What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious bloodborne disease that affects the liver. To get the condition, a person must come into contact with the blood or body fluids of a person with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C causes the liver to become inflamed. This can cause the healthy soft tissues in the liver to harden and scar. If left untreated, the inflammation and scarring can cause:
- Cirrhosis of the liver
How Is Hepatitis C Diagnosed
If a doctor suspects your child is infected with HCV, they may test the childs blood to see if it contains antibody to the virus. If the test comes back positive, the doctor will run additional tests for the virus itself and to see which genetic type, or genotype, of the virus your child is carrying. The results of this test will help the doctor recommend the next course of action.
Children and adults with chronic hepatitis C typically undergo periodic tests to monitor their liver inflammation and function and look for signs of serious liver disease.
What Is The Outlook For Children With Hepatitis C
Most children acquire HCV at birth through vertical transmission from their mother. Around 1 in 20 babies born to mothers with hepatitis C acquire the virus, according to the American Liver Foundation.
Of those babies with an infection, some 40 percent may clear it without treatment by the time they are 2 years old .
The outlook for older kids who acquire an HCV infection through other means of transmission is more similar to the outlook for adults.
Up to 80 percent of those who have hepatitis C may go on to develop a chronic infection that may progress into chronic liver disease with scarring in 20 to 30 years.
Read Also: Hepatitis A How Do You Get It
What Happens If My Child Has Hepatitis C
Approximately 1 in 5 children with hepatitis C clear the virus on their own. The others become carriers. Even though the virus stays in the liver of children who are carriers, most stay healthy.
Children who are hepatitis C carriers will see their doctors regularly and have blood tests. Treatment is usually not required for many years. However, as the evidence for use of new medications in children becomes available, it is likely that many children with chronic infection will be treated.
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But it’s important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
How Many Children Have Hepatitis
As of 27 May, 650 children worldwide have been reported to have severe hepatitis. At this point in the year, doctors would not expect to see this many cases.
However, occurrences are still rare. Of the roughly 8.7 million children under the age 10 in the UK, there are 222 cases currently under investigation by UKHSA. Of these, there are 158 children living in England, 31 in Scotland, 17 in Wales and 16 in Northern Ireland.
This is a very, very rare disease. So, as a mum, Im not hugely concerned, said Stamataki. But as a viral immunologist, it is raising an eyebrow, because the incidence of these cases are higher compared to pre-pandemic levels.
It could be that more children have had hepatitis by the same cause as with the severe cases, but that their symptoms were mild and their recovery quick, so they went unnoticed, said Stamataki.
Recommendations For Counseling Parents Regarding Transmission And Prevention In Children With Hcv Infection
RECOMMENDED RATING Parents should be informed that hepatitis C is not transmitted by casual contact and, as such, children with HCV infection do not pose a risk to other children and can participate in school, sports, and athletic activities, and engage in all other regular childhood activities without restrictions. I, B Parents should be informed that universal precautions should be followed at school and in the home of children with HCV infection. Educate families and children about the risk and routes of HCV transmission, and the techniques for avoiding blood exposure, such as avoiding the sharing of toothbrushes, razors, and nail clippers, and the use of gloves and dilute bleach to clean up blood. I, B
HCV-infected children often face discrimination and stigmatization in school and child-care settings that is driven by public misunderstanding regarding hepatitis C transmission. HCV is not transmitted by casual contact in the absence of blood exposure. Families should not be forced to disclose a childs HCV infection status, and children should not be restricted from any routine childhood activity.
You May Like: Early Signs Of Hepatitis C
Treatment For Hepatitis C
Some children will recover from the virus within weeks or months. They dont need treatment.
Other children might develop chronic hepatitis C and will live with the virus in the long term. This can put them at risk of liver scarring, liver failure and liver cancer in the future.
This is why its important for children with chronic hepatitis B to have checks on their livers and general health every 6-12 months.
There are some effective and safe anti-viral medicines for chronic hepatitis C. Health professionals might prescribe them for older children and teenagers, especially children with liver damage.
There is no immunisation for hepatitis C.
How Does Hepatitis A Spread
Hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of a person who has the virus. It spreads when a person puts something in his or her mouth that has the hepatitis A virus on it. Even if the item looks clean, it can still have virus on it that can spread to others. The amount of stool can be so tiny that it cannot be seen with the naked eye. You can get it by touching objects such as doorknobs or diapers or eating food that has the virus on it.
You May Like: How To Detect Hepatitis C
Can Hep C Be Treated In Children
Yes, hep C is treatable in kids.
In about 40 percent of cases, your babys immune system will clear the HCV on its own. If this happens, it generally occurs before 2 years old.
So, for the first few years of life, treatment usually only involves consistent monitoring by a pediatric hepatologist, who will monitor your babys liver function and growth.
Theyll likely also recommend vaccinations against hep A and B because the viruses could increase your kids chances of liver damage.
If your baby doesnt clear the HCV on their own by 3 years old or they start showing symptoms of liver disease theyll begin treatment with direct-acting antiviral therapy.
If treatment fails, they can develop complications and may even become eligible for a liver transplant.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Dont Miss: How Do People Catch Hepatitis B
You May Like: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis B
How We Treat Neonatal Hepatitis C
If your child has been diagnosed with congenital hepatitis C, you may be confused, frightened and overwhelmed. But you can rest assured that, at Boston Children’s Hospital, your child is in good hands.Our physicians are expert, compassionate, and committed to focusing on the whole child, not just his conditionthat’s one reason we’re frequently ranked as a top pediatric hospital in the United States.
It’s important to know the following about hepatitis C:
- If you have hepatitis C, your doctor will check your baby 4-6 months after birth to test for the presence of the virus.
- If the test is positive, Children’s physicians will continue to monitor your baby for any worsening of her condition and will treat any symptoms she may develop.
At Children’s, we consider you and your child integral parts of the care team and not simply recipients of care. You and your care team will work together to customize a plan of care for your child.
Prevention: The best treatment
There is no cure for hepatitis C, so it’s best to avoid infection.
Because hepatitis C is most often spread through contact with contaminated blood in needles shared among IV drug users, it’s important to never share needles. Of course, it’s best to stop using drugs altogether your doctor can help you find treatment if you are having problems with substance abuse.
Hepatitis C In Kids Up To Age 12
Hepatitis C goes away without treatment 40% of the time before a child’s second birthday. The virus has disappeared in some kids as old as 7.
If your child still has hepatitis C after they turn 2, you may hear your doctor call it a “chronic” infection. For most, the disease causes minor liver problems. About 25% of kids have a higher chance of getting scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis. Most of the time that doesn’t happen until the child becomes an adult.
If your child needs treatment, your doctor may suggest these medicines:
Interferon and ribavirin. Studies show it will end a hepatitis C infection in 50% to 90% of cases. It’s the only treatment approved for children under 12. Your child may have side effects that include fatigue, fever, chills, and depression.
Your doctor will likely recommend that your child get hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines, as well as a regular flu shot. Ask your doctor about medicines to avoid because they can cause liver damage, such as acetaminophen.
Also make sure your child sticks to a healthy diet. See that they eat regular, well-balanced meals, get plenty of fruits and veggies, enjoy whole grains and protein-rich foods, and avoid salt.
Read Also: How Is Hepatitis C And B Transmitted
Unique Aspects Of Hcv Diagnosis In Newborns/infants
In general, testing for HCV infection should occur in all children suspected to be at risk . However, unique to children is the sequence of testing recommended for infants born to mothers with HCV infection and who are in danger of becoming infected . Mothers infected with HCV will have circulating antiHCV immunoglobulin G, which crosses the placenta and can be measured in the serum of their infants. Maternal antibody can persist in the child for over a year, consequently testing for antiHCV in infants is not informative during this period. The American Academy of Pediatrics’ recommendations are to delay measurement of antiHCV antibody until after 18 months of age.4 HCV RNA testing can reliably indicate perinatal transmission however, infants should be at least 2 months old for this test to be reliable.4, 36 Retesting at 12 months should occur to confirm chronic HCV infection and to rule out the possibility of spontaneous seroconversion, defined as the absence of detectable HCV RNA on two occasions > 6 months apart,37, 38 which occurs in 25%40% of infants infected via perinatal transmission.4, 39 In the absence of evidence suggesting active liver disease, delaying testing until 1518 months of age is likely to produce the clearest results in cases of suspected perinatal transmission.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often does not have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged.
This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition.
Symptoms can include:
- feeling and being sick
The only way to know for certain if these symptoms are caused by hepatitis C is to get tested.
Also Check: How To Treat Hepatitis B Virus
How Is Hepatitis Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is.
Your childs treatment will depend on whats causing his or her hepatitis. The goal of treatment is to stop damage to your childs liver. Its also to help ease symptoms. Your childs treatment may include:
-
Medicines. These can control itching, treat the virus, or control an autoimmune disease.
-
Supportive care. This includes eating a healthy diet and getting enough rest.
-
Reducing risk. Not using alcohol or illegal drugs.
-
Blood testing. This can tell if the disease is progressing.
-
Hospital stay. This is done in severe cases.
-
Liver transplant. This is done for end-stage liver failure.
-
Helping to prevent the spread of viral hepatitis. Having good personal health habits, such as handwashing.
Is The Increase In Hepatitis Cases Due To Covid
Some have suggested that the sudden rise in cases could be due to COVID-19 lockdowns, as children had not been exposed to as many viruses and infections that have enabled them to build up their immune systems.
Its an interesting hypothesis, said Stamataki. Children need viral infection over the years to build up their immunity to incoming viruses. But this still doesn’t explain why only a handful of those children had severe disease, and how this has affected the liver.
Again, of the 8.7 million children affected by lockdown, only 222 hepatitis cases have been reported so far an occurrence of around 0.0026 per cent.
Read Also: What Causes Hepatitis C Symptoms
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C In Children
When babies acquire an HCV infection through transmission at birth, doctors may monitor and wait until after age 3 to see if the infection goes away without treatment. As many as 40 percent of kids in these cases may clear the hepatitis C virus on their own, according to the American Liver Foundation.
Antiviral medications used to treat the viral infection are not generally recommended for use in children under 3 years old. Instead, the doctor may simply monitor your child, especially if they remain asymptomatic.
Older children may take antiviral medications interferon or a combination of interferon with ribavirin for months to years to clear the infection. The specific treatment your child receives will depend on the genotype of the virus and how your child is responding to the medications.
If the virus does not clear with antiviral therapy, your childs doctor may recommend a liver transplant. However, the need for a liver transplant is extremely rare in children, and theres an increased chance that the new liver may contain the viral infection as well.
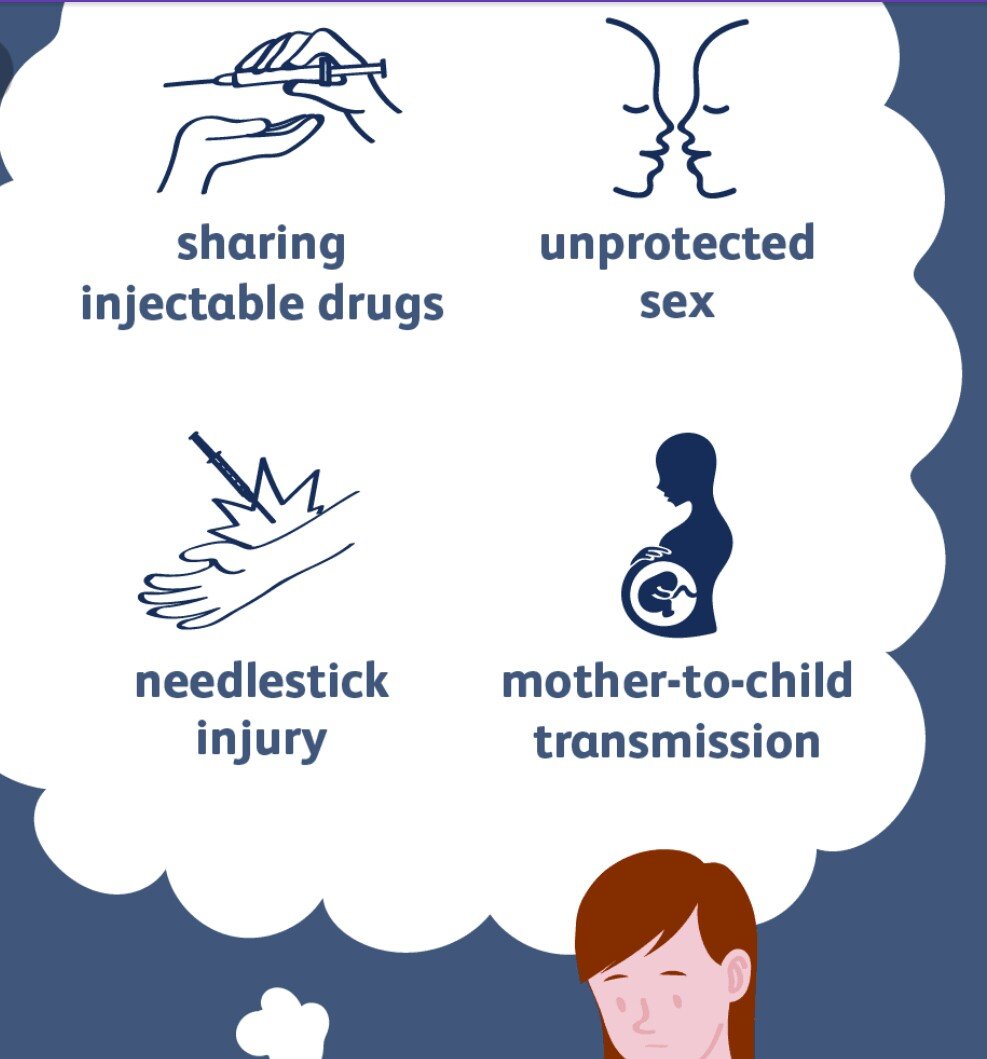
way kids are exposed to the virus. What this means is that a mother who has hepatitis C passes the virus to her unborn child.
Other ways hepatitis C is transmitted:
Ways hepatitis C is not transmitted:
- contact with unbroken skin
Our Areas Of Innovation For Hepatitis
Liver biopsies provide a great deal of information about the extent of damage in a childs liver, but the procedure is invasive and can be both painful and risky. Researchers at Boston Childrens use an ultrasound-based imaging technology called FibroScan that may be able to help doctors assess liver scarring without a liver biopsy.
Read Also: How Do People Catch Hepatitis C
Complications Of Hepatitis C
If the infection is left untreated for many years, some people with hepatitis C will develop scarring of the liver .
Over time, this can cause the liver to stop working properly.
In severe cases, life-threatening problems, such as liver failure, where the liver loses most or all of its functions, or liver cancer, can eventually develop.
Treating hepatitis C as early as possible can help reduce the risk of these problems happening.
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated

Yes, many adults and some children are treated with Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin.
From March 2016, oral only treatment has been approved on the PBS for adults and in April 2020, this was made available to children 12 years and older. Clinical trials of these oral medications have occurred, in the hope that it will also be available for treating younger children in the future. Children 11 years and younger will need to continue being monitored until the treatment becomes available to them.
The length of treatment is as little as 8 weeks with children receiving treatment monitored by a specialist. The treatment is dependent on how the childs liver is functioning, the impact of symptoms on their life, blood results, liver biopsy and ultrasound results.
You May Like: How To Catch Hepatitis C
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.