High Level Of Protection: The Hepatitis B Vaccine
The hepatitis B vaccine is the mainstay of hepatitis B prevention. Safe and effective vaccines are available that offer high levels of protection and most countries in Europe have implemented a universal vaccination programme.
With evidence of on-going transmission and continuing importation of cases, these vaccination programmes are essential in order to achieve the target of hepatitis elimination by 2030.
In addition to vaccination programmes the implementation of blood safety strategies and safe injection practices can prevent transmission of HBV. Safer sex practices can also protect against transmission.
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis B
In general, occupational groups with increased risk include:
- Health-care workers repeatedly exposed to blood or blood products or those who are at risk of needlestick injury.
- Pathologists, laboratory personnel, or embalmers.
- Dentists, dental assistants, and dental hygienists.
- Certain staff members of institutions for the developmentally handicapped.
- Staff of institutions where workers may be exposed to aggressive, biting residents.
Travellers to regions with intermediate or high rates of endemic HBV infection may also consider being vaccinated.
How Common Is Hepatitis B
The number of people who get this disease is down, the CDC says. Rates have dropped from an average of 200,000 per year in the 1980s to around 20,000 in 2016. People between the ages of 20 and 49 are most likely to get it.
About 90% of infants and 25-50% of children between the ages of 1-5 will become chronically infected. In adults, approximately 95% will recover completely and will not go on to have a chronic infection.
As many as 1.2 million people in the U.S. are carriers of the virus.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B And Liver Cancer
Efficacy Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
The ultimate goal of hepatitis B vaccination is to reduce the prevalence of chronic hepatitis B carriers, as well as to prevent the occurrence of acute hepatitis B. Vaccination is the most effective method for the decrease in the prevalence of HBV infection.
Hepatitis B vaccines have been evaluated in clinical trials to determine protective level of serum anti-HBs. Persons who respond to HBV vaccine with titers of anti-HBs 10 mIU/mL or greater are protected against acute hepatitis B and chronic infection.35 Antibody production rate is higher in the younger age at vaccination and lower for those older than 40 years of age. Thus, antibody test after vaccination is not required for healthy people, however, it should be tested after vaccination in hemodialysis patients, HIV positive people, those at occupational risk of infection such as workers in operation rooms and intensive care unit, babies born to HBsAg-positive mothers, and those with family history of HBV carriers. Since the antibody titer is at maximum around on 1 to 3 months after the completion of vaccine series, the tests for anti-HBs are performed at this time.
The antibody response to hepatitis B vaccine is 90% in healthy adults and 95% of infants, children, and adolescents.36 As for vaccine efficacy, complete protection has been achieved among immunocompetent persons who developed anti-HBs titers of 10 mIU/mL or greater after completion of vaccination.35,37
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Females
How Do I Know If I Have Hbv
A rapid point-of-care test after a finger prick or a simple blood test can tell if you are infected with the hepatitis B virus.
These tests can also help your doctor determine whether you are currently ill with hepatitis B, or if you are a chronic carrier. Although there is no treatment for the disease, bed rest and a good diet are important. Alcohol and medications should be restricted. Follow-up blood tests are necessary to tell if the disease has gone.
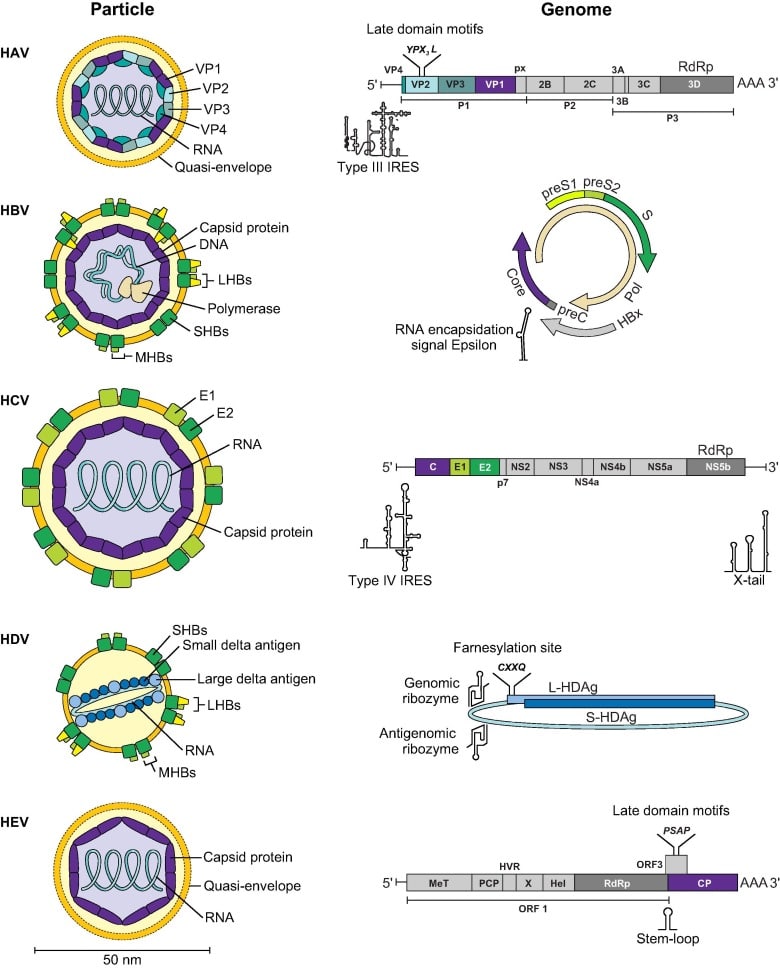
Hbv And Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Epidemiologic studies have demonstrated that there is a consistent and specific causal association between HBV infection and HCC . In patients with persistent HBV infection, the risk of HCC was 100 times higher than in non-infected individuals . The global distribution of hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with the geographic prevalence of chronic carriers of HBV, who number 400 million worldwide. The highest rates are in Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, with the HCC incidence > 50/100, 000 population .
Virological factors in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma have recently been defined. Both retrospective and prospective studies strongly supported the relation between positive HBeAg and the risk of HCC . A prospective study in Taiwan showed that relative risk of HCC among men who were positive for both HBsAg and HBeAg were much higher than that among men who were positive for HBsAg alone . HBV DNA was identified as the most important predictor of the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in HBsAg-positive patients with different clinical conditions . Therefore, efforts at eradicating or reducing the viral load may reduce the risk for HCC. Additionally, HBV genotype might play a role in the development of HCC. The data from Taiwan showed that genotype C is associated with more severe liver disease including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma , whereas genotype B is associated with the development of HCC in young noncirrhotic patients.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Genotype 3 Treatment
Hepatitis B Causes And Risk Factors
Itâs caused by the hepatitis B virus, and it can spread from person to person in certain ways. You can spread the hepatitis B virus even if you donât feel sick.
The most common ways to get hepatitis B include:
- Sex. You can get it if you have unprotected sex with someone who has it and your partnerâs blood, saliva, , or vaginal secretions enter your body.
- Sharing needles. The virus spreads easily via needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood.
- Accidental needle sticks.Health care workers and anyone else who comes in contact with human blood can get it this way.
- Mother to child.Pregnant women with hepatitis B can pass it to their babies during childbirth. But thereâs a vaccine to prevent newborns from becoming infected.
Hepatitis B doesnât spread through kissing, food or water, shared utensils, coughing or sneezing, or through touch.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
You can get hepatitis C when you have contact with the blood of a person with the virus. This through sharing needles, syringes, or other injection drug equipment.
Other less common routes of transmission are:
- having a needlestick injury
- being born to a birthing parent with hepatitis C
- having sex with someone with hepatitis C without a barrier method
- receiving a tattoo or piercing with nonsterile equipment
Also Check: Hey Google What Is Hepatitis B
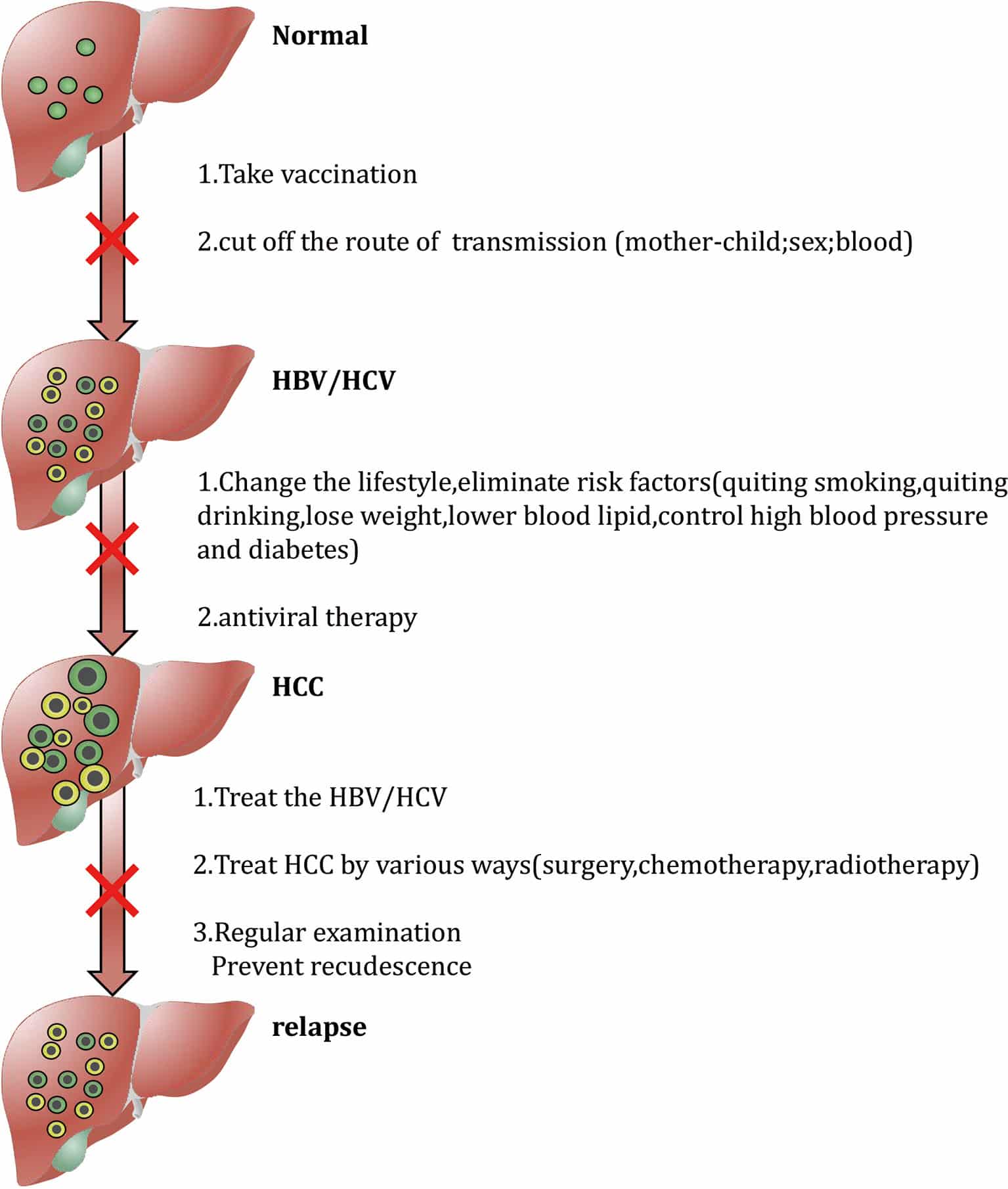
How To Prevent Transmission
Between 2% and 6% of adults infected with hepatitis B virus will develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to liver failure and liver cancer, so protecting yourself is important.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe for almost everyone and about 95% effective for providing long-term protection against hepatitis B infection.
While anyone can benefit from the vaccine, people who are at a greater risk of being exposed to the virusbecause of their work, lifestyle or medical historyare strongly encouraged to be immunized. In many countries, babies born to infected mothers get vaccinated at birth. All babies born in the United States are routinely vaccinated.
Hepatitis B immune globulin , is another way to prevent hepatitis B infection in babies born to infected mothers or after exposure to the virus. This uses concentrated antibodies to provide immediate protection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it is given as a shot and can provide short-term protection against hepatitis B.
Because the hepatitis B vaccine does not protect against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread through sex and contact with blood, it is still important to keep using basic protective strategies. Practicing safer sex and not sharing needles are recommendedeven if you’re immune to hepatitis B.
What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is a major global health problem and the most serious type of viral hepatitis. It can cause chronic liver disease and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Worldwide, an estimated two billion people have been infected with the HBV and about 250 million have chronic liver infections.A vaccine to prevent catching HBV has been available since 1982. Hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing HBV infection and its chronic consequences, and is the first vaccine against a major human cancer.
You May Like: Royal Canin Feline Hepatic Diet
The Types Of Viral Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis known as hepatitis A , hepatitis B , hepatitis C , hepatitis D , and hepatitis E . That said, there have been cases of acute hepatitis that could not be attributed to one of these five types of hepatitis viruses, alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune disease, which lead researchers to try to find another cause.
Though the etiology of these viruses have not yet been fully established, researchers have identified three other types of viral hepatitis , which they have named hepatitis F , hepatitis G , and transfusions transmitted virus . As relatively new diseases and viral discoveries, information about them and how they work is relatively scarce. We do know, however, that cases of TTV have only been associated with hepatitis in people who have had a blood transfusion.
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
Also Check: Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Who Is Most At Risk For Chronic Disease
The likelihood that an HBV infection will become chronic depends upon the age at which a person becomes infected, with young children who become infected with HBV being the most likely to develop chronic infections.
About 90% of infants infected during the first year of life develop chronic infections 30% to 50% of children infected between one to four years of age develop chronic infections. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood die from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis. About 90% of healthy adults who are infected with HBV will recover and be completely rid of the virus within six months.
Cytokines May Promote Hbv Infection In Trophoblasts
The placenta is a complex environment where a variety of soluble cytokines play key roles in gestation and are necessary for successful pregnancy. These include IL-1,3,4,6, transforming growth factor- , IFN-, and tumor necrosis factor- . Some cytokines in the placental microenvironment may also play a regulatory role in protecting the fetus or conversely, in driving viral expression.58 In support of this theory, two studies have provided evidence of enhanced HBV uptake into choriocarcinoma cell lines such as JAR, JEGIII and primary trophoblasts in the presence of TNF-.58,59 The susceptibility to HBV of JAR cells was significantly enhanced in the presence of the cytokine TNF-.58 Similar results showed that in vitro infection with HBV induces the accumulation of HBV DNA and HBsAg and leads to an increase in the secretion of HBsAg within JEGIII, all of which were significantly enhanced by the addition of TNF-.59
You May Like: Hepatitis B Cure Phase 3
Where Is Hbv Most Common
Hepatitis B is endemic in China and other parts of Asia. Most people in the region become infected with HBV during childhood.
In these regions, 8% to 10% of the adult population are chronically infected. Liver cancer caused by HBV is among the first three causes of death from cancer in men, and a major cause of cancer in women. High rates of chronic infections are also found in the Amazon and the southern parts of eastern and central Europe. In the Middle East and Indian sub-continent, an estimated 2% to 5% of the general population is chronically infected. Less than 1% of the population in western Europe and North American is chronically infected.
Hbx Reduces Apoptosis In Trophoblasts Via Egfr/akt Signaling Pathways
The intracellular EGFR/Akt signaling pathway has been recently identified to be involved in trophoblastic infection with HBV.63 A lower degree of apoptosis was observed in HBx-expressing JEGIII cells, while a higher level of pEGFR was detected both in placental tissues from HBV carriers and in HBx-transfected JEGIII cells.63 Both the upregulation of pAkt and reduced apoptosis could be offset by the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib. In addition, the knockdown of HBx suppressed the activation of the EGFR/Akt pathway and increased cellular apoptosis, whereas EGF stimulation counteracted this effect. This supports the hypothesis that HBx reduces apoptosis in trophoblasts, possibly through the activation of the EGFR/Akt signaling pathway. This suggested that HBx inhibits trophoblast cell apoptosis by activating the EGFR/Akt signaling pathway. In addition, a recent study demonstrates that HBx promotes HBV replication in trophoblasts via downregulation of Smc5/6, activates the EGFR promoter and inhibits trophoblast apoptosis via the PI3K/p-AKT downstream signaling pathway.64 Therefore, the anti-apoptotic pathways induced by HBx might contribute to the intrauterine transmission of HBV .
Read Also: How Many Types Of Hepatitis Are There
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
What Should You Do If You Think You Have Hep B
If you think you might be at risk for hep B, there are many ways we can help you. We can offer you support, answer questions and help you find health services near you:
- Get a hep B test: Take a look at our NSW Services Directory to find a hep B testing doctor near you.
- Speak to someone:
- call 1800 803 990 to speak confidentially with one of our Hepatitis Infoline workers
- use our online Live Chat, available on every page of our website.
Recommended Reading: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another person’s bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
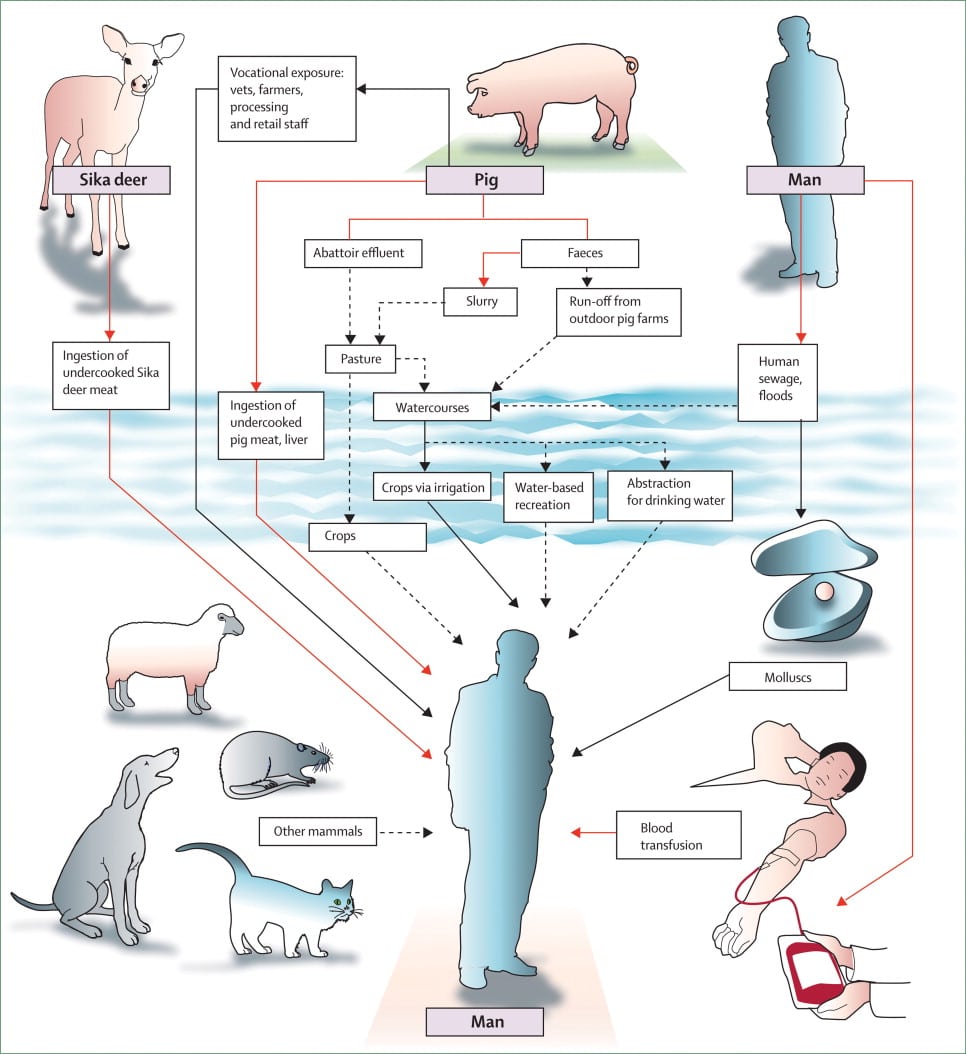
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Don’t Miss: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis And How Is It Treated
Symptoms And Causative Agent
Hepatitis is a general term for inflammation of the liver, which may result from infectious or non-infectious causes. Viruses responsible for many cases of infectious hepatitis include hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, hepatitis D, and hepatitis E. Hepatitis A and B are the only hepatitis viruses for which vaccines are currently available in the United States .
The hepatitis B virus is a partly double-stranded DNA virus in the hepadnavirus family. The hepatitis A virus is a single-stranded RNA virus in the Picornavirus family. Both viruses, though structurally unrelated, infect and replicate primarily in liver cells.
The symptoms of acute hepatitis A infection are identical to those of hepatitis B infection. Early symptoms are headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, rash, body aches and pains, and dark colored urine. Following this phase, jaundice , light stools, and liver pain may appear.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hbv
Hepatitis B virus can cause an acute illness with symptoms that last several weeks, including yellowing of the skin and eyes , dark urine, extreme fatigue, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. Most of the time HBV infection is ASYMPTOMATIC.
Joint pains, muscle aches, rash, and jaundice may occur in some people. People can take several months to a year to recover from the symptoms. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure. These people may not know that they are infected, and may therefore not go and see a doctor. People with chronic hepatitis B infection may later develop serious problems like liver cancer and liver failure.
You May Like: Where To Get Hepatitis B Booster Shot