Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Drugs To Treat Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
The goals of chronic hepatitis B treatment are to improve quality of life to prevent or reverse liver disease progression to liver failure to minimize the risk of HCC development and to decrease the risk of transmission. The first-line treatment should be an agent with the highest potency and barrier to resistance. The agent will be able to reduce viremia rapidly to undetectable levels and maintain HBV DNA at undetectable levels continuously. The ability to control HBV with finite duration of treatment will also be important.
For a patient, the choice of first-line therapy should be selected according to the advantages and disadvantages of the available treatments in the setting of the patients clinical characteristics and preference. Although the efficacy of IFN is low and IFN treatment can have significant side effects, IFN treatment can be an ideal treatment for some patients whose clinical characteristics favour a good response to a fixed duration of IFN treatment. Oral nucleosides are good at suppressing HBV replication and have few side effects. These oral nucleosides do require prolonged or continuous treatment to maintain the control of HBV. Most hepatitis B patients will have clinical improvement while on oral nucleoside treatment.
What Are The Symptoms
What happens to you when you contract hepatitis B depends largely on the age at which you first become infected and how well your immune system copes with the virus. If you are infected as an adult, you may have a brief illness with mild or moderate symptoms such as jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and loss of appetite. As an adult, you have a 95% chance of clearing the infection completely and developing lifelong protection against this virus. The acute infection rarely leads to severe illness that requires a liver transplant.
Most babies and children exposed to this virus never have signs and symptoms. Unfortunately, they are more likely to become carriers of hepatitis B for life because their immune system is unable to fight and clear the virus from their body. In these cases, chronic infections are often not detected or picked up until much later in life when the person becomes seriously ill with liver disease.
Chronic hepatitis B infection goes through different phases that also show how well your body is coping with the virus. Although most people with chronic hepatitis B have an inactive disease and will remain healthy, about one in four will have active disease that may lead to cirrhosis , liver failure, and liver cancer.
People who are healthy with an inactive disease may still be at risk of virus reactivation, especially when their immune system is weakened by medicines such as chemotherapy or by other viral infections.
Read Also: How Long Does Hepatitis B Vaccine Last
American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2016 AASLD guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B as well as select recommendations from the 2018 AASLD guidance update on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B are outlined below and in the Guidelines section.
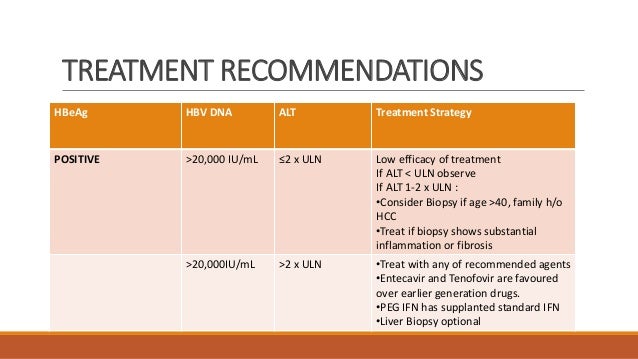
Adults with immune-active chronic hepatitis B infection
Administer antiviral therapy to lower the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
The recommended initial agent for adults is PEG-IFN, entecavir, or tenofovir.
Adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B infection
Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
The AASLD suggests obtaining ALT levels at least every 6 months to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or -inactive chronic hepatitis B.
For select patients older than 40 years, the AASLD suggests antiviral therapy in the setting of normal ALT levels, elevated HBV DNA , and significant necroinflammation or fibrosis on liver biopsy specimens.
Adults with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B who seroconvert to anti-HBe on nucleoside analog therapy
After a period of treatment consolidation , consider discontinuing NA therapy in noncirrhotic HBeAg-positive adults who seroconvert to anti-HBe while on NA treatment. If antiviral therapy is stopped, monitor the patient every 3 months for a minimum of 1 year for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation.
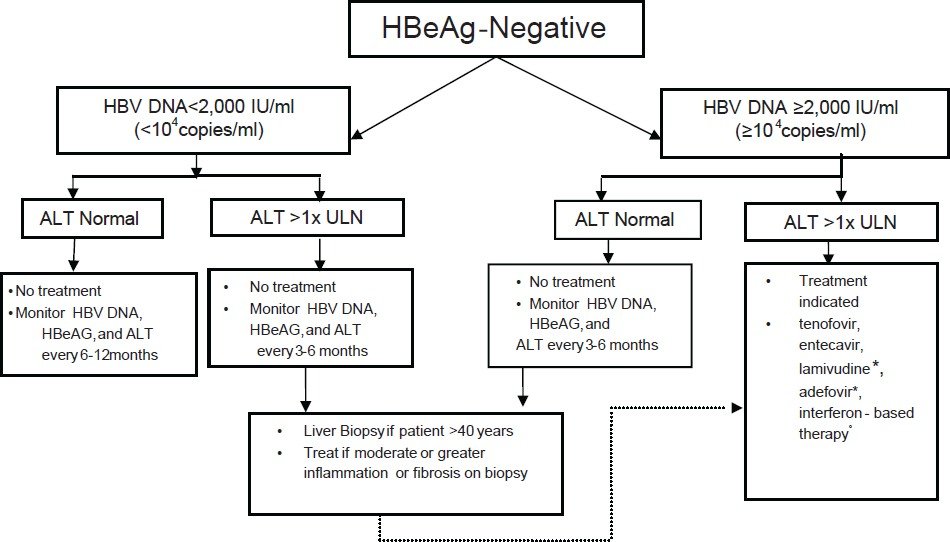
Adults with HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic HBV infection
Inpatient care
Management Of Chronic Hepatitis B Infection: Current Treatment Guidelines Challenges And New Developments
Correspondence to: Jun Yu, MD, PhD, Professor, Institute of Digestive Disease and Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, State Key Laboratory of Digestive Disease, LKS Institute of Health Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
Telephone: +852-3-7636099 Fax: +852-2-1445330
You May Like: Can You Donate Blood If You Had Hepatitis B
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Worst Hepatitis
Qhbsag As A New Marker Of Treatment Efficacy
Serum concentrations of qHBsAg, which reflect levels of cccDNA in the liver, vary during the course of CHB they are highest in the immune-tolerant phase, followed by a decline during the immune clearance phase and a further decrease after HBeAg seroconversion, becoming lowest in inactive carriers. With IFN-based antiviral therapy, a rapid reduction in qHBsAg is predictive of a sustained response thus, an early stopping rule has been proposed, suggesting that IFN therapy can be stopped or switched by week 12 in patients without qHBsAg decline because they are unlikely to achieve a response with further IFN treatment. In NUC-based therapy, the clinical relevance of qHBsAg is less well defined. qHBsAg reductions are generally less pronounced with NUCs compared with IFNs, and the data regarding a potential association of qHBsAg with serologic or virologic responses are inconsistent. Thus, more research is needed to understand qHBsAg kinetics during NUC therapy and allow potential tailoring of treatment duration to individual patients.
Hepatitis B Laboratory Testing
HBV DNA viral load testing:
HBV DNA assays have undergone significant evolution in the past few years. In the past, assays lacked sensitivity, and were poorly standardized, poorly reproducible and reported in different units. This made interpretation and comparison among studies difficult. Recently, the HBV DNA International Unit per mL was adopted , leading to improved comparability among commercial assays. Newer assays are now usually polymerase chain reaction based , with a wider dynamic range that allows accurate determination of the viral load in most patients . HBV DNA measurement is now a crucial tool in the evaluation of patients with hepatitis B. Indeed, it is not possible to properly manage hepatitis B patients without this assay. Furthermore, because it has become important to identify patients with undetectable HBV DNA in serum, the most sensitive assays available should be used. Currently, this is the Taqman PCR , which has a lower limit of sensitivity of 6 IU/mL and a dynamic range that encompasses all clinically significant variations in viral load. Viral load measurements usually need to be repeated at three to six monthly intervals, and sometimes more frequently to confirm viral resistance. Therefore, there should be no restriction on the frequency of testing.
HBV genotyping:
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis Of The Liver
Improvements In Drug Delivery Systems
The efficacy of existing antiviral therapies is partly dependent on their pharmacokinetics. Hence implementation of liver-targeting drug delivery systems may improve drug efficacy by overcoming the development of resistance, and tolerability by promoting selective accumulation in the liver to limit systemic side effects. Dextran is a complex polysaccharide which may be used as a carrier molecule for tissue-specific delivery of drugs. Recently, it was reported that lamivudine-dextran conjugates selectively accumulate in hepatocytes and Kupffer cells, resulting in a seven-fold higher concentration compared to controls. The inhibitory effects of adefovir loaded into nanoparticles on HBsAg, HBeAg, and serum HBV DNA levels in vitro were also significantly enhanced. Nevertheless, these drugs do not eradicate cccDNA, which perpetuates infection. Consequently, liver-targeting drug delivery systems must be used in conjunction with new anti-HBV drug candidates to improve viral clearance.
Signs & Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A symptoms range from mild to severe. Some infected people dont experience any noticeable symptoms, especially children under the age of six. The symptoms usually appear anywhere from two to six weeks after exposure to the virus. For some, the infection will last for a few weeks, but for others, the symptoms continue for months.
The most common symptoms of hepatitis A include :
- fatigue
- light-colored stool
- dark-colored urine
In older children and adults,jaundice occurs in more than 70 percent of cases. Jaundice causes a yellow discoloration to the skin and eyes. It can also darken your urine and lighten the color of your stool. This occurs in hepatitis A patients because their livers cannot metabolize red blood cells that are breaking down, which causes a buildup of bilirubin.
You May Like: Symptoms Of Hepatitis B In Males
Hbv Antiviral Resistance Testing
Mutations that confer resistance to antiviral agents may occur spontaneously and are not caused by the antiviral agents. Most resistant mutants have diminished replication competence and do not survive. However, in the presence of a selective pressure that inhibits the growth of wild-type virus, proliferation of some mutant virus species occurs until they come to be the dominant species. Depending on replication competence, mutants can replicate at high levels over time. Clinically, antiviral resistance is suspected when serial HBV DNA testing shows increases in viral load of more than 10-fold compared with nadir . Thus, monitoring for antiviral resistance requires regular assessment of HBV DNA concentrations. When resistance develops, particularly to lamivudine, secondary mutations may occur that may reduce susceptibility to other antivirals . Genotypic resistance can be detected by various methods, such as population sequencing, reverse hybridization, clonal analysis and ultra-deep sequencing methods. Sequencing requires that the mutant virus be present in at least 20% to 25% of the viral population. Reverse hybridization is more sensitive in detecting mutants at a lower level . A working knowledge of common HBV polymerase mutations is necessary, due to the cross-resistance, which will limit future treatment options.
Rates of resistance to antiviral agents by duration of therapy
Hbv Dna Viral Load Testing
HBV DNA viral load testing is a crucial tool to monitor and manage chronic hepatitis B patients. HBV DNA level is a predictor of cirrhosis and HCC development . The HBV DNA International Unit has been adopted to improve comparability among commercial assays . These assays have good dynamic range to enable accurate determination of the viral DNA levels in patients. HBV DNA measurements will usually need to be repeated at intervals of three to six months to monitor disease evolution. During treatment of the infection, HBV DNA measurements are frequently needed to monitor treatment response and noncompliance, and assess for treatment-resistant mutant development. Therefore, there should be no restriction on the frequency of HBV DNA viral load testing.
Also Check: Natural Ways To Cure Hepatitis C
Adults Living With Hepatitis B
If you test positive for the hepatitis B virus for longer than 6 months, this indicates that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection.
All patients with chronic hepatitis B infections, including children and adults, should be monitored regularly since they are at increased risk for developing cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
You should make an appointment with a hepatologist or gastroenterologist familiar with hepatitis B. This specialist will order blood tests and possibly a liver ultrasound to evaluate your hepatitis B status and the health of your liver. Your doctor will probably want to see you at least once or twice a year to monitor your hepatitis B and determine if you would benefit from treatment.
Not everyone who tests positive for hepatitis B will require medication. Depending on your test results, you and your doctor might decide to wait and monitor your condition. If your test results indicate that you would be a good candidate for treatment, then your doctor will discuss the current treatment options with you. Whether you start treatment or not, your doctor will want to see you every six months, or at minimum once every year.
Before you start any treatment, make sure you research each treatment option, and ask your doctor to thoroughly explain each option, so that you are well informed. It also might be a good idea to get a second opinion from another doctor before starting any treatment, because more information is always better!
How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated
Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. Most of the time, a doctor or healthcare professional will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever to help with any abdominal pain you have. Speak with a doctor about which medications can help your symptoms.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. For some people, monitoring their symptoms and getting regular liver tests is an appropriate care regimen.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce your symptoms and prevent liver damage, but they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is for you to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
You can lower your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
You May Like: Common Signs Of Hepatitis C
Prevalence Of Herbal Medicine Use
The use of herbal medicine was investigated at three levels: ever used during lifetime, use within the last 12months and use at the time of the study.
Lifetime exposure to herbal medicine was reported in 174/310 patients while herbal medicine use within the last 12months was reported by 143/310 patients.
About 11.9% of the patients were reportedly using herbal medicine at the time of the study.
The patients who reported never used of herbal medicine were asked to give reasons for never having used it. The main reasons given by patients for non-use of herbal medicine included: lack of trust in the effectiveness of herbal medicine generally , lack of knowledge about herbal medicine , a lack of interest in using herbal medicine , bad taste of herbal medicine , easier access to hospitals and lack of trust in the safety of herbal medicines .
This herb is widely used for liver disorders, including hepatitis B. Its active ingredient, silymarin, is thought to lower inflammation and spur new liver cells to grow. But the evidence is mixed on whether milk thistle works. Side effects can include nausea, bloating, and diarrhea.
Cannabidiol Oil
This compound comes from the plant or its relative, hemp. CBD is legal in some states for both recreational and medical uses, and most other states allow it with a prescription. But despite its popularity for all sorts of ailments, not much research has been done to show that CBD helps with hep C or if itâs safe.