Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
You can become ill any time between 2 and 4 weeks after coming into contact with the hepatitis A virus.
The average incubation period for the virus is 28 days.
Many infected people, particularly children less than 5 years old, show few or no symptoms.
For older children and adults, the symptoms of hepatitis A include:
- yellow skin and eyes .
Symptoms may last for several weeks. Most people fully recover from hepatitis A infection.
A single infection of hepatitis A leads to lifelong immunity. Prior infection with hepatitis B or hepatitis C does not offer immunity for hepatitis A.
Causes Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is caused by a virus. The virus can survive for several hours outside the body but persists on the hands and in food for even longer. It is resistant to heating and freezing.
The virus is spread when it enters the mouth, which can happen when hands, foods or other items are contaminated with the faeces of a person with hepatitis A. The disease can also be spread sexually by oral or anal contact.
A person with hepatitis A is infectious from 2 weeks before they show symptoms to one week after they become jaundiced .
If an infected person has no jaundice, they may pass on the virus until 2 weeks after they first have symptoms . Caution is advised beyond this period as the virus can be shed in stools for longer periods.
Side Effects Of Immunisation Against Hepatitis A
Immunisations against hepatitis A are effective and safe. All medications can have side effects.
For most people, the chance of a serious side effect from a vaccine is much lower than the chance of serious harm if you catch the disease.
Common side effects from the hepatitis A vaccine include:
- localised pain, redness and swelling at the injection site
- low-grade temperature
- headache.
Also Check: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
- Many people with HAV infection have no symptoms at all.
- Sometimes symptoms are so mild that they go unnoticed.
- Older people are more likely to have symptoms than children.
- People who do not have symptoms can still spread the virus so it is difficult to know when a person has been exposed to the virus.
Symptoms of hepatitis A usually develop between 2-6 weeks after infection. The symptoms are usually not too severe and go away on their own, over time. The most common hepatitis A symptoms are as follows:
- Nausea
- Jaundice
- Urine is dark brownish in color, like cola or strong tea.
- Pain in the area of the liver, on the right side of the abdomen just under the rib cage
If the vomiting is severe, dehydration may occur. Dehydration may become serious and life-threatening in some affected individuals, so symptoms of dehydration need to be quickly addressed, often by a medical caregiver. Symptoms of dehydration include the following:
- Feeling weak or tired
- Feeling confused or unable to concentrate
- Rapid heartbeat
- Urinating less frequently than usual
- Irritability
Symptoms of hepatitis A infection usually last less than 2 months, although they may last as long as 9 months. Some people infected with hepatitis A have symptoms that come and go for 6-9 months.
Hepatitis A Immunisation Is Recommended For High
In Victoria, the vaccine is recommended for:
- people travelling to places where hepatitis A is common
- people whose work puts them at increased risk of infection including:
- plumbers and sewage workers
- people who work with children
- people who work with people with developmental disabilities
Remember that immunisation against hepatitis A does not protect you against hepatitis B or hepatitis C.
You May Like: Ok Google What Is Hepatitis C
Looking After Yourself When You Have Hepatitis A
AlcoholSome people with acute hepatitis develop an aversion to alcohol in the acute phase. Previously people with this condition were told to avoid alcohol for six months following the illness. This advice is no longer thought necessary.
SmokingSmoking is dangerous to everyones health. Smoking can increase the severity of liver damage. People with liver disease are more vulnerable to infection and to poor health overall, so smoking or exposure to passive smoking is not advisable.
DietIf you have a short-term hepatitis infection, for example hepatitis A, you should try to eat a normal diet. However, some people may need extra nutrition to prevent unplanned weight loss, and may benefit from a high-energy and high-protein diet. A dietitian can advise on this.
If you develop nausea and vomiting, our coping with eating difficulties may help. Read more here.
Whats The Best Way To Stop The Spread Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccination is the best way to prevent hepatitis A. The hepatitis A vaccine is given in 2 doses, usually about 6 months apart.
Other ways to stop the spread of HAV are:
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water immediately after using the bathroom or changing a diaper
- Always washing your hands with soap and warm water before preparing or eating food
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body
How Can I Avoid Getting Hepatitis B
There is a safe and effective vaccine that can protect you from getting hepatitis B. The vaccine is usually given in three doses over a six month period. The vaccine will give you long-lasting protection. A combined vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B is also available.
Other ways to protect yourself or your loved ones include:
- Adopt safe sex practices.
- Avoid sharing personal hygiene items
- If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus , an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin may help protect you.
- If you are pregnant, make sure you are screened for hepatitis B. If the test result shows that you have the virus, make sure your baby receives the free hepatitis B vaccine. If you have hepatitis B, breastfeeding is safe if the baby has received both protective antibody called immune globulin, and the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine within the first 12 hours of life. Talk to your doctor about having your newborn immunized .
- If you decide to have a tattoo, piercing, manicure or pedicure, ensure that the facility uses single-use needles and inks and/or follows proper sterilization procedures.
Hurdles And Opportunities In Viral Hepatitis Treatment
In the last decade, rapid and significant advances in diagnosing and managing viral hepatitis were made and changed its treatment. These advances include the development of DAAs for the treatment of chronic hepatitis caused by HCV-with SVR rates greater than 95%, the improvement of HBV vaccination as well as enhancement of the immunogenicity of HBV vaccines, and the identification of antiviral therapies with low rates of viral resistance. Table summarises the current clinical management of viral hepatitis and areas of development for future treatments.
You May Like: How Can You Get Hepatitis C From Someone
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis A
Not all people infected with hepatitis A virus will have symptoms. Pre-school children often have no symptoms, and, in general, children will have milder symptoms than adults. Symptoms may occur 15 to 50 days from the time you first come in contact with the hepatitis A virus.
When you first become infected with the hepatitis A virus it is called acute infection. Typical symptoms of an acute hepatitis A infection include fatigue, nausea and vomiting, abdominal discomfort, jaundice , dark urine, low-grade fever and loss of appetite.
The older you are when you get hepatitis A, the more likely that you will experience more severe symptoms. Some people feel sick for one to two weeks, while in others the symptoms may last several months. Hepatitis A rarely causes death. However, persons with pre-existing chronic liver disease, including chronic hepatitis B and C, are at increased risk of serious complications from this infection.
Medical Treatment For Hepatitis A B & C
Treatment for hepatitis A, B, or C is based on which type of hepatitis is present in the bloodstream and the severity of the resulting liver damage. Depending on the results of diagnostic tests, our specialists at NYU Langone may recommend antiviral medication to stop the virus from replicating and protect your liver from further damage.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A B C Symptoms
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis A
Although anyone can get hepatitis A, you are at higher risk if you:
- Travel to developing countries
- Abdominal pain
- Yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
The symptoms usually last less than 2 months, although some people can be ill for as long as 6 months.
You are at a higher risk of getting a more severe infection from hepatitis A if you also have HIV, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C.
How Do You Prevent Hepatitis A
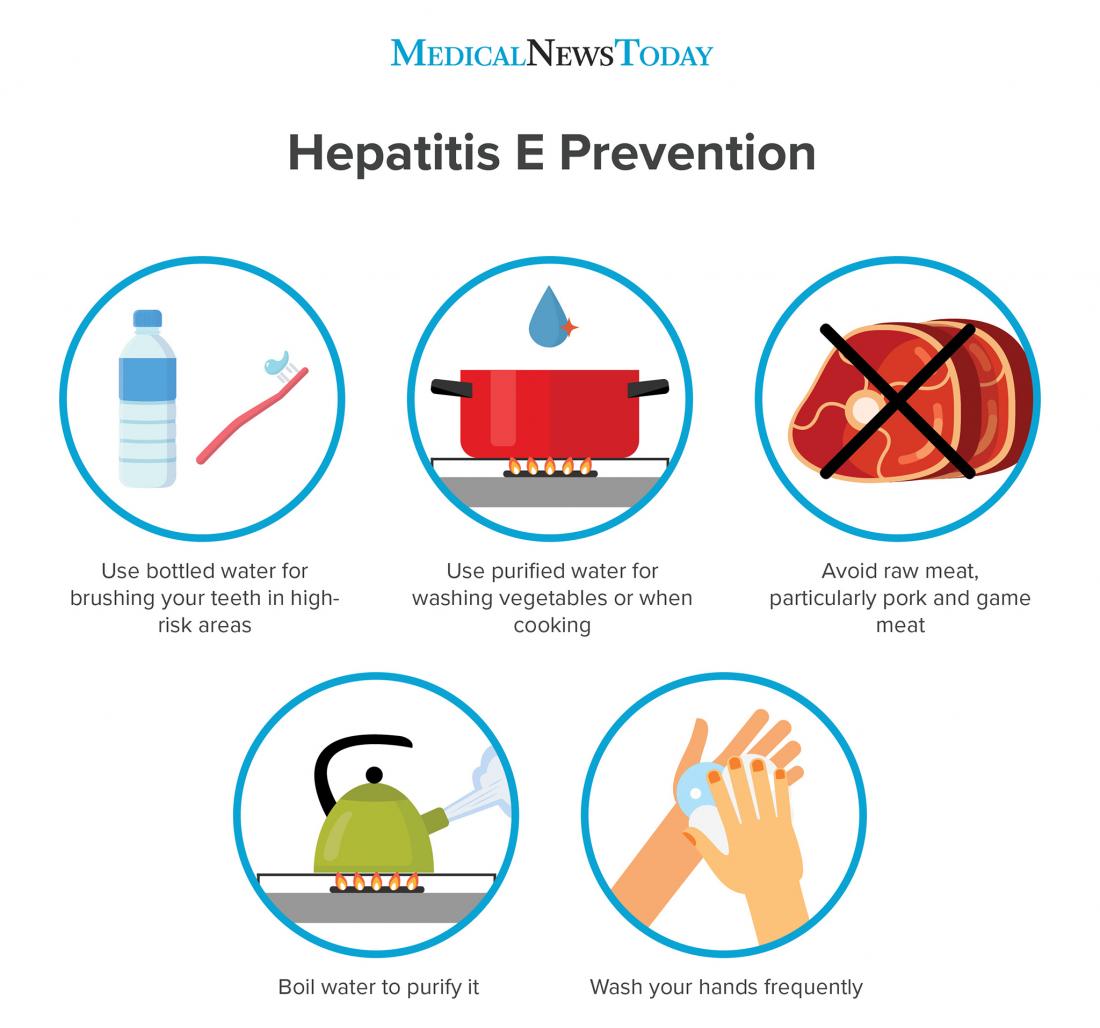
If a person has hepatitis A, strict personal hygiene and hand washing help prevent transmission of HAV to others. There are ways to help reduce or prevent HAV infection:
- Wash hands thoroughly every time after use of the bathroom, before touching or preparing food, and before touching others. Wash hands with soap and warm water, and then dry the hands thoroughly .
- Contaminated surfaces should be cleaned with household bleach to kill the virus.
- Heat food or water to 185 F or 85 C to kill the hepatitis A virus.
If people are not infected with HAV, they can reduce the chance of becoming infected by the following methods:
- Wash hands carefully with soap and warm water several times a day, including every time the bathroom is used, every time a diaper is changed, and before preparing food.
- Do not eat raw or undercooked seafood or shellfish such as oysters from areas of questionable sanitation .
- Individuals traveling to developing countries should not drink untreated water or beverages with ice in them. Fruits and vegetables should not be eaten unless cooked or peeled.
Hepatitis A Vaccine
In addition to the above methods, there are vaccines that work to prevent infection with HAV, but are not substitutes for good hygiene and careful food and drink consumption.
Not everyone needs to have the hepatitis A vaccines. However, the CDC recommends the HAV vaccine for the following groups:
Also Check: How Can You Contract Hepatitis C
Can Hepatitis A Be Prevented
Yes. The hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all children over 1 year old. The vaccine is given at 12 months of age, followed by a second dose at least 6 months later. Having many young kids vaccinated against HAV can limit the spread of the disease in a community.
The vaccine can be given as early as 6 months of age to babies who will travel to a place where hepatitis A is common .
The vaccine also is recommended for older kids, teens, and adults who have never gotten it.
The best way to prevent hepatitis A and many other infections is to wash hands well and often. This is especially important after using the toilet and before eating or preparing food.
Reducing The Risk Of Hepatitis A
Protecting yourself from hepatitis A
The most important action you can take to protect yourself against hepatitis A is to get vaccinated.
Practising strict personal hygiene is also essential to reducing the risk of hepatitis A. Steps you can take include:
- Wash your hands with soap and hot running water before handling food, after going to the toilet and after handling used condoms or having contact with nappies or the anal area of another person. Use a clean towel to dry your hands.
- Use barrier protection when engaging in oral-anal sex and avoid sex with someone who is infected with the hepatitis A virus.
- Vaccination may prevent illness if given within 2 weeks of contact with an infectious person.
- Clean bathrooms and toilets often, paying attention to toilet seats, handles, taps and nappy change tables.
- Boil your drinking water if it comes from an untreated source, such as a river.
- If you are travelling overseas, particularly to countries where hepatitis A is widespread, take special care to avoid hepatitis A. Before travelling, talk to your doctor about immunisation for protection.
Protecting others from hepatitis A
If you have hepatitis:
- Wash eating utensils in soapy water, and machine wash linen and towels.
Household contacts and sexual partners of an infectious person may need to be immunised.
All people who have hepatitis A should check with their doctor before returning to work or school.
Protecting yourself from hepatitis A when overseas
Also Check: Hepatitis C Test Results Non Reactive
Possible Complications Of Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A can cause more serious health problems. Keep in mind all that these are rare and more likely to happen in people who are over 50.
- Cholestatic hepatitis. Occuring in about 5% of patients, this means the bile in your liver is obstructed on its way to the gallbladder. It can cause changes in your blood and result in jaundice fever and weightloss
- Relapsing hepatitus. More common in the elderly, The symptoms of liver inflamation such as jaundice, reoccur periodlically but are not chronic.
- Autoimmune hepatitis. this triggers your own body to attack the liver. If left untreated, it could result in chronic liver disease, cirrhosis and ultimately liver failure.
- Liver failure. Happens in less than 1% and this usually affects people who are:
- Older
- Already have another type of liver disease
- Have a weakened immune system
If your doctor feels your liver isnât working well, they may admit you to the hospital to keep an eye on how well your liver is working. In severe cases, you might need to have a liver transplant.
Complementary And Alternative Medicines And Therapies
Many complementary and alternative medicines available suggest they can ease the symptoms of liver disease. As with any other medicine, you should use them with care before taking any medicine you should check with your doctor that it is safe to do so.
Most medicines are processed by the liver so they can be toxic to people with liver problems. Some can damage the liver and make you more severely ill. At present, healthcare professionals are not clear on the role and place of some complementary medicines in managing liver disease more research is needed on their use.
Licensing has been introduced for some traditional herbal medicines. However, many herbal products are not classified as a medicine and so can be legally sold as food or cosmetic this means there is no regulation of the product and so you cannot be sure how much of the active ingredient you are getting, or how pure it is. Unregulated products are not monitored or assessed for how effective or safe they are. Some remedies can damage the liver and make you more severely ill. It is wise to be cautious about the claims made about herbal remedies, particularly those advertised on the internet.
It is very important to discuss the use of these remedies with your doctor before considering taking them.
Read Also: Hepatic Metastasis From Colorectal Cancer
Can Hepatitis A Be Prevented Or Avoided
The best way to protect yourself against hepatitis A is to get the vaccine. The hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for all children older than age 1. It begins to protect you only 4 weeks after you are vaccinated. A 6- to 12-month booster is required for long-term protection. Ask your doctor if the vaccination is right for you.
You should also wash your hands with soap and warm water before and after cooking, after using the bathroom, and after changing diapers.
Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before eating and avoid raw or undercooked meat and fish.
You are at higher risk for hepatitis A if you:
- Live with or have sex with someone who has hepatitis A
- Travel to countries where hepatitis A is common
- Are a man who has sex with other men
- Use illegal drugs
- Have a clotting-factor disorder
Immunisation Against Hepatitis A
Immunisation is the best protection against hepatitis A infection and is recommended for people in high-risk groups, and for unvaccinated people who have been in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A.
Immunisation against hepatitis A includes a course of injections over a 6 to 12-month period. Healthy people 12 months of age and over receive 2 doses of hepatitis A vaccine, or 3 doses if the hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are given as a combination.
You can complete any missed vaccine doses, even if the recommended time frame has passed. You do not need to start the vaccine course again.
If you are in close contact with someone who has hepatitis A be sure to have the hepatitis A vaccine if you have not already completed a vaccine course.
Babies under 12 months of age and people who have a weakened immune system who are also in close contact with a person with hepatitis A can have an injection of normal human immunoglobulin instead of the hepatitis A vaccine.
Protection against hepatitis A is available free of charge under the National Immunisation Program Schedule for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children who live in high-risk areas .
Also Check: Causes Of Hepatitis C Virus
What Is Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, also called enteric hepatitis , is similar to hepatitis A, and more prevalent in Asia and Africa. It is also transmitted through the fecal-oral route. It is generally not fatal, though it is more serious in women during pregnancy and can cause fetal complications. Most patients with hepatitis E recover completely.
Thank You For Reading Nationafrica

I have not received any vaccination against Hepatitis B but recently had sexual intercourse with a man who tested positive for Hepatitis B. What is the best treatment option? Nightingale
Dear Nightngale,
Hepatitis means infection of the liver, which among others may be caused by viruses, bacteria, drugs or toxins.
Also Check: Royal Canin Veterinary Diet Hepatic Formula Dry Dog Food