Hcv Treatment Data In Persons With Compensated Cirrhosis
The impact of cirrhosis on the response to therapy has changed over time with evolving treatment regimens. The following summary of clinical trials involving persons with compensated cirrhosis illustrates a significant improvement in SVR rates among patients with cirrhosis with regimens that include direct-acting agents.
Elbasvir-Grazoprevir
- Integrated Analysis of Treatment in Persons with Compensated Cirrhosis: In this study, investigators performed an integrated analysis of 6 elbasvir-grazoprevir phase 2/3 clinical trials to determine SVR12 treatment responses in 402 study participants with HCV genotype 1, 4, or 6 and compensated cirrhosis. Participants received treatment with elbasvir-grazoprevir, with or without weight-based ribavirin the treatment duration was 12 weeks for treatment-naïve participants and 12, 16, or 18 weeks for treatment-experienced subjects . Notably, platelet counts less than 100,000 cells/mm3and serum albumin less than 3.5 g/dL were present in only 25% and 6% of participants respectively. Overall, using an intent-to-treatment analysis, SVR12 occurred in 96% of treatment-naïve participants and ranged from 89 to 100% among treatment-experienced subjects. Genotype 1a patients were most likely to experience viral relapse with the strongest predictor for treatment failure being the presence of baseline NS5A resistance-associated substitutions. Asymptomatic grade 3-4 increases in hepatic aminotransferase levels were observed in 2.3%.
Guidance For Hcv Treatment With Decompensated Cirrhosis
The AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance addresses this group of patients in the section Unique Patient Populations: Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis. The key recommendation the guidance is that general management and treatment of all patients with decompensated cirrhosis should be performed by a medical practitioner highly experienced in managing persons with chronic HCV infection and decompensated cirrhosis. Accordingly, referral of these patients to an expert, ideally at a transplant center, is strongly recommended. Patients with decompensated cirrhosis include patients who may or may not be a candidate for liver transplantation and may include patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Baseline Predictors Of Child
Male sex , platelet count lower than 100,000/L , increased international normalized ratio , presence of esophageal varices , history of HCC and history of decompensation were significantly associated with C-P class worsening at univariate analysis. At multivariate analysis, male sex , platelet count lower than 100,000/L and increased INR resulted independently associated with C-P class worsening. HIV coinfection was not associated with the C-P class worsening both at univariate and at multivariate analysis .
Table 4 – Baseline factors associated with Child-Pugh class worsening following viral eradication. Univariate and multivariate analysis
Don’t Miss: Tenofovir Hepatitis B Side Effects
Diagnoses Of And Deaths From Severe Liver Disease Due To Hepatitis C In England Between 2000 And 2005 Estimated Using Multiple Data Sources
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 16 September 2008
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- M. E. RAMSAY
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- L. J. BRANT
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- M. A. BALOGUN
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- A. COSTELLA
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- H. E. HARRIS
- Immunisation Department, Health Protection Agency Centre for Infections, London, UK
- *
- *Author for correspondence: Ms. A. G. Mann, Infectious Disease Epidemiology Unit, Department of Epidemiology & Population Health , London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, Keppel Street
Coping With A Diagnosis
According to the VA, although cirrhosis is progressive, some people with the condition can move from decompensated, or symptomatic, back to the asymptomatic stage. This is a challenging process, although one of the critical steps is avoiding alcohol of any kind.
To prevent progressing from the asymptomatic to the symptomatic stage, people can make the following lifestyle changes:
- exercising regularly
- keeping to a moderate weight
- getting treatment for conditions that might have caused cirrhosis, such as hepatitis C or B
- getting regular check-ups and prompt treatment for complications
- quitting smoking
Of people who develop cirrhosis, 2060% also develop malnutrition, additional complications, longer hospital stays, and a reduced life expectancy.
This means eating a healthful diet is crucial for those with this condition. Cirrhosis itself can affect diet and metabolism, so people should try:
- consuming a low-salt diet
- avoiding too much vitamin A and D
- avoiding taking vitamin C, if iron levels are high
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedy For Hepatitis B
Can You Prevent Hepatitis C Infection
Thereâs no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To avoid getting the virus:
- Use a latex condom every time you have sex.
- Don’t share personal items like razors.
- Don’t share needles, syringes, or other equipment when injecting drugs.
- Be careful if you get a tattoo, body piercing, or manicure. The equipment may have someone else’s blood on it.
Find out more on how to prevent hepatitis C.
How Common Is Hepatitis C In The United States
In the United States, hepatitis C is the most common chronic viral infection found in blood and spread through contact with blood.14
Researchers estimate that about 2.7 million to 3.9 million people in the United States have chronic hepatitis C.13 Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have this infection.
Since 2006, the number of new hepatitis C infections has been rising, especially among people younger than age 30 who inject heroin or misuse prescription opioids and inject them.15,16
New screening efforts and more effective hepatitis C treatments are helping doctors identify and cure more people with the disease. With more screening and treatment, hepatitis C may become less common in the future. Researchers estimate that hepatitis C could be a rare disease in the United States by 2036.17
Read Also: What Is The Meaning Of Hepatitis
Causes Of Chronic Hepatitis
The most common causes of chronic hepatitis are
-
Alcohol-related liver disease Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Alcohol-related liver disease is liver damage caused by drinking too much alcohol for a long time. In general, the amount of alcohol consumed determines… read more
Hepatitis C virus causes about 60 to 70% of cases of chronic hepatitis, and at least 75% of acute hepatitis C cases become chronic.
About 5 to 10% of hepatitis B cases in adults, sometimes with hepatitis D Hepatitis D Hepatitis D virus is infection of the liver that occurs only in people who have hepatitis B. Hepatitis D can be spread by contact with blood and other body fluids. Coinfection with hepatitis… read more coinfection, become chronic. Acute hepatitis B becomes chronic in up to 90% of infected newborns and in 25 to 50% of young children.
Rarely, hepatitis E virus causes chronic hepatitis in people with a weakened immune system, such as those who are taking drugs to suppress the immune system after an organ transplant, who are taking drugs to treat cancer, or who have HIV infection.
Hepatitis A virus does not cause chronic hepatitis.
Less often, chronic hepatitis results from
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
-
Drugs
In autoimmune hepatitis, the chronic inflammation resembles inflammation caused by the body attacking its own tissues . Autoimmune hepatitis is more common among women than men.
Baseline Characteristics Of Patients
A total of 108 HIV/HCV coinfected and 1242 HCV monoinfected patients were considered in the present analyses. Baseline characteristics of these patients are summarised in Table .
Table 1 – Baseline characteristics of cirrhotic patients
Coinfected patients were significantly younger and compared with monoinfected patients had significantly lower BMI . Current alcohol use is more frequently reported in coinfected compared with monoinfected patients .
A significantly different distribution in HCV genotypes in monoinfected compared with coinfected patients was observed. About half of the monoinfected patients were infected by HCV genotype 1b, whereas genotype 1a and 3 were prevalent in coinfected patients .
Higher prevalence of anti-HBc+/HBsAg- and anti-HBc+/HBsAg+ was detected in coinfected compared with monoinfected patients .
A significant difference in the prevalence of HCC between coinfected and monoinfected patients was observed .
Before starting therapy, 15 co-infected and 133 monoinfected patients had reported a previous liver decompensating event .
Coinfected patients had a more severe liver disease in terms of C-P class distribution , compared with monoinfected patients .
After adjusting for potential factors of liver disease severity before treatment, such as age, sex, HCV genotype, HBsAg positivity, alcohol use and HIV coinfection, HIV was the only factor independently associated with C-P class B/C vs A .
Read Also: Can You Ever Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
Prospective Evaluation On Changes In Liver Function After Viral Eradication
Coinfected and monoinfected patients were evaluated during a median follow-up of 27.1 and 24.7 months after viral eradication, respectively. Changes in the severity of liver disease in terms of C-P class worsening or improvement are shown in Fig. .
Fig. 1
Changes in the severity of liver disease in terms of C-P class improvement or worsening in monoinfected and coinfected patients
During the follow-up C-P class improved in 17/20 coinfected patients and in 53/82 monoinfected patients . C-P class worsened in 3/56 coinfected patients and in 84/1024 HCV-monoinfected patients .
No difference in the occurrence of a decompensating event following viral eradication was observed between coinfected and monoinfected patients. Of patients with decompensated cirrhosis prior to therapy in 7 of 15 coinfected and in 61 of 133 monoinfected patients a new decompensating event occurred following viral eradication. A total of 4 of 93 coinfected and 53 of 1109 monoinfected patients had their first decompensating event. Decompensating events recorded after viral eradication in both patients with or without a previous history of decompensation were mainly represented by the presence of ascites, however encephalopathy and variceal bleeding were also present .
Table 3 Occurrence of decompensating event following viral eradication
Read Also: Just Food For Dogs Hepatic
What To Expect If You Get Cirrhosis
In the early stages of hepatitis C, your liver still has enough cells to do its many jobs. But with time, more cells die, and pressure builds up in the vein leaving the liver.
When that happens, symptoms of cirrhosis like jaundice may show up.
These are some possible complications of cirrhosis:
- Swelling in your legs and abdomen, which can lead to a serious bacterial infection.
- Enlarged blood vessels in your esophagus or stomach, which can burst and cause serious internal bleeding. This requires immediate medical attention.
- Enlarged spleen , which may lead to a low white blood cell or platelet count.
- Gallstones , from bile not flowing freely to and from your gallbladder.
- Greater sensitivity to drugs because your liver canât filter them from your blood.
- Resistance to the hormone insulin , leading to type 2 diabetes.
- Kidney and lung failure.
- Problems fighting infection.
Two other serious complications of cirrhosis are liver cancer and a buildup of toxins in your brain. The latter can interfere with your thinking, and can lead to coma.
Youâll need to see your doctor more often to manage these complications. Youâll have tests to see how your body is reacting. Your doctor may try a new combination of medications.
Diagnosis And Disease Course For Chronic Hcv Infection
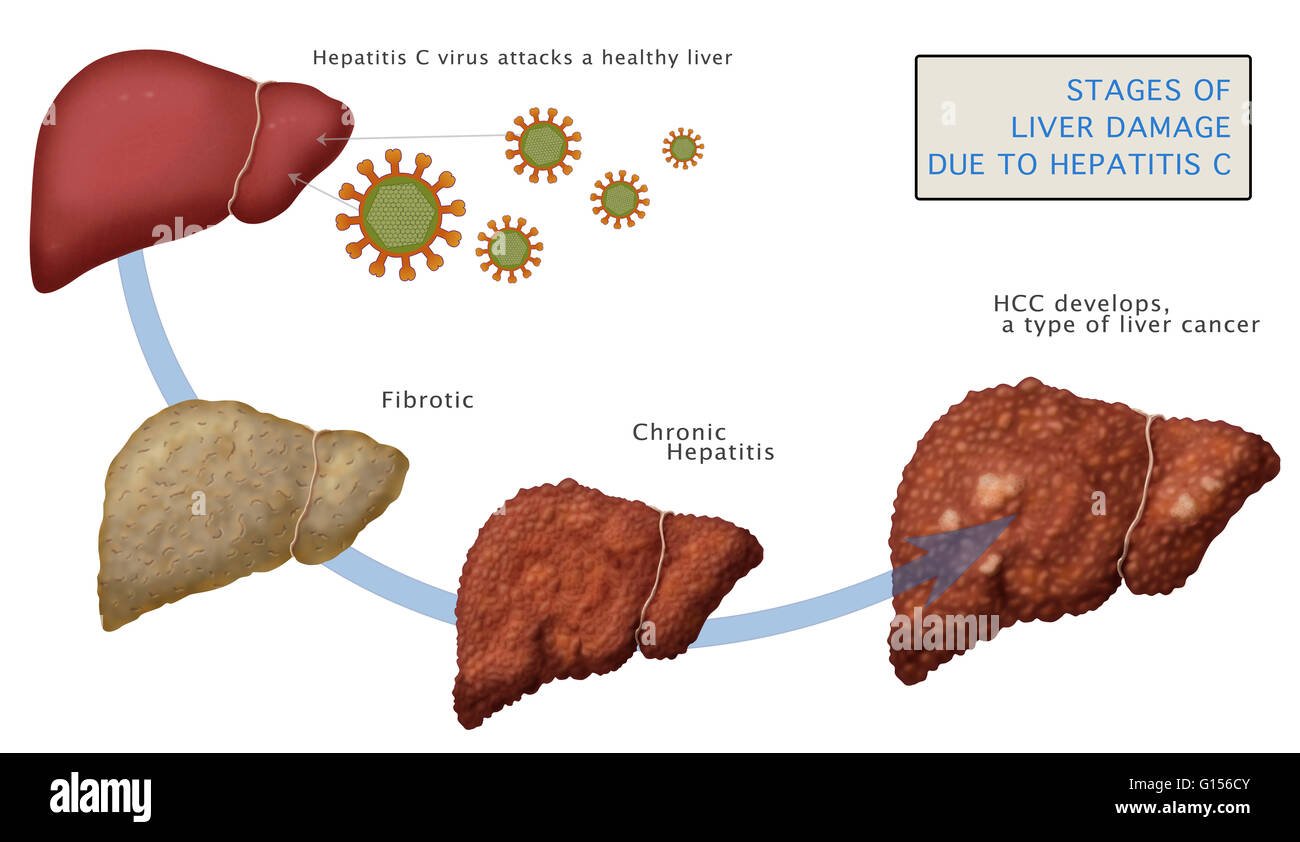
HCV infection is rarely diagnosed during in the acute phase of infection. Although a variety of host-factors play a role in eradication of HCV, only 15%-25% of adults spontaneously clear the infection. The remaining proportion of patients continue to have persistent viremia and retrospective studies on the natural history of HCV infection, have found that about 15%-30% of people with chronic infection would progress to cirrhosis over the duration of two to three decades. Progression to cirrhosis has been shown to occur at an accelerated pace in those with concomitant alcohol use , co-infection with HIV and hepatitis B virus , as well as male sex, and older age at time of infection . In the patients that develop HCV related cirrhosis, the risk of development of HCC has been shown to be 1%-4% per year and warrant surveillance for complications.
Natural progression of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States. HBV: Hepatitis B virus HCV: Hepatitis C virus HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus.
Read Also: What Is Non Reactive Hepatitis C
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Hepatitis C
Recommended For All Patients With Hcv Infection Who Have Decompensated Cirrhosis
RECOMMENDED RATING Patients with HCV infection who have decompensated cirrhosismoderate or severe hepatic impairment, ie, Child-Turcotte-Pugh class B or class Cshould be referred to a medical practitioner with expertise in that condition, ideally in a liver transplant center. I, C
Clinical trial data demonstrate that in the population of persons with decompensated cirrhosis, most patients receiving direct-acting antiviral therapy experience improvement in clinical and biochemical indicators of liver disease between baseline and posttreatment week 12, including patients with CTP class C cirrhosis . Improvements, however, may be insufficient to avoid liver-related death or the need for liver transplantation , highlighting that not everyone benefits from DAA therapy . Most deaths among those receiving DAA therapy relate to the severity of the underlying liver disease. Predictors of improvement or decline have not been clearly identified, although patients with a Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score > 20 or severe portal hypertension complications may be less likely to improve and might be better served by transplantation than antiviral treatment .
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
You May Like: How You Get Hepatitis C
Treatment Of Bleeding Varices
A bleed from swellings – described above – is a medical emergency. Seek medical help immediately if you have cirrhosis and:
- You bring up blood or
- You pass blood in your stools or
- Your stools become black.
Various surgical techniques can be used to stop the bleeding and to help reduce the risk of further bleeds.
Types Of Liver Disease
Liver disease generally refers to conditions that damage your liver. They can develop for many reasons, including:
- Damage from viruses
- Exposure to toxins
- Autoimmune conditions that block the liver’s ability to function properly
Depending on the underlying cause, liver disease can typically be managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes a liver transplant or surgery. If it’s left untreated, liver disease can cause serious complications that may be life-threatening.
Experts have identified more than 100 different types of liver disease.
Also Check: How Do Doctors Test For Hepatitis C