What Is Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis B is a potentially life-threatening liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. It is a major global health problem and the most serious type of viral hepatitis. It can cause chronic liver disease and puts people at high risk of death from cirrhosis of the liver and liver cancer.
Worldwide, an estimated two billion people have been infected with the HBV and about 250 million have chronic liver infections.A vaccine to prevent catching HBV has been available since 1982. Hepatitis B vaccine is 95% effective in preventing HBV infection and its chronic consequences, and is the first vaccine against a major human cancer.
How Common Is It
In 2006, the Public Health Agency of Canada reported the incidence of HBV as 2.0 cases for every 100,000 or about 650 cases reported annually in Canada. In the year 2013, the incident rate was 0.5 per 100,000 . Incidence of the disease varies from region to region but has been declining due to increasing use of the vaccine and universal immunization programs.
Return To School Or Child Care
- Your child may return to normal daily activity when the childs doctor or the doctor who discharges him or her from the hospital says it is OK. This will be when your child is no longer jaundiced or vomiting.
- A child who scratches, bites or “gets into fights, has an overall skin condition, or a bleeding problem should probably not attend child care while he or she has hepatitis. Your childs doctor can help you make this decision.
If you have any questions, be sure to ask your childs doctor or nurse.
HH-I-43 10/76, Revised 10/15 Copyright 1976, Nationwide Childrens Hospital
Also Check: Hiv Hepatitis B And C Test
Immunization Of Newborns And Follow
4 ml of blood from the femoral vein was taken immediately after birth for detection of serum HBV markers and HBV DNA. Newborns who were HBV positive were immunized with 20 µg of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine prepared by yeast gene engineering technology , and 200 IU HBIG . Newborns were immunized again at the age of 1 month and 6 months with 20 µg HBVac, while HBIG treatment was repeated once at the same dose 15 days later. HBVM and HBV DNA were measured once again at age of 1 month and 7 months.
How Hcv Is Spread
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through blood to blood contact, meaning that a person can become infected with the virus should the blood of a person who carries the virus be introduced into another person’s bloodstream.
Therefore, as with hepatitis B, blood transfusions , tattooing and body piercing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, and intravenous drug use can all lead to possible exposure to the virus. Unlike hepatitis B, however, sexual contact and childbirth have both been shown to be an inefficient route of exposure to HCV.
The hepatitis G virus is thought to be transmitted in a similar way to HCV.
Don’t Miss: Can You Spread Hepatitis B
Hbsag Detection By Histochemical Methods
The ovarian and placental tissue samples were processed by routine histological procedures and paraffin sections were prepared by the standard series of operations of fixation, dehydration and paraffin embedding. The slides were then stained with hematoxylin-eosin and observed using light microscopy to evaluate the histology.
Pearls And Other Issues
Hepatitis D has been long associated with HBV infections and cannot exert pathological influence without the presence of HBV infection. Two forms of infection exist coinfection and superinfection . Superinfection tends to be more severe than coinfection. Due to the preexisting hepatitis B infection, anti-HBcAg IgM is undetectable in superinfection states but can be noted in coinfection.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Treatment Cost In Us
Treatment For Chronic Hbv Infection
For chronic HBV infection, antiviral medications are available.
This is not a cure for chronic HBV. However, it can stop the virus from replicating and prevent its progression into advanced liver disease.
A person with a chronic HBV infection can develop cirrhosis or liver cancer rapidly and without warning. If a person does not have access to adequate treatment or facilities, liver cancer can be fatal within months of diagnosis.
People with a chronic HBV infection require ongoing medical evaluation and an ultrasound of the liver
Recommendation To Decrease Mtct
HBsAg screening:
All pregnant women should be tested routinely for HBsAg during an early prenatal visit in each pregnancy. Women who were not screened prenatally, those who engage in behaviors that put them at high risk for infection and those with clinical hepatitis should be tested at the time of admission to the hospital for delivery.68
Immunization of infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers:
Immunization of infants born to women with unknown HBsAg status:
Women admitted for delivery without documentation of HBsAg test results should have blood drawn and tested as soon as possible after admission. While test results are pending, all infants born to women without documentation of HBsAg test results should receive the first dose of single-antigen HBV vaccine 12 hours or less after birth. If the mother is determined to be HBsAg-positive, her infant should receive HBIG as soon as possible but no later than the age of 7 days, and the vaccine series should be completed according to a recommended schedule for infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers. If the mother is determined to be HBsAg negative, the vaccine series should be completed according to a recommended schedule for infants born to HBsAg-negative mothers. If the mother has never been tested to determine her HBsAg status, the vaccine series should be completed according to a recommended schedule for infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers. Administration of HBIG is not necessary for these infants.
Also Check: Is Hiv The Cause Of Hepatitis B
Mother To Child Transmission
The transmission of infections from mother to offspring is traditionally known as perinatal infection. By definition, perinatal period begins from 28 weeks of gestation and ends at 28 days after delivery. Therefore, the term perinatal transmission does not actually include infections that occur before or after this time period and thus can be replaced by the term mother to child transmission which takes account of all HBV infections contracted before birth, during birth and in early childhood the importance of which as a group is their remarkably greater risk of chronicity compared to infections acquired later in life.12
Theoretically, there are three possible routes for transmission of HBV from an infected mother to her infant:13
For a newborn infant whose mother is positive for both HBsAg and HBeAg, in the absence of post-exposure immunoprophylaxis, the risk for chronic HBV infection is 70%90% by age 6 months.9 HBV vaccination can prevent 70%-95% of HBV infections in infants born to HBeAg and HBsAg-positive mothers.14 In most post-exposure prophylaxis studies, HBV vaccine has been administered to infants within 12-24 hours of their birth. The efficacy of vaccine in preventing MTCT declines by time after birth.15 Therefore it has been postulated and widely accepted that most MTCT occur at or near the time of birth .
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Who Is Most At Risk For Chronic Disease
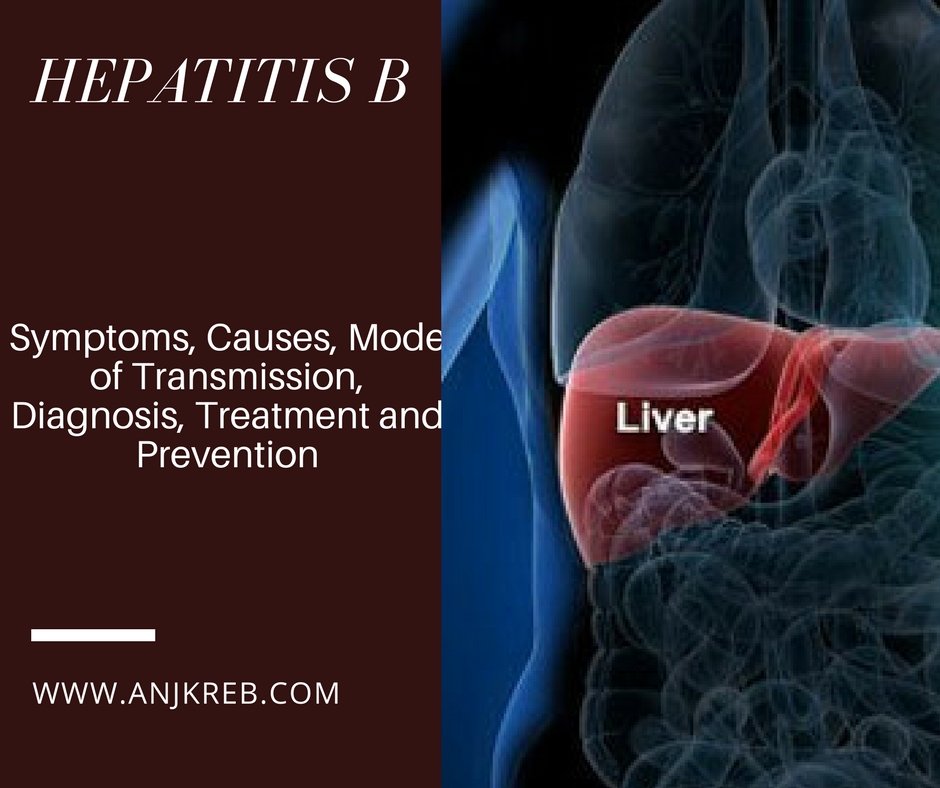
The likelihood that an HBV infection will become chronic depends upon the age at which a person becomes infected, with young children who become infected with HBV being the most likely to develop chronic infections.
About 90% of infants infected during the first year of life develop chronic infections 30% to 50% of children infected between one to four years of age develop chronic infections. About 25% of adults who become chronically infected during childhood die from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis. About 90% of healthy adults who are infected with HBV will recover and be completely rid of the virus within six months.
Recommended Reading: Where Does Hepatitis Come From
What Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infection of your liver. Itâs caused by a virus. There is a vaccine that protects against it. For some people, hepatitis B is mild and lasts a short time. These âacuteâ cases donât always need treatment. But it can become chronic. If that happens, it can cause scarring of the organ, liver failure, and cancer, and it even can be life-threatening.
Itâs spread when people come in contact with the blood, open sores, or body fluids of someone who has the hepatitis B virus.
It’s serious, but if you get the disease as an adult, it shouldnât last a long time. Your body fights it off within a few months, and youâre immune for the rest of your life. That means you can’t get it again. But if you get it at birth, itâ unlikely to go away.
âHepatitisâ means inflammation of the liver. There are other types of hepatitis. Those caused by viruses also include hepatitis A and hepatitis C.
What Laboratory Tests Are Available For Hepatitis B
Tests are available to detect the types of antigens used to identify the hepatitis B virus. The tests determine if the virus is present in the body tissue or blood. The amount of each type of antigen present indicates how advanced the disease is and how infective the individual has become.
Other tests are available to detect the body’s reaction to the viral infection or the body’s reaction to vaccination against the virus. These tests work by measuring the number of antibodies present in the blood.
Read Also: Combined Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
How To Prevent Transmission
Between 2% and 6% of adults infected with hepatitis B virus will develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B can lead to liver failure and liver cancer, so protecting yourself is important.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe for almost everyone and about 95% effective for providing long-term protection against hepatitis B infection.
While anyone can benefit from the vaccine, people who are at a greater risk of being exposed to the virusbecause of their work, lifestyle or medical historyare strongly encouraged to be immunized. In many countries, babies born to infected mothers get vaccinated at birth. All babies born in the United States are routinely vaccinated.
Hepatitis B immune globulin , is another way to prevent hepatitis B infection in babies born to infected mothers or after exposure to the virus. This uses concentrated antibodies to provide immediate protection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, it is given as a shot and can provide short-term protection against hepatitis B.
Because the hepatitis B vaccine does not protect against HIV, hepatitis C or other diseases spread through sex and contact with blood, it is still important to keep using basic protective strategies. Practicing safer sex and not sharing needles are recommendedeven if you’re immune to hepatitis B.
How Can I Catch Hbv
Hepatitis B virus is transmitted between people by contact with the blood or other body fluids of an infected person. In Africa the virus is mainly transmitted early in life, from mother-to-child or between children. HBV is spread through a break in the skin , or through sexual intercourse. HBV is 50 to 100 times more infectious than HIV. Unlike HIV, HBV can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected.
Unless vaccinated at the time of birth, these babies can become chronic carriers, which means they are infected with the virus for life. Of children who become infected with the virus between one and five years of age, 30-50 percent become carriers.
In many developed countries , patterns of transmission are different than those mentioned above. Today, the majority of infections in these countries are transmitted during young adulthood by sexual activity and injecting drug use. HBV is a major infectious occupational hazard of health workers.
HBV is not spread by contaminated food or water, and cannot be spread casually in the workplace.
The virus incubation period is 90 days on average, but can vary from about 30 to 180 days. HBV may be detected 30 to 60 days after infection and persist for widely variable periods of time.
Also Check: What Vitamins Are Good For Hepatitis B
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
Where Is The Hepatitis B Virus Found And How Is It Transmitted
Blood is the major source of the hepatitis B virus in the workplace. It can also be found in other tissues and body fluids, but in much lower concentrations. The risk of transmission varies according to the specific source. The virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days and still be able to cause infection.
Read Also: What Are The Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
When To Call The Doctor
- The child has not felt hungry or wanted to eat in the past 24 hours.
- Your childs fever is over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit for more than 2 days.
- Your child has a stomachache.
- Your child vomits more than 2 times in an hour.
- Your child’s skin or the white part of the eyes turns yellow.
- Your child is overly tired for more than 2 days.
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Also Check: Autoimmune Hepatitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Challenges To Hepatitis B Prevention In The United States
There has been a substantial reduction in the number of new HBV infections each year in the United States as a result of hepatitis B immunization. However, implementation of the comprehensive strategy to eliminate HBV transmission has been uneven, and transmission of HBV still occurs among groups for whom vaccine indications have been in place for more than a decade. The primary challenge in the prevention and control of hepatitis B in the United States is full implementation of existing immunization recommendations, particularly those related to the prevention of perinatally acquired infections and infections acquired in adulthood through sexual and needle-sharing exposures.
Recommended Reading: How To Live With Hepatitis C
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule Adults
Hepatitis B Vaccine Recommendations And Program Implementation
In 1992, the World Health Organization recommended the integration of hepatitis B vaccine into the national immunization programs of all highly endemic countries by 1995 and all other countries by 1997 . As of 2004, more than 150 of 192 World Health Organization member states had adopted universal childhood hepatitis B vaccination policies . Notably absent are several highly endemic countries, most of them located in sub-Saharan Africa, including the populous and rapidly growing nation of Nigeria. Several highly developed countries with low endemicity, including the United Kingdom, Japan, and the Scandinavian countries, do not routinely vaccinate children but have instead created policies targeting immigrant groups from highly endemic parts of the world, adolescents, and adults with risk factors for HBV infection .
Three-dose hepatitis B vaccine coverage among children aged 1935 months, by year of survey, United States, 19922004.
TABLE 2.