Hepatitis C Symptoms In Men
Hepatitis C symptoms in men are the same as in women. However, a 2014 study indicated that men may be less likely to clear the virus than women.
Hepatitis C in men may stay in their systems longer. It may also be more likely to cause symptoms in men compared to younger women.
Currently, there isnt a hepatitis C vaccine, though research is underway. However, avoiding contact with the blood of someone who has an HCV infection can help prevent you from acquiring the hepatitis C virus.
You can do this by:
- avoiding using someone elses razor, nail clippers, or toothbrush
- not sharing needles or syringes
- getting tattoos or piercings only at licensed facilities
- practicing safer sex with your partner by using condoms or other barrier methods
If you think you may have been exposed to HCV, its important to get tested as soon as possible.
Untreated chronic hepatitis C may eventually lead to complications, which can include severe scarring of the liver, which is called cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Some people with hepatitis C may need a liver transplant.
If you believe you contracted HCV, the sooner you receive a hepatitis C diagnosis, the sooner your doctor can start a treatment plan to help you avoid complications.
Symptoms And Signs Of Acute Hepatitis C
If the anti-HCV test is positive, HCV RNA is measured to distinguish active from past hepatitis C infection .
In hepatitis C, serum anti-HCV represents chronic, past, or acute infection the antibody is not protective. When cases are unclear or when suspicion for hepatitis C is high, HCV RNA is measured. Anti-HCV usually appears within 2 weeks of acute infection but is sometimes delayed however, HCV RNA is positive sooner.
Also Check: How Do You Contract Hepatitis A
Genotyping And Serotyping Of Hcv
Hepatitis C genotyping is helpful in defining the epidemiology of hepatitis C, but on an individual patient basis, genotyping is crucial in regard to treatment recommendations and duration. Genotyping is based on sequence analysis by sequencing or reverse hybridization. Although viral load can vary within a 0.5- to 1-log range, HCV genotype does not change during the course of infection. In case of suspected superinfection, another genotype might rarely be detected. For reliable genotyping, 5URT alone is insufficient, including parts of the core sequence enhance genotyping reliability. Sequencing of NS5b is the gold standard.
Serotyping is the only other option to test for the type of HCV in cases of remote infection. This, however, is relevant for epidemiologic studies only and is not used clinically.
Andrea D. Branch, in, 2004
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis Ca Sexually Transmitted Disease
Is Liver Transplantation An Option For A Person With Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is the leading reason for 40% to 45% of liver transplants in the U.S. Hepatitis C usually recurs after transplantation and infects the new liver. Approximately 25% of these patients with recurrent hepatitis will develop cirrhosis within five years of transplantation. Despite this, the five-year survival rate for patients with hepatitis C is similar to that of patients who are transplanted for other types of liver disease.
Most transplant centers delay therapy until recurrent hepatitis C in the transplanted liver is confirmed. Oral, highly effective, direct-acting antivirals have shown encouraging results in patients who have undergone liver transplantation for hepatitis C infection and have recurrent hepatitis C. The choice of therapy needs to be individualized and is rapidly evolving.
Symptoms Of An Acute Infection
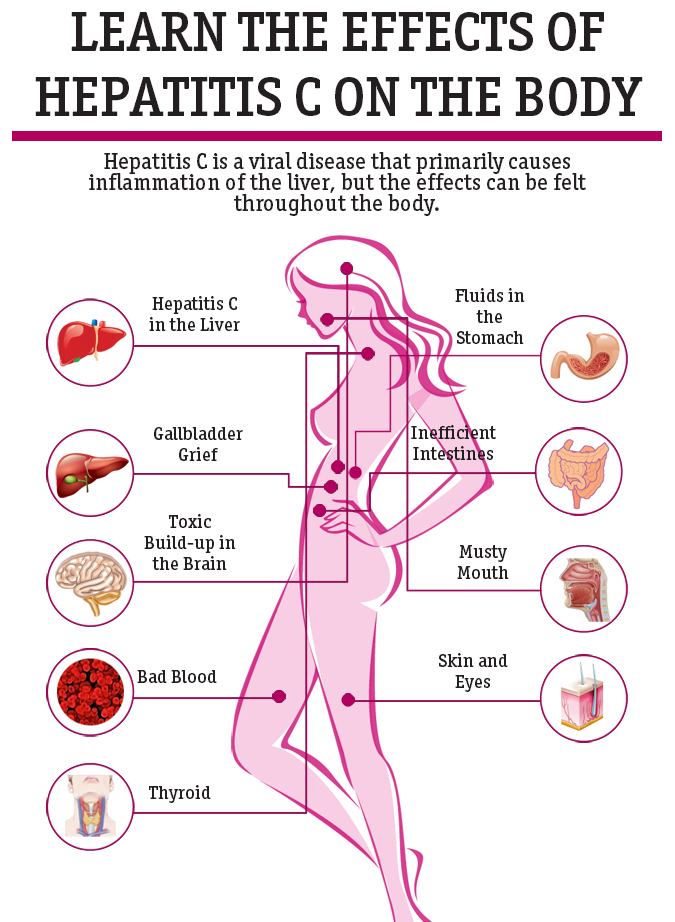
Few people show symptoms during acute infection . These symptoms can include: fatigue tenderness or an aching feeling on the right side of the abdomen decreased appetite perhaps with weight loss flu-like symptoms nausea tendency to bruise or bleed easily jaundice rash dark-coloured urine and light or clay-coloured stools. These symptoms often go away after a short time.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Flare Up Symptoms
Hepatitis C Symptoms And Treatment
Hepatitis C is part of a group of hepatitis viruses that attack the liver. It is commonly found in infected blood. It is also rarely found in semen and vaginal fluids.
The virus is usually passed on through using contaminated needles and syringes or other items with infected blood on them. It can also be passed on through unprotected sex, especially when blood is present.
It often has no noticeable symptoms. Some peoples bodies can clear the infection on their own but others may develop chronic hepatitis C and will need to take antiviral treatment to cure the infection and prevent liver damage.
- The basics
The 2019 Hcv Care Cascade For Women And Men In Bc
Figure displays the 2019 HCV care cascade for women and men in BC. In 2019, 52,638 people with known sex, including 19,522 women and 33,116 men were anti-HCV positive in 2019 . The proportion of anti-HCV positive women receiving a confirmatory RNA test was 86% compared to 82.6% of men. 34% of women RNA tested had negative results compared to 24.1% of men. Among people who had the virus they acquired genotyped, 68% of women and 67% of men initiated treatment, with 94% of women and 92% of men achieving SVR.
Fig. 2
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ways Of Transmission
General Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
As mentioned, many cases of hepatitis C infection often go unnoticed because they donât always present symptoms. If you do present symptoms, they manifest about four to 12 weeks after initial exposure to the virus. Symptoms can also vary between acute and chronic forms of the infection. Acute hepatitis C symptoms may include:
- Pain in your abdomen
- Fever
- Nausea and/or vomiting
Chronic hepatitis C infections can remain dormant for years, and it usually isnât apparent until the virus has caused significant damage to the liver.
How Can I Protect Myself And Others
- Never share injecting drug equipment or things that may have blood on them such as toothbrushes and razors. Also avoid sharing straws or rolled up banknotes if snorting drugs with others.
- Use condoms for anal and vaginal sex and latex gloves for fisting.
- During group sex, cover anything which goes from one partner to another with a fresh condom or fresh latex glove for each new person it enters. Clean objects with warm water and anti-bacterial soap before using on a new partner.
- Dont share enema equipment or pots of lubricant.
If you have hepatitis C you may want to tell a partner and explain that youre infectious. They can then decide if they’re happy to take any risks and whether they want to take precautions. That way they cannot accuse you of infecting them without them knowing that the risk was there.
Also Check: Facts About Hepatitis C Virus
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another persons blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Read Also: Is There An Immunization For Hepatitis C
What Does Hepatitis C Pain Feel Like
A person with hepatitis C may right upper quadrant pain. This quadrant is the location of organs such as the right kidney and the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
A person may feel this as abdominal pain, which can cause severe discomfort.
Some people may also experience aches and pains in their joints. The most commonly affected joints are the joints in the hands and wrists. The pain in the joints can range from mild to severe.
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis C Ab
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
Your body may clear a hepatitis C infection without treatment. An HCV infection that continues for longer than 6 months is considered chronic hepatitis. The goal of treatment is to prevent health problems hepatitis C can cause. Examples include cirrhosis and liver failure or cancer. You may need any of the following:
- Antiviral medicines are used to cure a hepatitis C infection. You will need to take these medicines for 8 to 12 weeks. Other kinds of medicines may be used to keep the virus from spreading or to prevent or decrease liver damage. The type of medicine you need will depend on how severe your hepatitis is. It will also depend on if you have liver damage.
- Surgery may be done to remove part of your liver. A liver transplant may be done if your liver stops working. Your diseased liver is removed and replaced with a healthy, donated liver.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis And How Do You Get It
What Effects Does Hepatitis C Have During Pregnancy
Hepatitis C can be passed on from a pregnant woman to her child during pregnancy and birth, but this is rare. The risk of passing hepatitis on is slightly higher for mothers with both HIV and hepatitis C .
Antivirals used to treat hepatitis are not currently recommended for pregnant women. This is because there isnt enough information to know if the drugs are safe for your unborn baby.
If you have hepatitis C and are pregnant speak to your doctor. They will be able to give you advice on how to keep yourself and your baby safe during pregnancy and birth.
If youre planning to have a baby, your doctor may recommend that you treat the hepatitis C before you get pregnant.
Breastfeeding with hepatitis C is considered safe. But if you have cracked or bleeding nipples, its generally recommended to stop breastfeeding until they have healed.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Contagious
What Are The Side Effects Of Treatments For Hepatitis C Infection
Side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon
- The most common side effects of interferon or pegylated interferon include fever, flu-like symptoms, and depression. Patients must be monitored closely for depression. Risk of suicide is a reason to avoid interferons.
- Interferons also reduce white blood cell and/or red blood cell counts . This may cause increased susceptibility to infection. Interferons also increase the risk of certain cancers. Death rarely occurs as a result of therapy, but may occur from progression of liver failure in patients with advanced cirrhosis.
Side effects of ribavirin
- Ribavirin most commonly causes anemia due to destruction of red blood cells . This can be severe enough that people with heart disease may suffer a heart attack from insufficient blood flow, so people with heart disease should not receive this drug. Anemia improves with a reduction in the dose of ribavirin. Injected growth factor that stimulates the production of red blood cells often is used to improve the anemia associated with ribavirin. Ribavirin also accumulates in the testicles and ovaries and causes birth defects in animals. Although no birth defects have been reported in humans, both men and women should use contraceptive measures to avoid pregnancy during and for at least six months after ribavirin treatment.
Side effects of DAAs
How Do I Get Tested
Hepatitis C is diagnosed with a blood test. Unlike hepatitis A and B, you can be infected more than once and you do not develop immunity if you contract hepatitis C. Speak to your doctor or healthcare provider to arrange a test for hepatitis C or visit your nearest sexual health clinic to organise a test for hepatitis C as part of your next test.
You May Like: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C
What Can I Do If I Think I Have Hepatitis C
A doctor or sexual health clinician can test you to see if you have hepatitis C. If you do, effective treatment with fewer side effects than the older medicine is available and you can discuss how to avoid infecting your sexual partners or people you live with.
It can take three to six months before the blood test for hepatitis C will be able to detect signs of infection in your blood. For people with HIV who may be immunocompromised, the antibody may not be detectable and it may be necessary to request an RNA test which detects the virus.
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis A Curable Or Not
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis C From
What Are The Different Stages Of Hepatitis C
There are three stages of hepatitis C: early, chronic, and final. Many people in the early hepatitis C stages do not even realize they have the disease because there are occasionally no symptoms, or the symptoms are so mild that people believe they are sick with the flu. Chronic hepatitis C occurs when people are unable to get rid of hepatitis C and it becomes an ongoing problem. In the final stage of hepatitis C, liver failure often occurs, which sometimes leads to death. There are many people in the early stages of hepatitis C who go for as long as 20 years before they experience any serious, life-threatening symptoms.
The most common symptoms people experience during the early stages of hepatitis C are vomiting, joint aches, and fever. Sometimes these symptoms are also accompanied by a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, also known as jaundice. People with hepatitis C may additionally notice that their urine is darker in color than normal and that their skin is unusually itchy. Many people who get hepatitis C are able to fight it off and never have any further problems with the disease, but some people go on to develop chronic hepatitis C, which is the second stage of the illness. People who are in the beginning stages of hepatitis C do not always require treatment if the illness goes away on its own.
What Laboratory Studies Should Be Ordered To Help Establish The Diagnosis How Should The Results Be Interpreted
The criteria used are: serum aminotransferase levels greater than 10 fold the upper normal limit, serum gamma globulin level greater than twice the upper normal limit, elevated conjugated bilirubin, interface hepatitis on biopsy.
Autoantibody testing includes ANA , ASMA with titers of 1:320 or greater generally reflective of the presence of specific antiactin antibodies which are usually not measured in most clinical laboratories, atypical perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies , soluble liver antigen and liver-pancreas antigen which is seen in 30% of patients, liver-kidney microsomal antibody type 1 , and anti-liver cytosol antibody type 1 . AMA may sometimes be seen although are typically seen in primary biliary cirrhosis.
Type 1 AIH is typically characterized by positive smooth muscle antibodies , +pANCA, +ANA, and +SLA/LP antibodies . Type 2 is usually characterized by antibodies to ALKM-1 and ALC-1. However, autoantibody testing alone is not diagnostic as positive testing can be seen in other liver disease. Additionally, circulating antibodies are absent in about 10% of patients.
Serologies for viral hepatitides should be ordered to exclude these from the diagnosis.
Also Check: Effects Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Fast Facts About Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is passed on from blood-to-blood contact
- Most cases of hepatitis C occur from unsafe injecting drug use, and some cases occur from unprotected anal sex
- If you contract hepatitis C, you may get flu-like symptoms, nausea or abdominal pain
- At the moment, there are no vaccines to prevent you from contracting hepatitis C
- If youre poz, make sure you get tested regularly for hepatitis C
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
Read Also: What Organ Does Hepatitis C Affect