General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
The Nonresponder Situation As A Challenge
New vaccine formulations have been and are being developed to meet the challenges of nonresponse or low response among older adults and immunocompromised individuals to current hepatitis B vaccines, for example, third-generation hepatitis B recombinant vaccines containing HBsAg, preS1, and pre-S2 antigens or adjuvanted hepatitis B recombinant vaccines . These vaccines are showing improved immune response in immunocompromised populations and older adults and, in addition, these new vaccines can offer the possibility of simplified schedules, which might be very promising for the future, for example, a 0, 1-month schedule instead of the traditional 0, 1, 6-month schedule .
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
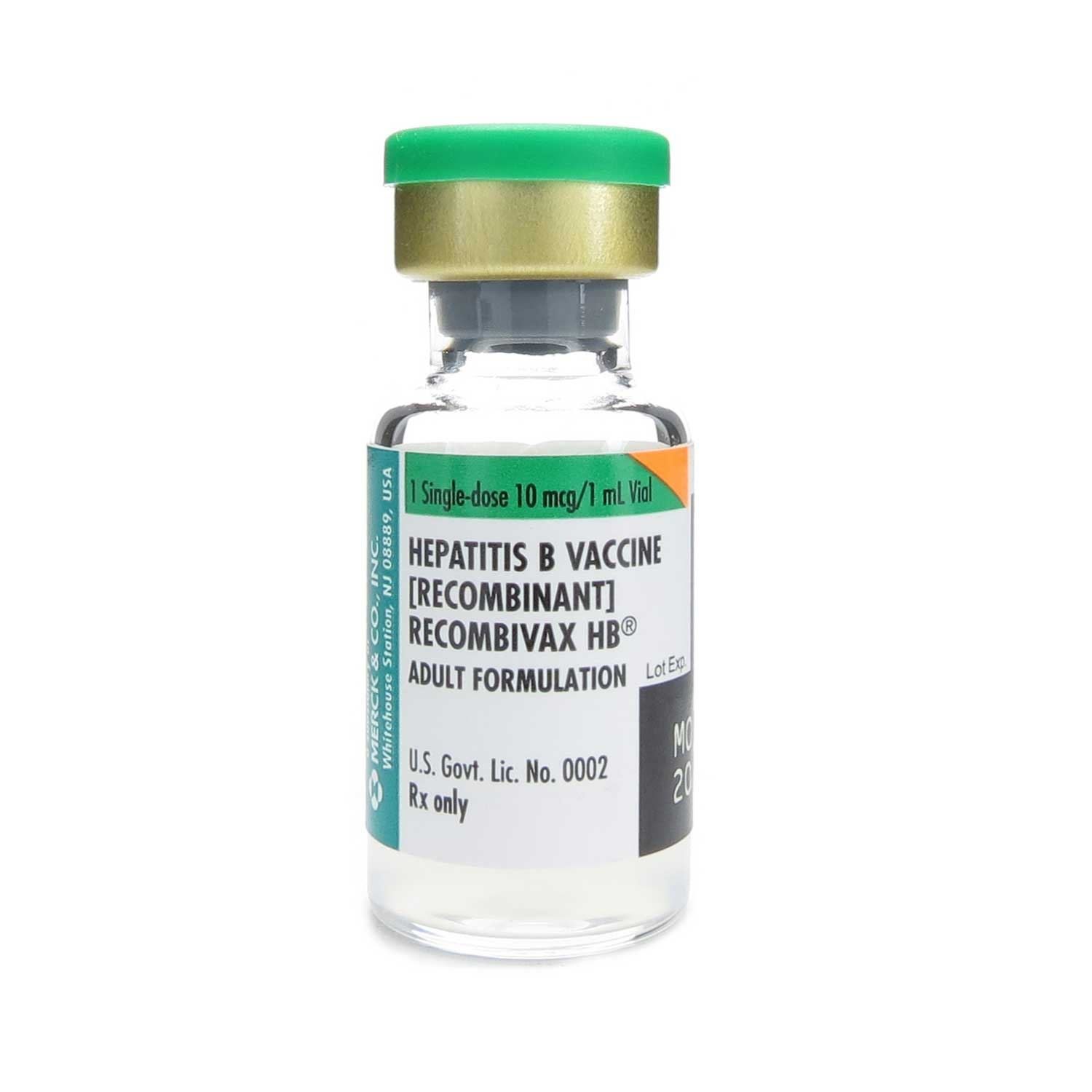
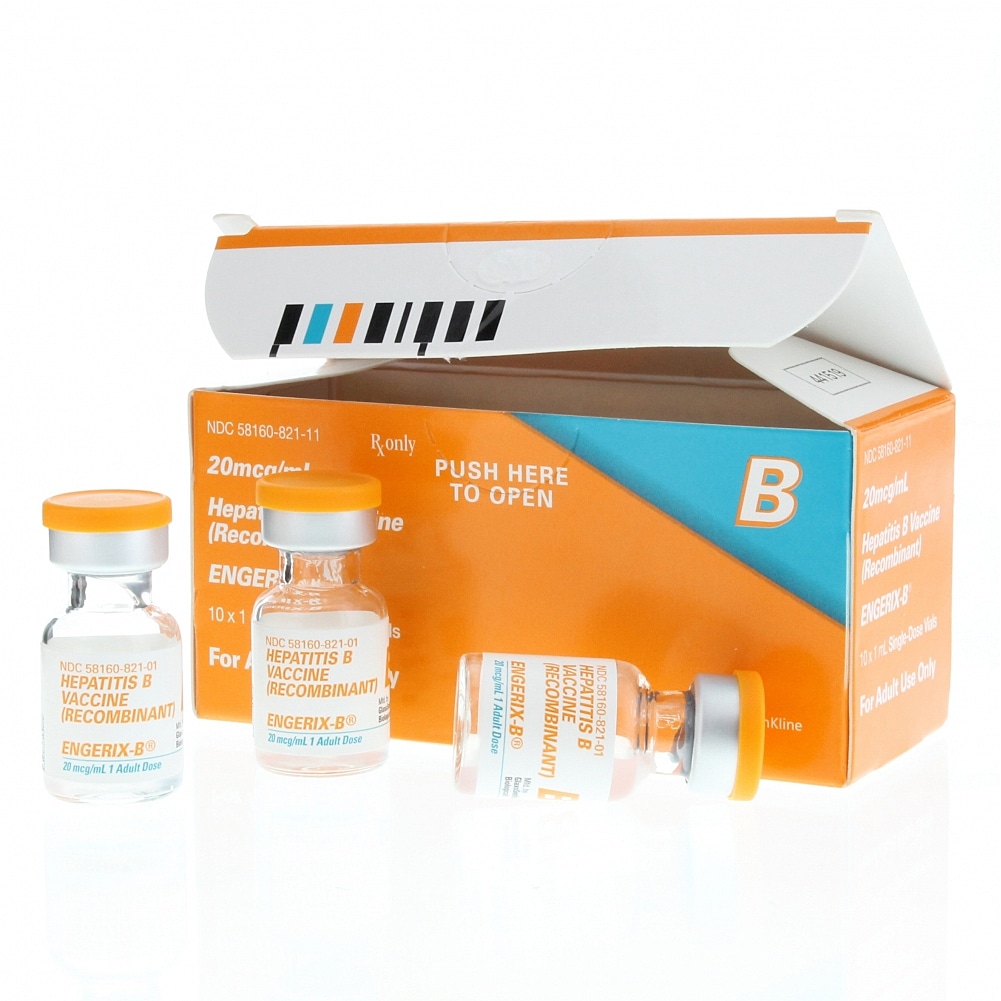
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
Read Also: How Can You Catch Hepatitis B
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
Tips For Protecting Yourself Against Hepatitis
The hepatitis A virus spreads through ingestion of the virus through sexual contact, caregiving, sharing drugs and consuming contaminated food or water. The virus can contaminate food at any time between when it is grown and cooked.
HAV is more common in environments with unsanitary conditions, poor sewage systems and no potable water. To reduce your risk, be vigilant about hand hygiene by washing your hands thoroughly before you leave the bathroom, after you change diapers, and any time you touch food.
Recommended Reading: The Difference Between Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
Most people only experience mild, short-term side effects from the hepatitis B vaccine. Common side effects include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the site of injection
Severe allergic reactions to the hepatitis B vaccine are very rare. If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction shortly after getting the HepB vaccinesuch as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or hivesseek medical help immediately.
The hepatitis B vaccine is safe and effective for most people. However, there are certain people who should not get the HepB vaccine, including:
- People who are moderately or severely ill at the time of vaccination
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to yeast
- People who have had a severe allergic reaction to a hepatitis B vaccine in the past
Facts About Hepatitis B
- Two billion people, or one in three, have been infected with hepatitis B worldwide. Of these, almost 300 million live with chronic hepatitis B. This means about 1 of every 26 people throughout the world are living with a chronic hepatitis B infection.
- Each year about 900,000 people die from hepatitis B worldwide, and about 2,000 of these deaths occur in the United States.
- Hepatitis B is transmitted through blood and is 100 times more infectious than HIV. An estimated one billion infectious viruses are in one-fifth of a teaspoon of blood of an infected person, so exposure to even a very small amount, such as on a shared toothbrush, can cause infection.
- Hepatitis B is sometimes referred to as the silent epidemic because most people who are infected do not experience any symptoms.
- Liver cancer accounted for about 5% of cancer deaths in the U.S. during 2020.
- Almost half of liver cancers are caused by chronic infection with hepatitis B.
- The World Health Organization recommends the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in immunization programs of all countries in 2019, more than 8 of 10 infants born throughout the world received three doses of hepatitis B vaccine.
You May Like: Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Cured
Which Vaccine Is Used And What Does It Contain
The products used in the national programme are called Engerix-B and HBVAXPRO. There are different vaccine products for children and adults:
Engerix-B vaccine in a 0,5 ml single-dose syringe is intended for children aged from 0 to 15 years.
HBVAXPRO 10 micrograms vaccine in a 1 ml single-dose syringe is intended for adolescents over 16 years of age and adults.
Vaccine composition:
- The vaccines do not contain live pathogens.
- The active substance is surface structures from hepatitis B viruses.
- The adjuvant is an aluminium compound.
- The excipients are salts and purified water.
- The vaccines contain no preservatives.
Who Strategy For Hepatitis B Immunization
Although major progress has been achieved in hepatitis B immunization, a number of challenges remain. That is why the WHO called for comprehensive prevention and control of HBV infection and the development of time-specific immunization goals in its member states. The strategy includes the following: universal vaccination of infants within 24 hours of birth, full immunization of infants by routine immunization programs, catch-up vaccination of unimmunized cohorts, and monitoring progress and assessing the impact of immunization .
Universal Vaccination of Infants Within 24 Hours of Birth: a Real Challenge
Full Immunization of Infants by Routine Immunization Programs and Catch-Up Vaccination of Unimmunized Cohorts
Wider provision of the existing, safe and effective HBV vaccine, through universal childhood vaccination and by catch-up vaccination of unimmunized cohorts, will further reduce new hepatitis B infections, reducing rates of chronic illness and death. However, to achieve and/or sustain high coverage, stronger and resilient immunization delivery systems will be needed. Still, some countries adopt risk-grouptargeted vaccination only, instead of adding a universal vaccination program. However, changing demography, increasing immigration, and the current vaccine costs make the cost-benefit ratios in these remaining low-endemicity countries strongly in favor of universal HBV vaccination.
Monitoring Progress and Assessing the Impact of Immunization
Read Also: Hepatitis C Genotype 1a Treatment
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
Babies And Hepatitis B Vaccination

Pregnant women have a routine blood test for hepatitis B as part of their antenatal care.
Babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B need to be given a dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of their birth, followed by further doses at 4, 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age, plus a final dose when they’re 1 year old.
Babies of mothers identified by the blood test as particularly infectious might also be given an injection of HBIG at birth on top of the hepatitis B vaccination to give them rapid protection against infection.
All babies born to mothers infected with hepatitis B should be tested at 1 year of age to check if they have become infected with the virus.
Don’t Miss: Best Medication For Hepatitis C
How Common Is Hepatitis B
One U.S. study following trends in hepatitis B infection over a three-year periodfound that 4.3% of the population had a past or present HBV infection.
Estimates suggest that about 240 million people around the world have chronic hepatitis B. Up to 1.89 million people in the United States have a chronic HBV infection.
Routine Administration Schedule For Hepatitis B Vaccine In Adults
- The dosing schedule is 0, 1 to 2 months, and 4 to 6 months.
- There is some flexibility in the schedule, but be sure to keep in mind the minimum intervals between doses:
- At least four weeks between doses #1 and #2
- At least eight weeks between doses #2 and #3
- At least 16 weeks between doses #1 and #3
- If your patient falls behind on the hepatitis B vaccination schedule , continue vaccinating from where your patient left off. The series does NOT need to be restarted.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Is It Contagious
Why A Variety Of Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules Have Been Used
Generally, the recommended number of doses of hepatitis B vaccine required to induce protective immunity varies by product and with the age of the recipient. Historically, the standard 3-dose hepatitis B vaccine series has consisted of 2 priming doses administered 1 month apart and a third dose administered 6 months after the first dose. Today, the WHO recommends multiple options for adding hepatitis B vaccine to existing infant immunization schedules. Several options are considered to be appropriate for infants: 1 birth dose followed by either 2 doses of monovalent or hepatitis B containing combination vaccine at 1 and 6 months of age or at 2, 4, and 6 months of age or at 3, 5, and 11 months of age or at 8, 12, 16 weeks and 12 or 15 months or at 6, 10, and 14 weeks of age, according to the WHOs Expanded Programme on Immunization schedule . Currently, a variety of hepatitis B vaccine schedules have been used successfully worldwide. In general, preference is given to effective options that require minimal additional visits for immunization, to increase compliance and to reduce the logistics burden.
Active Vaccination To Prevent Infection
Hepatitis B vaccination is available for preexposure and postexposure prophylaxis and provides long-term protection. Hepatitis B vaccines are produced recombinantly in yeast cell systems. The vaccines contain noninfectious HBsAg , a small amount of yeast protein, and aluminum hydroxide as an adjuvant. Pediatric formulations contain trace or no thimerosal. Administration is via the intramuscular route. Adverse effects are generally mild and mainly consist of local tenderness and low-grade fever. After a vaccine series, more than 95% seroconversion is achieved, which results in > 90% efficacy. Studies are ongoing to determine length of immunity, but it is at least 20 years.
Two hepatitis B single antigen vaccines are available in the United States: Recombivax from Merck & Co. and Engerix-B from GlaxoSmithKline. Both vaccines come in doses for pediatric and adult populations. High-dose vaccines are available for adult hemodialysis and immunocompromised patients. Both vaccines are given in a three-dose series and are generally interchangeable. A fourth dose may be given if a birth dose was administered. The birth dose must be a single antigen formulation.
Booster doses of hepatitis B vaccine beyond the initial series are generally not recommended. The long incubation period of hepatitis B theoretically allows for the development of a protective anamnestic immune response after exposure.
Fabrizio Fabrizi MD, … Paul Martin MD, in, 2017
You May Like: How To You Get Hepatitis C
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
What Is Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine gives protection against infection from the hepatitis B virus. The vaccine works by causing the body to produce antibodies against the virus responsible for hepatitis B infection and in this way protects against the disease. Hepatitis B is a virus that is easily spread through contact with the blood or bodily fluids of an infected person. For example, it can be passed on through unprotected sex, by sharing injection gear, through a needle stick injury or from mother to child during childbirth. Hepatitis B infection can cause serious problems including liver failure, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Preventing infection can prevent these problems. Read more about hepatitis B.
Also Check: How To Test For Hepatitis C
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links: