Uk First To Approve Mercks Covid
The United Kingdom became the first country to approve Merck and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics COVID-19 antiviral pill, according to Reuters. Britains Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency recommended use of the drug, molnupiravir, for the treatment of people with mild to moderate COVID-19 and at least 1 risk factor for developing severe illness, such as obesity, older age, diabetes, and heart disease. The pill will be administered as soon as possible after a patient receives a positive COVID-19 test and within 5 days of the onset of symptoms. The green light is the first for an oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19, and US advisors are expected to meet in late November to vote on molnupiravirs authorization.
Study Setting And Participants
A prospective cohort study was established in February 2015 at St. Pauls Hospital Millennium Medical College, a tertiary care hospital in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Ethiopia is the second most populous nation in Africa with a population size close to 100 million , and an estimated seroprevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen of 7.4% .
Patients who started antiviral therapy between March 18, 2015, and August 1, 2017, were included in this study. The participants were adults with chronic hepatitis B, defined as having a positive HBsAg for at least 6months. Patients were referred to the treatment center based on symptoms of chronic liver disease, or they were asymptomatic individuals found to be HBsAg positive by routine screening at blood banks, antenatal clinics, etc. Patients co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus were excluded from the study, as were patients with known HCC or other terminal disease. As this was the first public treatment center in the country, many of the initial patients were enrolled with clinical signs of advanced liver disease. Early experiences from the treatment center was published previously .
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Read Also: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Predicting Survival In Hepatitis B
Alanine aminotransferase level alone is not an appropriate indication for therapy in chronic hepatitis B infection, and other criteria in addition to ALT must be used to determine eligibility for therapy Predictors of survival in chronic hepatitis B infection are surprisingly not well described. Various studies have identified different factors that were associated with adverse outcomes.
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
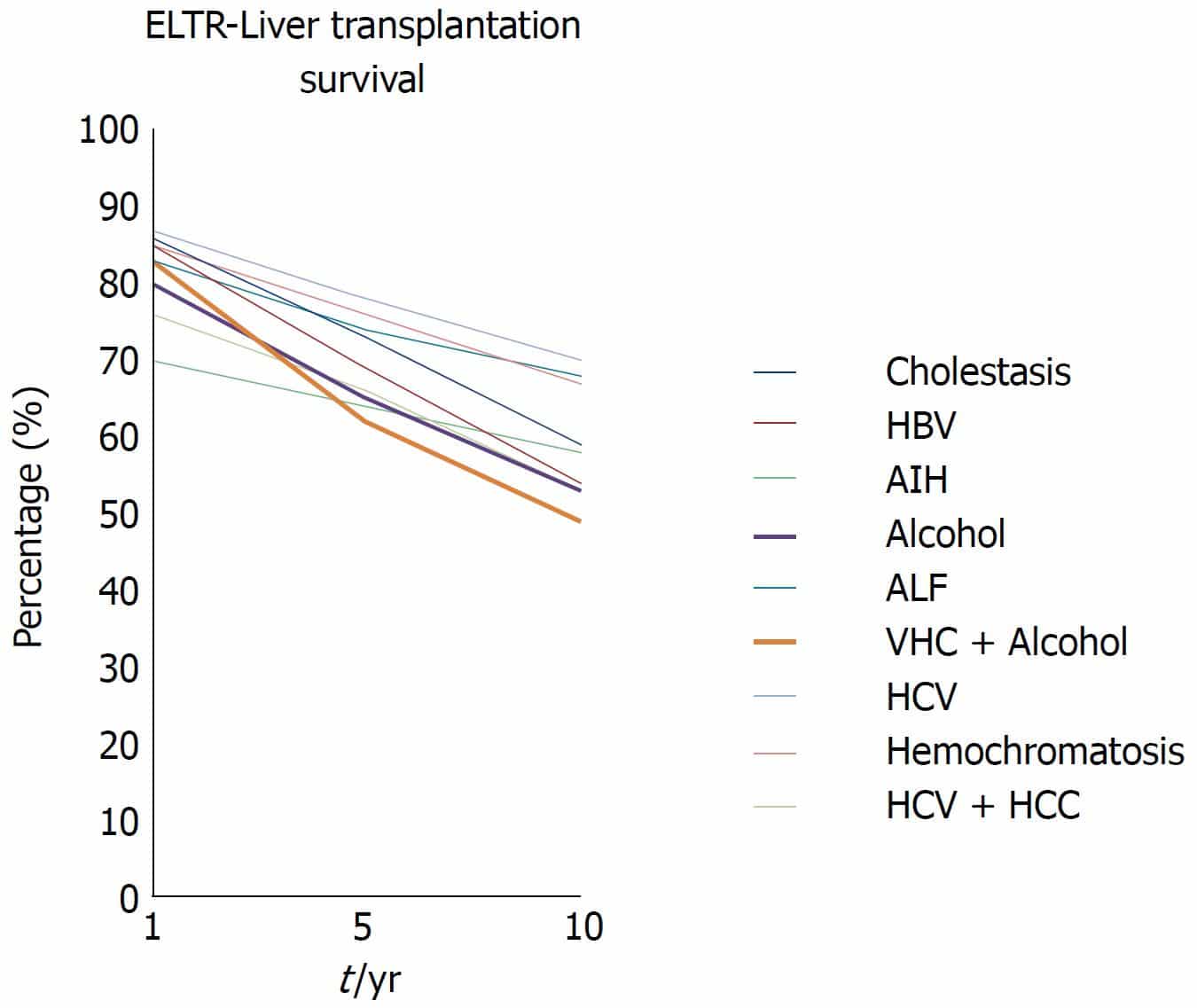
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Read Also: How Many Types Of Hepatitis Are There
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover.
However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become carriers, which means they have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Carriers are more likely to pass hepatitis B to other people. Most carriers are contagious meaning they can spread hepatitis B for the rest of their lives.
Hepatitis B infections that last a long time may lead to serious liver diseases like cirrhosis and liver cancer. About 1 in 5 people with chronic hepatitis B die from it. There are medicines that can help treat chronic hepatitis B infections.
Most babies who get hepatitis B during birth develop chronic infection, unless they get treated right away. But treatments are almost always effective if your baby gets them quickly. Thats why its important for pregnant people to get tested for hepatitis B.
Cases Of Hepatitis C In The United States
The CDC reports that in 2018, a total of 15,713 U.S. death certificates had hepatitis C as an underlying or contributing cause of death. This is likely lower than the actual numbers since so many infections go undocumented.
Studies show that baby boomers are more likely than other groups to have been exposed to HCV. Most of them contracted infections between 1970 and 1990 during a peak of new infections.
And since people with an HCV infection might not show symptoms, they may unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
Today, the most common risk factor for hepatitis C in the United States is injection drug use.
Since an HCV infection can show no symptoms, the number of new cases is likely higher than reported, according to the CDC.
Also Check: Drinking Alcohol With Hepatitis C
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
How You Can Get Hepatitis B
You can get hepatitis B from:
- injecting drugs using shared needles
- being injured by a used needle
- having a tattoo or piercing with unsterilised equipment
- having a blood transfusion in a country that does not check blood for hepatitis B. Blood transfusions in the UK are checked for hepatitis B.
If you’re pregnant and have hepatitis B, you can also pass it onto your baby during pregnancy or birth.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Homeopathy Treatment In Hindi
Will The Price Go Up In The Future
Yes, the price of these drugs is certain to increase as competition increases and the market becomes more profitable.
The current drugs have a 90% cure rate and very few side effects, compared to interferon which has a 40% cure rate but leaves 60% of patients too sick to work or carry out their normal daily activities for a year or more.
The current drugs are a one time treatment and last for the rest of your life.
Newer drugs that have a higher cure rate with fewer side effects are in development and will probably be available over the next two years.
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
Also Check: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Can You Die From Hepatitis C
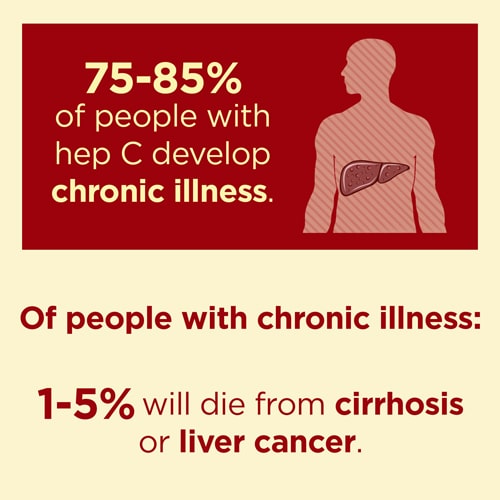
Complications from untreated hepatitis C, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, can be fatal, though HCV itself is rarely fatal.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , people who develop cirrhosis from HCV have a
more than half of people with an HCV infection will develop chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C is long term and can lead to permanent cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C usually has no symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis C may not even know they have it. But once symptoms appear, it means that damage to the liver has already begun.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis Ab And C
What Are The Risk Factors For Getting Hepatitis B
Due to the way that hepatitis B spreads, people most at risk for getting infected include:
- Children whose mothers have been infected with hepatitis B.
- Children who have been adopted from countries with high rates of hepatitis B infection.
- People who have unprotected sex and/or have been diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection.
- People who live with or work in an institutional setting, such as prisons or group homes.
- Healthcare providers and first responders.
- People who share needles or syringes.
- People who live in close quarters with a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
- People who are on dialysis.
Who Is Most Likely To Get The Hepatitis C Virus
People who received blood transfusions before 1992 are at a high risk of having been exposed to the hepatitis C virus, as this is when reliable tests began to be used in the USA. Also people who received injected drugs and had multiple sexual partners before 1990 are also considered to be at high risk.
Recommended Reading: Could I Have Hepatitis And Not Know It
Hepatitis B And Pregnancy
If youâre pregnant, you might pass the virus to your baby at birth. Itâs less likely to happen during your pregnancy.
If your baby gets the virus and isnât treated, they could have long-term liver problems. All newborns with infected mothers should get hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine for hepatitis at birth and during their first year of life.
Whats The Prognosis For Hepatitis B
Your doctor will know youâve recovered when you no longer have symptoms and blood tests show:
- Your liver is working normally.
- You have hepatitis B surface antibody.
But some people don’t get rid of the infection. If you have it for more than 6 months, youâre whatâs called a carrier, even if you donât have symptoms. This means you can give the disease to someone else through:
- Unprotected sex
- Contact with your blood or an open sore
- Sharing needles or syringes
Doctors donât know why, but the disease does go away in a small number of carriers. For others, it becomes whatâs known as chronic. That means you have an ongoing liver infection. It can lead to cirrhosis, or hardening of the organ. It scars over and stops working. Some people also get liver cancer.
If youâre a carrier or are infected with hepatitis B, donât donate blood, plasma, body organs, tissue, or sperm. Tell anyone you could infect — whether itâs a sex partner, your doctor, or your dentist — that you have it.
Show Sources
CDC: âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for Health Professionals,â âHepatitis B Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Mayo Clinic: âHepatitis B.â
UpToDate: âHepatitis B virus: Screening and diagnosis.â
CDC.
HealthyPeople.gov: âHepatitis B in Pregnant Women: Screening.â
Annals of Internal Medicine: âScreening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement.â
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Shot Side Effects
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C
Treating hepatitis C has become simpler over the last few years with newer drugs that have fewer side effects and fewer strains of the virus these drugs are not without controversy however. Since the gold standard for treating hepatitis C used to include the drug interferon and a ribavirin, many physicians believe treatment will be more effective if these two drugs are also used.
Most physicians also believe that the new drugs should not be used alone but in combination with each other.
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Hepatitis And Not Know It
Our Areas Of Innovation For Hepatitis B
Liver biopsies provide a great deal of information about the extent of damage in a childs liver, but the procedure is invasive and can be both painful and risky. Researchers at Boston Childrens are investigating an ultrasound-based imaging technology called FibroScan that may be able to help doctors assess liver scarring without the need for a biopsy.
Treatment Monitoring And Endpoints
Treatment eligibility criteria were based on the European Association for the Study of the Liver 2012 guidelines, with some modifications as previously described . The standard therapy was tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300mg once daily. After initial adherence counselling, TDF was dispensed for 1 month thereafter the patients received drug supply for 3months at each follow-up visit.
The following laboratory tests were performed during follow-up:
-
Every 3 months: complete blood count, liver enzymes , creatinine, and HIV rapid test
-
Every 6 months: HBsAg, HBV viral load
Liver fibrosis was assessed with transient elastography prior to starting treatment and was repeated 6-monthly thereafter. Significant fibrosis was defined as > 7.9kPa and cirrhosis as > 9.9kPa . Decompensated cirrhosis was defined as current or past evidence of ascites, either by clinical examination or by ultrasonography. Clinical examination was done at the initial visit and was focused on signs of liver disease. Ultrasound of the liver was performed in all patients who started antiviral treatment, and was repeated annually, mainly to detect HCC.
Body mass index was used to assess nutritional status. Body weight was measured at baseline using a manual scale, and height was measured using a stadiometer mounted on the scale. BMI below 18.5kg/m2 defined underweight, in accordance with the WHO classification .
Recommended Reading: Natural Cure For Hepatitis C
What Is The Latest News Concerning Hepatitis C
The number of people in the United States who die from hepatitis C has dropped from 15,000 to 6,400 a year. This drop is due to a combination of factors, including more people getting tested, more people being treated successfully and the success of safer practices in hospitals.
Another factor is that people who get infected with both hepatitis A and B viruses have a lower risk of developing severe liver disease.
But the most startling new news is that a new and better treatment has been released that treats all types of hepatitis C. In February 2013, the Food and Drug Administration approved another new drug for hepatitis C called sofosbuvir. It is a nucleotide analogue that prevents the hepatitis C virus from multiplying in your body and stops liver damage from occurring. It is sold under the brand name Sovaldi.
Sofosbuvir works in a very different way than older treatments and can be taken orally alone. It can lead to a better chance of cure in just eight to 24 weeks. It is very effective in various types of hepatitis C, including genotypes 1, 2 and 3, which cause the most damage to the liver.
Sofosbuvir was tested in combination with other drugs in 1,650 people with hepatitis C and preliminary results show it has a 95% cure rate.
Approved uses of sofosbuvir are for people with genotype 1 or 4 chronic hepatitis C who have had a liver transplant. It can also be used in people with genotype 2 or 3 who cant take the DAA drugs for some reason.