American Association For The Study Of Liver Diseases Recommendations
The 2016 AASLD guidelines for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B as well as select recommendations from the 2018 AASLD guidance update on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B are outlined below and in the Guidelines section.
Adults with immune-active chronic hepatitis B infection
Administer antiviral therapy to lower the risk of morbidity and mortality associated with chronic hepatitis B infection.
The recommended initial agent for adults is PEG-IFN, entecavir, or tenofovir.
Adults with immune-tolerant chronic hepatitis B infection
Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
The AASLD suggests obtaining ALT levels at least every 6 months to monitor for potential transition to immune-active or -inactive chronic hepatitis B.
For select patients older than 40 years, the AASLD suggests antiviral therapy in the setting of normal ALT levels, elevated HBV DNA , and significant necroinflammation or fibrosis on liver biopsy specimens.
Adults with HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis B who seroconvert to anti-HBe on nucleoside analog therapy
After a period of treatment consolidation , consider discontinuing NA therapy in noncirrhotic HBeAg-positive adults who seroconvert to anti-HBe while on NA treatment. If antiviral therapy is stopped, monitor the patient every 3 months for a minimum of 1 year for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation.
Adults with HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic HBV infection
Inpatient care
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Considerable progress has been made by past clinical trials in the medical treatment of hepatitis C. The rate of cure has increased with the development of direct-acting, all-oral antiviral regimens, and the length of therapy is much shorter. Treatment recommendations continue to change as new medicines become available. Treatment helps to reduce progression of liver damage to cirrhosis, may prevent liver cancer, and may prevent spread of the infection to other people.
Skin Adverse Effects Related To Standard Of Care Treatment Of Chronic Hcv Infection
The fingerprint detector effect
The combination of pegylated interferon and ribavirin , which is the current standard of care in the management of chronic HCV infection, has significantly improved the treatment outcome. Due to the side effect profile of both drugs, a considerable number of chronic hepatitis C patients are ineligible for PEG-INF/RBV-based treatment because of medical contraindications. Moreover, vast rates of patients are unable to tolerate antiviral therapy, and account for nearly 10% of premature treatment discontinuations .
Cutaneous adverse events reported under INF plus RBV treatment of patients with chronic HCV infection
References cited in this table are partly compiled from the works of Cacoub and coworkers , Mistry and coworkers , Lübbe and coworkers , and Jadali .
Figure 17.
Erythematous patches at the site of injection of INF
Figure 18.
Vague eczematous patches on the extensor aspects of the limbs
Figure 19.
Eczema involving areas exposed to friction
Figure 20.
A coin shaped, sharply demarcated eczematous lesion ( nummular eczema
Prurigo nodularis â Bottom left corner: closeup of an excoriated nodule
Figure 23.
Clinical grading of eczema: A, acute B, subacute C, chronic
Figure 24.
Read Also: How Do You Get Hepatitis B And C
How Does Hepatitis Get Diagnosed
Several blood tests and examinations can determine which hepatitis an individual has. Since hepatitis is usually a viral infection, HBV and HCV can spread through contaminated blood. On the contrary, hepatitis A may be tested by using antibodies in the blood produced by the immune system in response to a hepatitis A infection. Hepatitis A and E are both curable on its own but still may become chronic, depending on the risk factors.
Also Check: How Did I Get Hepatitis
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
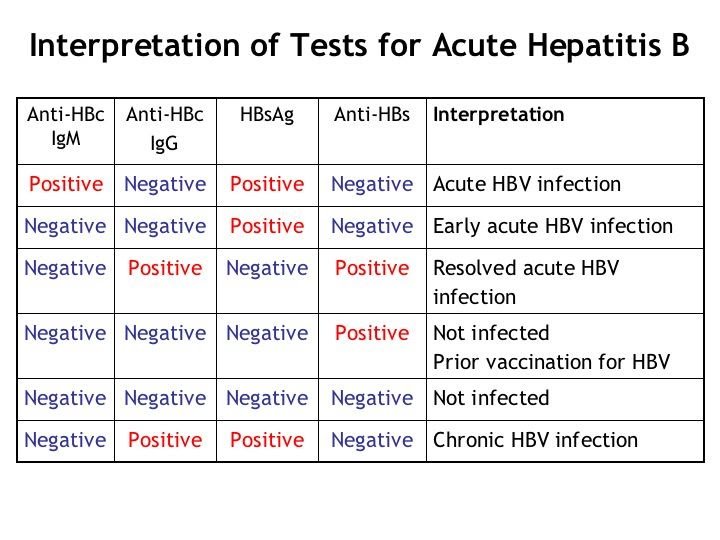
There are three main ways to diagnose HBV infection. They include:
- Blood tests: Tests of the blood serum shows how your bodys immune system is responding to the virus. A blood test can also tell you if you are immune to HBV.
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to show the size and shape of your liver and how well the blood flows through it.
- Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis.
The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit. Often, people whove become infected first learn they have hepatitis B when they go to donate blood. Blood donations are routinely scanned for the infection.
The virus can be detected within 30 to 60 days of infection. About 70% of adults with hepatitis B develop symptoms, which tend to appear an average of 90 days after initial exposure to the virus.
Also Check: How To Test For Hepatitis C Virus
Should All Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Be On Treatment
Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B need to be on treatment. The decision to treat HBV is based on several factors including blood tests results, the patient’s age, and the risk of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer. Sometimes a liver biopsy is needed to see if there is significant liver damage to make a decision.
Hepatitis B medications are recommended for patients with detected HBV virus on a blood test and evidence of liver damage. Liver damage can be detected with a liver enzyme known as ALT. People with cirrhosis should be considered for treatment even if the liver enzymes appear normal.
Chronic hepatitis B may change over time. Patients can go through different phases with low amounts of virus and normal level of ALT followed by high viral loads and ALT levels. These bursts of virus activity usually don’t cause any symptoms but may cause liver damage overtime. It is important that people with chronic hepatitis B have blood tests on a regular basis to see if treatment is needed.
There are some medications which can cause hepatitis B “reactivation” which can lead to life threatening liver failure. These medications are used to treat some cancers, inflammatory conditions and hepatitis C. Reactivation reactions can be prevented and it is important to let your provider know you have HBV before you start any new medications.
Are There Blood Tests For Hepatitis B
Yes. Many chronically infected persons show no outward signs of hepatitis B infection. Therefore, screening for hepatitis B is important and necessary. Ask your doctor for the following blood tests:
HEPATITIS B SURFACE ANTIGEN : Tells if you have chronic hepatitis B. Only the HBsAg blood test can tell if you have chronic hepatitis B.
HEPATITIS B SURFACE ANTIBODY : Tells if you are protected against hepatitis B.
| Test Result |
Dont Miss: Unspecified Hepatic Cirrhosis Type Hcc
You May Like: New Cure For Hepatitis B
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hbv Infection
HBV can cause a wide range of symptoms, from a mild illness and general feeling of being unwell to more serious chronic liver disease that can lead to liver cancer. Someone with hepatitis B may have symptoms similar to those caused by other viral infections, like the flu. The person might:
- be extra tired
- have a mild fever
HBV also can cause darker than usual pee, jaundice , and belly pain.
People exposed to hepatitis B may start to have symptoms from 1 to 6 months later. Symptoms can last for weeks to months.
In some people, hepatitis B causes few or no symptoms. But even someone who doesnt have any symptoms can still spread the disease to others.
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Be Transmitted Sexually
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Having Hepatitis C
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Hepatitis B Causes Symptoms And 6 Natural Treatments
It is estimated that over 300 million people are living with hepatitis B. In 2015, it resulted in 887,000 deaths worldwide. Although many people with hepatitis B dont experience any symptoms, its a chronic infection that can lead to severe liver conditions like cirrhosisand liver cancer. The scary part is that it is 50100 times more infectious than HIV. An even scarier note: coinfection with hepatitis B and HIV is common. Seventy to 90 percent of people with HIV in the U.S. show evidence of past or active HBV infections. HBV is also more infectious than hepatitis C. Both hepatitis B and C are transmitted through infected blood, but hepatitis A is transmitted through infected fecal matter. The virus can live outside of the body for many days and infect you unknowingly. Thats why people at risk of acquiring hepatitis B should be screened. That way those infected can limit the spread of the virus.
There is no cure for hepatitis B, but there are natural ways to support your immune system and reduce your risk of developing a chronic infection. There are also remedies for relieving the symptoms of acute hepatitis B, which for some people can last for months.
Also Check: How To Convert Hepatitis B Positive To Negative
Stool Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
**When you think about hepatitis, the first thing that comes to mind is probably your liver.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
** But infection with the hepatitis C virus can lead to stool symptoms as well. Diarrhea can occur in the early or late stages of hepatitis C infection, or it may be a side effect of medications used to treat the virus. Severe liver disease may also cause pale, oily, bloody or tar-like stools. If you have hepatitis C, it is important to be aware of stool symptoms, as they are often an indicator of disease severity, and some require prompt medical care.
What Is Hepatitis D And How Is It Associated With Hepatitis B
Hepatitis D is another virus that can cause liver infections, but only if hepatitis B is also present. A person may become infected with both viruses at the same time or may first be infected with hepatitis B and then become infected with HDV . In the U.S., the incidence of HDV is low. There is no vaccine for HDV, but since it causes infections only in the presence of HBV, it may be prevented with the HBV vaccine.
Dont Miss: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Curable
Recommended Reading: Should I Get Hepatitis B Vaccine
Current Cdc Recommendations For Hepatitis A And Hepatitis B Vaccination
Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for:
-
All children at age 1
-
Children and adolescents ages 2-18 who live in states or communities with a high incidence of disease
-
Travelers to intermediate or high rates of hepatitis A
-
Men who have sex with men
-
Users of illegal injection and non-injection drugs
-
Persons with clotting factor disorders
-
Persons how work with hepatitis A infected primates or with hepatitis A in a research laboratory
-
Persons with chronic liver disease
-
Anyone else who seeks long-term protection
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for:
-
All infants beginning at birth
-
Older children not previously vaccinated
-
Sex partners of people that are hepatitis B surface antigen positive
-
Men who have sex with men
-
People seeking evaluation or treatment of a sexually transmitted disease
-
Injection drug user
How Is Hepatitis A Diagnosed
The health care professional will ask questions about the illness and symptoms, and about any possible exposures to other people diagnosed with hepatitis, especially the type of hepatitis .
If the healthcare professional determines that the patient may be at risk for contracting hepatitis, then it is likely the patient will undergo blood tests.
- The blood will be tested to determine how well the liver is functioning.
- A test will be ordered to detect antibody to hepatitis A. The results of this test will also determine if the patient has been recently exposed to HAV.
- Blood probably will be tested for the hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses, as well as others others. For example, if a patient has had a large amount of vomiting or has not been able to take in liquids, the blood electrolytes may be out of balance. Blood chemistry may be tested to check electrolytes.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
There are no specific medicines to cure infection with hepatitis A. Most people require no treatment except to relieve symptoms. However, if symptoms become severe or dehydration develops, the person should seek medical care emergently.
There is a vaccine for hepatitis A . If you have been exposed to someone who is infected with HAV, a treatment called immune serum globulin is available and may prevent you from becoming infected. Immune serum globulin is more likely to be effective when given within 2 weeks of exposure.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Tested For Hepatitis B
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Your healthcare provider will treat you based on what type of hepatitis B you have, acute or chronic.
Acute hepatitis B infections
If you develop an acute form of the condition, you probably wont need medical treatment. Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
Chronic hepatitis B infections
If you have chronic hepatitis B, you might be a candidate for drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets.
You will need to take these medications every day. They help by slowing the viruss ability to multiply in your system. This helps reduce swelling and liver damage. Youll need to be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will want to see you once or twice a year.
Do People With Hepatitis B Need To Take Additional Safety Precautions Against Covid
If you have severe hepatitis B or cirrhosis, you may need to take extra precautions against COVID-19.
This includes taking your prescription medication and attending medical appointments as usual. Additionally, you may need more frequent hepatitis B testing and lab monitoring if you get COVID-19.
You should also follow the preventive measures recommended for everyone:
- Wear a well-fitting mask.
- Avoid crowds as much as possible.
- Avoid poorly ventilated spaces.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cost Walgreens
Treating Hepatitis B With Tenofovir
Violetta Shamilova, PharmD, is a board-licensed pharmacist. She is an assistant professor at the Touro College School of Health Sciences, and has worked at CVS pharmacy for five years. She completed the certified APhA Delivering Medication Therapy Management Services course.
Tenofovir, also called tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, is an antiviral drug for treating chronic hepatitis B in adults and children who are 12 years and older. It is also used, in combination with other drugs, to treat the human immunodeficiency virus or HIV. Its sold under the brand name Viread by Gilead Sciences, Inc.
What Is My Risk
Your risk depends of several factors: destination, length of stay, what you do when you are travelling and whether you have direct contact with blood or other body fluids. In certain destinations, your risk may be higher, as some areas have higher numbers of people with chronic hepatitis B in the general population.
The risk increases with certain activities, such as unprotected sex, sharing needles, tattooing and acupuncture.
Aid and health care workers and anyone who receives medical or dental care with unsterilized or contaminated equipment in a country where hepatitis B occurs are also at greater risk.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Cvs Cost
Is There A Cure For Hepatitis B
The long and short answer is that there is not yet a cure for hepatitis B. Understanding why requires insight into the virus itself and the challenges cure researchers face.
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus . While most people exposed to hepatitis B will spontaneously clear the virus soon after infection, a proportion will go on to develop a chronic infection.
Of these, around one in four will develop severe liver complications, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, typically years after the initial infection.
Efforts to find a cure for hepatitis B have been underway since the virus was first identified by scientists at the National Institutes of Health in 1966. It soon became clear, however, that numerous hurdles would need to be overcome before an actual cure could be achieved. Chief among these are:
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
Also Check: Why Screen For Hepatitis C