Hepatitis C And Liver Damage
THe HCV virus causes hepatitis C.
People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles. The virus is not easy to kill.
The CDC offers advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach might kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning, and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment may reduce the amount of HCV, but it might not stop a person contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so be sure to rinse the syringe thoroughly. Only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
A person cannot contract the virus from casual contact, breathing, kissing, or sharing food. There is no evidence that mosquito bites can transfer the virus.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
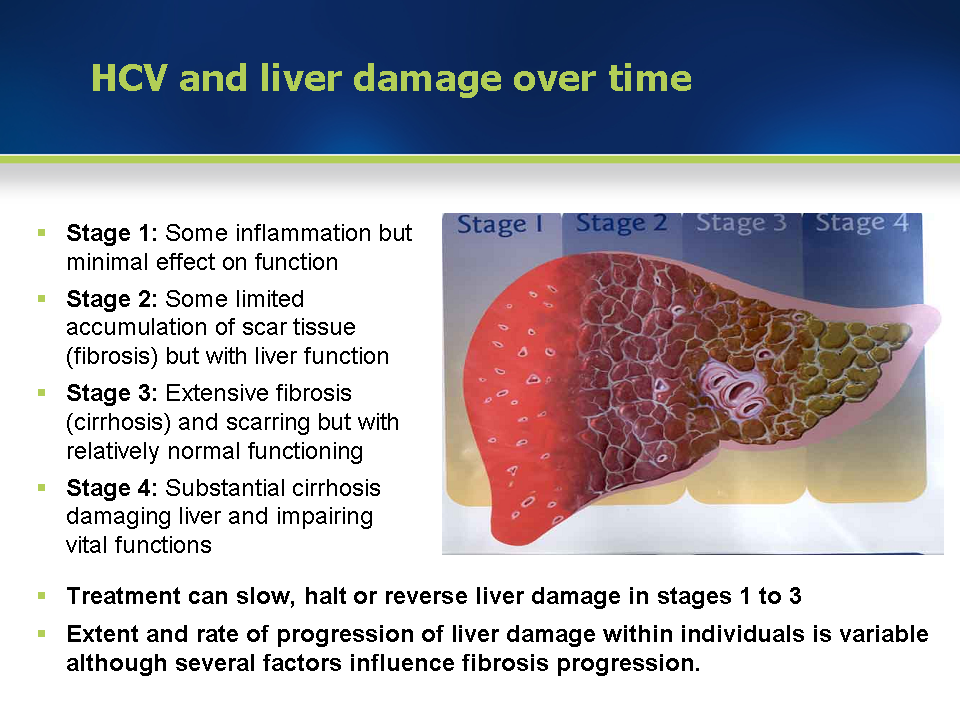
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
What Is Viral Hepatitis
In general terms, hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis is not one, but many diseases in which the liver becomes inflamed, and its cells are damaged as a result of inflammatory chemicals being produced and released in the liver.
Though hepatitis commonly results from one of five recognized hepatitis viruses A, B, C, D, or E it can also be caused by excessive alcohol, toxins, an unhealthy diet, various drugs, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disorders, poisons, fungal infections, and certain other viral infections , as well as some diseases of the biliary system.
Some forms of hepatitis are sudden and short-term while others are long-lasting and sometimes lifelong. While some types can become life-threatening, others have few or no long-lasting effects.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Symptoms How Do You Get It
Human Herpesvirus Type 8
Risk factors and epidemiology
Human herpesvirus 8 is a -herpesvirus, which has potential for malignant transformation. Although primary HHV-8 infection can cause rash and fever in children and immunocompromised individuals, the onset of HHV-8-related diseases usually occurs several years after HHV-8 acquisition: Kaposi sarcoma, body cavity lymphoma, and multicentric Castlemans disease are the typical presentations of HHV-8 infection but bone marrow aplasia and multiple myeloma has also been described in association with HHV-8 infection .
Clinical presentation
In autopsy studies Kaposi sarcoma involved the liver in approximately 20% of patients with AIDS and was usually part of a widespread cutaneous and visceral disease. Due to highly active antiretroviral combination therapy, Kaposi sarcoma has become a rare complication of HIV infection. However, fulminant hepatic Kaposi sarcoma may occur after organ transplantation . Macroscopically there are dark-red tumors on the skin, the liver capsule and the parenchyma. Under the microscope the typical lesion is a mesh of spindle-cell-like tumor cells and dilated thin-walled vessels .
Kaposi sarcoma after liver transplantation. Brownish nodules appear in the abdominal scars 12 weeks after liver transplantation. Histology reveals a spindle-cell rich tumor confirming the clinical diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma. In situ detection of human herpesvirus 8 in the Kaposi tissue.
Diagnosis
Contact The Hepatitis Infoline For More Information
Have questions about the causes of liver damage and disease? Get in touch with the Hepatitis Infoline and have your questions answered today. You can also browse our key services if youd like to know more about how we can help you understand hepatitis A, B, C and your liver.
Your health is more than just about your liver. If you want other information about your health, see our Commonwealth partner HealthDirect.
Read Also: Hepatitis A Vaccine For Adults
Know The Signs: What Liver Disease Looks Like In Hepatitis C
As many as 80% of people with hepatitis C have no symptoms of liver disease until it has started to progressa process that can take decades.
While getting tested for C if you are at risk is the best way to stay ahead of the disease, knowing the early and late-stage warning signs of liver damage also makes sense.
Your liver is tasked with a lot of important jobs from cleaning your blood to turning all that you eat and drink into energy and nutrients that your body can use. When it becomes infected with hepatitis C, the symptoms will affect all systems and organs related to the livers many functions.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis A Include Fatigue And Tummy Pain
Hepatitis A is a liver infection caused by the highly contagious Hepatitis A virus. Most people are vaccinated against the virus, and dont need any treatment if they come in contact with it.
The CDC recommends that unvaccinated people who encounter it to get a hepatitis A shot, and possibly an antibody drug, within two weeks of exposure.
Symptoms usually start within 15 to 50 days of coming into contact with the virus.
For most people, symptoms of hepatitis A include fatigue, loss of appetite, tummy pain, nausea, vomiting, yellow skin, dark urine, and pale poop.
Symptoms range in severity and usually last between a few weeks to about two months, without any long-term liver damage.
But in rare cases, the condition can become chronic and lead to liver failure and death. Older people and those with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of severe illness.
Kids younger than 6 years old with hepatitis A dont tend to get symptoms.
You May Like: Hepatitis B E Antibody Positive
Read Also: Hepatitis B How Do You Catch It
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
The hepatitis C virus is spread through contact with infected blood and bodily fluids, such as semen and vaginal fluid. You will only be infected if the virus enters your bloodstream.
In Canada, most people are infected by:
- using or sharing drug paraphernalia contaminated with infected blood, including:
- pipes
If you have hepatitis C, you can pass the virus to your baby during:
- pregnancy
- childbirth
- breastfeeding if your nipples are cracked and bleeding, and your baby also has bleeding in or on the mouth
- it can be hard to tell if a baby has bleeding in or on the mouth
- cracked nipples may not be bleeding but may begin to during breastfeeding
You can also be infected if you receive contaminated:
- blood
- organs
- blood products
Although rare, hepatitis C can also be spread through unprotected sex especially if it involves blood contact, such as:
- contact with:
- open sores, cuts or wounds
- semen or vaginal fluid if blood is present
Unprotected sex means having sex without using a condom or other barrier safely.
Hepatitis C is not spread through:
- breast milk
Treatment And Medication For Hepatitis C
If you have acute hepatitis C, there is no recommended treatment. If your hepatitis C turns into a chronic hepatitis C infection, there are several medications available.
Interferon, peginterferon, and ribavirin used to be the main treatments for hepatitis C. They can have side effects like fatigue, flu-like symptoms, anemia, skin rash, mild anxiety, depression, nausea, and diarrhea.
Now youâre more likely to get one of these medications:
Find out more on treatment options for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis B Test
Treatments For Chronic Hepatitis C
If the infection has lasted more than 6 months, doctors may start treatment with two drugs: peginterferon and ribavirin. Doctors do not treat children with hepatitis C until they reach age 3 because of concerns of possible toxicity and the low chance that a child younger than 3 will have significant liver damage from HCV.
Some children with other medical conditions, such as those with thalassemia, other viral infections, or serious kidney disease, may need to be treated differently. You should tell your doctor if your child has any other medical conditions before starting treatment for hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C And Injecting Drugs
If you inject drugs, avoid sharing needles, syringes or other equipment such as tourniquets, spoons, swabs or water.
Where possible, always use sterile needles and syringes. These are available free of charge from needle and syringe programs and some pharmacists. To find out where you can obtain free needles, syringes and other injecting equipment, contact DirectLine
Try to wash your hands before and after injecting. If you cant do this, use hand sanitiser or alcohol swabs from a needle and syringe program service.
Recommended Reading: When Should You Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Managing Symptoms When Hepatitis Gets Worse
Your doctor will help you manage specific symptoms like itchy skin or pain. You can also make lifestyle changes that can help you feel better and might stop further damage to your liver.
Eat a balanced diet. No matter how advanced your cirrhosis, a well-balanced, nutritious diet is one of the best ways to stay healthy. If you have fluid buildup, your doctor may tell you to cut back on salt.
Avoid alcohol and certain medications, supplements, and herbs. Ask your doctor what’s safe for you.
What Is Fatty Liver Disease
As the name implies, fatty liver disease occurs when fat deposits build up in your liver. The fat in the liver can damage it, causing inflammation and scarring, explains Rena Fox, M.D., a professor of general internal medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and a UCSF Health hepatitis specialist. Although doctors still arent sure exactly what causes it, NAFLD is linked to obesity, insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and high triglycerides levels.
There are different types of fatty liver disease, but NAFLD is the most common, affecting 30% to 40% of adults in the United States, according to the National Institutes of Health . While some types of fatty liver disease are linked to heavy alcohol use, people with NAFLD are not over-drinkers.
One of the challenging things about this disease is that it can be hard to detect, since it often has no obvious symptoms until the liver damage is already extensive. When someone is at a very advanced stage, they may have some pain in the upper-right part of the abdomen, and they may feel tired, says Dr. Fox. At a very late stage, they could have fluid in the abdomen, and they could develop yellowing of the eyes and skin. We want to help patients avoid getting to this point.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Rapid Test Kit
What To Know If You Have Hep C
When youre diagnosed with hepatitis C, your doctor might bring up NAFLD and ways to reduce your risk, Dr. Fox says. If they dont, its a good idea to bring it up with them yourself. If patients can avoid developing fatty liver disease, theyre going to benefit their hepatitis C in terms of limiting damage to the liver, Dr. Fox says.
If you do have NAFLD along with hep C, treating both conditions will help lessen the toll on your liver and overall health in the long run. The damage can go on for decades and patients could be unaware that they have fatty liver disease unless their clinician is looking for it, Dr. Fox says. Its worth knowing about because you may be able to make some modifications to avoid liver damage that might otherwise go on.
Questions For Your Doctor
When you visit the doctor, you may want to ask questions to get the information you need to manage your hepatitis C. If you can, have a family member or friend take notes. You might ask:
You May Like: What Happens When You Get Hepatitis C
Prevention Treatment And Caring For Your Liver
There are vaccines for hepatitis A and B, and these are recommended for those at risk such as health care workers or those traveling to areas where hepatitis is common.
Vaccines are also available for people whove already been exposed to hepatitis A or B and, if given soon after exposure, can be quite effective.
Hepatitis infection can be avoided by the implementation of certain lifestyle regimens:
- Boil water thoroughly, and wash fruits and vegetables before eating when traveling in undeveloped areas
- Do not share needles with other intravenous drug users
- Do not share personal items of the skin damaging variety, such as toothbrushes, razors, scissors, and nail files
- Use condoms during oral, vaginal, and anal sex
- Wash hands frequently, especially after toilet use or contact with anothers blood
- When living and working in unsanitary or heavily populated conditions, it is especially important to implement these precautions
Facts About Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus . HCV can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis infection, ranging in severity from a mild illness that lasts only a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness resulting in cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The virus is mainly acquired by contact through broken skin with infectious blood. In Europe, the main route of HCV transmission is via injecting drug use as a result of sharing contaminated needles. More rarely, the virus can be transmitted sexually, in healthcare settings due to inadequate infection control practices or perinatally from an infected mother to the baby.
A silent disease with no symptoms
Most people with acute HCV infection do not have any symptoms. Those who develop chronic infection are often asymptomatic until decades after infection when symptoms develop secondary to serious liver damage.
Around 30% of people with chronic hepatitis C suffer from liver damage and a small number of those develop cancer. Hepatitis C is considered to be one of the leading causes of liver cancer and liver transplants in Europe.
HCV: no vaccine but a cure
The infection can be cured, especially if it is detected and treated with the appropriate antiviral drug combinations. Antiviral treatment can now cure over 90% of persons with HCV infection.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
What Hepatitis C Medicines Are We Working On
We developed a safe, effective, and easy-to-use direct-acting antiviral regimen, to be used as an affordable combination paving the way for a public health approach to hepatitis C. Our goal is now to increase access to affordable treatments by supporting policy change and encouraging political will to treat hepatitis C. To do so, we are working on innovative programmes to improve access to hepatitis C diagnosis and treatment in a variety of countries.
Find out about our work on hepatitis C
Lifestyle Diet And Liver Damage
Lifestyle and diet play a big role in your liver health. Too many saturated fats, salts and processed sugars can make it harder for the liver to work as it should, which can lead to inflammation and even scarring.
There are some high risk lifestyle factors that may lead to liver damage or disease. Heavy drinking, obesity, diabetes and high cholesterol can all affect your liver health.
You can speak to your doctor, nurse or nutritionist about changes to your lifestyle and diet that can help your liver health.
You May Like: Can A Hepatitis B Carrier Get Vaccinated
Hepatitis C And Liver Cancer: What To Know
Several viruses besides HPV have been linked to cancer, includinghepatitis C, which is linked to liver cancer.
If you think HPV is the only virus that causes cancer, think again. Several other viruses have been linked to cancer, including hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is the most common blood-borne infection in the United States. Its also the leading cause of liver cancer.
About 30 percent of people who get exposed to the hepatitis C virus will clear it on their own. The rest will go on to have chronic hepatitis C.
This ongoing infection causes inflammation in the liver. This extended inflammation can cause scarring, called cirrhosis, and can ultimately lead to liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C also increases the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and head and neck cancers.
Unlike hepatitis A and B, there is no vaccine against hepatitis C, and there are few if any symptoms, says Harrys Torres, M.D., associate professor of Infectious Diseases.
Its a silent infection, he says. And its a very clever virus that mutates very fast, so it has been difficult to develop a vaccine.
Knowing the risk factors and getting screened are your best defenses against cancers caused by hepatitis C. Treatment of this virus can reduce your risk of liver cancer by 75%.
Risk factors
About 75% of those infected with hepatitis C in the United States are baby boomers people born between 1945 and 1965.
Other risk factors for hepatitis C infection include: