What Does A Reactive Hcv Antibody Test Result Mean
A reactive or positive antibody test means you have been infected with the hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true if they have cleared the virus, have been cured, or still have the virus in their blood.
A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you currently have hepatitis C and a follow-up test is needed.
Question 4 What Do These Test Results Mean: < 15 Detected And < 15 Not Detected
A < 15 Detected viral load result means the assay detected HCV RNA in the patients specimen at a very low level , but could not measure the precise level. A < 15 Not Detected viral load result means the assay did not detect HCV RNA in the patients specimen.
This test is performed using a Taqman® assay. The lowest viral load this assay can accurately quantify is 15 IU/mL, but the qualitative limit of detection is in the 10 to 13 IU/mL range. Therefore, even when the viral load is below 15 IU/mL, we can still report qualitative detection of HCV RNA consistent with active infection in some cases.
Summary Of The Literature
For the all-adult review, the initial literature search yielded 4,867 studies. Twenty-nine duplicates were identified. Of 4,838 unique studies, 4,170 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 668 full texts for review. Among these, 368 studies had data available to extract.
For the pregnancy review, the initial literature search yielded 1,500 studies. Two duplicates were identified. Of 1,498 unique studies, 1,412 were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 86 full texts for review.
The supplementary review yielded an additional 1,038 and 195 studies among all adults and pregnant women, respectively. Of these, 912 and 168 , respectively, were deemed irrelevant by title/abstract screening, resulting in 126 and 27 , respectively, full texts for review. One study was added to the pregnant women review outside of the formal literature search .
Considering all 104 applicable studies, the median anti-HCV positivity prevalence among all adults was 6.6% . Median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.7% for the general population , 7.5% for ED patients , 3.3% for birth cohort members , 9.3% for others/multiple risk factors , 54.2% for persons who use drugs , 5.2% for persons with HIV or sexual risk , and 4.7% for immigrants . Considering 26 applicable studies among pregnant women, median anti-HCV positivity prevalence was 1.2% .
Don’t Miss: How Do They Check For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C: Diagnosis And Treatment
THAD WILKINS, MD JENNIFER K. MALCOLM, DO DIMPLE RAINA, MD and ROBERT R. SCHADE, MD, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia.
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Jun 1 81:1351-1357.
An estimated 170 million persons, or 3 percent of the worlds population, are chronically infected with the hepatitis C virus .1 In the United States, the prevalence of hepatitis C antibody is 2 percent in adults 20 years and older, but the prevalence is higher in groups at increased risk .2,3 HCV, a single-stranded RNA virus, is transmitted through percutaneous exposure to infected blood.4 HCV is categorized into nine genetically distinct genotypes.5 In the United States, 72 percent of patients with HCV infection have genotype 1 16 to 19 percent have genotype 2 8 to 10 percent have genotype 3 and 1 to 2 percent have other genotypes.6 This article focuses on chronic HCV infection in adults and excludes special groups, such as children, pregnant women, transplant recipients, and persons coinfected with hepatitis B virus or human immunodeficiency virus .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Persons who are not at increased risk should not be screened for HCV infection.
HCV = hepatitis C virus.
*Recommendation for treatment is C because the outcome is a surrogate marker rather than mortality.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Persons who are not at increased risk should not be screened for HCV infection.
HCV = hepatitis C virus.
Hcv Core Antigen Testing
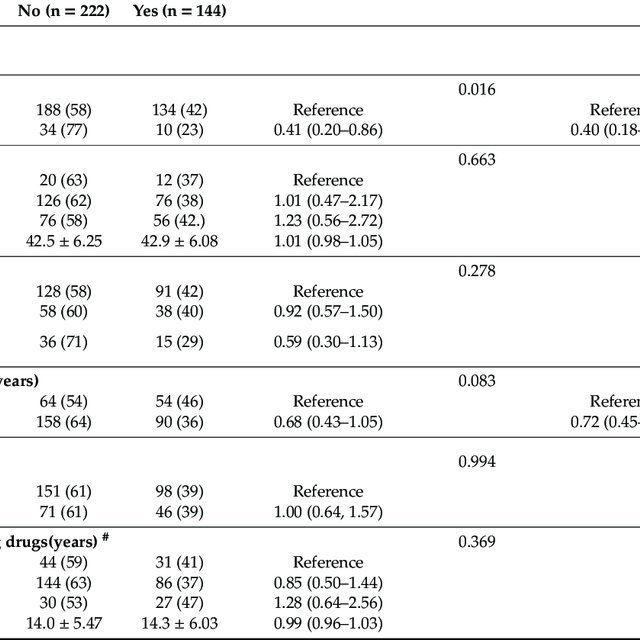
The hepatitis C core antigen is a viral protein. Since the core antigen is part of hepatitis C virus, it can usually be found in the bloodstream two weeks after infection.
Since HCV core antigen testing is simpler and less expensive than viral-load testing, some experts suggest using it in resource-limited settings. Core antigen testing can be usedoften with HCV antibody testingto detect acute HCV or to confirm chronic HCV infection. HCV core antigen testing can also be used to measure treatment outcome. Although it does not detect low levels of HCV , usually the hepatitis C viral load is much higher in people who relapse after HCV treatment.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Persons With Chronic Diseases
Refer to Immunization of Persons with Chronic Diseases in Part 3 for additional general information about vaccination of people with chronic diseases.
Chronic renal disease and patients on dialysis
People with chronic renal disease may respond sub-optimally to HB vaccine and experience more rapid decline of anti-HBs titres, and are therefore recommended immunization with a higher vaccine dose. Individuals undergoing chronic dialysis are also at increased risk for HB infection. In people with chronic renal disease anti-HBs titre should be evaluated annually and booster doses using a higher vaccine dose should be given as necessary.
Neurologic disorders
People with conditions such as autism spectrum disorders or demyelinating disorders should receive all routinely recommended immunizations, including HB-containing vaccine.
Chronic liver disease
HB immunization is recommended for non-immune persons with chronic liver disease, including those infected with hepatitis C, because they are at risk of more severe disease if infection occurs. Vaccination should be completed early in the course of the disease, as the immune response to vaccine is suboptimal in advanced liver disease. Post-immunization serologic testing may be used to confirm vaccine response.
Non-malignant hematologic disorders
Persons with bleeding disorders and other people receiving repeated infusions of blood or blood products are considered to be at higher risk of contracting HB and should be offered HB vaccine.
Question 6 Why Didnt The Test Reflex To Hcv Genotype When My Patient Had A Detectable Viral Load
The LiPA usually requires a minimum viral load of 300 IU/mL to successfully obtain a genotype. Since the viral load assay used in this reflex test has a much lower limit of quantitation, it is possible for the patient to have a detectable viral load and not have a reportable genotype result. Therefore, this test code does not reflex to HCV genotype if the patients viral load is < 300 IU/mL.
You May Like: How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs — even if it was just once or a long time ago.
- Youâre on kidney dialysis.
- You have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels .
- You had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992.
- Youâve ever gotten clotting factor concentrates made before 1987.
- You received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C virus.
- Youâre a health care worker, first responder, or have another job that exposes you to HCV-infected needles.
- You were born to a mother with HCV.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hepatitis C From Food
Adverse Effects Of Treatment
Adherence to treatment remains a major factor influencing the rates of sustained virologic response.33,42 Discontinuation of therapy because of adverse events is common and has been reported in up to one third of patients. Approximately 50 to 60 percent of patients may exhibit self-limited influenza-like symptoms with interferon-based therapy.2 Effective management of treatment-related adverse events is essential to improve adherence to treatment therefore, patients should be monitored closely for hematologic, renal, and thyroid abnormalities. Approximately 30 percent of patients undergoing treatment for HCV infection experience depression, emotional lability, or anger, but treatment is rarely associated with suicidal ideation or hallucinations.43 Treatment for HCV infection is contraindicated in persons with uncontrolled major depression.32 A recent randomized trial found that the overall adverse effects of pegylated interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin and pegylated interferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin were similar.40 Adverse effects of pegylated interferon and ribavirin for the treatment of HCV infection are listed in Table 8.32
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
Adverse Effects of Pegylated Interferon and Ribavirin for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Information from reference 32.
What Is Being Tested
Hepatitis C is a virus that causes an infection of the liver that is marked by liver inflammation and damage. Hepatitis C tests are a group of tests that are performed to diagnose hepatitis C infection and to guide and monitor treatment of the infection.
Hepatitis C tests include:
Hepatitis C is one of five viruses identified so far, including A, B, D, and E, that are known to cause hepatitis.
HCV is spread when contaminated blood enters the body, primarily though sharing needles and syringes during IV drug use. HCV is spread less commonly by sharing personal items contaminated with blood , through sex with an infected person, needlestick injuries to healthcare workers, unregulated tattooing, and from mother to baby during pregnancy and childbirth. Before tests for HCV became available in the 1990s, HCV was often transmitted by blood transfusions. Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Organ Does Hepatitis C Affect
Question 2 Why Are Hcv Rna Results Being Reported In Iu/ml
Results are reported in international units per milliliter to facilitate comparisons between results generated by different test methods. This is important because the various methods used by different laboratories are not standardized against each other. Use of IU/mL reporting units helps to make the comparison of viral load results across different methods more reliable.
Determining The Prevalence Threshold For The Recommendations
Although the intent of public health screening is usually to identify undiagnosed disease, many persons previously diagnosed with hepatitis C are not appropriately linked to care and are not cured of their HCV infection, thereby representing an ongoing source of transmission. Therefore, the prevalence threshold of 0.1% should be determined on the basis of estimates of chronic hepatitis C prevalence, regardless of whether hepatitis C has been diagnosed previously.
Recommended Reading: How To Know If I Have Hepatitis
Question 3 Why Does Quest Diagnostics Also Report Results As Log Iu/ml
This makes it easier to understand whether a change in viral load is clinically meaningful.
Replicate PCR test results using the same specimen can vary analytically by as much as 0.5 log IU/mL thus, only changes greater than 0.5 log IU/mL from one measurement to the next are considered to represent true changes in viral load.3 Reporting the viral load results in log IU/mL units helps the healthcare provider accurately interpret changes in viral load and better assess a patient’s response to antiviral treatment.
Viral Loads During Treatment
Checking your virus count before, during, and after treatment tells your doctor if and how well your drugs are working. A rising viral load doesnât always mean youâre getting sicker, and a drop in the virus count isnât a sign that youâre on your way to being cured.
Unlike with HIV, where lower viral counts usually mean longer, healthier life, HCV viral loads donât say much about how fast your hep C is progressing or how your disease might turn out. For that, your doctor will need to check your liver enzymes and your liver tissues and run other tests.
Usually, your hep C treatment will be the same no matter how high or low your viral load is. Your doctor will use your virus levels to monitor how you respond to the medication. The drugs youâre prescribed will depend less on your viral count than on your overall health, genetic makeup of your HCV, and other things.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Hepatitis C Sexually
Additional Tests You Might Need
Once youve been diagnosed with Hepatitis C, your doctor will likely order a number of tests to find out about the health of your liver and decide on a treatment plan thats most appropriate for you.
Hepatitis C genotype
The Hepatitis C genotype refers to a specific strain or type of the Hepatitis C virus. There are six major types of Hepatitis C around the world: genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. In the United States, genotypes 1, 2, and 3 are common:
- Genotype 1: Most Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 2: About 10% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
- Genotype 3: About 6% of Americans with Hepatitis C have this type
The genotype of Hepatitis C does not change over time, so you only need to get tested once.
Genotype tests are done before a person starts treatment. Hepatitis C treatment works differently for different genotypes, so knowing your genotype helps your doctor choose the best treatment for you.
Testing for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
Your doctor may test to see if your body is immune to Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B. If these tests show no prior exposure or protection, he or she will recommend that you be vaccinated against these two viruses to eliminate the chance of becoming infected.
Liver function tests or liver enzymes
- ALT
- AST
Liver function tests also include ALP and total bilirubin, among other things.
Tests to measure liver scarring or fibrosis
- Liver Biopsy
- Elastography
- Serum markers
Imaging tests
What Is Hepatitis C Test
Hepatitis C Test is a blood test that is used for the detection of the Hepatitis C virus. There are several types of Hepatitis C test that is used by doctors for the diagnosis of Hepatitis C. The varied Hepatitis C tests are
Hepatitis C Antibody Test : Hepatitis C antibody test is used by doctors to ascertain whether or not a person has been affected by the HCV at any point of his/her life by detecting Hepatitis C antibodies in the blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test : Also referred to as PCR test, this test screens for current infection of the virus.
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test: As the name suggests it is a quantitative test and measures the amount of Hepatitis C virus in the body. The Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test is also referred to as viral load test.
Recommended Reading: Is Milk Thistle Good For Hepatitis C
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
Should pregnant women be tested for HCV antibodies?
Yes. All pregnant women should be screened for anti-HCV during each pregnancy, except in settings where the prevalence of HCV infection is < 0.1% . Pregnant women with known risk factors should be tested during each pregnancy, regardless of setting prevalence. Any pregnant women testing positive for anti-HCV should receive a PCR test for HCV RNA to determine current infection status.
Can a mother with hepatitis C infect her infant during birth?
The overall risk of an infected mother transmitting HCV to her infant is approximately 4%8% per pregnancy . Transmission occurs during pregnancy or childbirth, and no prophylaxis is available to protect the newborn from infection. The risk is significantly higher if the mother has a high HCV viral load, or is coinfected with HIV with which the rate of transmission ranges from 8%15% . Most infants infected with HCV at birth have no symptoms.
Should a woman with hepatitis C be advised against breastfeeding?
When should children born to HCV-infected mothers be tested to see if they were infected at birth?
How Hepatitis C Is Diagnosed
To determine a hepatitis C diagnosis, your doctor will:
- Get your medical history .
- Perform a physical exam, especially checking for changes in skin color, swelling in your lower extremities, and tenderness in your abdomen.
- Order certain diagnostic blood tests.
The first diagnostic tool in the screening process is a blood test that screens for HCV antibodies proteins the body produces in response to the virus. An enzyme immunoassay is used to perform this test.
A negative result for the antibody test means that you’ve never had HCV in your blood, while a positive result means you were exposed to the virus at some point in your life. Up to a quarter of people spontaneously clear the virus from their blood within six months of contracting it.
Because EIA sometimes produces false-positive results, a test called recombinant immunoblot assay may be used to confirm that you have the HCV antibody. This test is not necessary for most patients, and it is more commonly performed by blood banks to check for the virus in donated blood.
A negative EIA result may just mean that your body has not yet produced the HCV antibody , and you may need to be tested again in a few months.
If you have a positive antibody test, your doctor will then use another blood sample to conduct a qualitative polymerase chain reaction test or a process called transcription-mediated amplification , which looks for the presence or absence of RNA of HCV in your blood.
Also Check: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C