What Causes Skin Changes With Viral Hepatitis
Skin changes in acute viral hepatitis can be nonspecific such as the itch secondary to jaundice. Chronic viral hepatitis can cause progressive liver failure and skin changes due to cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Skin changes seen with viral hepatitis can be due to:
- Direct viral infection of skin cells with viral particles detected in keratinocytes and lymphocytes
- Autoimmune origin as HCV is lymphotropic promoting B-cell proliferation and circulating autoantibodies can be detected
- Effects on the liver seen in acute viral hepatitis and subsequent chronic liver disease.
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis A
There is no specific treatment needed for hepatitis A. It is usually a self-limiting illness, which means it usually goes away on its own. Your immune system will normally clear away the infection. Most people with hepatitis A infection dont need to be admitted to hospital. However, admission to hospital may be suggested if you are severely ill or you are being sick and are lacking in fluid in the body .
Treatment is aimed at relieving your symptoms. It is common to feel more tired than usual when you have hepatitis A so you may need to have plenty of rest. Your doctor may be able to suggest some painkillers and some antisickness medication if needed. To help ease the symptom of itch, keep cool, wear loose clothing and avoid hot baths or showers. Avoiding fatty foods may help to reduce the feeling of sickness. Also, you should not drink alcohol whilst you are ill.
During your illness, your doctor may also want to keep a check on how your liver is working by repeating blood tests from time to time to look at this.
It is important to have excellent personal hygiene to reduce the risk of passing the virus on to others. Thoroughly wash your hands after going to the toilet. You should also avoid handling food and having unprotected sex when you are infected with the virus. Ask your doctor when it is safe for you to return to work, or for your child to return to school or nursery.
Liver Disease Rash: A Symptom And A Sign
What is a liver disease rash?Dermatologists find that our skin often shows what is happening inside of the body. A liver disease rash could indicate a further health problem. An example of where this effects your liver would be jaundice, where the skin and the whites of the eyes become yellow. Although yellowing skin is not the only skin change that indicates liver disease, darkening of the skin and bronzing of the skin can point to liver disease or failure and rashes can point to a number of liver health problems.
Whats in this article
- A liver disease rash and hepatitis C
- When does liver disease rash occur?
- Signs & symptoms
A liver disease rash and hepatitis C
Skin rashes may be a sign of hepatitis C, and should not be ignored. Rashes that appear on your skin as a result of hepatitis c show that your body is busy trying to fight the infection on its own. This rash is called urticaria and is the most common rash for those suffering from acute hepatitis c virus. This is a short-term infection, according to the National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse, acute HCV typically lasts for six months or less. Urticaria can also cause the skin to swell, rashes on your face and often comes in rounds that can last for several hours. Urticaria can also develop as a result of certain allergic reactions.
Signs & symptoms
If a rash is due to liver damage skin symptoms may include:
Additional symptoms may include stomach swelling and bleeding that does not stop.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hepatitis C Non Reactive Mean
Who Is At High Risk And Should Be Tested For Hepatitis C Infection
The U.S. Preventive Health Services task force recommends that all adults born between 1945 and 1965 be tested once routinely for hepatitis C, regardless of whether risk factors for hepatitis C are present. One-time testing also is recommended for:
- People who currently inject drugs or snort drugs, or ever did so, even once many years previously
- People with persistently elevated alanine aminotransferase level, a liver enzyme found in blood
- People who have HIV infection
- Children born to HCV- or HIV-infected mothers
- People who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- People who got a tattoo in an unregulated setting, such as prison or by an unlicensed person
- People who received clotting factor produced before 1987
- People who received transfusions or organ transplants before July 1992, or who were notified that they received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C infection
- Health care, emergency medical, and public safety workers after a needlestick, eye or mouth exposure to hepatitis C-infected blood
People who may have been exposed to hepatitis C in the previous 6 months should be tested for viral RNA load rather than anti-HCV antibody, because antibody may not be present for up to 12 weeks or longer after infection, although HCV RNA may be detectable in blood as soon as 2-3 weeks after infection.
Eat Regular Nutritious Meals
Sometimes people with hepatitis C have a hard time eating. You may have no appetite, feel nauseated, or have different tastes than you are used to. Even if you dont feel like eating, its very important to eat small meals throughout the day. Some people have nausea in the afternoon. If this happens to you, try to eat a big, nutritious meal in the morning.
If you have cirrhosis, it may not be a good idea to eat salty foods or foods that are high in protein. If you want to know more about which foods to avoid and which foods are good to eat, ask your doctor about meeting with a registered dietitian to discuss a healthy eating plan.
Recommended Reading: Can Hepatitis C Cause Liver Cancer
How Is Autoimmune Hepatitis Diagnosed
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may be mild at first and are similar to the flu, so it may not be diagnosed immediately. The doctor will perform a physical examination of the patient and ask about the family medical history. The doctor may also order certain tests, including:
- A blood test to check for inflammation in the liver, to evaluate the patients liver function, and to check for antibodies associated with autoimmune hepatitis.
- Ultrasound of the liver. Ultrasound is a procedure that transmits high-frequency sound waves through body tissues. The echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photographic images of the inside of the body.
- If necessary, the doctor may also order a liver biopsy, the removal of a small piece of tissue from the liver to be analyzed in the lab for disease.
Skin Signs Of Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis not only affects the liver but also the blood and circulatory system. Abnormal blood clotting accompanied by bleeding and/or dilation of blood vessels near the surface of the skin can cause symptoms like:
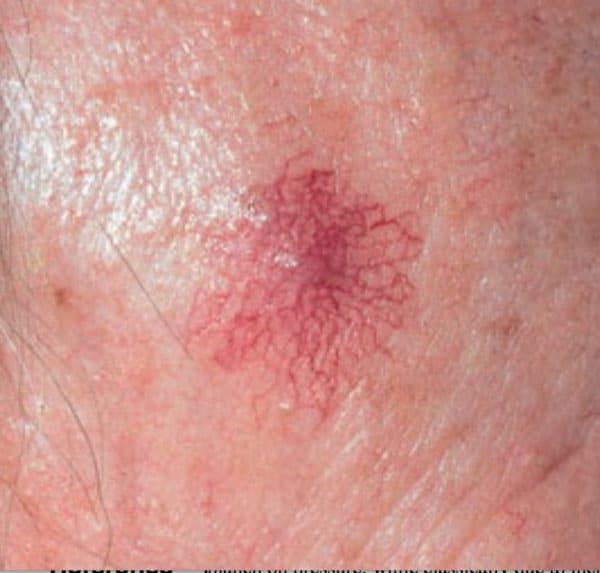
- Spider angiomas: Also known as spider veins or spider nevus, these are thin reddish or purplish lines on the skin’s surface that look like a spider’s web.
- Petechiae: These are purplish dots on the skin caused by burst and bleeding capillaries, most often on the lower legs.
- Purpura: Also known as skin hemorrhages or blood spots, these purple-colored spots are larger than petechiae, mainly on the lower legs and ankles.
Also Check: Hiv And Hepatitis Are Transmitted Through What Modes
Skin Signs Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis
At least 20% of patients with chronic hepatitis due to HBV or HCV develop skin changes, only a few of which are diagnostic of viral hepatitis.
Skin conditions associated with both HBV and HCV
- Cryoglobulinaemia types II and III can present with skin signs of cutaneous vasculitis or systemic vasculitis
- Skin cancer cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
- Dermatomyositis has been reported in association with HBV or HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma, and HCV-induced autoimmunity
- Anti-cardiolipin antibodies without thrombocytopenic thrombosis can be associated with both HBV and HCV, and antiphospholipid syndrome with HCV
Skin conditions more often associated with HBV
Skin conditions more often associated with HCV
Skin signs of possible hepatitis C infection
What Causes Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is caused when blood from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. These are the most common methods of infection:
- An infected person shares needles or syringes for injecting intravenous drugs. Even people who have used IV drugs infrequently may be at risk for infection.
- Healthcare workers who accidentally stick themselves with needles used on infected patients are at risk of getting hepatitis C.
- Patients who received donated blood or blood products or who had organ transplants before 1992 are at higher risk for hepatitis C.
Less common ways of spreading hepatitis C include the following:
- Sexual contact with an infected person. Although the risk of getting hepatitis C through sexual intercourse is low, the risk increases for people who have several sex partners or those with HIV infections.
- Sharing a razor, toothbrush or other personal item that may have come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
- Becoming infected through body piercing or tattooing, if the facility does not use sterile equipment or does not follow infection control practices.
Babies born to mothers who have hepatitis C might become infected, although this is not common. In addition, baby boomers are at increased risk of having hepatitis C and should be screened for it.
Hepatitis C cannot be spread by simple contact or by coughing or sneezing.
Recommended Reading: Pro Plan Hepatic Dog Food
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted
Dermatomyositis Causes A Skin Rash
Dermatomyositis is an inflammatory disease that causes a skin rash on the face and eyelids, as well as on the shoulders, upper chest, and back, and around the knuckles. Other symptoms include muscle weakness, shortness of breath, and trouble swallowing. It is most common in children between ages five and 15 and in adults between ages 40 and 60.
The autoimmune disorder is treated with immunosuppressants and corticosteroids. In children, the symptoms often go away completely. Adults need to be more careful as this may be a sign of another underlying disease and could develop pneumonia or lung failure, which can be fatal in some cases.
Also Check: What Are The Signs Of Having Hepatitis C
Thyroid Disease Can Cause Dry Skin Hair Loss And Weight Gain
An underactive thyroid means you are producing too few thyroid hormones, in turn, your metabolism may slow down. Symptoms of hypothyroidism develop over time and may include dry skin, hair loss, weight gain, fatigue, and a sensation of being cold. Often hypothyroidism is a result of Hashimotoâs disease, when the immune system attacks the thyroid.
Hypothyroidism cant be cured, but it is generally easy to treat. You will have to take a synthetic form of the hormone as a daily pill. Periodic blood tests will help your doctor ensure you are taking the right dose. Once you have the condition under control, your symptoms will start to improve.
Read Also: Which Oil Is Good For Hepatitis B Patient
What Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Look Like
Hepatitis C infection can go through two stages: acute and chronic. In the early, or acute stage, most people dont have symptoms. If they do develop symptoms, these can include:
- flu-like symptoms, tiredness, high temperature and aches and pains
- loss of appetite
- jaundice, meaning your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow
While for some people, the infection will clear without treatment, in most cases, acute infection will develop into long-term chronic infection. Chronic infection may not become apparent for a number of years until the liver displays signs of damage. These symptoms can include:
- mental confusion and depression these are specific to hepatitis C
- constantly feeling tired
- feeling bloated
- joint and muscle pain
Without treatment, chronic hepatitis C can cause scarring of the liver , which can cause the liver to stop working properly. A small number of people with cirrhosis develop liver cancer and these complications can lead to death. Other than a liver transplant, theres no cure for cirrhosis. However, treatments can help relieve some of the symptoms.
Search For A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
- Viral infections such as mumps or varicella
- Cancer or cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- Bug bites or other problems with your skin
Also Check: Hepatitis B E Antibody Positive
Treatments For Hepatitis A
There’s currently no cure for hepatitis A, but it will normally pass on its own within a couple of months. You can usually look after yourself at home.
While you’re ill, it’s a good idea to:
- get plenty of rest
- take painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen for any aches and pains ask your GP for advice about this, as you may need to take lower doses than normal or avoid certain medications until you’ve recovered
- maintain a cool, well-ventilated environment, wear loose clothing, and avoid hot baths or showers to reduce any itching
- eat smaller, lighter meals to help reduce nausea and vomiting
- avoid alcohol to reduce the strain on your liver
- stay off work or school and avoid having sex until at least a week after your jaundice or other symptoms started
- practise good hygiene measures, such as washing your hands with soap and water regularly
Speak to your GP if your symptoms are particularly troublesome or haven’t started to improve within a couple of months. They can prescribe medications to help with itchiness, nausea or vomiting, if necessary.
Read more about treating hepatitis A.
How Can I Manage Itchy Skin
- Take short showers in warm water. Avoid using hot water for your showers. Use only a small amount of mild skin cleanser.
- Apply moisturizer or cooling creams after you bathe and throughout the day.
- Use a cool mist humidifier to moisten the air in your home and maintain a cool temperature. Cool, humid air can decrease skin dryness and itching.
- Avoid allergens and skin irritants. Do not use perfume, fabric softener, or makeup that irritates your skin. Use a mild detergent to wash your clothes. Wear loose cotton clothes and use cotton sheets. Avoid wool.
You May Like: Titer Test Hepatitis B Vaccine
What Kind Of Liver Disease Causes Itching
Itching is common in autoimmune liver diseases, such as primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and obstructive biliary disease. It also occurs with cancer of the head of the pancreas, hepatitis, and drug-induced liver disease. However, it is less common with alcohol-induced liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Clinical Features And Diagnosis
Symptoms of psoriasis may vary slightly from person to person, but the characteristic symptoms are patches of red skin with white scaling. These scales may itch and sting. They can occur anywhere, but some common sites include the scalp, elbows, and knees.
Doctors typically diagnose psoriasis based on a physical examination. They may ask questions about the joints or other areas of the body to determine the extent of the psoriasis. They might also carry out a skin biopsy to rule out other conditions, such as eczema.
Typically, people with a HCV infection present any symptoms. This makes regular screening for hepatitis C important, especially for people with psoriasis taking immunosuppressive drugs. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms 1-3 months after viral exposure, which can include:
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis C Do To Your Body
You May Like: How You Get Hepatitis C
Vaccination Against Hepatitis A
Vaccination against hepatitis A isn’t routinely offered in the UK because the risk of infection is low for most people.
It’s only recommended for people at an increased risk, including:
- close contacts of someone with hepatitis A
- people planning to travel to or live in parts of the world where hepatitis A is widespread, particularly if levels of sanitation and food hygiene are expected to be poor
- people with any type of long-term liver disease
- men who have sex with other men
- people who inject illegal drugs
- people who may be exposed to hepatitis A through their job this includes sewage workers, staff of institutions where levels of personal hygiene may be poor and people working with monkeys, apes and gorillas
The hepatitis A vaccine is usually available for free on the NHS for anyone who needs it.
Read more about the hepatitis A vaccine.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis
The following are the most common symptoms for hepatitis. However, each child may experience symptoms differently and some children may experience no symptoms at all.
Symptoms of acute hepatitis may include the following:
- Flu-like symptoms
- Not feeling well all over
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Itchy red hives on skin
- Clay-colored stools
Later symptoms include dark-colored urine and jaundice . The symptoms of hepatitis may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your childâs doctor for a diagnosis.
You May Like: What Is The Medication For Hepatitis C