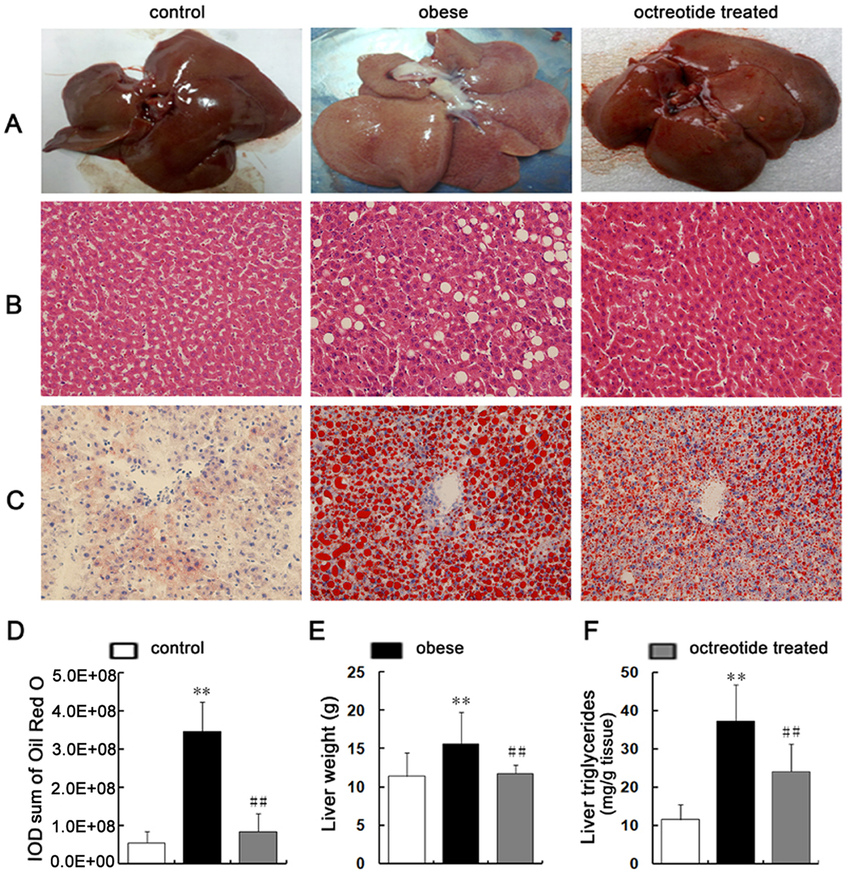
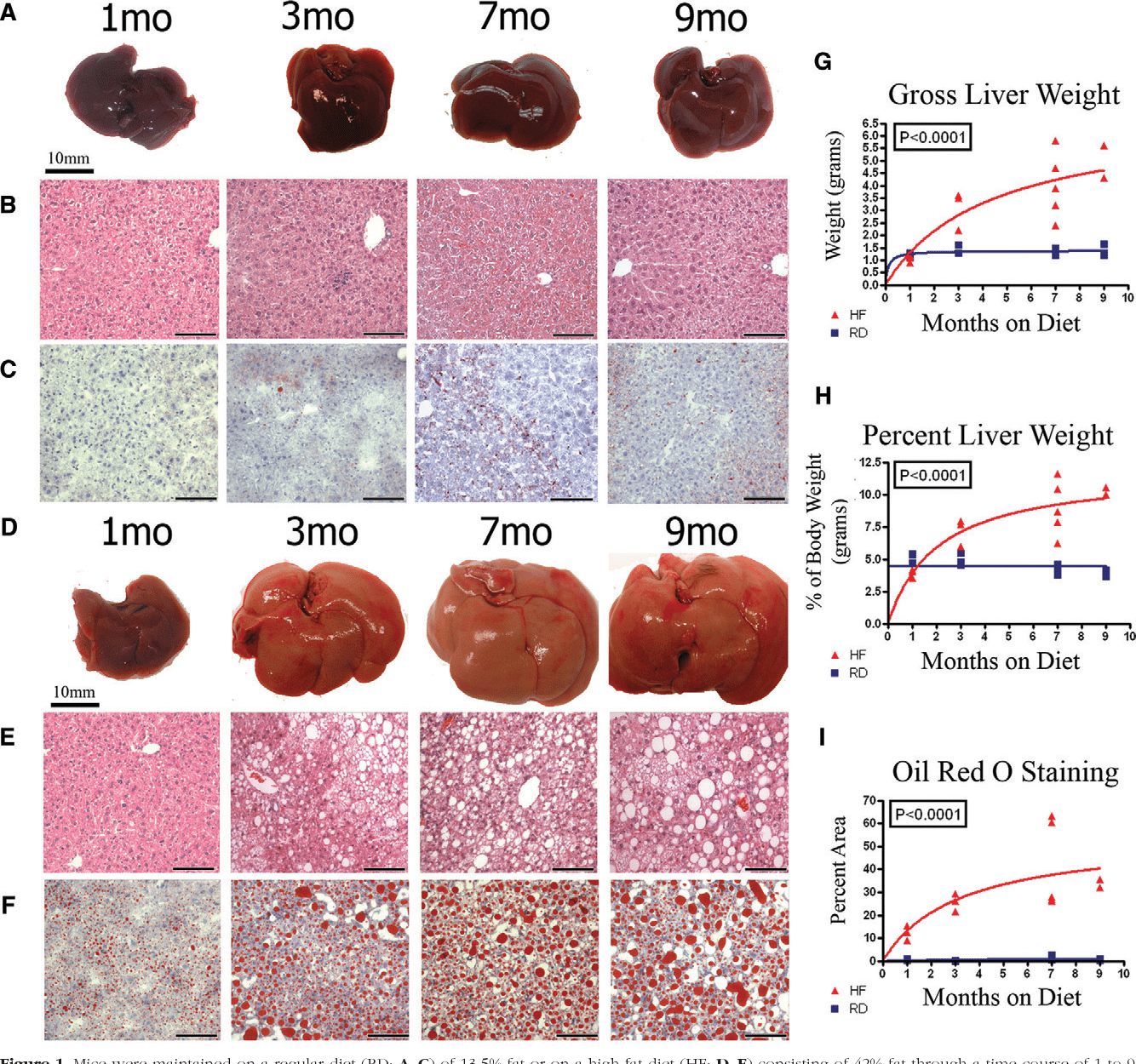
Obesity And Hepatic Steatosis Paradox
Hepatic steatosis is linked to a constant positive energy balance associated with obesity, expansion of adiposity, and ectopic storage of fat in nonadipose tissues. Although greater obesity undoubtedly correlates with intrahepatic fat storage in examination of large numbers of patients, the degree of intrahepatic fat between subjects at the same BMI varies widely . Certain genetic polymorphisms , ethnicity, and sex also powerfully modulate the associations between BMI status and steatosis . There are also normal weight patients who develop hepatic steatosis . Moreover, greater intrahepatic fat storage does not always correlate with pathological outcomes like insulin resistance, further highlighting the heterogeneity of this condition . In addition, the composition and the lipid species present in the liver beyond total triglyceride accumulation are another very importance factor to consider. Here, we posit that the paradox in these findings may be driven by individual differences in physical activity, exercise, and aerobic capacity.
Predictors Of The Presence Of Fatty Liver
In entire study population, a higher platelet count and higher HSI predicted the presence of fatty liver .
In patients with NAFLD, age, hypertension, and liver cirrhosis were negatively associated with the presence of fatty liver, whereas serum albumin level, platelet count, and HSI were positively associated with the presence of fatty liver in univariate analysis . No predictor of fatty liver was identified in multivariate analysis .
In all patients with CHB, a higher platelet count and a higher HSI independently predicted the presence of fatty liver . When patients with CHB were stratified into two groups with and without AVT, a higher HSI was the only predictor of fatty liver in CHB patients without AVT , whereas a higher platelet count and a higher HSI independently predicted the presence of fatty liver in CHB patients receiving AVT .
You May Like: Primary Biliary Cirrhosis And Autoimmune Hepatitis
Treatment For Fatty Liver Disease
There are no medications approved for NAFLD, though some are in clinical trials.
Usually the first line of treatment is to lose weight. It helps reduce fat, inflammation, and scarring in your liver. Losing just 3% to 5% of your body weight can cut down on how much fat is in your liver. Weight loss surgery is also an option if you have a lot to lose.
Youâll also need to quit drinking. Itâs the only way you can keep liver damage from getting worse. You may even be able to undo some of the liver damage thatâs already happened. Talk to your doctor about how you can get help. You may need a medically supervised detox program to safely quit drinking and manage withdrawal symptoms.
If you have complications due to NASH, such as cirrhosis or liver failure, you may need to have a liver transplant. In general, people with NASH who get a liver transplant do very well.
Also Check: What Does It Mean To Be Reactive To Hepatitis B
How Is Fatty Liver Treated And Is It Reversible
Currently, no medications have been approved to treat fatty liver disease. More research is needed to develop and test medications to treat this condition.
In many cases, lifestyle changes can help reverse most stages of fatty liver disease. For example, your doctor might advise you to:
- limit or avoid alcohol
- take steps to lose weight
- make changes to your diet
- avoid medications and supplements that are hard on your liver
If you have AFLD, your doctor will instruct you to completely abstain from alcohol. They may also recommend a detoxification program and counseling if you have alcohol use disorder .
Several viral infections can also damage the liver. To protect your liver health, your doctor may advise you to receive vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B. Depending on your situation, they may also recommend regular screenings for hepatitis C.
Cirrhosis can also cause a variety of complications, including:
- portal hypertension, which is when blood pressure in the portal vein of the liver is too high
- an increased risk of infections
If youve developed complications from cirrhosis, your doctor might recommend additional treatments, such as medications or surgery.
Cirrhosis can also lead to liver failure. If you develop liver failure, you might need a liver transplant.
Lifestyle changes are the first-line treatment for fatty liver disease. Depending on your current condition and lifestyle habits, it might help to:
For example, they might advise you to do the following:
Once Significant Fibrosisfibrosis Stage F2 Or F3 As Defined Histologically34 Develops It Is Important To Actively Manage Patients With Nash23
- Due to the increased risks of morbidity and mortality, identification of patients with significant fibrosisFibrosis stage F2 or F3 as defined histologically.3,4 is important to target efforts at preventing disease progression2,3,24
- The absence of a validated approach to predict the speed of progression for any individual patient further underscores the need for active monitoring
Don’t Miss: Which Of The Following Are Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Treatment For Hepatic Steatosis With Hepatomegaly
In addition to the treatments noted above for ALD and NAFLD, there are specific treatment options related to the other conditions that lead to an enlarged liver, or hepatomegaly.
Hepatitis treatments vary according to the type of hepatitis a person has. There are no specific treatments for Hepatitis A most people will recover fully within several weeks or months. There are also no specific treatments for acute Hepatitis B. Physicians prescribe antiviral medications to reduce liver damage and increase long-term survival in the case of chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatitis can be treated over 3 to 6 months with direct-acting antiviral drugs, depending on the severity of the liver damage. Hepatitis D requires interferon-alpha drugs, which will slow the progression of the condition.
Potential treatment options for liver cancer will vary based on the size and stage of cancer, but they will typically include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, surgery to remove the tumor, or a liver transplant.
Lifestyle changes will help manage heart failure and prevent further complications, including quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, managing stress, losing weight, increasing physical activity, and eating a healthier diet. Medications and surgery are also options to mitigate heart failure.
Is Hepatic Steatosis Dangerous
Asked by: Mohamed Brakus
Hepatic steatosis is a reversible condition in which large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in the liver cells, causing nonspecific inflammation. Most people with this condition experience few, if any, symptoms, and it does not usually lead to scarring or serious liver damage.
You May Like: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
The Digestive Health Centers Of North Texas Team Can Help
If you are experiencing any symptoms that you think might be related to liver disease, its important to get with a specialist right away to evaluate your symptoms and your lifestyle, especially since the progression of the most common forms of liver disease can be thwarted or reversed. Digestive Health Centers can help, and were ready to have a conversation with you. Contact us today.
Diagnosis Of Fatty Liver Disease
Your doctor may see something unusual in a blood test or notice that your liver is slightly enlarged during a routine check-up. These could be signs of a fatty liver. To make sure you dont have another liver disease, your doctor may ask for more blood tests , an ultrasound, a computed tomography scan or medical resonance imaging .If other diseases are ruled out, you may be diagnosed with NASH. The only way to know for sure is to get a liver biopsy. Your doctor will remove a sample of liver tissue with a needle and check it under a microscope.Some questions to ask your doctor after diagnosis include:
- What is the likely cause of my fatty liver?
- Do I have NASH? If not, how likely am I to develop NASH?
- Do I have cirrhosis? If not, how likely am I to develop cirrhosis?
- Do I need to lose weight? How can I do so safely?
- Should I be taking any medication to control my cholesterol and triglyceride levels?
- What medications or other substances should I avoid to protect my liver?
Also Check: Hepatitis C At Home Test
What Is The Livers Function
Your liver is an essential organ with multiple life-supporting functions. The liver:
- Produces bile, which helps with digestion.
- Makes proteins for the body.
- Converts nutrients into energy.
- Creates substances that help your blood clot .
- Helps you resist infections by making immune factors and removing bacteria and toxins from your blood.
Fatty Liver Disease Has A Genetic Component
The likelihood of developing fatty liver disease is influenced in part by genetics. But the heritability of fatty liver is not so simple to determine. Research has shown that there is not just one gene that determines the risk of developing fatty liver disease, but rather an interaction of many genes in your DNA.
Research published in Clinical and Molecular Hepatology describes three genes PNPLA2, GCKR, and TM6SF2 that may influence the likelihood of fat accumulation in the liver. Specific variants of each gene are associated with increased risk of conditions associated with fatty liver disease, such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Of the three genes, PNPLA3 is the most well-studied gene and directly plays a role in liver metabolic processes. Moreover, a certain variant of the PNPLA3 gene is associated with a higher risk of fatty liver disease progression to NASH, fibrosis, and cirrhosis.
Recommended Reading: Test For Chronic Hepatitis B
What Are The Symptoms Of Fatty Liver
Fatty liver can progress through four stages:
Both AFLD and NAFLD present similarly. However, in many cases, fatty liver causes no noticeable symptoms. But you may feel tired, or experience discomfort or pain in the upper right side of your abdomen.
Some people with fatty liver disease develop complications, including liver scarring. Liver scarring is known as liver fibrosis. If you develop severe liver fibrosis, its known as cirrhosis, a potentially life threatening condition that can cause liver failure.
The liver damage due to cirrhosis is permanent. Thats why its so important to prevent it from developing in the first place.
Cirrhosis may cause symptoms such as:
There are two main types of fatty liver disease: nonalcoholic and alcoholic.
Fatty liver can also happen during pregnancy, although this is uncommon.
Treatment Of Steatosis Of The Liver
Steatosis of the liver is a rather serious disease, the treatment of which should be based on the reduction of the causes of the pathological process in the liver. During treatment, the patient should not physically or mentally overwork. With remission, mild physical activity will help reduce dystrophic changes in the liver.
Nutrition during treatment is an important point, because it is the diet that helps to reduce the load on the liver, restore the body, improve the overall well-being of the patient. In addition, medicines are used. At the discretion of a specialist, folic acid or anabolic steroids can be prescribed.
Recommended Reading: Who Need Hepatitis B Vaccine
Can You Prevent Fatty Liver Disease
To prevent ALD:
- Drink in moderation: Thatâs one drink a day for women and men over 65 and up to two for men 65 and younger.
- Protect yourself from hepatitis C: This viral liver infection can make you more likely to get cirrhosis if you drink.
- Check before you mix meds and alcohol: Ask your doctor if itâs OK to drink alcohol with the prescription medications youâre taking. Read the warning label on over-the-counter meds. Donât drink when youâre taking products like acetaminophen, which can damage your liver when combined with alcohol.
For NAFLD and NASH, It boils down to making better choices:
- Eat healthy food. Choose a plant-based diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Stay at a healthy weight. Lose weight if you need to. If your weight is healthy, work to maintain it by choosing a healthy diet and exercising.
- Exercise. Get a workout most days of the week. Talk to your doctor first if you haven’t been active in a while.
Show Sources
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: âDefinition & Facts of NAFLD & NASH,â âCirrhosis,â âSymptoms & causes of NAFLD & NASH,â âDiagnosis of NAFLD & NASH,â âTreatment for NAFLD & NASH,â
American Liver Foundation: âAlcohol-Related Liver Disease.â
Mayo Clinic: âNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease,â âAlcoholic hepatitis.â
American Academy of Pediatrics: âNonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Management.â
Cleveland Clinic: âAscites.â
Degrees Of Hepatic Steatosis
Liver fat can be classified according to its severity into:
- Grade 1 or Simple Hepatic Steatosis: Excess fat is considered harmless. There are usually no symptoms and the problem is only discovered through a routine blood test
- Grade 2 or Non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis: in addition to excess fat, the liver is inflamed, which can lead to the emergence of some symptoms such as pain in the right side of the abdomen and swollen belly
- Grade 3 or Liver Fibrosis: There is fat and inflammation that causes changes in the organ and blood vessels around it, but the liver still functions normally
- Grade 4 or Liver Cirrhosis: It is the most serious stage of the disease and arises after years of inflammation, characterized by a change in the entire liver that causes a reduction in its size and leaves its irregular shape. Cirrhosis can progress to cancer or death of the liver, requiring an organ transplant.
Thus, in addition to assessing the amount of fat in the organ, it is also important to check for the presence of inflammation, as it is the main cause of cell death in this organ. To assess the progression of the disease, the doctor may indicate the performance of hepatic elastography, which is a quick and painless exam and is very effective in monitoring the person with liver disease. Understand how hepatic elastography is performed.
Read Also: Can Hiv Lead To Hepatitis
Hepatic Steatosis Hepatic Resection And Liver Transplantation
Macrovesicular steatosis is an important criterion defining extended-criteria donor organs. Several studies have reported a poor impact of steatosis on postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver resection. A national analysis of the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients demonstrated that macrovesicular steatosis of greater than 30% was an independent predictor of reduced 1-year graft survival. Steatotic livers are particularly vulnerable to ischemia/reperfusion injury, resulting in an increased risk of postoperative morbidity and mortality after liver surgery, including liver transplantation. In a retrospective review of 450 living liver donors who underwent right hepatectomy, a mild degree of hepatic steatosis was associated with higher postoperative peak aspartate and alanine aminotransferase values. Furthermore, biliary complications remain a persistent problem in orthotopic liver transplantation. The presence of macrovesicular steatosis in 20% to 50% of a liver graft emerged as a newly defined risk factor for postoperative biliary complications in 175 adult patients undergoing living donor liver transplantation. Thus, hepatic steatosis poses a challenge after liver resection or transplantation.
Steatosis In Chronic Hepatitis C
In chronic hepatitis C patients, the prevalence of steatosis ranges from 40% to 86% . The majority of patients with steatosis have mild steatosis affecting less than 30% of hepatocytes. Thus, steatosis occurs more frequently in patients with chronic hepatitis C than in the general population of adults in the Western world. Macrovesicular steatosis is found in the periportal region of the liver-different from the centrilobular distribution characteristic of NASH patients. Mild steatosis had been reported in nearly 40% of patients with HCV genotype 4.
Moderate or severe steatosis is significantly less frequent in genotype 4 than 3 chronic hepatitis C patients and similar between genotype 4 and 1. In non-diabetic, overweight patients, moderate or severe steatosis is present in only 10%-15% of genotype 4 or 1 compared with 40% of genotype 3 patients. Thus, hepatic steatosis in genotype 4 is mostly associated with metabolic factors, similar to those in genotype 1.
Also Check: Autoimmune Disease Hepatitis Of The Liver
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease means you have extra fat in your liver. You might hear your doctor call it hepatic steatosis.
Heavy drinking makes you more likely to get it. Over time, too much alcohol leads to a buildup of fat inside your liver cells. This makes it harder for your liver to work.
But you can get fatty liver disease even if you donât drink a lot of alcohol.
The Fatty Liver Disease Diet Plan
Following a diet plan for fatty liver disease can help you reverse fatty liver disease and prevent fatty liver disease progression to NASH and liver cirrhosis.
How long does it take to reverse fatty liver? The length of time required to reverse fatty liver depends on how progressed your condition is.
For more details about making lifestyle changes for fatty liver disease, check out this article on the fatty liver disease diet plan.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Alcoholic Hepatitis
Stay Away From Refined Grains And Added Sugar
Refined grain and added sugar are significant contributory components to fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Refined grain and added sugar are quickly broken down into glucose molecules in the digestive system. These glucose molecules then enter the bloodstream and spike blood sugar. Insulin is released and signals to body tissues to utilize the glucose as energy, but inevitably, there is leftover glucose that must be stored throughout the body, including the liver. Eating too many refined carbs and added sugar could, over time, contribute to fatty liver disease as well as metabolic conditions like insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Steer clear of products that contain added sugar, such as candy, soda, pastries, cookies, cakes, and ice cream. Even products like granola bars, breakfast cereals, salad dressing, and condiments can contain more added sugars than you think.
To avoid refined grains, stay away from foods like white rice, white pasta, and white bread. Just like added sugar, refined grains are broken down into glucose.