Hepatitis C Virus Antibody Test
Antibodies are proteins that travel through the blood as part of the immune systems response to neutralize foreign substances or antigens in the body, such as viruses or bacteria. The body produces antibodies to fight specific antigens.
An HCV antibody test detects antibodies in the blood that the immune system has created to respond to an HCV infection.
Healthcare professionals use HCV antibody tests to determine if people may have had any previous exposure to HCV or if they have a current hepatitis C infection.
However, the test cannot tell the difference between previous exposure or current infection.
If results are negative or nonreactive, a person has not acquired the hepatitis C infection. However, if results are positive or reactive, it means an individual has had exposure to HCV at some point.
However, positive test results do not always mean an active virus people who are clear or cured of the virus will still have antibodies in their blood.
If individuals test negative for HCV antibodies and have a low suspicion for any recent exposure to HCV, they will not need to take any further action.
Additionally, if people have a negative antibody test result but suspect they have had exposure to HCV, they can take a second test, called an HCV RNA test. This is important, as the body may not develop antibodies against HCV until 2 months after exposure to the virus.
If people test positive for HCV antibodies, they will also need to take an HCV RNA test.
Monitoring In The Postpartum Period
Although HCV RNA levels tend to rise during pregnancy, they can drop quite substantially in the postpartum period. This fluctuation in HCV RNA levels during pregnancy likely reflect the relatively immunosuppressed state of pregnancy, followed by immune reconstitution that occurs during the postpartum period. The documented decline in HCV RNA levels in the postpartum period has also been associated with spontaneous clearance of HCV, and as such, HCV RNA-positive women should have repeat HCV RNA testing performed at 9 to 12 months postpartum to assess for the possibility of spontaneous clearance, which occurs in approximately 10% of postpartum women.
Therapeutic Attitude In Case Of Primary Hcv Infection In Patients And Hcws
When a primary HCV infection is documented in a patient or a HCW either serologically or by molecular testing, it must be ascertained by a second testing on a different blood sample in order to prevent a false-positive result or a mistake in the specimen identification. Then, two attitudes may be proposed either a specific treatment is initiated immediately, consisting usually in pegylated interferon for 12-24 wk, or the treatment is delayed for a few wk in the eventuality of a spontaneous clearance of HCV infection . By now, it is difficult to define which the best strategy is: the first one is more prone to cure the infection definitively but the second one avoids a useless treatment and its side effects in a proportion of cases. A recent paper suggested that patients with acute infection without jaundice or belonging to the IL28B CT/TT genotype have less chance to control the infection these patients would be good candidates to an immediate treatment. Globally, acute hepatitis C can be cured in more than 95%, whatever the genotype.
Read Also: What Type Of Cirrhosis Is Caused By Hepatitis C
Can You Be A Blood Or Organ Donor
People with hepatitis C cant currently donate blood. The American Red Cross eligibility guidelines prohibit people who have ever tested positive for hepatitis C from donating blood, even if the infection never caused symptoms.
According to the Department of Health and Human Services , information on organ donation, those with underlying medical conditions shouldnt rule themselves out as organ donors. This reflects new guidelines for organ donation announced by the HHS.
People with HCV are now able to be organ donors. This is because advances in testing and medical technology can help the transplant team determine which organs or tissues can be safely used for transplantation.
Is There A Cure
Though there is no vaccine for Hepatitis C, treatments can reduce the viral load to undetectable levels which is considered cured or in remission.
The virus is considered cured when it is not detected in your blood 12 weeks after treatment is completed. This is otherwise known as a sustained virologic response .
Hepatitis C is one of the most serious hepatitis viruses. However, with newer treatments developed over the past few years, the virus is much more manageable than it was in the past.
Current antiviral drugs that help cure hepatitis C may also help prevent the health complications of chronic liver disease.
The reports less than half of people who contract the hepatitis C virus may clear it from their bodies without treatment. For this group of people, the virus will be a short-term acute condition that goes away without treatment.
But for most people, acute hepatitis C will likely develop into a chronic condition that requires treatment.
Since the virus often doesnt produce symptoms until after more significant liver damage occurs, its important to get tested for hepatitis C if you think you might have been exposed.
approved the antiviral drug Mavyret for an 8-week treatment period for people with all genotypes of hepatitis C.
This treatment is now being used for many people instead of the 12-week treatment that was previously required.
Noninvasive ways to test for liver damage caused by hepatitis C are also now available to aid in diagnosis.
Also Check: What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis C Virus
Hepatitis C And Health
How can health-care personnel avoid exposure to HCV?
Avoiding occupational exposure to blood is the primary way to prevent transmission of bloodborne illnesses among health-care personnel. To promote blood safety in the workplace, health-care personnel should consult infectious-disease control guidance from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health and from CDC. Depending on the medical procedure involved, Standard Precautions may include the appropriate use of personal protective equipment .
What is the risk of acquiring hepatitis C after being accidentally exposed to HCV-contaminated blood or body fluids in the workplace?
Although sharps injuries have decreased in recent decades due to improved prevention measures, they continue to occur, placing health-care personnel at risk for several bloodborne pathogens like hepatitis C. A recent analysis of several studies revealed an overall 0.2% risk for infection among those exposed to HCV-antibody-positive blood through needlestick or sharps injuries . Updated guidelines for management and treatment of hepatitis Cexternal icon are available to provide guidance for health-care personnel who become infected via exposure to contaminated blood at the workplace.
Other than needlesticks, do other exposures place health-care personnel at risk for hepatitis C?
Should HCV-infected health-care personnel be restricted in their work?
Living With Hepatitis C: Your Lifestyle
People living with HIV and hepatitis C can benefit from adopting a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet. Try to maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight is linked to fatty liver disease, which can worsen liver damage.
Since people living with HIV and hepatitis may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes, your clinic should regularly monitor your blood fats or lipids and blood sugar .
People living with hepatitis C should limit how much alcohol they drink, and those with liver damage should avoid alcohol altogether. Not smoking and cutting down or stopping recreational drug use are also important for overall health.
- Eat a balanced diet including vegetables, fruit and wholegrains.
- Get regular moderate exercise.
Don’t Miss: Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Cured
Hope For An Hcv Preventive Vaccine
More than 25 years after the discovery of HCV, searchers failed to set up an effective preventive vaccine against this agent despite huge efforts to reach this goal . Despite the rapid development of DAAs that are theoretically able to make possible the global eradication of HCV, their very high cost may constitute a strong restraint to the rapid completion of this objective, especially in resource-limited countries. Given this fact, there is still an urgent need for an HCV preventive vaccine, especially in intravenous drug users and HCWs that would be the two main targeted populations for HCV immunization.
However, the obstacles to the development of an HCV vaccine are numerous: the variability of HCV is huge, with multiple types and subtypes together with the rapid emergence of a quasi-species in chronically-infected subjects the natural HCV infection is not fully protective against a re-exposure to the virus despite efforts to understand the respective role of neutralizing antibodies against envelop glycoproteins E1 and E2 and specific cytotoxic cellular immunity, there are no clear correlates of protective immunity against HCV and animal models able to experiment candidate vaccines are limited .
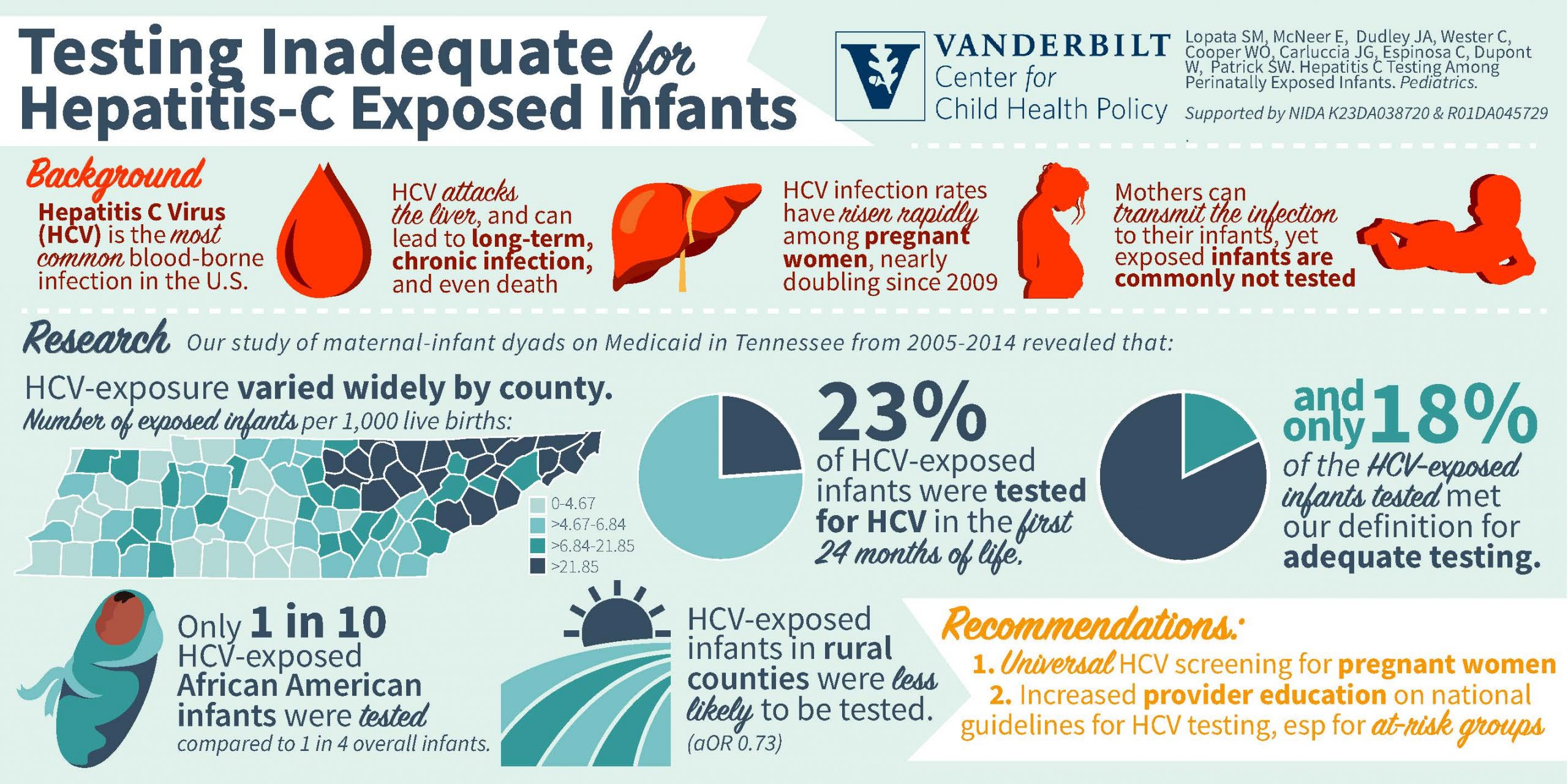
Risk Factors Of Hcv Perinatal Transmission
Although HCV perinatal transmission is lower than that of HBV and HIV , it has a disadvantage, there being no currently available vaccines that can prevent or reduce its transmission , with almost 33% of the infected children acquiring infection intrauterine and up to 50% intrapartum .
There are many factors that can increase or decrease the risk of HCV perinatal infection, as shown in Table II . It has to be kept in mind that viremia per se is a risk factor for perinatal transmission independently of HCV RNA levels . As a consequence, each condition associated with the possible contact of HCV-infected maternal blood with the fetus or the newborn can be theoretically considered a risk factor .
Table II
On the other hand, some factors seem to play no role in HCV perinatal transmission, such as HCV genotype , intrauterine device insertion , and past history of liver disease, blood or blood products transfusion, and hepatitis during pregnancy. Also, no consistent relation was observed between the presence or absence of HCV infection in the first versus the second or subsequent infants , even in identical twins .
Don’t Miss: Natural Cure For Hepatitis B
Administration Of Blood Products
As shown in Table Table1,1, the administration of blood products, mainly labile but also stable ones, appears as a major risk factor for acquiring HCV infection in many parts of the world. In developed countries, this assessment is true for past infections contracted before the nineties when no specific test was available for screening the status of donors towards this agent. With the systematic implementation of HCV serology in blood donors in a great number of world areas together with the detection of HCV RNA by nucleic acid testing in several wealthy countries, the risk of acquiring HCV via blood products decreased dramatically. When both measures are associated, this risk becomes negligible, close to 0.1 per million of blood supplies. In resource-limited countries, the situation is more alarming: according to the WHO database on blood safety, 39 countries performed no routine screening of HCV in blood products in 2012 and 47% of donations were tested in settings without quality insurance. These figures show clearly that the eradication of HCV transmission by blood supplies depends mainly on the quality of the screening of both donors and products, which is still out of range for several developing countries due to financial constraints.
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Vaccine During Pregnancy
Why Is The Viral Load Test Important
Viral load testing is important because it shows whether someone has an active hepatitis C infection or not. People can have antibodies in their blood from previous exposure to hepatitis C, but they may not have an active infection.
Viral load also shows the amount of the virus in the bloodstream. This can help indicate the effectiveness of treatments in reducing the virus by comparing viral load before, during, and after hepatitis C treatment.
However, the viral load does not indicate the condition of the liver people will need liver function tests to assess any damage to the liver.
Transmission Of Hcv In Hemodialysis Units
The prevalence of HCV infection is historically high in patients attending hemodialysis units. In developed countries, a significant decrease was observed in this population during the last decades: from 10.4% in 1995 to 7.8% in 2002 in the United States from 13.5%, 42% and 20% in 1991 to 6.8%, 30% and 16% in 2000 in Belgium, France and Italy, respectively. A meta-analysis of HCV incidence rates in hemodialysis patients showed an overall estimation of 1.47 per 100 patient-years with extremes ranging from 0.00 to 8.05 the countrys development level together with initial prevalence were able to explain 68% of the observed heterogeneity.
It is important to note that HCV infection is an independent predictor of mortality in hemodialysis patients. This finding stresses the need to reinforce the hygienic measures and to monitor at least annually the markers of HCV infection in this population. For hemodialysis patients already contaminated by HCV, ribavirin is usually contraindicated however a treatment based on continuous pegylated interferon could be recommended in order to reduce the risk of progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma and of HCV transmission to HCWs or other patients.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Contact Hepatitis C
Facts About Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by infection with the hepatitis C virus . HCV can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis infection, ranging in severity from a mild illness that lasts only a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness resulting in cirrhosis and liver cancer.
The virus is mainly acquired by contact through broken skin with infectious blood. In Europe, the main route of HCV transmission is via injecting drug use as a result of sharing contaminated needles. More rarely, the virus can be transmitted sexually, in healthcare settings due to inadequate infection control practices or perinatally from an infected mother to the baby.
A silent disease with no symptoms
Most people with acute HCV infection do not have any symptoms. Those who develop chronic infection are often asymptomatic until decades after infection when symptoms develop secondary to serious liver damage.
Around 30% of people with chronic hepatitis C suffer from liver damage and a small number of those develop cancer. Hepatitis C is considered to be one of the leading causes of liver cancer and liver transplants in Europe.
HCV: no vaccine but a cure
The infection can be cured, especially if it is detected and treated with the appropriate antiviral drug combinations. Antiviral treatment can now cure over 90% of persons with HCV infection.
Recommendations For Hcv Screening During Pregnancy
In the setting of increasing HCV prevalence among women of reproductive age and emerging data supporting the cost-effectiveness of universal screening for HCV during pregnancy, routine HCV screening is now recommended by multiple agencies for all pregnant women in the United States, as outlined below.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention : Routine HCV screening is recommended for all pregnant women during each pregnancy, except for in settings where the prevalence of HCV RNA positivity is less than 0.1% .
- United States Preventive Services Task Force : The USPSTF recommends screening for HCV in adults aged 18 to 79 years, including pregnant persons.
- American Association for the Study of the Liver Diseases/Infectious Diseases Society of America : As part of prenatal care, all pregnant women should be tested for HCV infection with each pregnancy, ideally at the initial visit.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Hepatitis C Getting Worse
Natural History Of Hcv Infection In Infected Pregnant Women
Pregnancy is considered a state of relative immunodeficiency , especially T-cell mediated immunity , with a shift in the Th1/Th2 balance toward the Th2 response, and expansion of regulatory T-cells , to safeguard against rejection of the newly developing embryo by the maternal immune system . This alteration in the immune system directly alters the natural course of HCV infection, giving more room for the virus to replicate while suppressing its immune-mediated damage to hepatocytes, which is demonstrated by the surprising finding of increasing viral RNA load with concomitant decreasing ALT levels .
It was reported that estrogen suppresses the intra-thymic T-cell differentiation while activating the extra-thymic pathways during pregnancy . After delivery, the maternal immune system regains its baseline activity with the resultant decrease in viral load and increase in immune-mediated hepatocyte damage and consequently ALT level . Spontaneous resolution of HCV viremia postpartum has also been reported .
Another maternal obstetric complication of HCV is the earlier and more frequent development of cholestasis in HCV infected than non-infected women, which could be attributed to the altered transport of sulfated hormones in the liver, a failure in the transport of toxic substances, and a defect of the bile salt export pump .