that cruciferous vegetables are especially good at protecting the liver.
- Exercise regularly.
- Dont smoke and dont drink. Both tobacco and alcohol are bad for your liver.
- Do things that help you cope with stress, like journaling, talking with others, meditating and doing yoga.
- Avoid inhaling toxic fumes.
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
Read Also: Can Hepatitis C Kill You
Deterrence And Patient Education
Patient education remains one of the most important components in preventative measures regarding HBV infection.
Education should be provided to expecting parents about the importance of vaccination and to clarify erroneous beliefs about vaccinations.Patient education should also include counseling about the avoidance of risky behaviors that predispose an individual to be infected, including promiscuous sexual activity or intravenous drug abuse. They should also be advised not to share items such as shaving razors, toothbrushes, or hair combs due to possible transmission via mucosal contact or through microtrauma to protective barriers.
Treatments For Chronic Hbv Infection
Family physicians should become familiar with the evaluation of patients with newly diagnosed HBV infection, including the recommended laboratory work-up .9 The decision to treat chronic HBV generally is based on a combination of clinical, laboratory, and histologic factors .9,16
| Laboratory studies to assess liver disease: aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, bilirubin, and albumin levels complete blood count prothrombin time tests for anti-HBc, anti-HDV, HBeAg, anti-HBe, anti-HCV, HBV DNA level, anti-HAV alpha-fetoprotein level |
| Human immunodeficiency virus serology |
| Hepatic ultrasonography |
| Liver biopsy to grade and stage disease |
| Assessment for other sexually transmitted diseases |
| Assessment for family history of hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Counseling: safe sexual practices, abstinence from alcohol |
| Serologic testing for hepatitis A |
| Testing of sexual and household contacts |
Treatments are not curative because they rarely produce permanent remission of the disease. Therefore, the goals of therapy are long-term suppression of viral replication and prevention of end-stage liver disease.16 Markers of successful therapy include HBeAg seroconversion, decreased or undetectable levels of HBV DNA, and lack of disease progression.
Also Check: Can You Give Hepatitis C To Yourself
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection can lead to the development of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and HCC. As well as in HCV, chronic HBV infection is associated with age, cell cycle arrest, and CS. In one study the authors assessed the HBV antigen production in relation to cell cycle arrest and CS in vitro using hepG2 and hepG2.2.15 cell lines . HepG2.15 cells were transfected with sub-genomic HBV thus HBV production is a result of transcription of the transgene. The authors found that in vitroinduced cell cycle arrest by the addition of hydrogen peroxide caused increased levels of supernatant HBsAg and HBV DNA also an increased expression of HBcAg expression was noted. In contrast no effect on HBsAg or HBV DNA production was observed in senescent cells, with only a minor increase in cytoplasmic HBcAg staining. The authors also found that fewer telomeres were detected in patients with chronic HBV infection compared with controls of healthy livers however, when telomeres were detected they were shorter than controls . Widespread telomere shortening is consistent with accelerated aging in chronic HBV .
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
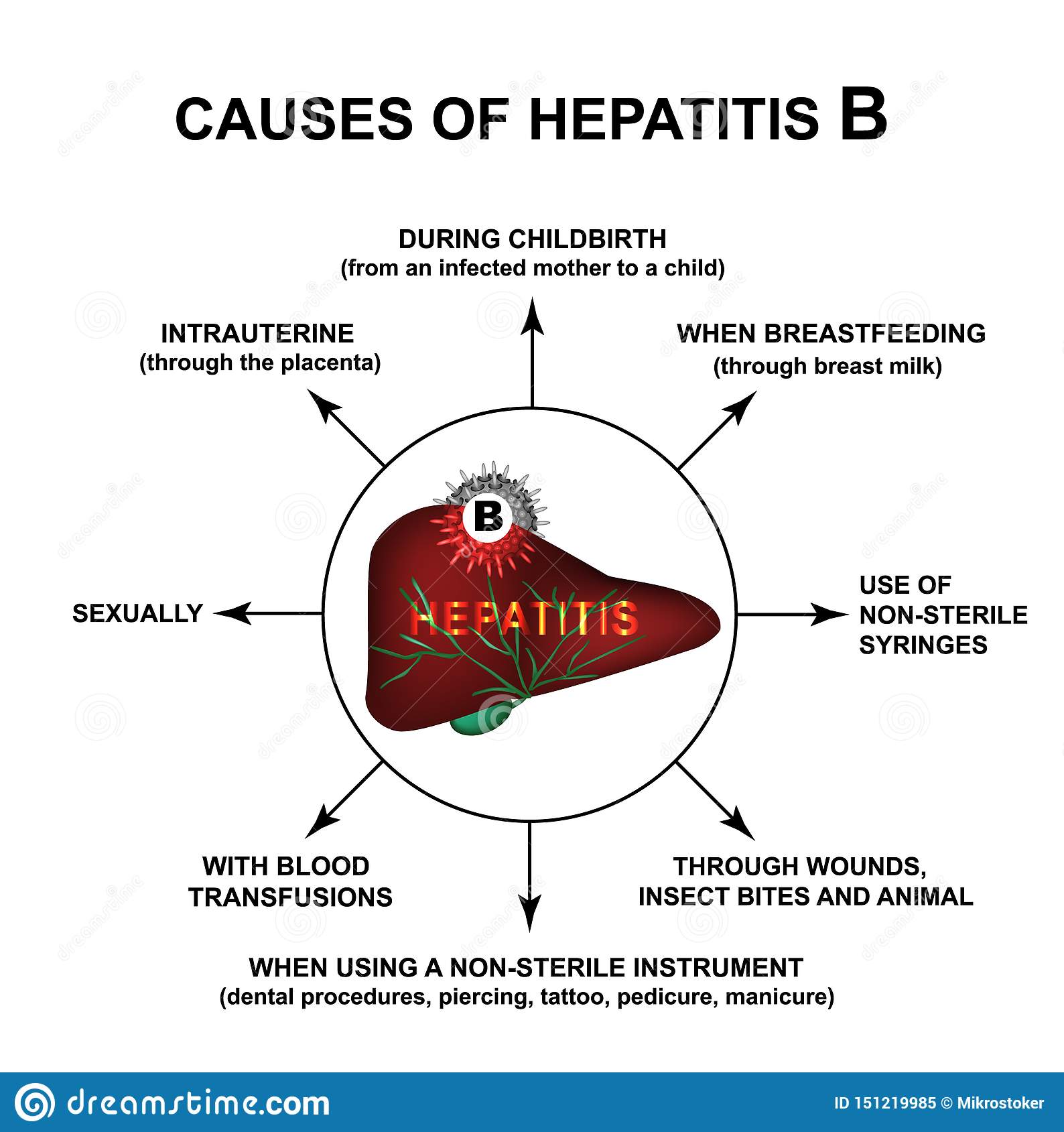
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Symptoms
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk In Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis B is now recognized as one of the most important cause for the development of HCC, accounting for over 50% of the HCC cases worldwide. However, it was not until the mid-1970s that scientists recognized the causative role of chronic hepatitis B in HCC development. This was following the discovery of the hepatitis-associated antigen, now known as the HBsAg, which has been reported to persist in patients with chronic hepatitis B with or without cirrhosis, leading to HCC development in a significant proportion of patients.41 Various mechanisms have been proposed in the pathogenesis of HCC in patients with chronic HBV infection. Integration of the HBV DNA into the hepatocyte genome and the epigenetic regulation of the minichromosome cccDNA result in chromosomal instability and activation of cancer-related genes along with inactivation of cancer-suppressive genes through interference with various cellular transcription and signal transduction processes.42 In addition, chronic hepatitis B results in release of cytokines and growth factors as part of the adaptive immune response, leading to hepatocyte necrosis and fibroblast proliferation, resulting in liver fibrosis/cirrhosis.43
As such, patients with chronic hepatitis B, especially those at high risk, should be continuously screened for HCC, regardless of the virologic remission .27
James E. Balow, … Howard A. AustinIII, in, 2008
Don’t Miss: Signs You Have Hepatitis C