Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than 7 days post collection will not be tested.
Questions For Your Doctor About Test Results
Patients receiving hepatitis C testing may find it helpful to ask questions about their test results. Questions to consider include:
- What type of hepatitis C test did I receive?
- What was my test result?
- How do you interpret the results of the hepatitis C tests that I had?
- Do I need any follow-up tests based on my test result?
Read Also: How Can I Get Hepatitis
Summary Of The Literature
For the all-adult review, the initial literature search yielded 4,867 studies. Twenty-nine duplicates were identified. Of 4,838 unique studies, 4,170 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 668 full texts for review. Among these, 368 studies had data available to extract.
For the pregnancy review, the initial literature search yielded 1,500 studies. Two duplicates were identified. Of 1,498 unique studies, 1,412 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 86 full texts for review.
The supplementary review yielded an additional 1,038 and 195 studies among all adults and pregnant women, respectively. Of these, 912 and 168 , respectively, were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 126 and 27 , respectively, full texts for review. One study was added to the pregnant women review outside of the formal literature search .
Considering all 104 applicable studies, the median anti-HCV positivity prevalence among all adults was 6.6% . Median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.7% for the general population , 7.5% for ED patients , 3.3% for birth cohort members , 9.3% for others/multiple risk factors , 54.2% for persons who use drugs , 5.2% for persons with HIV or sexual risk , and 4.7% for immigrants . Considering 26 applicable studies among pregnant women, median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.2% .
Also Check: How Do You Know If You Have Hepatitis
You May Like: How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
There is no specific treatment for acute hepatitis B infections. Symptoms are usually treated with supportive care. This usually involves making sure that you are getting plenty of rest and enough fluids and nutrition by eating and drinking small amounts several times a day.
Chronic forms of hepatitis B may be treated with antiviral medications such as interferon, entecavir, tenofovir, lamivudine, and adefovir. However, some antiviral drugs can have serious side effects and not all people need to be treated. Often, people with chronic hepatitis will be closely monitored to see if they develop cirrhosis or liver cancer. It is important to talk to your healthcare provider about your treatment options and the risks and benefits of those currently available.
What Is The Treatment For Hcv
There are several drugs that can be used to treat HCV infection. Most commonly, a combination of drugs is used, and new drugs are under development. Before 2000, chronic HCV was curable in only 10% of cases. Now, treatments for HCV can cure over 90% of people with hepatitis C before late complications occur, but even those with advanced liver disease often respond to treatment. This increases the opportunity to intervene early and prevent HCV-associated deaths.
- According to the CDC, recent treatment guidelines recommend monitoring people with acute HCV but only considering treatment if the infection persists longer than 6 months.
- Chronic HCV is usually treated with a combination of drugs.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And C Coinfection Treatment 2020
Read Also: Treatment For Liver Cirrhosis Hepatitis B
Diagnosis And Hepatitis C Elimination
In one report, the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine explored the feasibility of hepatitis C elimination and concluded that hepatitis C could be eliminated as a public health problem in the United States, but that substantial obstacles exist . In another report, specific actions were recommended to achieve elimination considering information, interventions, service delivery, financing, and research . These reports were the culmination of decades of progress in the development of HCV infection diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Contagious
Hepatitis B Blood Tests
The Hepatitis B Panel of Blood Tests
Only one sample of blood is needed for a hepatitis B blood test, but the Hepatitis B Panel includes three parts. All three test results are needed to fully understand whether a person is infected or not. Below is an explanation of the 3-part Hepatitis B Panel of blood test results.
You May Like: Why Are Baby Boomers Being Tested For Hepatitis C
Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
Dont Miss: Liver Cancer From Hepatitis C
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patientâs vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Read Also: Common Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Arrow 7b: How Well Does Antiviral Treatment Improve Health Outcomes In Asymptomatic Patients With Hepatitis C
Several factors complicate our ability to assess the long-term benefits of treatment of HCV, including the long duration for important complications to develop and the relatively short time period that treatments have been available. There is no data showing long-term benefits after treatment with pegylated interferon, alone or in combination with ribavirin, due to the relatively recent introduction of pegylated interferon.
We independently reviewed the three RCTs that provided long-term outcomes data after treatment with interferon-alfa monotherapy. These studies are summarized in and . In an unblinded, good-quality Japanese trial of 90 patients randomized to interferon-alfa for 24 weeks or to symptomatic treatment, after 8.7 years there was a significant long-term reduction in the rate of developing HCC and in mortality . Cirrhosis was also decreased in the treatment group. Rates of cirrhosis, HCC, and mortality were much higher in this study than in studies in US and European populations. The relative risk of progressing to Child B cirrhosis was 0.230 in the treatment versus the control groups.
Do Medical Conditions Outside The Liver Occur In Persons With Chronic Hepatitis C
A small percentage of persons with chronic hepatitis C develop medical conditions outside the liver . These conditions are thought to occur due to the body’s natural immune system fighting against itself. Such conditions include: glomerulonephritis associated with kidney disease, essential mixed cryoglobulinemia, and porphyria cutanea tarda-a skin condition.
Also Check: Can Hiv Lead To Hepatitis
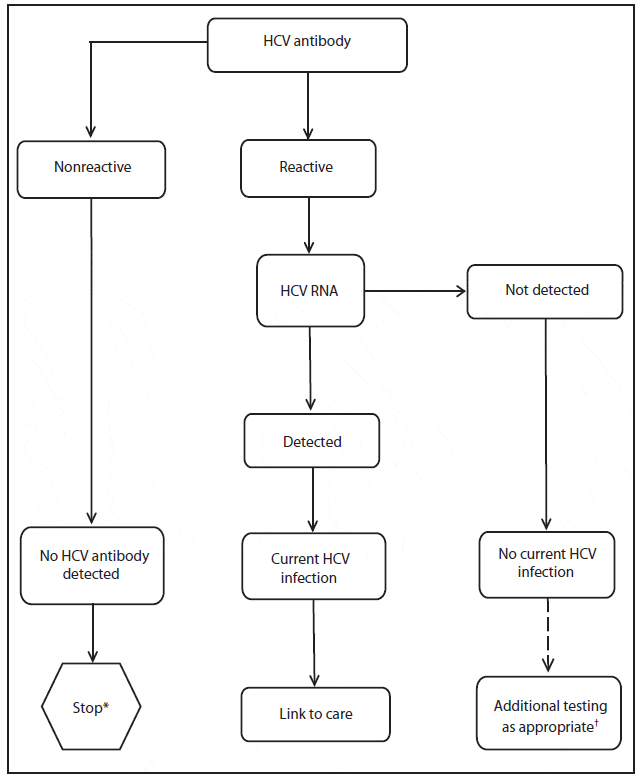
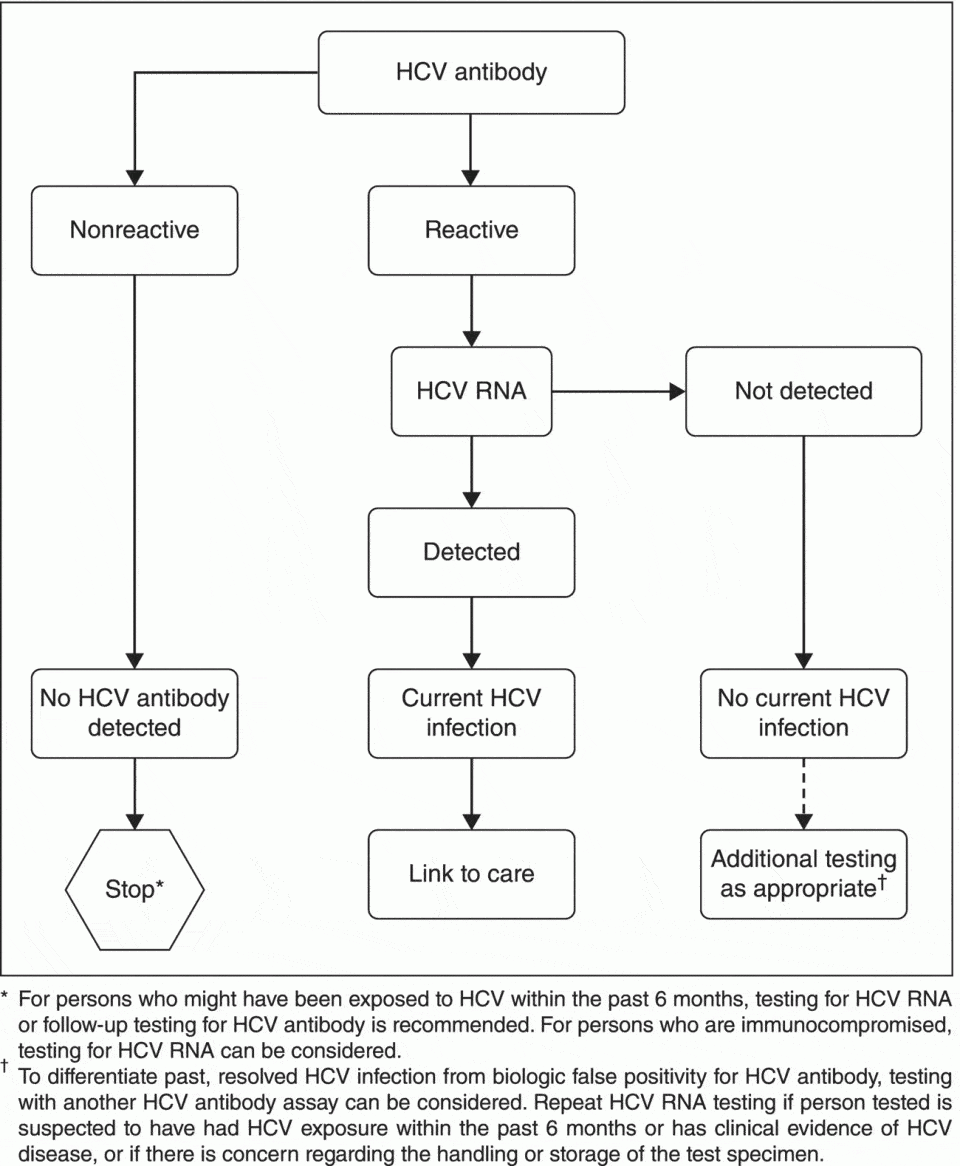
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Are There Supplements That Are Good For My Liver
If a person eats a balanced diet, they will normally get enough vitamins and minerals. People with liver disease should avoid taking large amounts of supplements or mega-vitamins. This is because the liver has to do extra work to process them. Your provider may put you on a general multivitamin without iron.
Don’t Miss: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
Are Test Results Accurate
Although no test is perfect, hepatitis C testing is an important and accepted method of testing for HCV. In order to reduce the risk of inaccurate results, doctors take steps to verify a patients diagnosis. For example, a positive test result for hepatitis C antibody requires confirmation with HCV RNA testing.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Treatment Antiviral Drugs
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis B And C
Specific Hcv Rna Assays And Range Of Detectable Virus
HCV RNA tests use target amplification techniques. Several assays exist for HCV RNA testing. Methods include polymerase chain reaction , transcription mediated amplification , and branched chain DNA tests. Results are expressed as international units/mL . The different methods and different commercial assays each have a lower limit of quantification and lower limit of detection , therefore a patient’s results could be reported differently depending on the assay used. HCV RNA tests must have an LLOQ of 25 IU/mL or lower when used to assess treatment response with DAAs.
LLOQ = the lowest HCV RNA level that is within the linear and analytically acceptable range of the assay.
LLOD = the lowest level of HCV RNA that is detected 95% of the time.
Who Should Get Tested
You should consider getting tested for hepatitis C if youre worried you could have been infected or you fall into one of the groups at an increased risk of being infected.
Hepatitis C often has no symptoms, so you may still be infected if you feel healthy.
Some groups of people are at an increased risk of hepatitis C, including:
- ex-drug users and current drug users, particularly users of injected drugs
- people who received blood transfusions before September 1991 or blood products before 1986 in the UK
- UK recipients of organ or tissue transplants before 1992
- people who have lived or had medical treatment in an area where hepatitis C is common high-risk areas include Africa, the Middle East and central Asia
- babies and children whose mothers have hepatitis C
- anyone accidentally exposed to the virus, such as health workers
- people who have received a tattoo or piercing where equipment may not have been properly sterilised
- sexual partners, family members and close contacts of people with hepatitis C
If you continue to engage in high-risk activities, such as injecting drugs frequently, regular testing may be recommended. Your doctor will be able to advise you about this.
You May Like: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis C
Also Check: Rx Vitamins For Pets Hepato Support
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis C testing identifies antibodies to the hepatitis C virus, detects viral RNA, and/or determines the strain of hepatitis C. Hepatitis C testing may involve several different tests:
- Hepatitis C antibody test: Antibodies are a part of the bodys response to an infection. Testing for hepatitis C antibodies determines whether or not a patient has been exposed to the hepatitis C virus at some point in their life. If this test is positive, the next step is to test for hepatitis C RNA which can tell you if you have a current infection.
- Hepatitis C RNA test: RNA is a type of genetic material from the hepatitis C virus that can be detected in the blood. If test results are positive after a hepatitis C antibody test, doctors use a hepatitis C RNA test to look for and/or measure the amount of the virus in the blood. Qualitative HCV RNA tests can detect the presence of HCV RNA, while quantitative HCV RNA tests measure the amount of HCV RNA. Understanding the amount of HCV in the blood helps to monitor response to treatment.
- Genotype test: There are at least six types of hepatitis C, which are also called strains or genotypes. Treatment for hepatitis C depends on the strain, so genotype testing to guide treatment is performed in patients who are diagnosed with an HCV infection.
Reactivation Risk In Anti
Table 1 American Gastroenterological Association classification of reactivation risk in HBsAg/anti-HBc patients Full size table
The risk of HBV reactivation can be assessed based on positivity for HBV serum biomarkers and the type, duration, combination of agents, and dosing of immunosuppressive or chemotherapeutic agents . HBV reactivation risk can be as high as 4070% in anti-HBc-only, patients who are undergoing chemotherapy with B cell depleting antibodies like rituximab .
Noting that reactivation after immunosuppressive therapy is associated with significant morbidity and mortality, the AGA recommends antiviral prophylaxis for patients classified as at either moderate or high risk for reactivation for low-risk patients, there is no prophylaxis recommendation monitoring is per provider preference but seemingly sufficient . Entecavir and tenofovir prodrugs should be used as first-line prophylaxis or therapy due to their stronger antiviral potency and high threshold for resistance.
Read Also: Gilead Sciences Hepatitis C Cure
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period â from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
Case Reporting And National Notification
Cases of acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B, and hepatitis B during pregnancy should be reported to HDs as specified by state, territorial, or local regulations. Acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B are nationally notifiable conditions . Hepatitis B cases are identified using an event code corresponding to the hepatitis B condition . Data are sent weekly or more frequently, depending on the infrastructure of the jurisdiction sending the data. Cases might be re-classified or removed as needed after the initial transmission to CDC, as long as the changes occur before surveillance data are finalized each year.
You May Like: What Is Chronic Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C 0.1 S/co Ratio
Molecular Hcv Rna Tests
Molecular diagnostic tests for hepatitis C specifically detect HCV RNA and the process is commonly referred to as a Nucleic Acid Test or Nucleic Acid Amplification Test . The HCV NAT becomes positive approximately 1 to 2 weeks after initial HCV infection. The NAT test has become the gold standard supplemental test for patients who have a positive HCV EIA screening test. The NAT can determine whether a patient with a positive HCV antibody test has current or resolved HCV infection. In addition, the NAT can be used in combination with other laboratory studies, such as prior antibody test results or hepatic aminotransferase levels, to suggest the possibility of acute HCV infection. The results for the commercially available quantitative HCV RNA assays, which were previously reported as copies/mL, are now given in International Units /mL.