Are Fatty Liver Disease & Hepatitis C Related
According to recent research, there is a strong connection between fatty liver disease and hepatitis C. You can develop the fatty liver disease by itself, or accompanying a hepatitis C infection. According to data gathered, about 50% of people with hepatitis C also have fatty liver disease.
A fatty liver disease is a form of chronic liver damage that may or MAY NOT be caused by hepatitis C. There are two forms of fatty liver disease that people with hepatitis C face:
- Metabolic fatty liver is classified into three distinct types: non-alcoholic fatty liver, Fabry’s disease, and steatosis. Obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood fat levels, or insulin resistance might induce it.
- The HCV virus is the root cause of hepatitis C-induced fatty liver disease.
You can have both forms of fatty liver disease simultaneously. Both conditions cause damage to the liver, which harms hepatitis C symptoms.
Should You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Since you can live with hep C for decades without knowing itit can take 10 to 40 years for hep C to progress from mild disease to cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancerthe Centers For Disease Control and Prevention recommends a one-time blood screening test for anyone born between 1945 and 1965. This population is more at risk of having received a tainted blood transfusion.
Hepatitis C can only be diagnosed through a simple blood test called an HCV antibody test. True to its name, it looks for antibodies, proteins released into the bloodstream, that show up in someone infected with the hep C virus. If you have a positive HCV antibody test, youll then be given a follow-up HCV RNA test to learn whether you have an active infection.
What Exactly Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection thats super sly half of those who have it are unaware they have it. Most people dont show any symptoms so they can live with itsome for decadesand not feel a thing until major complications crop up.
The virus can cause both acute and chronic illness, ranging in severity from a mild illness that lasts a few weeks, to a serious lifelong condition. Its estimated that 58 million people around the world have chronic hep C, according to the World Health Organization. And a 2021 report from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows hep C infections are steadily rising among 18- to 40-year-oldsinjected drug use being the main culprit.
Though it may be silent, hep C can become deadly when it lingers in your system for too long. Too much time inside your body takes a toll and can lead to major issues like cirrhosis , liver disease, and cancer of the liver.
For reasons unknown, not everyone who has hep C needs treatment. In fact, 30% of people with the disease clear the infection through their own immune system, typically within 6 months of infection , without requiring any treatment. But for the 70% whose condition becomes chronic, treatment is necessary.
While all this may sound scary, hep C isnt what it used to beit can be completely cured with a relatively quick course of treatment.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Is It Contagious
Recent Increases In Hepatitis C Infections
Between 2013 and 2020, the reported number of acute HCV infections more than doubled. High rates of new infections were predominantly among young adults aged 20-29 years and aged 30-39 years. The number of cases continues to increase, in 2020 an estimated 66,700 new HCV infections occurred in the United States. For the most recent surveillance data visit CDC Viral Hepatitis Surveillance.
How Can The Spread Of Hepatitis C Be Prevented
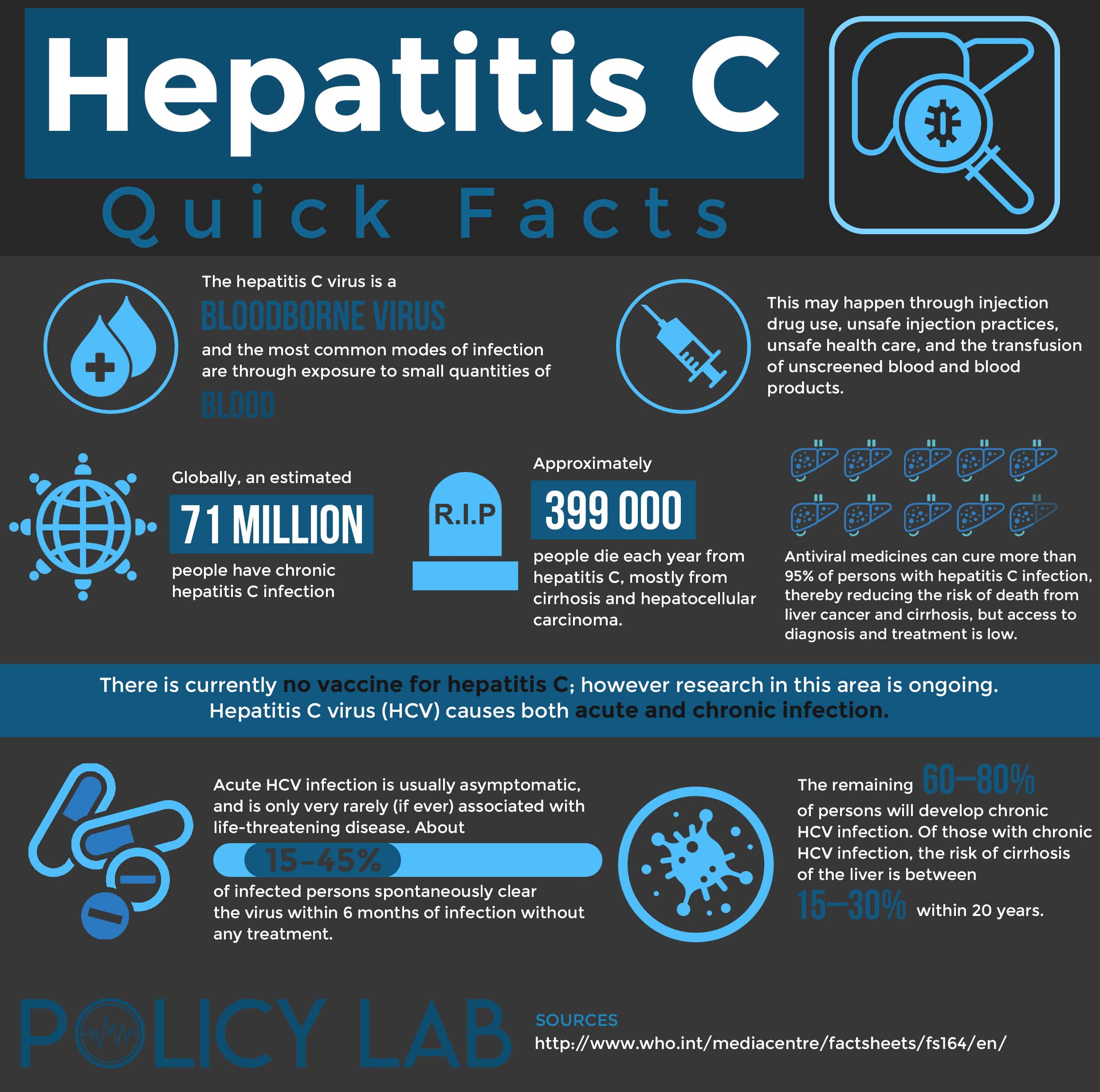
People who have had hepatitis C should remain aware that their blood is potentially infectious.
- Do not shoot drugs if you shoot drugs, stop and get into a treatment program if you can’t stop, never share needles, syringes, water or “works”, and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Do not share personal care items that might have blood on them .
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, always follow routine barrier precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about getting a tattoo or body piercing. You might get infected if the tools have someone else’s blood on them or if the artist or piercer does not follow good health practices.
- HCV can be spread by sex, but this is rare. If you are having sex with more than one steady sex partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases. You should also get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- If you are infected with HCV, do not donate blood, organs or tissue.
You May Like: Cost Of Medicine For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C A Silent Killer Lurks Among Us
Hepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver caused by, you guessed it, the hepatitis C virus. As a disease, it can be a scary and often unknown entity. Often known as the silent killer since many infected are asymptomatic, hepatitis C, or HCV, is more common than many people know. But despite its scary nature, treatment is highly effective, and with widespread testing, we can help end hepatitis C as a silent killer.
Who Gets Hepatitis C
Persons at highest risk for HCV infection include:
- persons who ever injected illegal drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago,
- people who had blood transfusions, blood products or organ donations before June 1992, when sensitive tests for HCV were introduced for blood screening, and
- persons who received clotting factors made before 1987.
Other persons at risk for hepatitis C include:
- long-term kidney dialysis patients,
- health care workers after exposures to the blood of an infected person while on the job,
- infants born to HCV-infected mothers,
- people with high-risk sexual behavior, multiple partners and sexually transmitted diseases,
- people who snort cocaine using shared equipment, and
- people who have shared toothbrushes, razors and other personal items with a family member who is HCV-infected.
You May Like: Hepatitis A What Is It
What Are The Most Common Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
It sounds strange, but there really are no symptoms of hep C. In fact, about half of people with hep C don’t even know they’re infected, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Those who do have symptoms may experience minor issues like fatigue and muscle aches, which can be chalked up to any number of reasons, like an intense workout or just life in general. But because these symptoms are so ubiquitous, theyre easy to miss, and you likely wouldnt associate them with hep C.
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis Rash Look Like
What Are The Symptoms Of Hcv
Many cases of HCV are not found because there are no symptoms, or the symptoms are vague and may seem like the flu. Symptoms may start from two weeks to six months after exposure, though the average is six to seven weeks.
Some people with HCV may have:
- Muscle and joint aches.
- Changes in the color of urine and stool.
- Jaundice . Jaundice may also cause itching.
- Take your medical history.
- Do a physical exam.
- Order blood tests.
- Many blood tests are used to look for HCV, so your doctor may choose to do one or many at once.
- In the past, this was the widely used treatment for HCV.
- Patients stay on these drugs for 2448 weeks.
- It only cures 2040% of patients and is associated with significant side effects.
- These are newer option to care for HCV. They are sometimes called direct-acting antivirals .
- These treatments do not use interferon.
- Patients stay on these for 1214 weeks.
- Most cases on these treatments have a greater than 90% chance of cure.
- Patients on these have fewer side effects, are better tolerated and have much better success rates than earlier treatments.
- These drugs are very high priced and not all health plans cover them.
A variety of drugs that work in different ways are used together to treat HCV so that the virus can be attacked in different ways to increase your chance of a cure. Your gastroenterologist or liver specialist, called ahepatologist, will help guide you through complex treatment options.
Hepatitis C Antibody Testing
Testing is essential in the fight against HCV, as if left untreated, hepatitis C can lead to serious lifelong diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. The body tries to fight HCV by making an anti-HCV antibody, which will be found in your blood if exposed or infected with HCV. If a persons test comes back positive, a doctor will perform a viral load test to measure ribonucleic in the blood.
Hepatitis C is easier to treat if caught earlier on. To get tested, please visit your local clinic or learn more about the INSTI rapid hepatitis C test kits, which is the worlds fastest HCV antibody test.
Read Also: How Do You Know If Have Hepatitis C
Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Hepatitis C can be passed from person to person. Most people with HCV get it through direct contact with blood containing the virus.
People with hepatitis C can pass on the virus to others by sharing needles and syringes. Hepatitis C is easily transmitted among people who use intravenous drugs.
Its also possible, but much less common, to acquire the HCV by:
- sharing a razor with a person who has the virus
- sharing a toothbrush with a person who has the virus at the same time that you have bleeding gums
- having sexual contact with a person who has the virus
How Is Hepatitis C Treated
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. The aim of treatment for hepatitis C is to eradicate the virus from the blood completely, and to protect the liver from developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Several medications are available to treat hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus has six different types or strains . The type and length of treatment may vary. Some hepatitis strains do not respond to antiviral medications as well as others. Some medications may not be suitable for all patients with hepatitis C, because of the side effects or the patients other medical conditions.
These are the medications approved for treatment of hepatitis C infection:
- Sofosbuvir : Tablet taken once a day. Used in combination with other antiviral drugs.
- Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir : Pill taken once a day for 12 to 24 weeks, depending on how serious the disease is.
- Simeprevir : Capsule taken once a day with other medications called peginterferon alfa and ribavirin
- Combination of paritaprevir/ombitasvir/ritonavir/dasabuvir
- Daclatasvir : Used in combination with other drugs
- Elbasvir/grazoprevir : Tablet taken once a day
- Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir : Tablet taken once a day
- Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir : Three pills a day in one dose
- Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir : Tablet taken once a day
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir : Two tablets once a day in the morning, in combination with ribavirin
Read Also: Hepatitis B And C Transmission
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Ab W Reflex Hcv Rna Quant Rt Pcr
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Hepatitis A B And C: What Is The Difference
A, B, C D and E.
Aside from the letters associated with it, how much do you know about hepatitis? Whats the difference between the types? And if you get a vaccination for hepatitis, which are you protected from?
We spoke with Moises Ilan Nevah, MD, a transplant hepatologist/gastroenterologist and medical director of the Liver Transplant Program at Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, to help better understand the similarities and differences between the various types of hepatitis, who is at risk and when to get vaccinated.
You May Like: Reactive Hepatitis B Core Antibody
Baby Boomers Are Especially Vulnerable
“The hepatitis C virus didn’t have a name or a screening test until in 1989,” Reau says. “That means people born between 1945 and 1965, the group referred to as ‘baby boomers,’ are at highest risk of infection. They grew up before health care facilities started taking standard precautions, like not sharing vials of medicine among patients and requiring staff to wear gloves.”
The CDC reports that baby boomers are five times more likely to have Hepatitis C than other adults, accounting for 75% of those living with the disease.
These are some other reasons you may be at risk:
- You have engaged in high-risk behaviors like IV drug use or unprotected sex
- Your biological mother has/had hepatitis C
- You received blood transfusions, an organ transplant or dialysis before 1989
- You were or are currently incarcerated
Who Should Get Tested
Since universal screening of blood and blood products did not occur until 1992, anyone who had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before that time should be tested. It is recommended that people be tested for hepatitis C if they were/are:
- Born between 1945 and 1965
- Exposed to blood and body fluids
- Sharing toothbrushes, razors, nail clippers or other personal items with an infected individual
- Using and/or sharing needles to inject drugs
- Receiving tattoos and body piercings with unsterile needles
- Women thinking about becoming pregnant
- Born to an infected mother
- Receiving long-term hemodialysis
- Having unprotected sex with multiple sex partners or have a history of sexually transmitted diseases
Read Also: Can Liver Disease Cause Hepatitis C
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
What Are The Different Types Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic. How long you experience symptoms will depend on the type you have.
Acute hepatitis C involves more short-term symptoms that typically last 6 months or less but acute hepatitis often leads to chronic hepatitis. When hepatitis C lasts longer than 6 months, its considered chronic.
Without treatment, you may have chronic hepatitis your whole life, since your body often cant get rid of the virus easily. Some people do get better without treatment, although treatment can go a long way toward improving the outlook.
Hepatitis C wont necessarily become chronic.
As a matter of fact, for anywhere from 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C, the virus will clear up without treatment. In other words, if you dont have any symptoms, hepatitis C could improve on its own before you ever know you have it.
However, if your body cant get rid of the hepatitis C virus, the infection wont go away. Instead, it will become chronic, or long-term.
Experts arent sure why some people develop the chronic form of the disease and others dont. But more than half of all people with the hepatitis C virus will eventually develop the chronic form, according to the
Since hepatitis C symptoms can resemble those of other health conditions, your symptoms alone if you have any may not make it clear that you have hepatitis C.
A doctor or other healthcare professional may recommend getting tested if you:
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse