Sometimes The Infection Goes Away On Its Own
Acute hepatitis is C is a short-term illness that occurs within the first six months after being exposed to the virus. Like the human papillomavirus , early acute hepatitis C can clear on its own without treatment this happens about 25% of the time.
However, it’s more likely that the virus will remain in your body longer than six months, at which point it’s considered to be chronic hepatitis C infection.
“Being younger or a woman tends to be a factor in whether the virus clears on its own, and genetics may play a role,” Reau says. “But we can’t determine with certainty which people are certain to clear the infection and which aren’t.”
Coinfection And Viral Interactions
Other conditions, such as HIV and hepatitis B, can alter your treatment plan.
For example, having hepatitis C and B infections simultaneously can progression, and antiviral treatment of either condition can also reactivate the other. In addition, certain hepatitis C treatments may not be suitable for people with HIV due to possible drug interactions.
To prevent adverse outcomes, your doctor will screen for possible coinfections and alter your medication programs accordingly.
What To Do For Relapsers After Hepatitis C Treatment
DOCTOR’S VIEWS ARCHIVE
Topic: Hepatitis C, June 2000
Dr. Lee: I have a viewer who underwent six months of treatment with interferon alone. After the treatment his hepatitis C RNA test initially dropped and now is back at high levels again. What can we offer this patient who has developed disease relapse after treatment?
Dr. Edward Block:Since he was initially treated with a single agent , he couldbe re-treated with combination treatment . We can hope for re-treatment success rate of up to 30 to 40% with this combination.
Dr. Lee: If we can achieve sustained eradication of virus for six months after completing treatment, are these patients considered cured forever?
Dr. Edward Block: Well, we are a little reluctant to use the term “cured” at this time, since we have only a few years of data available.
But I believe that if one is disease-free at six months following treatment completion, you are essentially cured.
We now have data that goes out 5 to 6 years. The recurrence rate of Hepatitis C in patients who are free of the virus at six months after treatment is extremely low . So for the majority of patients successfully treated, they can consider themselves essentially cured.
Dr. Lee: Another viewer has undergone six months of combination therapy with interferon injections with ribavirin. This viewer also experienced a relapse several months after cessation of treatment. What would you do now?
Back to Doctors’ Dialogue Index
SLIDESHOW
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B Or C Contagious
Know Who Is At Risk For Reinfection And Treat Accordingly
Providers should advise patients that having antibodies for hepatitis C does not confer protection against reinfection. Antibody screening tests for hepatitis C are not useful in individuals who have already been infected and then treated, Reau points out.
“A hepatitis C antibody test remains positive after spontaneous clearance or cure through antiviral therapy,” she says. “So if your patient is concerned about re-exposure, you have to look for the virus through polymerase chain reaction.”
Providers should also counsel patients about avoiding exposure. Some risk factors for reinfection include injected illegal drugs, exposure through contaminated blood, and injections in substandard healthcare settings.
In one recent meta-analysis, hepatitis C virus-monoinfected patients at low risk for recurrence had a 1% rate of hepatitis C virus RNA positivity at 5 years compared with 11% among people at high risk, such as intravenous drug users and prisoners.
Among people who inject drugs, the rate of reinfection is 2%-3% annually. Similarly, about 3% of HIV-infected men who have sex with men are reinfected per year. Men who have sex with men while taking prophylaxis for HIV may also run an increased risk for reinfection, Terrault says.
Terrault recommends annual hepatitis C testing for people who inject drugs, in HIV-positive men who have sex with men, as well as those with increased alanine aminotransferase levels.
Tables
Can Hepatitis C Be Treated
Yes, since 2010 enormous progress has been made in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. New therapies called direct-acting antivirals are pills that act on the virus itself to eradicate it from the body, unlike older medicines like interferon injections which work by stimulating an immune response. These new treatments are very effective and can achieve cure rates of over 90%. In most situations now, there is no need for interferon, which was responsible for many of the side effects previously associated with HCV treatment. The new treatment combinations require shorter treatment durations , have reduced side effects and appear to be effective at all stages of the disease.
Because these new therapies are very new, they remain very expensive. As such, drug coverage from both government and private companies may require that your liver disease has progressed to a certain stage before they are willing to cover the cost of these drugs.
Your primary care physician may refer you to a specialist to determine whether you are eligible for treatment. A specialist will help you decide which drug therapy is best for you based on the severity of your liver disease, your virus genotype and whether or not you have been treated in the past.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Treatment Options For Hepatitis C
What To Do To Avoid Relapsing After Hep C Treatment
Over the years of walking through Hepatitis C treatment with hundreds and hundreds of people, I have developed a very simple formula for avoiding relapse.
If you follow these tips your chances of having a relapse will be very, very low.
Click this link for more information on preventing relapse from Hep C treatment
- Post Categories
Getting Tested For Hepatitis C
Seek medical advice if you have persistent symptoms of hepatitis C or there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you do not have any symptoms.
A blood test can be carried out to see if you have the infection.
GPs, sexual health clinics, genitourinary medicine clinics or drug treatment services all offer testing for hepatitis C.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent or limit any damage to your liver, as well as help ensure the infection is not passed on to other people.
Also Check: What Type Of Hepatitis Can Be Cured
After Treatment Begins When Is A Patient ‘cured’
For the pivotal trials leading to the approval of the current hepatitis C antiviral drugs, the researchers defined treatment success as an undetectable RNA level for the virus 12 weeks after completing the therapy, otherwise known as sustained virologic response 12.
Relapses beyond SVR 12 are extremely rare. In a large study evaluating late relapse, hepatitis C RNA was detected in just 12 of 3004 patients with SVR12 between weeks 12 and 24. Phylogenetic sequencing showed 7 to be new infections.
Still, providers should test for the virus at 24 to 48 weeks after the end of treatment , Terrault says. When no hepatitis C RNA is detectable at SVR48, providers can confidently tell patients they are cured and do not need any further testing for hepatitis C. The exception to this, she says, is if a patient is determined to be at risk for reinfection.
What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a bloodborne virus that causes inflammation of the liver. This virus is present in the blood of a person living with hepatitis C and can be spread through blood-to-blood contact.
In Australia, hepatitis C is commonly spread through sharing injecting equipment including needles, syringes and other equipment. It is not spread by kissing, hugging or sharing food.
Current treatment is effective at curing hepatitis C for more than 95% of people. Treatment cures the infection, decreases inflammation in the liver and reduces the long-term risk of health problems including chronic liver disease and liver cancer.
Accessing curative treatment also prevents transmission to others. There is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C infection.
Don’t Miss: What Hepatitis Vaccines Are Available
If You Notice Symptoms See A Doctor Right Away
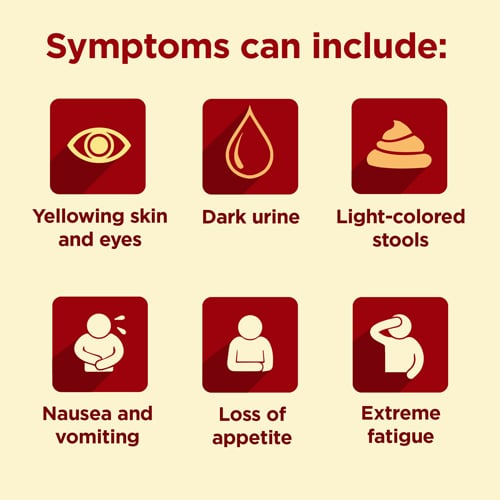
Symptoms of hepatitis C include the following:
- Jaundice a yellowish tone to the eyes and skin
- Mild, chronic right belly pain
- Loss of appetite
If you believe you have been exposed to hepatitis C or notice any symptoms, visit your primary care doctor as soon as possible. If you test positive for the virus, your doctor can refer you to a hepatologist to discuss your options.
“I strongly encourage all baby boomers and others who are at high risk to get tested, even if you don’t look or feel sick,” Reau says. “If you do have hepatitis C, the earlier we discover it, the more likely we can prevent it from progressing and causing more serious damage.”
I Normally Go For Regular Liver Check
All doctors, specialists, nurses, and health staff are doing everything they can to make clinics as safe as possible at this time. We recommend calling your doctor or specialist before any appointment to check. They might do an appointment over the phone or there might be extra steps and precautions to take when you visit.
For more information on what healthcare is available through Telehealth > > >
You May Like: What Does Chronic Hepatitis C Mean
Also Check: What Do You Get Hepatitis C From
You May Still Need To Have Follow
Once youve been treated for hepatitis C, your doctor will perform another blood test to see if the virus is still present, says Omar Massoud, MD, chief of hepatology at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio.
Then you will be tested after another three months to make sure the virus has not come back. If all tests are negative, you are cured, says Dr. Massoud.
Since hepatitis C doesnt always cause any symptoms, you may not feel any different after being cured. If you were experiencing symptoms fatigue is the common one you should start to feel stronger and more energetic, which should continue to improve after you finish treatment, says Massoud.
Can I Be Re
For sure. Whatever contributed to you getting Hepatitis C the first time, if you do it again, youll probably have the same outcome. Injecting drugs and unsafe sex practices are among the most common ways that people are infected and re-infected with HCV. If youre doing either, its important to have an annual HCV RNA screening to check for re-infection. You can lower your risk by using clean needles and condoms for sex.
Don’t Miss: How Much Are Hepatitis B Shots
Treatments For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be treated with medicines that stop the virus multiplying inside the body. These usually need to be taken for several weeks.
Until recently, most people would have taken 2 main medicines called pegylated interferon and ribavirin .
Tablet-only treatments are now available.
These new hepatitis C medicines have been found to make treatment more effective, are easier to tolerate, and have shorter treatment courses.
They include sofosbuvir and daclatasvir.
Using the latest medications, more than 90% of people with hepatitis C may be cured.
But its important to be aware that you will not be immune to the infection and should take steps to reduce your risk of becoming infected again.
Read Also: How Can You Transmit Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Relapse After Treatment
One of the saddest and most difficult things for a person who has gone through Hepatitis C treatment is to learn at the end of treatment that the treatment has not been successful. That the Hepatitis C virus has returned.
This is called a relapse, but what it really means is that the Hepatitis C virus was never completely removed from the patients system.
A Hep C treatment relapse means that at the end of the treatment there were still some live viruses somehere in the patients body. As soon as the treatment stopped the Hep C virus began replicating again. The Hep C virus replicates very fast, which means if there is just one surviving virus particle at the end of treatment it can create billions of new virus particles within a few days of treatment ending.
In clinical situations about one in 35 people relapse after hepatitis C treatment. That what the statistical studies say. However in my personal, real-world experience, when people follow the treatment path I suggest, the release rate is more like one in 1,000.
I will talk in more detail about why people doing Hepatitis C treatment relapse at the end of this blog post because first I would like to share an email I received today from a guy in the USA who relapsed after 8 weeks treatment with Harvoni, which he got through his doctor and his health insurance. Later I will explain why he relapsed and how I was able to help him to be completely and finally cured.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Ql Meaning
Blood And Vessel Problems
People with hepatitis C often get a condition called cryoglobulinemia. This happens when certain proteins in your blood stick together in cold weather. They can build up in vessels and block blood flow, which causes swelling and damage. The condition can affect your skin, organs, nerves, and joints.
Hepatitis C also can cause problems with blood itself. You may not make enough white blood cells, which fight infections, or platelets, which help your blood clot.
The infection can also make you bruise easily or get red or purple spots under your skin. Those are signs of a bleeding disorder called immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
You Can Get Hepatitis C Again
Hepatitis C is unlike many other viruses, in the sense that you can be reinfected, even after youve been cured. While people whove been cured of the virus do have antibodies, they dont protect against the virus, says Massoud.
To avoid being reinfected, its important to take steps to avoid the virus. For example, dont share razors or syringes, and avoid sharing toothbrushes with others. Its also a good idea to ask your partner to be tested for hepatitis C, even though the risk of sexual transmission is low.
People who work in healthcare should take additional steps to protect themselves from accidental needlestick injuries.
Read Also: Causes Of Hepatitis C Transmission
What If I Want To Get Pregnant After Hcv Treatment
You should be OK, Dr. Terrault says. If you have mild fibrosis, pregnancy after HCV treatment should be very straightforward.
If you have stage F4 scarring, or cirrhosis, you do have potential risks of increased complications during pregnancy, but its pretty rare. If this is you, you might want to see a high-risk obstetrical group during your pregnancy. Not that the Hep C is causing any issuesits gone and its not going to be at any risk to the babybut you have underlying liver disease and do need a higher level of monitoring, says Dr. Terrault.
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis C Go Away
Preventing The Spread Of Hepatitis C
There is no vaccine available to prevent a person from being infected with hepatitis C. Recommended behaviours to prevent the spread of the virus include:
- Always use sterile injecting equipment. This can be accessed from your local needle and syringe program service.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as toothbrushes, razors, nail files or nail scissors, which can draw blood.
- If you are involved in body piercing, tattooing, electrolysis or acupuncture, always ensure that any instrument that pierces the skin is either single use or has been cleaned, disinfected and sterilised since it was last used.
- If you are a healthcare worker, follow standard precautions at all times.
- Wherever possible, wear single-use gloves if you give someone first aid or clean up blood or body fluids.
- Although hepatitis C is not generally considered to be a sexually transmissible infection in Australia, you may wish to consider safe sex practices if blood is going to be present, or if your partner has HIV infection. You may wish to further discuss this issue and personal risks with your doctor.
How Hepatitis C Medications Work
Hepatitis C is an infection that spreads through blood. In some cases, the body clears the virus on its own. Otherwise, the infection becomes chronic. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can lead to liver problems, including scarring of the liver , liver cancer, and liver failure.
Today, direct-acting antiviral oral medications cure both acute and chronic hepatitis C in more than 90 percent of people who take them within just 8 to 12 weeks. We would expect to be able to get rid of the virus in about 99.9 percent of people, even if it required more than one course, says Reau.
Although these new antiviral drugs effectively treat an infection, they cant prevent you from getting the virus again if youre exposed. Once youre cured of hepatitis C, your body develops antibodies, but they dont act against the virus, says K. V. Narayanan Menon, MD, a hepatologist and the medical director of liver transplantation at Cleveland Clinic.
You May Like: How Do You Get Tested For Hepatitis C