Hepatic Encephalopathy: What The Multidisciplinary Team Can Do
Accepted for publication 9 February 2017
24 March 2017Volume 2017:10 Pages 113119
Introduction
Classifications of HE
Diagnosis of HE
The importance of recognizing MHE
Ammonia levels
Management of OHE
Secondary prophylaxis of OHE
Primary prophylaxis of OHE
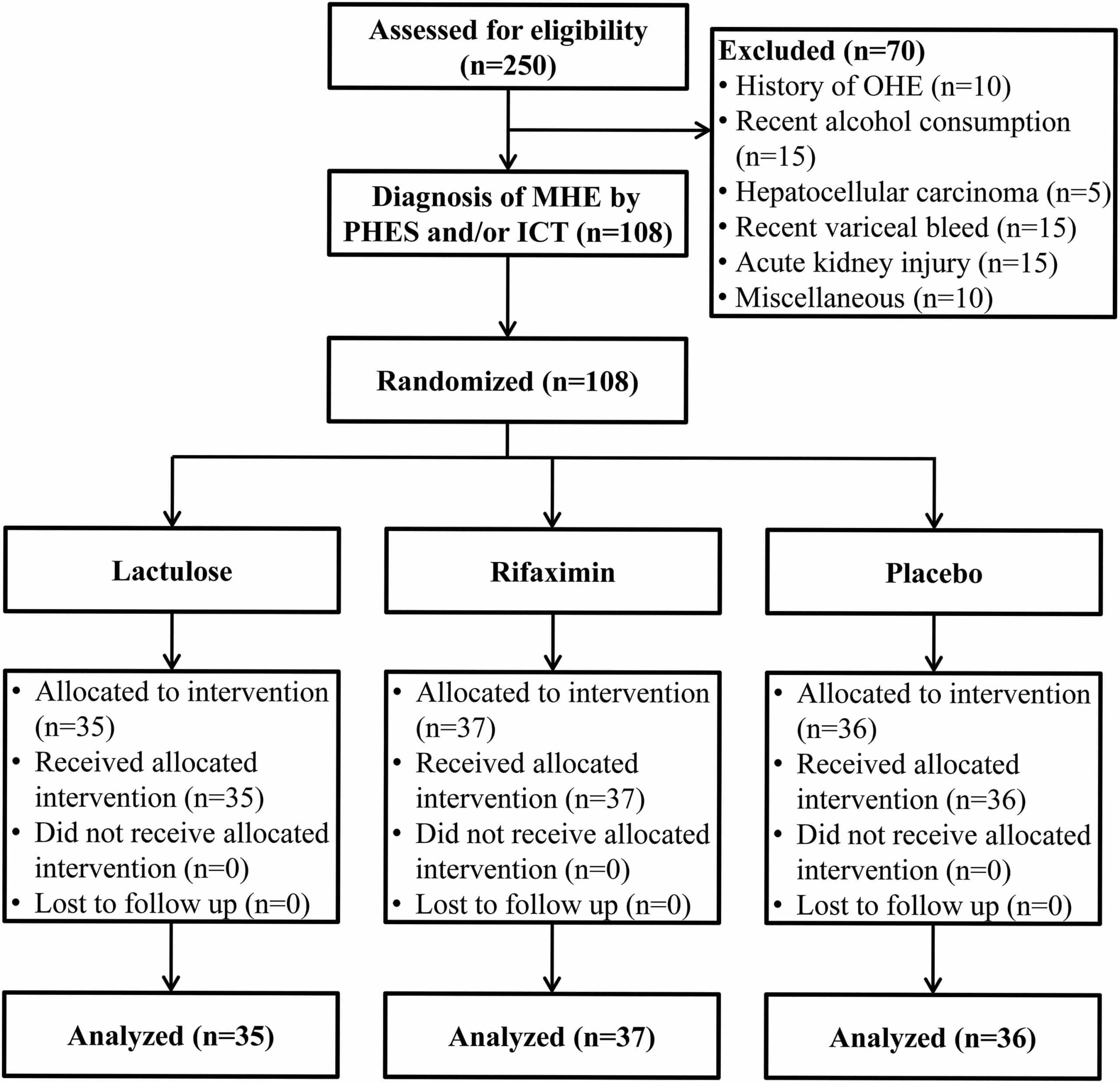
Episodes of OHE are associated with worsening quality of life and recurrent hospitalizations, which ultimately worsen the prognosis. In 2012, Sharma et al randomized patients to placebo or lactulose and followed them over a 12-month period.41 Eleven percentage of patients in the lactulose group and 28% of patients in the placebo group developed OHE during this study. Both groups had comparable numbers of patients with MHE, and lactulose was shown to effectively improve symptoms of MHE in 66% of patients. While lactulose therapy has been studied in patients with MHE, studies of empiric lactulose for cirrhotic patients with no prior episodes of OHE are lacking future studies should look into this further.
The role of nutrition in HE
Disclosure
|
Agrawal A, Sharma BC, Sharma P, Sarin SK. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open-label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 107:10431050. |
What Are The Complications Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Liver disease needs treatment, such as medications and lifestyle changes, including not drinking alcohol. If the underlying cause of liver disease isnt treated, liver function deteriorates, and toxins continue to build. Some people with advanced hepatic encephalopathy lose consciousness and go into a hepatic coma.
How Should This Medicine Be Used
Lactulose comes as liquid to take by mouth. It usually is taken once a day for treatment of constipation and three or four times a day for liver disease. Your prescription label tells you how much medicine to take at each dose. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take lactulose exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Dont Miss: Hepatitis C Rapid Test Kit
You May Like: New Medicine To Treat Hepatitis C
Reduction Of Nitrogenous Load From The Gut
Cathartics
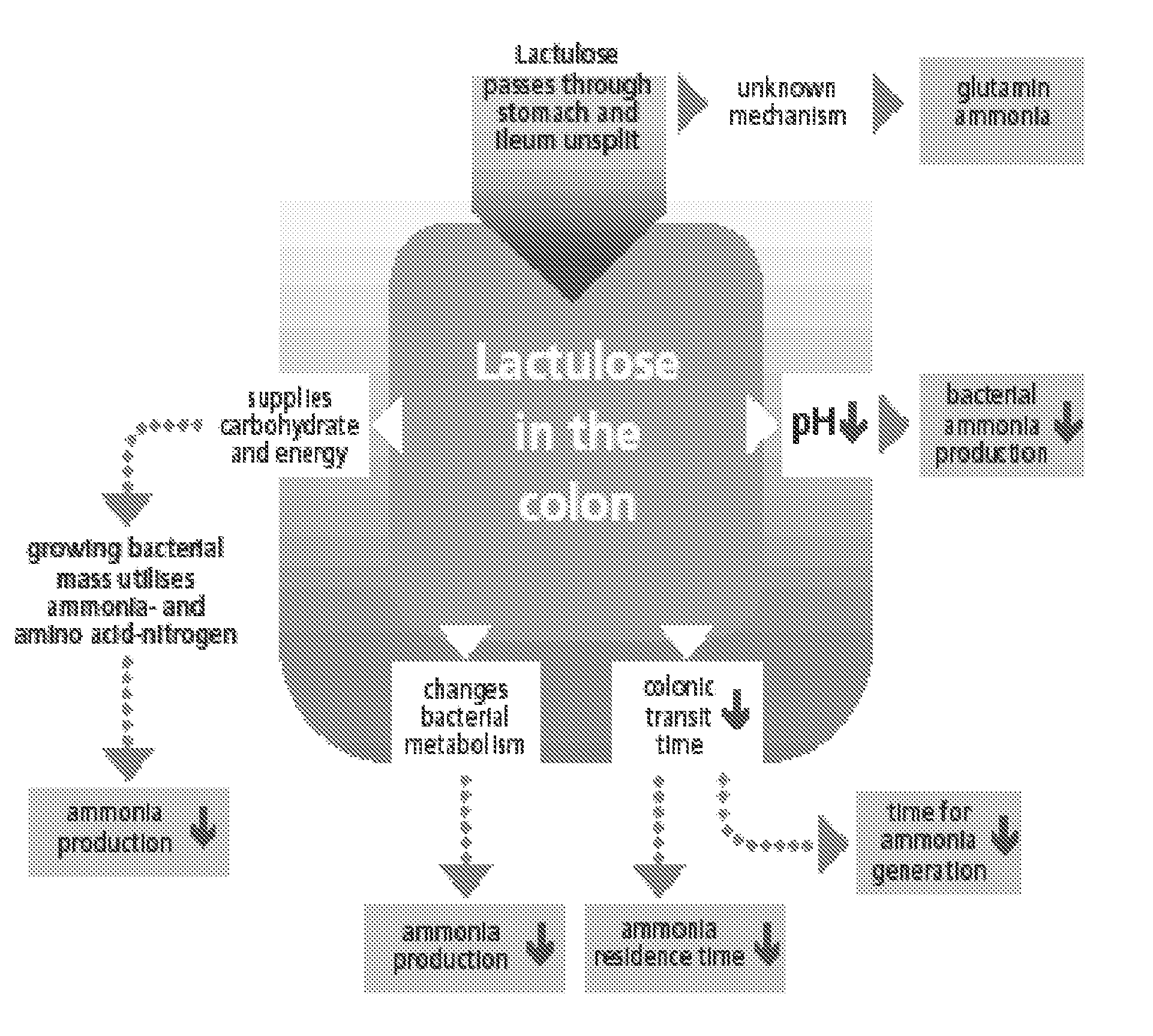
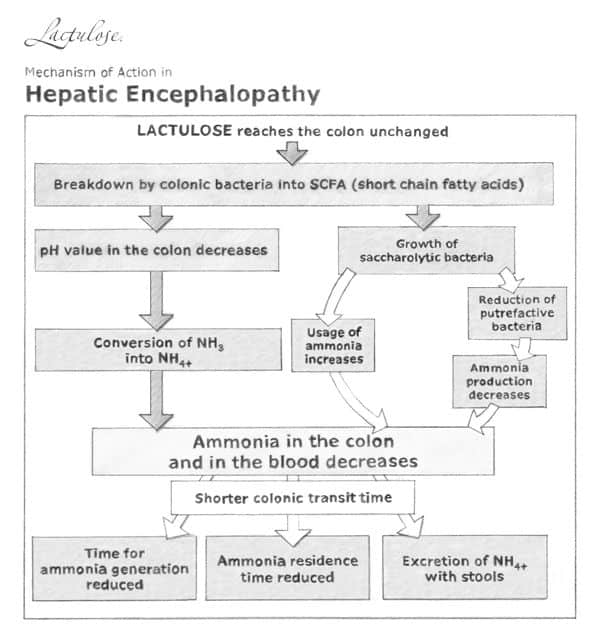
Lactulose and lactilol are nonabsorbable disaccharides in common clinical use since the early 1970s . They are degraded by intestinal bacteria to lactic acid and other organic acids.
Lactulose appears to inhibit intestinal ammonia production by a number of mechanisms. Colonic metabolism of lactulose to lactic acid results in acidification of the gut lumen. This favors conversion of ammonium to ammonia and the passage of ammonia from tissues into the lumen. Gut acidification inhibits ammoniagenic coliform bacteria, leading to increased levels of nonammoniagenic lactobacilli. Lactulose also works as a cathartic, reducing colonic bacterial load.
Initial lactulose dosing is 30 to 40 mL orally, daily or twice daily. The dose may be increased as tolerated. Patients should be instructed to reduce lactulose dosing in the event of diarrhea, abdominal cramping, or bloating. Patients should take sufficient lactulose as to have two to four loose stools per day.
Care must be taken when prescribing lactulose. Overdosage can result in ileus, severe diarrhea, electrolyte disturbances, and hypovolemia. Hypovolemia may be sufficiently severe as to actually induce a flare of encephalopathy symptoms.
Antibiotics
Table 2: Summary of the Antibiotic Regimens Commonly Used for Hepatic Encephalopathy
| Drug | |
|---|---|
| Nephrotoxicity | $20-$30 |
What Are The Important Considerations
Talk with your health care provider about completing a Release of Information form. This form says that your health care team can give your medical information to a family member or friend chosen by you. You need to update and sign this form every year.If you have not already done so, you may want to complete a healthcare directive in which you appoint someone to act on your behalf for medical matters. Or you may want to assign someone to have power of attorney to make health care decisions if you cannot. Talk with a legal attorney about this.
You May Like: Do You Ever Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
High Blood Ammonia Levels In Liver Cirrhosis
Ammonia is a substance that is made in our bodies as a by-product of various metabolic processes. Ammonia is toxic to your nervous system at high levels, but the levels of it in your blood are normally kept under control by your liver, which stops ammonia from entering your circulation by converting it into other substances. Your muscles are also able to remove ammonia from the blood.1
In advanced liver disease, dysfunction of the liver and wasting of the muscles means that both of these important ammonia-clearing processes are impaired. Ammonia levels start to build up in the blood and contribute to the development of HE.1
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Having Hepatitis C
Reversibility Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Classically, hepatic encephalopathy was regarded as a reversible condition. Patients appeared to improve with either drug therapy or liver transplantation. However, a recent study assessed cirrhotic patients who had apparently recovered from an episode of overt hepatic encephalopathy. After careful psychometric testing, it was discovered that these clinically improved patients had residual cognitive impairment compared with cirrhotic patients with either minimal hepatic encephalopathy or no encephalopathy.
In 2009, Sotil et al evaluated 39 patients who had undergone liver transplantation about 1.5 years before the study. The 25 patients who had hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation, on the whole, performed worse on psychometric testing than the 14 patients with no history of overt encephalopathy prior to transplantation.
In 2011, Garcia-Martinez et al assessed the cognitive function in 52 patients who had undergone liver transplantation. Global cognitive function after transplantation was worse in patients with a history of alcohol-induced cirrhosis, patients with diabetes, and patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation. Furthermore, the brain volume after transplantation was smaller in patients with a history of hepatic encephalopathy prior to transplantation than in patients with no overt encephalopathy. These are provocative findings that require additional investigation.
Also Check: How Can You Get Hepatitis B And C
Identification And Removal Of Precipitating Factors
When there is obvious worsening of HE , a vigorous search to identify and eliminate a precipitating factor or factors should be instituted.
In most cases of cirrhosis with acute or chronic HE, a precipitating factor is found, such as the following:
GI hemorrhage. Exploration requires stool analysis and/or placement of a nasogastric tube.
Infections. This factor requires culture of all appropriate body fluids blood, urine, ascites, and pleural fluid when present. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and pneumonia may present with HE.
Use of psychoactive medication. This factor may require a urine screen for benzodiazepines, narcotics, and other sedatives.
Constipation. Noncompliance with lactulose doses at home.
Renal and electrolyte disturbances. These include renal failure, metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia, dehydration, and diuretic effects.
Acute deterioration of liver function in cirrhosis. HE in cirrhosis seldom reflects the acute impact of liver failure. Exceptions include the presence of superimposed alcoholic hepatitis, the development of an acute circulatory disturbance , and the impairment of liver function seen after surgery in cirrhosis.
TIPS. Precipitating events should also be sought with the development of encephalopathy after placement of TIPS for control of portal hypertension.
Spontaneous encephalopathy should raise the suspicion of an abnormal collateral circulation imaging of the abdomen should be performed looking for spontaneous splenorenal shunt.
Comparison Of Treatment Groups
The 2 groups were similar with respect to demographics and clinical features . The precipitants of HE included a total of 80 potential contributing factors identified in 50 patients . Admission laboratory data were also similar in the 2 groups , with the exception of blood urea nitrogen level, which was higher in the PEG group . Admission ammonia levels were elevated in both groups . Nineteen patients in the lactulose group and 18 patients in the PEG group underwent head computed tomography scanning. No acute CT findings were identified in any patient.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Find Out If You Have Hepatitis
Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy symptoms vary from person-to-person and depend on the underlying cause of hepatic damage.
Provision Of Supportive Care
Standard supportive care is required for all hospitalized patients with HE. Patient safety and frequent bedside monitoring of mental status are crucial. This can require additional personnel and, in the case of comatose patients, admission to the intensive care unit, endotracheal intubation, or both. Although temporary restriction of dietary protein may be necessary, patients with HE should avoid prolonged periods of fasting. Although the restriction of dietary protein at the time of acute HE can be part of therapy, protracted nitrogen restriction can lead to malnutrition. Appropriate enteral nutrition, by mouth or nasogastric feeding tube, should be administered as soon as feasible.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Antibody Test Positive
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
In the context of hepatic encephalopathy management, there are multiple decision-making steps involved to ensure the best form of patient care. These would range from the mode of administration of lactulose , the monitoring of the number of bowel movements to achieve the required frequency of 2-3 stools per day.
Treatment And Prevention Of Ohe
The initial treatment of OHE is non-absorbable disaccharides like lactulose. The dosing of lactulose should be initiated with 25mL of lactulose every 12hours and the dose should be titrated to achieve two soft or loose bowel movements per day. The working mechanism of lactulose is not fully understood, but it is assumed that the prebiotic effects and acidifying nature of lactulose have an additional benefit beyond the laxative effect.
There is currently no treatment registered for primary prevention of HE. Secondary prevention of HE can be achieved by combination therapy of lactulose with rifaximin, a poorly absorbed antibiotic. In the Netherlands, rifaximin has been approved since 2016 and will be reimbursed only to prevent a third episode of OHE.
Read Also: How Can Hepatitis C Be Transmitted Sexually
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Meaning
Symptoms Of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Symptoms are those of impaired brain function, especially reduced alertness and confusion. In the earliest stages, subtle changes appear in logical thinking, personality, and behavior. The person’s mood may change, and judgment may be impaired. Normal sleep patterns may be disturbed. People may become depressed, anxious, or irritable. They may have trouble concentrating.
At any stage of encephalopathy, the person’s breath may have a musty sweet odor.
As the disorder progresses, people cannot hold their hands steady when they stretch out their arms, resulting in a crude flapping motion of the hands . Their muscles may jerk involuntarily or after people are exposed to a sudden noise, light, a movement, or another stimulus. This jerking is called myoclonus Myoclonus Myoclonus refers to quick, lightning-like jerks of a muscle or a group of muscles. Myoclonus may occur normally … read more . Also, people usually become drowsy and confused, and movements and speech become sluggish. Disorientation is common. Less often, people with encephalopathy become agitated and excited. Eventually, as liver function continues to deteriorate, they may lose consciousness and lapse into a coma. Coma often leads to death, despite treatment.
Nutritional Support & Gut Access
- Intubated patients with hepatic encephalopathy should receive enteral nutrition just like any other intubated patient.
- Recent guidelines don’t recommend restricting protein intake among these patients.
empiric thiamine for Wernicke’s encephalopathy in alcoholism
- Patients with alcoholism and cirrhosis may be at risk for Wernicke’s encephalopathy.
- Differentiation of Wernicke’s encephalopathy from hepatic encephalopathy is basically impossible.
- There are no lab tests capable of doing this promptly.
- Physical examination signs of Wernicke’s encephalopathy may be absent in a comatose patient.
place a small-bore nasal feeding tube prior to extubation
Don’t Miss: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Saliva
Gaba/benzodiazepine Receptor Complex Theory
GABA is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans and acts through binding to the GABA-receptor complex . Elevated levels of endogenous benzodiazepines as well as other neurosteroids lead to inhibition of neurotransmission. Changes in the GRC as well as cerebral GABA levels have also been reported in HE.
Hepatic Encephalopathy Versus Alcohol Withdrawal
Occasionally, in a patient with cirrhosis due to alcoholism there will be a question of sorting out hepatic encephalopathy versus alcohol withdrawal. These are fundamentally nearly opposite pathologies:
Generally, this differentiation can be made on the basis of history and physical examination. The importance of an accurate drinking history cannot be over-emphasized
Be careful about over-diagnosing patients with alcohol withdrawal, because the treatment for alcohol withdrawal can be disastrous in a patient who actually has hepatic encephalopathy:
- Patients with hepatic encephalopathy have excess GABA stimulation, so they are very sensitive to GABAergic medications .
- Administration of benzodiazepines or barbiturates to a patient with hepatic encephalopathy risks inducing a prolonged comatose state.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus
How To Use Lactulose For Hepatic Encephalopathy
There are two ways to use lactulose for H.E. You can either use it by mouth or rectally. However, we must clarify that lactulose is not a cure for H.E, but it can only improve your mental status.
Lactulose is an artificial sugar solution and an acidifier of the colon. It decreases how much ammonia can pass into your blood from your colon. But Lactulose has many uses. H.E is not the only condition that lactulose treats. So how you would use it will rely on what you are using it to treat.
If you are using lactulose to treat liver disease, you would have to take it like 3 to 4 times daily. But if your doctor recommends otherwise, follow his directions.
Lactulose may not have so much of a great taste. But you can improve its taste by mixing the drug into fruit juice, soft dessert, or even just water. The goal of using lactulose is for you to have about two to three soft stools daily.
Sometimes, your doctor will adjust your dosage with how you are responding to the therapy. This is determined by how many soft stools you are passing each day.
You can use lactulose as an enema to treat H.E or any other liver disease. You would mix the recommended amount with 24 ounces of normal saline or water. Then, you can pass the liquid into your rectum. Keep the solution inside for about 30 to 60 minutes, except your doctor directs otherwise.
Lactulose May Interact With Other Medications
Lactulose oral solution can interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs you may be taking. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well.
To help avoid interactions, your doctor should manage all of your medications carefully. Be sure to tell your doctor about all medications, vitamins, or herbs youre taking. To find out how this drug might interact with something else youre taking, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Examples of drugs that can cause interactions with lactulose are listed below.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Cure Of Hepatitis B
Treatments To Improve Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are more common in patients with cirrhosis than in control subjects. Whether or not this relates to hepatic encephalopathy is unclear. A trial compared the histamine H1 blocker hydroxyzine with placebo in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Sleep efficiency and the patients subjective quality of sleep improved in patients receiving hydroxyzine at bedtime. However, there was no accompanying improvement in cognition, as measured by neurophysiologic tests. The authors urged caution when prescribing hydroxyzine, on account of the risk of worsening encephalopathy in some patients.
Differential Diagnosis For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Distinguishing hepatic encephalopathy from other acute and chronic causes of altered mental status may be difficult in patients with cirrhosis. A decision to perform additional neurologic studies should be based on the severity of the patient’s mental dysfunction, the presence of focal neurologic findings , and the patient’s responsiveness to an empiric trial with cathartic agents. Even patients with severe hepatic encephalopathy should demonstrate steady improvement in mental dysfunction after initiation of treatment with lactulose.
Differential diagnoses of encephalopathy are as follows :
-
Intracranial lesions, such as subdural hematoma, intracranial bleeding, stroke, tumor, and abscess
-
Infections, such as meningitis, encephalitis, and intracranial abscess
-
Metabolic encephalopathy, such as hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, anoxia, hypercarbia, and uremia
-
Hyperammonemia from other causes, such as ureterosigmoidostomy and inherited urea cycle disorders
-
Toxic encephalopathy from alcohol intake, such as acute intoxication, alcohol withdrawal, and Wernicke encephalopathy
-
Toxic encephalopathy from drugs, such as sedative hypnotics, antidepressants, antipsychotic agents, and salicylates
-
Organic brain syndrome
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Mental Health
Avoid Sedating Medications Like The Plague
avoid sedating medications!
- Patients with hepatic encephalopathy are often exquisitely sensitive to sedating medications .
- For an intubated patient with hepatic encephalopathy, it is best to avoid any sedative or analgesic, except agents with extremely short half-lives .
- Even small doses of a long-acting sedative may delay extubation.
- One trick to facilitate extubation is to allow all other sedating medications to wash out of the patient.
- Patients who are comatose due to hepatic encephalopathy are usually very sensitive to sedation, so they often don’t require much propofol to achieve comfort .
Neuropsychological Test In Mhe
Neuropsychological testing is useful methodology for quantifying cognitive impairment due to various forms of encephalopathy, including low-grade or MHE. Neuropsychological tests directly measure cognitive functions that are directly relevant to activities of daily living. They have been applied for the diagnosis of HE for more than 50 years.
The neuropsychological features of MHE point to a disorder of executive functioning, particularly selective attention, visuospatial abilities and fine motor skills. Although these domains are most commonly implicated in MHE, impairments of memory have also been reported.
The attention impairments in MHE are observed on a variety of measures. These include measures of cognitive processing speed involving psychomotor responding, such as the Number Connection tests , block design test ,the Digit Symbol test , line drawing test, circle-dotting test, serial-dotting test, figure connection test. Impairments on measures of cognitive processing speed and response inhibition that do not require a motor response have also been reported . Visuospatial impairments have been primarily reported on block design tasks , but also on more pure measures of visuospatial perception, such as line orientation or the Hooper test. Fine motor skill impairments have been noted on measures such as the grooved pegboard task, and on line tracing tasks .
Read Also: Hepatitis C Symptoms And Causes