Finding Help For Hepatitis
If youve been diagnosed with viral hepatitis, there are a variety of resources that are available to help you. Lets explore a few of them below:
- Your doctor. Your doctor is a great first point of contact for questions and concerns. They can help you to better understand the type of hepatitis you have, as well as how it will be treated.
- American Liver Foundation . ALF is dedicated to ending liver disease through education, research, and advocacy. Their site has educational material about viral hepatitis, as well as ways to find doctors, support groups, and clinical trials in your area.
- Patient assistance programs. If you have hepatitis C, the cost of antiviral drugs can be high. The good news is that many drug manufacturers have patient assistance programs that can help you pay for these medications.
The chart below is an at-a-glance summary of some of the key differences between hepatitis A, B, and C.
| Hepatitis A |
|---|
Generic Name: Haemophilus B/hepatitis B Vaccine
BRAND NAME: Comvax
Medication Uses | How To Use | Side Effects | Precautions | Drug Interactions | Overdose | Notes | Missed Dose | Storage
USES: This medication is used in infants to help prevent infection from a certain bacteria and the hepatitis B virus. Haemophilus influenzae b bacteria can cause a serious, sometimes fatal brain infection and lung infection . Hepatitis B infection can cause serious problems including liver failure, persistent hepatitis B infection, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Protecting against these infections can prevent these problems.This vaccine contains killed Haemophilus bacteria and a man-made piece of the hepatitis B virus. It does not contain live virus, so your infant cannot get either of these infections from the vaccine. This vaccine causes the body to make immune defensive substances that can protect you from these infections.This vaccine is recommended for all infants 6 weeks to 15 months old who are born to mothers who do not have current hepatitis B infection.This vaccine is not for use in adults.
OVERDOSE: If overdose is suspected, contact a poison control center or emergency room immediately. US residents can call their local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Canada residents can call a provincial poison control center.
NOTES: Laboratory and/or medical tests may be performed periodically for some patients at risk of a poor response to the vaccine. Consult your childs doctor for more details.
Whats The Difference Between Hpv And Herpes
Human papillomavirus virus and herpes are often confused as they can be sexually transmitted and cause genital lesions, however, they are caused by two different and unrelated viruses. Because of this, they cause slightly different symptoms and have different treatment options. Get to know the differences between these common sexually transmitted infections.
Read Also: Royal Canin Hepatic Wet Cat Food
What Other Problems Can Hepatitis B Cause
In rare cases, acute hepatitis B can cause liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease that causes long-term health problems such as cirrhosis , liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have ever had hepatitis B, the virus may become active again, or reactivated, later in life. This could start to damage the liver and cause symptoms.
Prevention Of Acute Hepatitis B
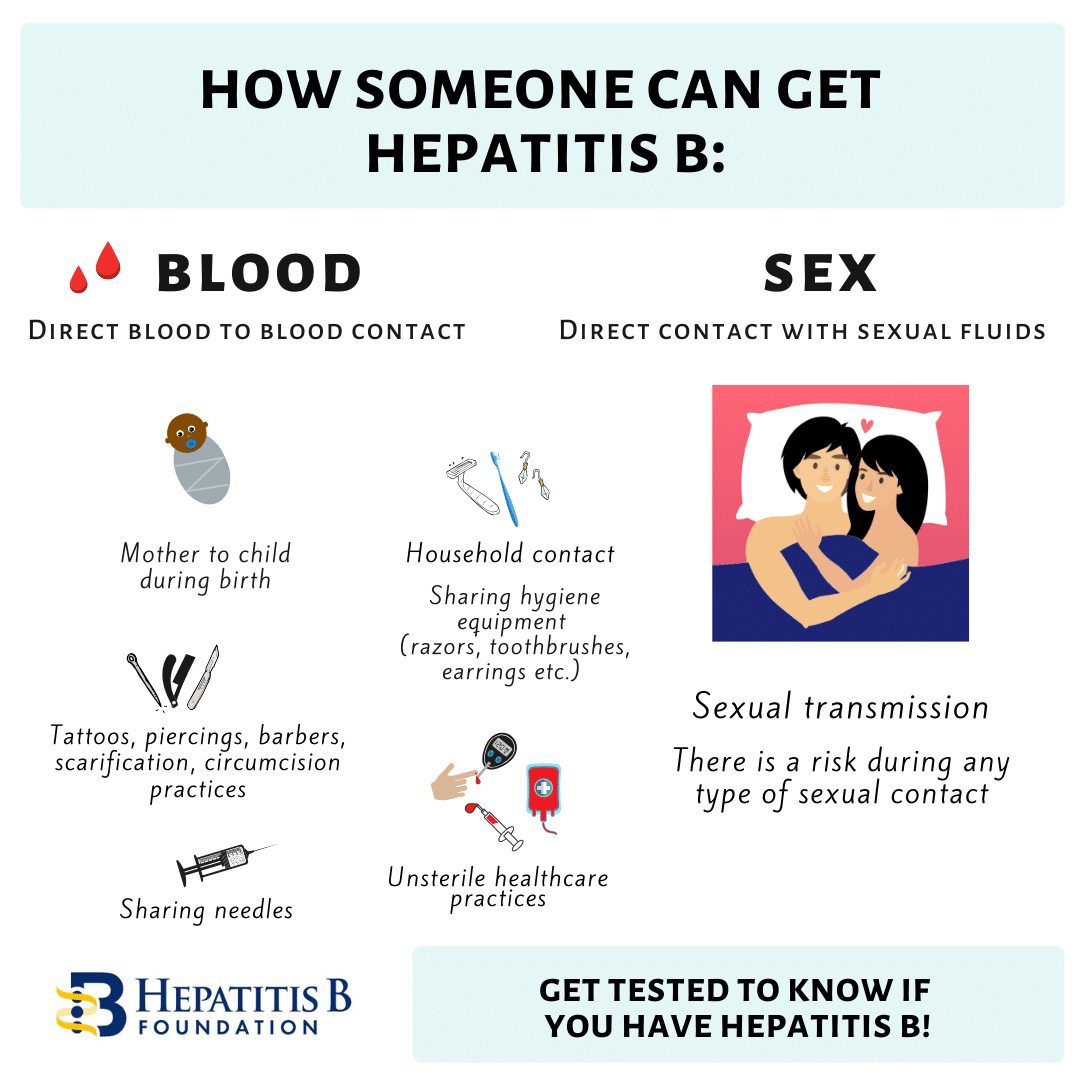
High-risk behavior, such as sharing needles to inject drugs and having several sex partners, should be avoided.
All blood donors are tested for hepatitis B to prevent the spread of hepatitis B virus through transfusions. Also, even though the chance of getting hepatitis from transfusions is remote, doctors use transfusions only when there is no alternative. These measures have dramatically decreased the risk of getting hepatitis from a blood transfusion.
-
Any adult who wishes protection from hepatitis B
-
All unvaccinated adults whose risk of getting hepatitis B is increased, including pregnant women
-
People with chronic liver disease
If family members and close contacts of people with chronic hepatitis B have not been vaccinated, they should be vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
If the level of hepatitis B virus is high in pregnant women, they are often given antiviral drugs during the last trimester of pregnancy to prevent transmission of the virus from mother to child.
People who are not vaccinated and have been exposed to hepatitis B, including infants born to mothers with hepatitis B, are given hepatitis B immune globulin and the vaccine. This combination prevents chronic hepatitis B in 75%, or it makes the disease less severe. Hepatitis B immune globulin contains antibodies obtained from the blood of people who have high levels of antibodies to hepatitis.
Read Also: How Do You Test For Hepatitis
Can Hepatitis B Be Controlled By Eating Right And Exercising
It is important that people with liver disease follow a healthy, nutritious diet as outlined by Health Canada in Eating Well with Canadas Food Guide.
Alcohol can also damage the liver so it is best that people with hepatitis B do not drink. Following a healthy lifestyle may also prevent fatty liver disease, another liver disease highly prevalent in Canada.
However, hepatitis B cannot be controlled by healthy eating and exercise alone. Hepatitis B can only be controlled by currently available treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will need to do regular blood tests to know how much of the active virus is in your blood . The viral load test is used to monitor and manage hepatitis B patients. Viral load can tell your doctor if you need treatment for hepatitis B and how well you are responding to treatment.
Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that happens in the first six months after being infected by HBV. It is estimated that 90 per cent of persons infected with hepatitis B will be able to overcome the infection within six months.
In such cases, these persons also develop permanent immunity to hepatitis B. Generally, most healthy adults and children above five years of age are more likely to recover from acute hepatitis B.
If it persists for more than six months, then the acute condition has become chronic. Chronic hepatitis B lasts longer, maybe even throughout your lifetime, as the virus multiplies in the liver.
Chronic hepatitis B can cause severe inflammation and scarring of the liver, significantly impairing liver functions. There is also a risk of developing liver cancer or other health complications.
To make things more complicated, symptoms may not develop immediately up until you or your loved one develops liver-related complications.
There are also rare instances where hepatitis B recurs in people who have had it before, which also causes further liver-related complications.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Hepatitis C Virus
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Declination Form
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Treating The Symptoms Of Hpv
Most cases of HPV dont require any treatment. The virus will go away on its own in many people. However, there are treatment options available for treating the symptoms of HPV.
Genital warts from HPV may occasionally go away without medication. Sometimes, medications are used to help lessen the effects of the warts. These include:
- imiquimod
- podofilox
- sinecatechins
Your doctor may also apply trichloroacetic acid or bicloroacetic acid, or cryotherapy to help treat genital warts.
Sometimes a doctor will remove the warts, though this removes the wart not the virus itself. If a high-risk HPV is found, your doctor may monitor you to ensure that cancer doesnt occur, or is caught early.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Can It Be Cured
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis B
If you think you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may administer the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and a shot of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. This is a combination of antibodies that provide short-term protection against the virus.
Though both can be given up to a week after exposure, theyre most effective at preventing infection if administered within 48 hours.
If you receive a diagnosis of acute hepatitis B, a doctor may refer you to a specialist. They may advise you to get regular blood tests to ensure you dont develop chronic hepatitis.
Many people with acute hepatitis B dont experience serious symptoms. But if you do, it can help to:
- get plenty of rest
- take over-the-counter pain mediation, like naproxen, when needed
Other lifestyle changes may also be needed to manage your infection, such as:
- eating a nutritious, balanced diet
- avoiding substances that can harm your liver, such as:
- alcohol
- certain herbal supplements or medications, including acetaminophen
If blood tests show you still have an active infection after 6 months, your doctor may recommend further treatment, including medications to help control the virus and prevent liver damage.
Blood Tests For Hepatitis B
If you test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen , you have HBV in your blood. You have a chronic infection if you test positive for HBsAg consistently for at least 6 months.
If you test negative for HBsAg but positive for the hepatitis B surface antibody , you are protected from HBV because you’ve received the vaccine or recovered from an acute infection.
Another test to detect acute hepatitis B looks for the IgG antibody to hepatitis B core antigen .
Testing positive for the antibody to this antigen the hepatitis B core antibody means either that you’re currently infected with HBV, or that you were in the past, depending on the results of the HBsAg and anti-HBs tests.
The hepatitis B “e” antigen can only be found in the blood during an active infection and signifies high levels of the virus .
On the other hand, having the hepatitis B “e” antibody means that you have chronic hepatitis B but low levels of the virus, and thus a lower risk of complications.
Unlike these antigen and antibody tests, the hepatitis B viral DNA test can directly detect the presence of the virus’s DNA in your blood.
Remember that only your doctor can interpret the results of your tests.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy
Treatment For Suspected Exposure
Anyone who has had potential exposure to HBV can undergo a postexposure prophylaxis protocol.
This consists of HBV vaccination and hepatitis B immunoglobin . Healthcare workers give the prophylaxis after the exposure and before an acute infection develops.
This protocol will not cure an infection that has already developed. However, it decreases the rate of acute infection.
What Are The Complications Of Hepatitis B
The course of hepatitis B infection depends mostly on the age at which a person is infected.
People infected as infants are likely to develop long term infection and can get complications such as scarring of the liver or liver cancer. Infants have a 9 in 10 chance and children have a 3 in 10 chance of developing a chronic, lifelong infection.
People infected as teenagers or adults are likely to become unwell with symptoms , but have a smaller chance of developing a chronic infection. Others develop a silent infection, without any symptoms.
Most people infected as adults clear the virus from the body within 6 months. They develop immunity to future hepatitis B infections and do not develop long-term liver damage.
However, approximately 1 in 20 adults cannot clear the virus and develop chronic hepatitis B. They are at risk of developing complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer in the longer term.
Read Also: Signs N Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Risk Factors Of Hepatitis B
The risk of developing hepatitis B will increase if you or your loved one:
- Have unprotected sex.
- Live or care for someone with chronic hepatitis B.
- Receive treatment from someone who does not use properly sterilised equipment.
- Provide treatment to someone, where there is a high likelihood of direct exposure to body fluids.
- Work or live in institutional facilities, such as prisons or hospitals.
- Travel to areas with a high risk of HBV infection.
Note that having any of these risk factors does not mean that you will develop hepatitis B.
What Are The Chances Of Getting Hepatitis C From Sex
Hepatitis C can spread through sexual intercourse, but its rare. And its extremely rare among monogamous couples. In fact, the CDC considers the risk of sexual transmission between monogamous couples so low that it doesnt even recommend using condoms. Also, theres no evidence that hepatitis C is spread by oral sex. But you should avoid sharing razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers, and sex during menstruation.
If you have HIV or if you have multiple partners, you should take precautions. Using condoms will protect you and your partners.
You May Like: Home Remedies For Hepatitis C
What Are The Symptoms
- Symptoms can take 2 to 6 months to appear.
- Many people who are infected with hepatitis B have either no symptoms or only mild symptoms.
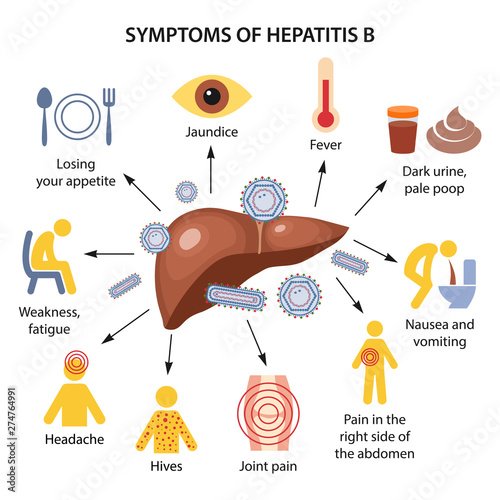
- Symptoms of acute hepatitis B can include fatigue, loss of appetite, joint pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and dark urine. A small number of people will develop jaundice .
- Some people develop chronic hepatitis B and most remain contagious for the rest of their lives. Chronic infection may lead to cirrhosis and/or liver cancer. Most people with chronic hepatitis B are unaware of their infection.
What Exactly Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus, abbreviated as HBV. HBV spreads through blood, semen, open sores or wounds or other bodily fluids.
However, it cannot be spread to others by sneezing or coughing. Hepatitis B causes liver inflammation that can if it persists cause lasting liver damage.
For many people, hepatitis B is a short-term illness that goes away on its own after some time. For others, however, it can become a chronic condition.
Younger people, especially infants and children below the age of five, who are infected by HBV have a much higher risk of developing chronic hepatitis B.
People from certain regions in the world also carry a higher risk of developing chronic hepatitis B, including persons from Sub-Saharan Africa, the Pacific islands, the Middle East, as well as parts of Northeast and Southeast Asia.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Shot For Newborns
About The Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus that belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. Related viruses in this family are also found in woodchucks, ground squirrels, tree squirrels, Peking ducks, and herons.
Structure of the Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus contains an outer envelope and an inner core.
- The outer envelope of the virus is composed of a surface protein called the hepatitis B surface antigen or HBsAg. The HBsAg can be detected by a simple blood test and a positive test result indicates a person is infected with the hepatitis B virus.
- The inner core of the virus is a protein shell referred to as the hepatitis B core antigen or HBcAg, which contains the hepatitis B virus DNA and enzymes used in viral replication.
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis B Virus
The hepatitis B virus has a complex life cycle. The virus enters the host liver cell and is transported into the nucleus of the liver cell. Once inside the nucleus, the viral DNA is transformed into a covalently closed circular DNA , which serves as a template for viral replication . New HBV virus is packaged and leaves the liver cell, with the stable viral cccDNA remaining in the nucleus where it can integrate into the DNA of the host liver cell, as well as continue to create new hepatitis B virus. Although the life cycle is not completely understood, parts of this replicative process are error prone, which accounts for different genotypes or genetic codes of the hepatitis B virus.