How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Helpful Tips While Taking Hepatitis C Medications
- Always follow your health care providers’ advice, particularly the instructions on taking your medicine.
- If you have to cancel an appointment, call your provider and schedule a new one as soon as possible.
- Take good care of yourself. Eat well, drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day, and try to get a full night’s sleep.
- Learn about the hepatitis C medications you are taking. This includes special risks and warnings.
- If taking ribavirin, use sunscreen, wear long sleeves and a hat, and limit sun exposure.
- Write down your doctor’s name and phone number. Carry this information with you at all times.
- Write the names and amounts of the medicines you are taking. Carry this information with you at all times.
What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B
When you first get hepatitis B, it is called acutehepatitis B. Most adults who have hepatitis B willrecover on their own. However, children and someadults can develop chronic hepatitis B.
Acute hepatitis B: Signs of acute hepatitis B canappear within 3 months after you get the virus.These signs may last from several weeks to 6 months.Up to 50% of adults have signs of acute hepatitis Bvirus infection. Many young children do not show anysigns. Signs include:
- Yellow skin or eyes
- A longer than normal amount of time for bleedingto stop
You May Like: Pcr Test For Hepatitis C
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
You May Like: Combined Hepatitis A And B Vaccine
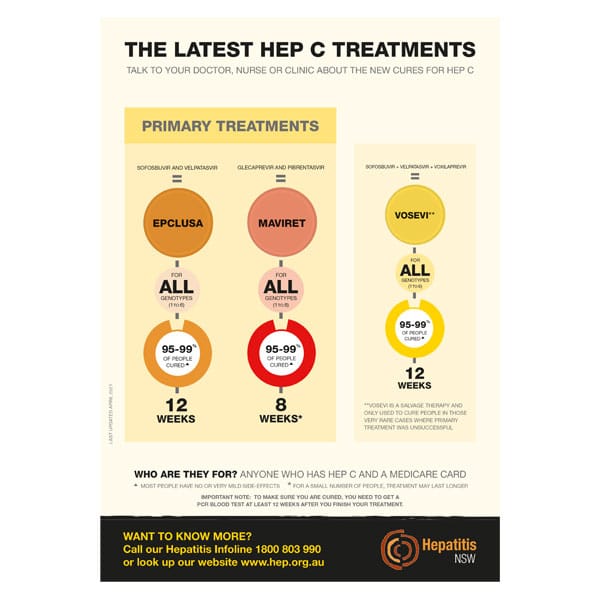
How Much Does Hepatitis C Treatment Cost
The cost of hep C treatment varies depending on the type of drug. However, an 8- to 12-week course can range from $54,000 to $95,000 .
For example, the price of a 12-week course of Zepatier can be as much as $54,600, and a 12-week course of Harvoni can cost as much as $94,500.
Without insurance, youre responsible for the full amount out-of-pocket. And even with insurance, the cost can range into the thousands, after adding in drug copays and coinsurance.
If you qualify for patient assistant programs, you might receive your medication for as little as $5 out-of-pocket.
What Are Dosages Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Dosages of Hepatitis B Vaccine:
Dosage Considerations Should be Given as Follows:
- Engerix B: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Recombivax HB: 1 mL intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
- Adults receiving dialysis or other immunocompromising conditions
- Recombivax HB : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months, OR
- Engerix-B : 40 mcg intramuscularly at 0, 1, and 6 months
Routine vaccination
Catch-up vaccination
- Unvaccinated children should complete a 3-dose series
- Children aged 11-15 years: 2-dose series of adult formulation Recombivax HB is licensed for use in children aged 11 through 15 years
Dosing Considerations
- Administer intramuscularly in the deltoid muscle
- Do not give IV/intradermal
Pediatric:
- low blood pressure
- pain when urinating
Suspected adverse events after administration of any vaccine may be reported to Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System , 1-800-822-7967
This document does not contain all possible side effects and others may occur. Check with your physician for additional information about side effects.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis A
Also Check: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The Pandemic And A Spike In Drug Use Has Exacerbated The Disease But Some States Are Beginning To Lift Barriers That Have Prevented People From Getting Treatment
While national efforts to eliminate hepatitis C have faced setbacks because of increased drug use, the impact of COVID-19 and insurance complications, theres a bright spot: Some states are now making it easier for patients to treat the disease.
Hepatitis C a viral inflammation of the liver spread through blood and other bodily fluids that infects more than 2 million adults and contributes to 14,000 deaths annually has grown more widespread in recent years, with the Infectious Diseases Society of America estimating that hepatitis C infections spiked 71 percent from 2014 through 2018.
Theres a cure for it. Gileads two direct-acting antiviral drugs, Sovaldi and Harvoni, have been available for nearly a decade. The Food and Drug Administration approved Sovaldi in December 2013 and Harvoni in October 2014. Since then, the FDA has approved other antivirals.
Still, a high price tag and administrative hurdles to covering and prescribing the drug have complicated uptake.
Without treatment, hepatitis C is a chronic condition that can lead to liver cancer or advanced liver disease and even be fatal. But antivirals can cure a patient in eight to 12 weeks and have been proven to be 95 percent successful at curing hepatitis C.
That same report found that the number of people receiving treatment for hepatitis C is far below the trajectory needed to hit federal goals to eliminate viral transmission by 2030.
Considerations For Hepatitis C Cases Who Were Transplant Recipients
With the availability of curative treatment for HCV infection, an increasing number of transplant recipients are receiving organs from anti-HCV and HCV-RNA positive donors . This can result in transmission of hepatitis C to the recipient, which is then treated with DAA agents . In some jurisdictions, these expected donor-derived HCV transmissions might represent a significant proportion of new acute HCV infections therefore, jurisdictions are encouraged to reach out to transplant facilities and discuss public health reporting of expected donor-derived HCV infections.
A listing of transplant facilities in the United States, including facility location and phone number, can be found on the OPTN websiteexternal icon . As these patients are already linked to testing and treatment, the infections should be notified to CDC as new acute cases. However, the jurisdiction need not investigate beyond indicating that the infection was donor-derived.
Typically, there are two outstanding questions that only the public health jurisdiction can answer: 1) Did the recipient have any behavioral or other risks for hepatitis C and 2) Does the jurisdiction have any ongoing investigations of health care-associated hepatitis C that might be related to this investigation?
Table 4-3. Considerations for hepatitis C cases who were organ transplant recipients*
| Organ Recipient Pre-transplant |
|---|
Don’t Miss: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Integration Is Essential In Providing Patient
Program integration is the bedrock of Nasarawas journey to HCV elimination. The Nasarawa State Elimination program is employing a model that ensures easy access by communities in need. These include:
- Timely testing to ensure patients know their status and are initiated on treatment as soon as possible.
- Integrating HCV testing on seven out of 19 GeneXpert devices used for tuberculosis testing in the state.
- Leveraging existing tuberculosis sample transportation networks to ensure that patients do not have to travel or wait for long turnaround times to know their status.
- Implementing multi-month dispensing to minimize loss-to-follow-up meaning that all patients are successfully linked to care and complete their treatment doses while minimizing multiple facility visits.
A patient recently commented that when I tested positive for hepatitis, I was worried because I could not afford the treatment. Thanks to the Nasarawa state government for providing free hepatitis services.
Task shifting: Capacity building for ART care providers
How Many People Have Hepatitis C
During 2013-2016 it was estimated that about two and half million people were chronically infected with HCV in the United States. The actual number may be as low as 2.0 million or as high as 2.8 million.Globally, hepatitis C is a common blood-borne infection with an estimated 71 million people chronically infected according to the World Health Organization .
Recommended Reading: Rx Hepato Support For Dogs
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
Preventing The Spread Of Hepatitis C
There is no vaccine available to prevent a person from being infected with hepatitis C. Recommended behaviours to prevent the spread of the virus include:
- Always use sterile injecting equipment. This can be accessed from your local needle and syringe program service.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors, nail files or nail scissors, which can draw blood.
- If you are involved in body piercing, tattooing, electrolysis or acupuncture, always ensure that any instrument that pierces the skin is either single use or has been cleaned, disinfected and sterilised since it was last used.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow standard precautions at all times.
- Wherever possible, wear single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or clean up blood or body fluids.
- Although hepatitis C is not generally considered to be a sexually transmissible infection in Australia, you may wish to consider safe sex practices if blood is going to be present, or if your partner has HIV infection. You may wish to further discuss this issue and personal risks with your doctor.
Also Check: Sign Symptoms Of Hepatitis B
Interpretation Of Laboratory Test Results
The two tests used primarily for hepatitis C screening and diagnosis are an antibody test and an RNA test , respectively . A description of hepatitis C laboratory markers can be found in Appendix B. Figure 4-1 describes the typical serologic course of HCV infection .
Figure 4-1. Typical serologic course of hepatitis C virus infection
In 2013, CDC provided updated guidance on the recommended testing sequence for identifying current hepatitis C . Hepatitis C testing should be initiated with an anti-HCV screening test, and if positive, an HCV RNA test should be performed. In settings serving high-risk populations , rapid anti-HCV testing can be used in lieu of laboratory-based anti-HCV testing to deliver results to the patient at the time of visit. For people who tested anti-HCV positive through rapid screening, an on-the-spot blood draw to be sent for HCV RNA testing should be performed or a referral and/or evaluation for HCV RNA testing should be provided. For blood draws collected for anti-HCV testing, all positive specimens should reflex to HCV RNA testing to reduce the number of patients lost to follow-up.
Table 4-1. Interpretation of hepatitis C laboratory results
| Test Outcome* |
|---|
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Blood tests are used to diagnose hepatitis B. Blood tests can tell your doctor whether your liver is working properly, and they can also be used to monitor your condition during treatment.
Your doctor may want to look at your liver with an ultrasound exam or X-rays. You may also need a liver biopsy. During a liver biopsy, a small piece of the liver is removed and looked at under a microscope. A liver biopsy can help your doctor diagnose your illness and see the condition of your liver directly.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does A Person Live With Hepatitis C
How Do I Get Hepatitis B Treatment
Usually for adults, hepatitis B goes away on its own and you wont need treatment. Your doctor might tell you to rest, eat well, and get plenty of fluids. You may also get medicines to help with any symptoms you might have but be sure to talk with your doctor or nurse before taking anything.
If you have chronic hepatitis, there are medicines you can take to treat it. Your doctor will tell you about your options and help you get whatever treatment you need.
Shop Health Insurance Plans
Even though health insurance can be expensive, your monthly premium through an employer might be considerably less than the cost of treating hep C without it. If thats not an option, you can research coverage options on the U.S. Health Insurance Marketplace during open enrollment periods.
Keep in mind, though, even with private or individual health insurance, your provider might not cover the cost of hep C treatment until youre very sick, and only if you dont use drugs or alcohol. Be sure to find out all you can about your coverage before applying.
Also Check: What Is The Cure Of Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
Why Is Hepatitis C Treatment So Expensive
Hep C drugs are in high demand, with an estimated 2.4 million people in the United States living with the virus. This contributes to the high cost of medications.
The cost of research and development of the drugs is expensive, too. And since these medications have a high cure rate and there isnt a lot of competition theres little incentive for drug companies to lower the cost.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Is It Curable
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18