Transmission Symptoms And Treatment
How is HBV transmitted?
HBV is transmitted through activities that involve percutaneous or mucosal contact with infectious blood or body fluids , including
- sex with an infected partner
- injection-drug use that involves sharing needles, syringes, or drug-preparation equipment
- birth to an infected mother
- contact with blood from or open sores on an infected person
- exposures to needle sticks or sharp instruments and
- sharing certain items with an infected person that can break the skin or mucous membranes , potentially resulting in exposure to blood.
How long does HBV survive outside the body?
HBV can survive outside the body and remains infectious for at least 7 days .
What should be used to clean environmental surfaces potentially contaminated with HBV?
Any blood spills should be disinfected using a 1:10 dilution of one part household bleach to 10 parts of water. Gloves should be worn when cleaning up any blood spills.
Who is at risk for HBV infection?
The following populations are at increased risk for becoming infected with HBV:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected people
- Men who have sex with men
- People who inject drugs
Who should be screened for HBV?
CDC recommends that the following people be screened for HBV :
What Is Hepatitis Positive
A positive HBsAg test result means that you are infected and can spread the hepatitis B virus to others through your blood. anti-HBs or HBsAb A positive or reactive anti-HBs test result indicates that a person is protected against the hepatitis B virus.
What is hepatitis AB?
On the other hand, hepatitis B begins as a short-term infection, but in some cases, it can progress into a chronic, or life-long, infection. Chronic hepatitis B is the worlds leading cause of liver cancer and can lead to serious liver diseases such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
How can I reduce my hepatitis B viral load?
Several antiviral medications including entecavir , tenofovir , lamivudine , adefovir and telbivudine can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth. Talk to your doctor about which medication might be right for you.
How fast does hepatitis B progress?
The incubation period of the hepatitis B virus ranges from 30 to 180 days. The virus may be detected within 30 to 60 days after infection and can persist and develop into chronic hepatitis B, especially when transmitted in infancy or childhood.
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis C And B Transmitted
What Is The Normal Range Of Hbv
Any value between 1 and 5 s/c is indeterminate and should be repeated. For hepatitis B surface antibody , a level less than 5 mIU is considered negative, while a level more than 12 mIU is considered protective. Any value between 5 and 12 mIU is indeterminate and should be repeated.
What does a positive Hbeab mean?
What HBeAg Test Results Mean. A positive test for the hepatitis B e-antigen means that there is an active infection with the hepatitis B virus and the virus is actively multiplying. Anyone who is in contact with your blood without protection may be at risk of contracting hepatitis B from you.
What does HBV DNA positive mean?
The presence of HBV DNA in serum is a reliable marker of active HBV replication. HBV DNA levels are detectable by 30 days following infection, generally reach a peak at the time of acute hepatitis, and gradually decrease and disappear when the infection resolves spontaneously.
What are the stages of HBV?
It comprises the immunetolerant phase, immuneactive chronic phase, inactive HBsAg phase and reactivation. The four phases differ from each other in certain parameters such as serum ALT level, HBeAg status and viral load.
What Is The Relationship Between Hbv And Hbeag
Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
What was the viral load on the first HBV test?
To compare apples to apples, your viral load during your first test was around 498 IU/mL and now your viral load is 272 IU/mL. Bottom line, your viral load has stayed the same, and is very low, which is excellent news.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity Qn 5
Membranous Nephropathy And Hepatitis B
Children with HBV-related MN show positivity of HbsAg and usually hepatitis B surface antibody is not detected. The hepatitis B early antigen can be detected in serum of 90% of patients.27 Hypocomplementemia is observed at the onset of disease , but titers of C3, C4 return to normal in the later part of disease.27 Circulatory immune complexes are detected in 80% of patients. Serum levels of transaminases may be raised on presentation.20,24 Liver biopsy shows evidence of chronic persistent hepatitis mainly in children, but chronic active hepatitis is seen in adults.
David O. Freedman, ⦠Elaine C. Jong, in, 2008
What Does It Mean When Hbsab Is Positive For Hepatitis B
When HBsAb is positive it usually means that you have recovered from a hepatitis B infection and have some immunity, or that you once received the hepatitis B vaccination and are immune. 2
What does a positive IgM test for HBV mean?
IgM anti-HBc a positive blood test result indicates a person has a new acute hepatitis B infection.IgM anti-HBc is generally detectable at the time symptoms appear and declines to sub-detectable levels within 6 9 months. Note: An acute exacerbation in a chronic HBV infection can also result in a positive anti-HBc IgM test
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
The Immunological Effect Of Booster Vaccination In Non
To confirm the efficacy of booster HBV vaccination in non-responders and low-responders, we evaluated 33 subjects at 1 year after booster vaccination and 10 subjects at 2 years after booster vaccination. Although the anti-HBs titer increased significantly after booster vaccination, this response was not sustained .
Serial changes in the anti-HB titers of subjects who received a booster vaccination. The vertical axis shows the change in anti-HB titer over time. The horizontal axis shows the indicated time points at which the anti-HB titer was measured at 1 year and 2 years after vaccination. Statistical significance was evaluated using the Friedman test. P values of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. n.s.: not significant
Efficacy And Safety Of Hepatitis B Virus Vaccines
Completion of HBV vaccination produces adequate lifelong antibody response in over 90% of healthy adults. Similar efficacy has been reported among the different three-dose formulations. The newer two-dose vaccine demonstrated comparable efficacy to traditional vaccines . However, PWID are one distinct population in whom HBV vaccine response may be attenuated. Reported seroprotection rates among PWID have ranged between 55% and 97% . Nonstandardized timing of anti-HBs measurement may impact estimates, with highest rates seen when testing for anti-HBs is performed 2 months following the third dose . Older age, active drug use, and coinfection, including HIV infection, have been linked with lower responses in individual studies. Safety concerns regarding the HBV vaccine are minimal. Anaphylaxis is extremely rare, estimated at 1 per 1.1 million doses . Although various conditions have been reported , no causal link between these conditions and the vaccine has been established.
PIERRE VANDEPAPELIÃRE, in, 2000
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Negative
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Chronic Hepatitis B
What Hbv Dna Level Is High
A baseline high HBV-DNA level > 10 000 copies/mL was associated with a significant increased risk of HCC and with progression towards cirrhosis.
Why are my hep B antibodies high?
If your HBsAb is positive, it either means you have had the infection in the past or received the vaccine and are now immune. Many people who become infected with the hepatitis B virus have no obvious risk factors for getting the infection.
Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B virus infection, also known as serum hepatitis, is endemic throughout the world. The infection is spread primarily through blood transfusion or percutaneous contact with infected blood products, such as sharing of needles among injection drug users. The virus is also found in virtually every type of human body fluid and has been known to be spread through oral and genital contact. HBV can be transmitted from mother to child during delivery through contact with blood and vaginal secretions, but it is not commonly transmitted via the transplacental route.
The incubation period for HBV infection averages 60 to 90 days . Common symptoms include malaise, fever, gastroenteritis, and jaundice . After acute infection, HBV infection becomes chronic in 30% to 90% of infected children younger than 5 years of age and in 5% to 10% of infected individuals age 5 or older. Some of these chronic carriers are asymptomatic, while others progress to chronic liver disease, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatitis B surface antigen is the first serologic marker, appearing in the serum 6 to 16 weeks following HBV infection. In acute cases, HBsAg usually disappears 1 to 2 months after the onset of symptoms with the appearance of hepatitis B surface antibody . Anti-HBs also appears as the immune response following hepatitis B vaccination.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis B Do
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Hepatitis B
Data Analysis And Statistics
All analyses were done using nonparametric statistical software with penalized maximum likelihood to remove first-order bias. A p-value < 0.05 for two-sided tests was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables were expressed as means plus/minus standard deviation or mean , categorical variables as numbers . Conditional logistic regression analysis was used to estimate risk ratios and 95% confidence intervals for loss of anti-HBs putative associated factors included age, sex, type of rheumatic disease, conventional DMARDs, biologic DMARDs , comorbidity, and baseline anti-HBs titer.
How Much Does The Test Cost

The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
Recommended Reading: Are There Different Types Of Hepatitis C
What Is The Normal Range For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are measured in blood samples in milli-International Units/milliliter mIU/mL). The ranges for hepatitis B surface antibodies are:
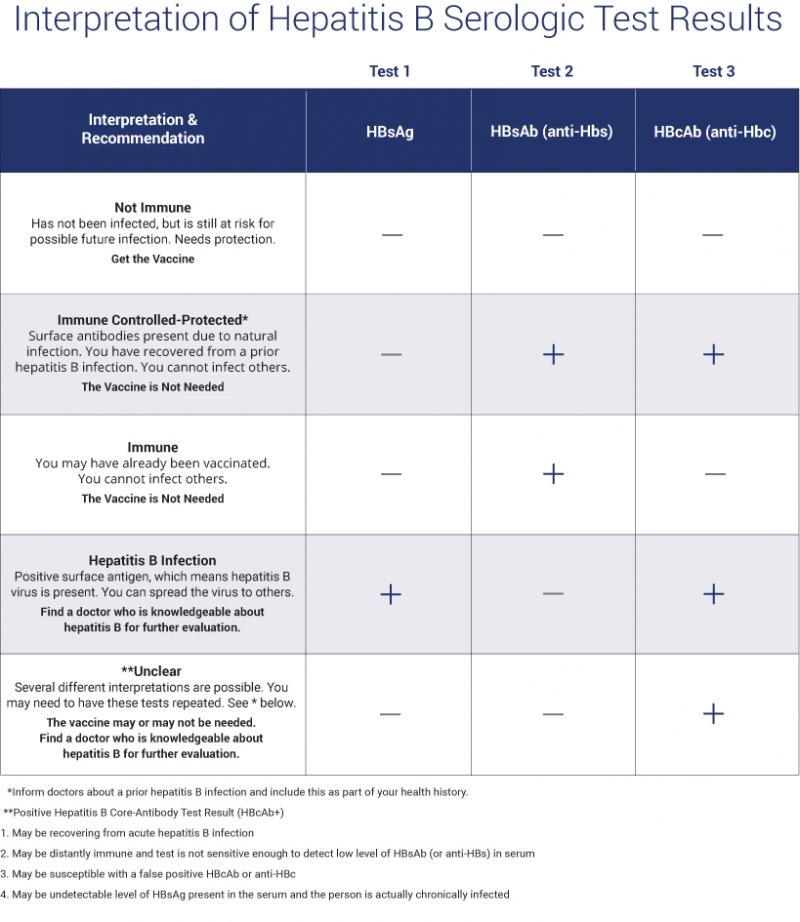
- Anti-HBs greater than 10-12 mIU/mL: Protected against hepatitis B virus infection, either from vaccination or successful recovery from a previous HBV infection.
- Anti-HBs less than 5 mIU/mL: Negative for HBV infection, but susceptible and hence requires vaccination.
- Anti-HBs from 5-12 mIU/mL: Inconclusive results and the test should be repeated.
However, there is no standardization of these values so it is advisable to check the manufacturers values it is the reason values are mainly reported as positive or negative.
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Also Check: How Do I Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B Vaccine And Surface Antibody Titer Faqs
PLEASE NOTE: This is program specific some programs require 3 Hepatitis B vaccines AND a positive Hepatitis B Surface Antibody titer while others will accept 3 vaccines OR a titer. Please read the information in your CastleBranch account carefully so that you know exactly what you need to meet your programs requirements. If you have any questions, please email and a team member will respond.
You May Like: Causes And Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Screening For Viral Hepatitis
The purpose of screening for viral hepatitis is to identify people infected with the disease as early as possible, even before symptoms and transaminase elevations may be present. This allows for early treatment, which can both prevent disease progression and decrease the likelihood of transmission to others.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A causes an acute illness that does not progress to chronic liver disease. Therefore, the role of screening is to assess immune status in people who are at high risk of contracting the virus, as well as in people with known liver disease for whom hepatitis A infection could lead to liver failure. People in these groups who are not already immune can receive the hepatitis A vaccine.
Those at high risk and in need of screening include:
- People with poor sanitary habits such as not washing hands after using the restroom or changing diapers
- People who do not have access to clean water
- People in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- People who use illicit drugs
- People with liver disease
- People traveling to an area with endemic hepatitis A
The presence of anti-hepatitis A IgG in the blood indicates past infection with the virus or prior vaccination.
Hepatitis B
The CDC, WHO, USPSTF, and ACOG recommend routine hepatitis B screening for certain high-risk populations. Specifically, these populations include people who are:
Other
Read Also: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Be Cured Without Treatment
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
What Does Anti Hbs Positive Mean
Anti-HBS is a type of laboratory test that is performed on people who are thought to have hepatitis B. The test, which can be used to determine whether the person has already been immunized by exposure to Hepatitis B virus or by vaccination, can also be used to determine whether the virus has been destroyed by the body and acquired immunity for life. The anti-HBS test is also used to check whether the vaccine is retained, or in other words, whether the body produces antibodies against HBsAG, which is defined as the surface antigen of the Hepatitis B virus. Anti-RLS test is also performed to determine whether the person is immune to this virus before the hepatitis B vaccine is administered.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.