Hepatitis C: New Drug Treatment ‘is A Breakthrough’
A new treatment for hepatitis C “cured” 90% of patients with the infection in 12 weeks, scientists said.
The study is a “major breakthrough” and marks a “turning point” in hepatitis C treatment, said experts.
More than 200,000 people are infected with hepatitis in the UK, and deaths from the infection have increased threefold since 1996.
Only 3% of patients in the UK currently opt for the existing treatment, which only works half of the time.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis C
The new hepatitis C medicines have not been tested in pregnancy.
You should not become pregnant while taking treatment as it could be harmful to unborn babies.
If you’re pregnant, you must delay treatment until after your baby is born.
Speak to your doctor before starting hepatitis C treatment if you’re planning to become pregnant in the near future.
You’ll need to wait several weeks after treatment has ended before trying to get pregnant.
Women taking ribavirin should use contraception during treatment and for another 4 months after the end of treatment.
Men taking ribavirin should use a condom during treatment and for another 7 months after the end of treatment. This is because semen can contain ribavirin.
If you become pregnant during treatment, speak to your doctor as soon as possible to discuss your treatment options.
Treatment Of Hepatitis C In The Future New Models Of Care
Treatment of hepatitis C currently occurs in specialist liver clinics, typically within tertiary hospitals. This system is very effective and necessary to manage the complexities of interferon-based treatment. However, capacity is limited. Patients with advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis will need to remain in the tertiary system for management of their liver disease. However, patients who do not have cirrhosis may not need to be managed in a specialist clinic if they can be treated with simple interferon-free regimens. This will allow new models of care involving GPs, nurse practitioners, opioid-substitution therapy clinics and the custodial system. The PBAC has recommended that newer hepatitis C therapies are listed on the general schedule to promote treatment in primary care.
Don’t Miss: Where Do I Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Complementary And Alternative Options
For patients preferring a more natural option, there are a few complementary and alternative remedies that may help improve liver health. One type of alternative option that has been studied a lot is dietary supplements, some of which have found promising effects.
They include:
- Milk Thistle an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant that appears to inhibit lipid peroxidation and provide hepatoprotective properties, such as what is found in UltraThistle
- Stronger Neominophagen C potential benefits include hepatic cellular membrane stabilization and PGE2 production inhibition
- Cathy Herbal Tablet a combination of 19 Chinese herbs that may lower alanine transaminase levels
- Thymus Extract which some studies have found to help reduce HCV RNA
Is Hep C Curable
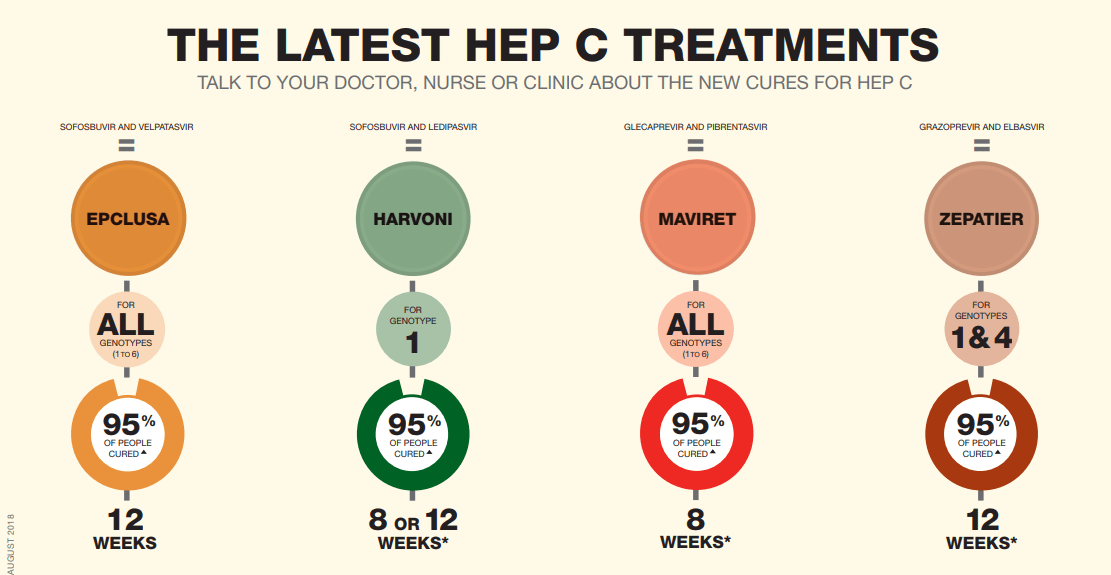
The latest drugs available for hepatitis C have high success rates when it comes to curing the condition.
In conversations with your doctor, you can discuss the full range of treatment options. Some of these are combination drugs.
But its important to note that not every medication may be effective for you, even if its for the right genotype.
You May Like: Types Of Hepatitis B Virus
First Hepatitis C Treatment Developed Through South
- New treatment combination for hepatitis C virus is an additional affordable option for millions still waiting for access to lifesaving treatments in middle-income countries
- Combination is safe and effective, including for hard-to-treat cases and people with HCV and HIV
- New drug ravidasvir is the first HCV drug to be developed through South-South collaboration and with support from non-profit organizations
The National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency of Malaysia has granted a conditional registration for a safe, effective hepatitis C treatment developed by a public-private partnership bringing together the Malaysian Ministry of Health, not-for-profit research and development organization Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative , Egyptian pharmaceutical company Pharco, Malaysian pharmaceutical company Pharmaniaga Berhad, and non-governmental-organization Médecins Sans Frontières/Doctors Without Borders .
This is the very first drug for HCV to be developed through South-South collaboration and with funding and clinical support from non-profit organizations.
The approval on 4 June concerns a new drug, ravidasvir, for the treatment of chronic HCV infection in adults in combination with other medicinal products. Ravidasvir was developed by the partnership for use with sofosbuvir, an existing DAA, as an affordable, simple, and efficacious public health tool.
Plans to register the new ravidasvir + sofosbuvir combination are advancing in other countries, including in Latin America.
Why Are The New Hepatitis C Treatments Better
The new treatments are highly effective with a cure rate of 95-97 per cent. Treatment time is reduced to 12 weeks, drugs are tablets and there are very few side effects.
This is a major change from just a few years ago, when hepatitis C treatment time was from six to twelve months, with toxic side effects, and only a 50 percent chance of being cured.
This means that people newly diagnosed with hepatitis C, as well as those who have been living with chronic hepatitis C for many years, will now have access to a fast, effective and well-tolerated cure.
You May Like: How Do You Get Hepatitis B And C
Exacerbation Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis
In the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, HBe seroconversion was sometimes preceded by transient and moderate worsening of serum transaminases, but severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection and fatal liver failure can occur. Such fatalities were reported in under 0.5% of patients with hepatitis B . Patients with active cirrhosis or a previous history of decompensated cirrhosis are particularly susceptible to these complications .
Acute exacerbation of hepatitis is an extremely rare complication of chronic hepatitis C treatment. An exaggerated immune response to hepatitis virus was supposedly the cause of acute icteric hepatitis in two patients .
-
A 43-year-old man had a moderate rise in hepatic transaminase activities after 4 weeks of interferon alfa treatment. His liver tests normalized after withdrawal, but the aspartate transaminase activity increased dramatically shortly after treatment was restarted. His condition rapidly deteriorated, with a diagnosis of hepatorenal failure, and he finally required liver transplantation. Histological examination of the liver showed advanced micronodular cirrhosis, a feature not found on pretreatment liver biopsy.
In another study, only four of 11 241 patients treated with interferon alfa died of fulminant liver failure .
Talia B. Baker, Juan Carlos Caicedo, in, 2017
What Will My Doctor Need To Know To Treat Me
If you want to be assessed for treatment, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. They will be mostly interested in the condition of your liver. Your doctor will organise, if possible, for you to have a Fibroscan examination. If Fibroscan is not available, your doctor will probably use an APRI test. This is an online calculator that estimates the health of your liver. It involves a blood test called a liver function test.
Dont forget, its very important to get a PCR test 12 weeks after finishing treatment this will mean the doctor can make sure you are cured.
You May Like: Which Is Worse Hepatitis B Or C
You May Like: Hepatitis C Non Reactive Test Result
Treating Chronic Hepatitis C
A Promising New Drug: PeginterferonIn January 2001, the FDA approved Peg-Intron to treat hepatitis C. Peginterferon is a form of interferon-alpha that stays active in the immune system longer than interferon-alpha. As a result, it can be taken once a week, as opposed to three times a week.Two recent studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine compared the effects of another brand of peginterferon, called Pegasys, with interferon-alpha on patients with chronic hepatitis C. Both studies revealed that peginterferon is significantly more effective in managing the virus. It was also better tolerated and had fewer side effects.In the clinic, interferon-alpha is usually given in combination with ribavirin, which has been shown to double the effectiveness of interferon-alpha. Researchers regard testing a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin the next logical step in determining how to treat this disease more successfully.
Role Of Ribavirin In The Era Of Direct
Ribavirin was a critical component of hepatitis C treatment in the era of interferon-based therapy however, its role in DAA regimens was initially unclear. At this time, guidelines do recommend the use of ribavirin in combination with DAAs, depending on genotype and presence or absence of cirrhosis. For example, there is evidence to support the use of ribavirin in specific situations, such as patients using sofosbuvir-based regimens who are either HCV genotype 1, treatment-experienced, and cirrhotic, or HCV genotype 3 with cirrhosis . SVR rates tend to be lower among HCV genotype 3 patients with advanced liver disease . In the ALLY-3+ study, ribavirin was investigated in combination with daclatasvir and sofosbuvir in patients who were HCV genotype 3, both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced, and with advanced fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis. They achieved an overall SVR rate at 12 weeks of 90% . These results, in combination with other studies, support the addition of ribavirin to achieve higher rates of SVR, allow shortening of treatment, and decrease the cost of treatment.
You May Like: Hepatitis A B C Difference
How Many Victorians Are Affected By Hepatitis C And Who Is Affected
Hepatitis C is the most common blood borne virus in Australia with approximately 230,000 people currently living with hepatitis C in Australia and around 65,000 in Victoria.
The population most at risk of acquiring hepatitis C are people who currently inject drugs including people from Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander and culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds, prisoners, older people, and young injectors and/or new initiates to injecting drug use.
Oral Antiviral Hepatitis C Medications

Before 2014, hepatitis C was treated with interferon and ribavirin and required getting a shot once a week along with taking the drug in pill form. Yet, the problem with interferon was not just that it was typically unsuccessful, but patients taking this drug also often experienced numerous adverse effects.
Fast forward to today and people diagnosed with HCV have many antiviral medication options that can help treat this virus and without the effects of interferon. Ribavirin is still one, although the National Institute of Health indicates that it doesnt treat HCV unless it is combined with another medication.
Other combinations of HCV drugs available in 2022 include:
- Elbasvir and Grazoprevir a combination HCV NS5A inhibitor and protease inhibitor that is taken once daily for 12 to 16 weeks
- Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir a combination HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor and HCV NS5A inhibitor that is taken once daily for 8 to 16 weeks
- Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir a combination HCV NS5A inhibitor and nucleotide polymerase inhibitor that is taken once daily for 8 to 24 weeks
- Sofosbuvir and Velpatasvir a combination HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor and HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitor that is taken once daily for up to 12 weeks
- Sofosbuvir, Velpatasvir, and Voxilaprevir a combination non-nucleoside NS5B polymerase inhibitor, HCV NS5A inhibitor, and HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor that is taken once daily for up to 12 weeks
You May Like: Hepatitis A What Is It
A Promise Of A Cure With A Cost
These new medicines are expensive. Researchers believe that as more come to the marketplace, prices will drop to stay competitive. If you have life-threatening liver damage due to the hepatitis C virus, you might be eligible for “compassionate care” rates, which can greatly reduce your out-of-pocket cost. Ask your doctor or case manager or directly contact the drug manufacturers.
Remember, there is no one-size-fits all treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Which medication is best for you depends on many things, including:
- The amount of liver damage
- Your previous treatments
Another Potential Curative Drug For People With Chronic Hepatitis C Will Be Made Available On The Nhs
New draft guidance published today from NICE recommends elbasvir-grazoprevir – one of the newer hepatitis C antiviral drugs that can offer patients more effective treatment.
In clinical trials, elbasvir-grazoprevir showed cure rates above 90% for people with genotypes 1 and 4. The cure rate is dependent on the genotype, treatment history and presence of liver damage.
Professor Carole Longson, director of the NICE centre for health technology evaluation, said:Treating chronic hepatitis C had previously been a major challenge with patients having to experience long and unpleasant courses of treatment.
Elbasvir-grazoprevir, like other newer direct acting anti-viral treatments, is a drug that provides considerable health benefits to patients without some of the adverse side effects associated with earlier anti-viral treatments, such as peginterferon alpha with ribavirin.
A 12-week course of treatment with elbasvir-grazoprevir usually costs £36,500 per patient, but the NHS will pay less than this as the company has offered a confidential discount.
Taken once daily, the tablet could treat around 4,000 patients in the first year, alongside other options already available for hepatitis C.
Professor Longson continued:Our positive recommendation for elbasvir-grazoprevir means that more treatment options will become available to patients with hepatitis C. And as these types of anti-viral drugs are more effective, the spread of the virus can be reduced.
Also Check: Does Hepatitis C Cause Itching
Mechanism Of Action Of Ther Apy For Hcv Infection
Basic research aimed at understanding the molecular pathways of the life cycle of the virus has been the engine that has driven the development of therapies for HCV infection over the past 20 years. HCV is a positive-strand RNA virus encoding a polyprotein that undergoes proteolytic cleavage to 10 polypeptides, each with distinct functions . The structural proteins consist of two envelope glycoproteins, both of which are targets of host antibody response, and the core protein, which interacts with progeny viral genomes for assembly of the virus.8 The nonstructural proteins NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B form a complex with viral RNA to initiate viral replication in a cytoplasmic membranous structure.8 Assembly of HCV requires close interactions with lipid droplets and lipoprotein metabolism.9 Mature virus is released from cells as lipoviral particles.10 HCV infects predominantly hepatocytes and has an uncanny ability to evade the host immune response in multiple ways.11
Life Cycle of the Hepatitis C Virus and Targets of Therapy
Treatments For Hepatitis C
The goal of treatment is a virological cure . This is defined as undetectable viral RNA in plasma 24 weeks after treatment has finished. A sustained virological response prevents the development of cirrhosis. In patients who already have cirrhosis, a sustained virological response reduces the risks of liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma.
The approved treatment combinations for hepatitis C in Australia are summarised in Tables 2 and 3. Currently, all PBS-subsidised regimens involve peginterferon plus ribavirin.
TABLE 3 TGA-approved interferon-free regimens for hepatitis C
| Viral genotype |
|---|
F0-3 METAVIR fibrosis stage 0-3
F4 METAVIR fibrosis stage 4
* Not listed on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme at the time of writing.
Response rate was defined as proportion of patients with a sustained virological response measured at 3 or 6 months after the end of treatment.
8 weeks may be considered in treatment-naïve patients with no cirrhosis and a baseline viral RNA concentration < 6 x 106 IU/mL.
§ 24 weeks is recommended for patients who have failed treatment with peginterferon + ribavirin with or without a protease inhibitor.
# 24 weeks is recommended for patients who have had a previous null response to peginterferon + ribavirin, defined by a decrease in the viral RNA level of < 2 log10 IU/mL at week 12 or < 1 log10 IU/mL at week 4 during previous peginterferon + ribavirin treatment.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
The Future Of Hcv Treatment
More research is being conducted every day to help identify any new treatment remedies that are effective for curing or reducing the progression of HCV.
As scientists begin to learn more about and better understand these remedies and their effects, its likely that more options will be added to this list as time goes on, offering even more hope for people who have the hepatitis C virus.
A New Way To Beat The Disease
So far, hepatitis C drugs target the virus itself, but research is under way to create new drugs that target the cells that host the virus.
âThere are two ways to prevent a virus from growing: You target the virus or target the cell,â Polyak says. âHepatitis C is capable of mutating, which can lead to resistance to drugs that target the virus. In theory, development of drug-resistant viruses is less of an issue with drugs that target the cell.â
Read Also: Rx Vitamins For Pets Hepato Support
What About Patients With Hepatitis C Who Also Have Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus can flare in patients who are co-infected with hepatitis B and hepatitis C and are taking medication for hepatitis C. This has been reported as a potential risk for patients who are taking hepatitis C treatment and have underlying hepatitis B as well. The flare usually occurs within a few weeks after the patient starts taking medication for hepatitis C. Therefore, patients who have both hepatitis B and hepatitis C should be seen by a hepatitis expertbeforestarting treatment of the hepatitis C they may need to start taking hepatitis B treatment to avoid a hepatitis B flare.
What Can People Do To Help The Medications Work Best

- Take the medications every day
- Stay in touch with pharmacy to be sure that all refills are ready on time
- Take the medications exactly as prescribed
- Do not skip doses
- Get all blood tests done on time
- Go to all visits with providers as recommended
- Tell the provider about all other medications that are being taken – including over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbs, and supplements
- Complete the entire course of medication
Also Check: How Do You Screen For Hepatitis C