How Do You Prevent Hepatitis C
Researchers have yet to develop a vaccine that prevents hepatitis C .
Just as you might not know you have hepatitis C, other people with the condition may not know they have it, either. But you can take a few key precautions to avoid contracting it:
- Avoid sharing needles.
- When getting piercings or tattoos, check to make sure the piercer or tattoo artist uses only sterile, unopened needles and ink.
- Avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, and toothbrushes.
- Use sterile gloves when caring for someone elses wound.
Since hepatitis C is transmitted through blood, you wont get it by sharing food and drinks with someone who has the condition or by hugging, touching, or holding hands.
Hepatitis C is not commonly transmitted through sexual contact. But using a condom or another barrier method when having sex can always help lower your chances of contracting a sexually transmitted infection.
Keep in mind that you can contract hepatitis C again, even if youve had it already.
How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Hepatitis B is spread in several distinct ways: sexual contact sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment or from mother-to-child at birth.
In the United States, in 2018, injection drug use was the most common risk factor reported among people with an acute HBV infection, followed by having multiple sex partners. Less commonly reported risk factors included accidental needle sticks, surgery, transfusions, and household contact with a person with HBV infection. In the United States, healthcare-related transmission of HBV is rare.
Mother-to-child transmission of HBV is especially concerning, because it is preventable. An estimated 25,000 infants are born to mothers diagnosed with HBV each year in the United States, and approximately 1,000 mothers transmit HBV to their infants. Without appropriate medical care and vaccinations, 90% of HBV-infected newborns will develop chronic infection, remaining infected throughout their lives. Up to 25% of people infected at birth will die prematurely of HBV-related causes. For this reason, the standard of care for pregnant women includes an HBV test during each pregnancy so that the appropriate steps can be taken to prevent HBV-positive mothers from transmitting the disease to her infant.
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis B And C
In most patients, hepatitis B develops slowly over the course of several decades, and thus most patients have no symptoms. People who have advanced liver disease such as cirrhosis of the liver may experience complications and symptoms that reflect liver failure. Other symptoms include:
- A buildup of fluid within the abdominal cavity
- Confusion and tremors , which are complications due to the inability of the liver to filter out toxins that are normally cleaned out by a healthy liver
- Vomiting of blood, or blood within the stool . This is a complication in which enlarged veins within the esophagus or stomach bleed as a consequence of increased pressure around the diseased liver.
Most patients with chronic hepatitis C infection report no symptoms. But some patients may have very nonspecific symptoms related to fatigue and discomfort on the right side of the abdomen. Often, symptoms that lead to a diagnosis of hepatitis C are noticeable only at the end stage of liver disease, when the patient has developed liver cirrhosis and liver failure.
Because hepatitis B and C typically have no specific symptoms, many people who have the viruses dont even know it.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Effects Of Hepatitis B
What If You Test Positive
If a test says you have viral hepatitis, you can take steps to protect the ones you love. For hepatitis A, wash hands frequently. For hepatitis B and C, avoid sharing nail clippers, razors, or toothbrushes. Hepatitis B, and sometimes hepatitis C, can be passed through sexual contact. Make sure everyone in your household gets the hepatitis B vaccine. An important step is to see a specialist to discuss treatment options.
What Are The Risk Factors
Some people are at an increased risk for contracting HAV, including:
- people traveling to areas of the world where hepatitis A is common
- men who have sex with men
- people who use injectable or noninjectable drugs
- caregivers for those who have hepatitis A
- people who are experiencing homelessness
- people living with a child whos been adopted from an area where hepatitis A is common
Also Check: Hepatitis B What Is It
What Is The Outlook
Most people with hepatitis A recover without any complications. Once youve had hepatitis A, you cant get it again. Antibodies to the virus will protect you for life.
Some people may be at an increased risk for serious illness from hepatitis A. These include:
- older adults
acute hepatitis B infections in the United States in 2018.
What Are The Different Hepatitis Viruses
Hepatitis A, B and C are among the most common types of hepatitis viruses. Each type of virus is found in different bodily fluids, spreads differently and can have different symptoms.
Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus , and the virus is found in the poo of HAV-infected people.
This type of hepatitis spreads from person to person by putting something contaminated with the stool of an infected person in your mouth.
It commonly spreads when people don’t wash their hands properly after using the toilet and then touch or prepare other people’s food.
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus and is found in blood and certain other bodily fluids. HBV spreads when a person who is not immune to it comes in contact with blood or bodily fluid of an infected person.
The virus most commonly spreads through unprotected sex with an infected person, sharing of needles or from an infected mother to her baby during vaginal birth. However, exposure to blood in any situation can be risk for transmission.
Hepatitis V is caused by the hepatitis C virus , which is also found in the blood and bodily fluids of an infected person. Similar to hepatitis B, HCV spread through sharing needs or from an infected mother to her baby during vaginal birth.
While it’s possible to get hepatitis C from sex, it’s quite uncommon.
Recommended Reading: Is There A Vaccine For Hepatitis C Virus
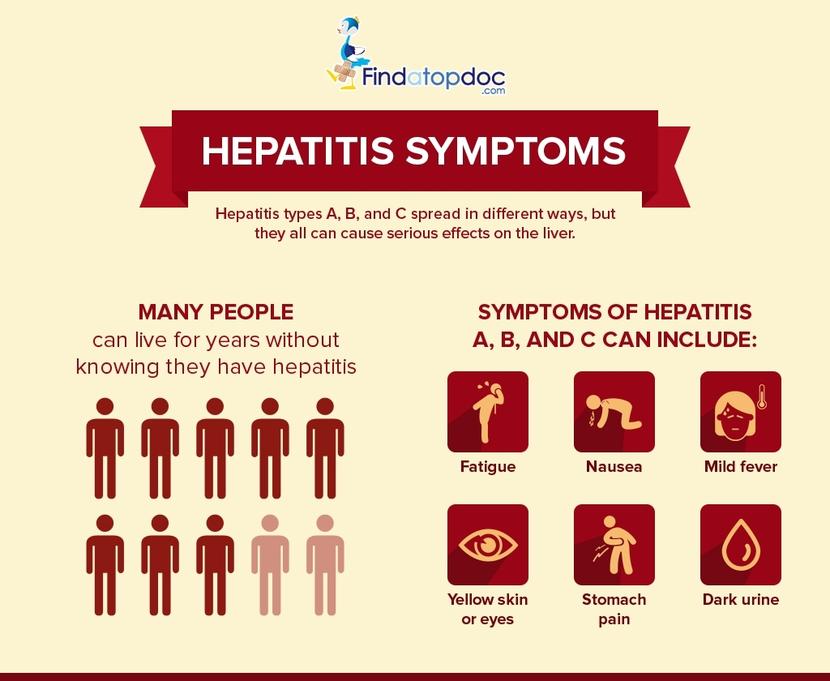
Symptoms Of Hepatitis A B And C
Hepatitis A often presents no symptoms in an infected person. Children are more likely to experience no symptoms of the virus. Mild symptoms of hepatitis A include fever, diarrhea, nausea, and jaundice. While serious complications including liver failure are possible, most people who contract the virus do not have lasting effects.
Hepatitis B may not cause symptoms in an infected person. Many people are unaware that they have the virus because they either have no symptoms or mild, flu-like symptoms. Symptoms include loss of appetite, fatigue, fever, stomachache, jaundice, and problems with digestion. Since hepatitis B affects liver function, some people with the virus develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. However, serious complications are rare.
Hepatitis C usually causes no symptoms when a person is first infected, but symptoms tend to develop over time. Common symptoms include muscle weakness, joint pain, extreme fatigue, jaundice, itchiness, and dark urine. Because symptoms are either not present or very mild, many people do not discover that they have hepatitis C until they experience serious complications involving the liver.
How Can I Prevent Spreading Hepatitis B To Others
If you have hepatitis B, follow the steps above to avoid spreading the infection. Your sex partners should get a hepatitis B test and, if they arent infected, get the hepatitis B vaccine. You can protect others from getting infected by telling your doctor, dentist, and other health care professionals that you have hepatitis B. Dont donate blood or blood products, semen, organs, or tissue.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Sex
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Hepatitis A: Who Is At Risk
A prime risk factor for hepatitis A is traveling to or living in a country with high infection rates. You can check the CDC’s travel advisories to learn about recent outbreaks. Eating raw foods or drinking tap water can raise your risk while traveling. Children who attend daycare centers also have a higher risk of getting hepatitis A.
How Can Hepatitis A B Or C Be Treated
Most cases of hepatitis A will resolve spontaneously within two months. More severe liver complications will be observed in less than 1% of cases. Therefore, no treatment is necessary except in some acute cases where support and comfort measures can be used to alleviate situations such as fluid loss due to vomiting or diarrhea. In addition to rest, a healthy diet and the avoidance of substances toxic to the liver such as alcohol and certain drugs are indicated. Resolution of the infection will be accompanied by the production of antibodies against hepatitis A, which will confer lifelong immunity against subsequent infections by the virus. Immunization with a potent hepatitis A vaccine constitutes the best preventive measure, particularly for children and travellers.
The production of antibodies against the hepatitis C virus will help clear the virus within six months. But contrary to hepatitis A or B, these antibodies will not confer lifelong immunity against re-infection. Cases of hepatitis C also tend to develop in chronic infections much more often than with hepatitis A or B. Chronic hepatitis C cases can degenerate and cause serious liver complications such as cirrhosis or liver cancer. Some of these cases can only be cured by a liver transplant. As with chronic hepatitis B treatment, the use of interferon and other antiviral drugs constitutes the basis of chronic hepatitis C treatment.
Need more information?
You May Like: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis A B C Symptoms
How One Black Man Was Cured Of Hep C Despite Racial Bias
According to the CDC, approximately 10 to 20 percent of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over a period of two to three decades.
People with cirrhosis have a 1 to 5 percent annual risk of developing liver cancer and a 3 to 6 percent risk of hepatic decompensation . Theres a 15 to 20 percent risk of death in the year following the development of decompensation.
Age and gender have been shown to affect how chronic hepatitis C progresses, warns Adalja. It doesnt advance to cirrhosis and liver cancer as quickly in premenopausal women as it does in men, according to a report published in July 2013 in Southern Medical Journal.
Adalja notes that other factors that may accelerate chronic hepatitis C progression, increasing the risk of liver damage. These include HIV or hepatitis B coinfection, alcohol overuse, and cigarette smoking. The symptoms of chronic hepatitis C vary depending on the type of liver damage.
Cirrhosis can produce a variety of symptoms:
- Itchiness
- Abdominal bloating from a buildup of fluids
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, or legs
- Spider angiomas
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
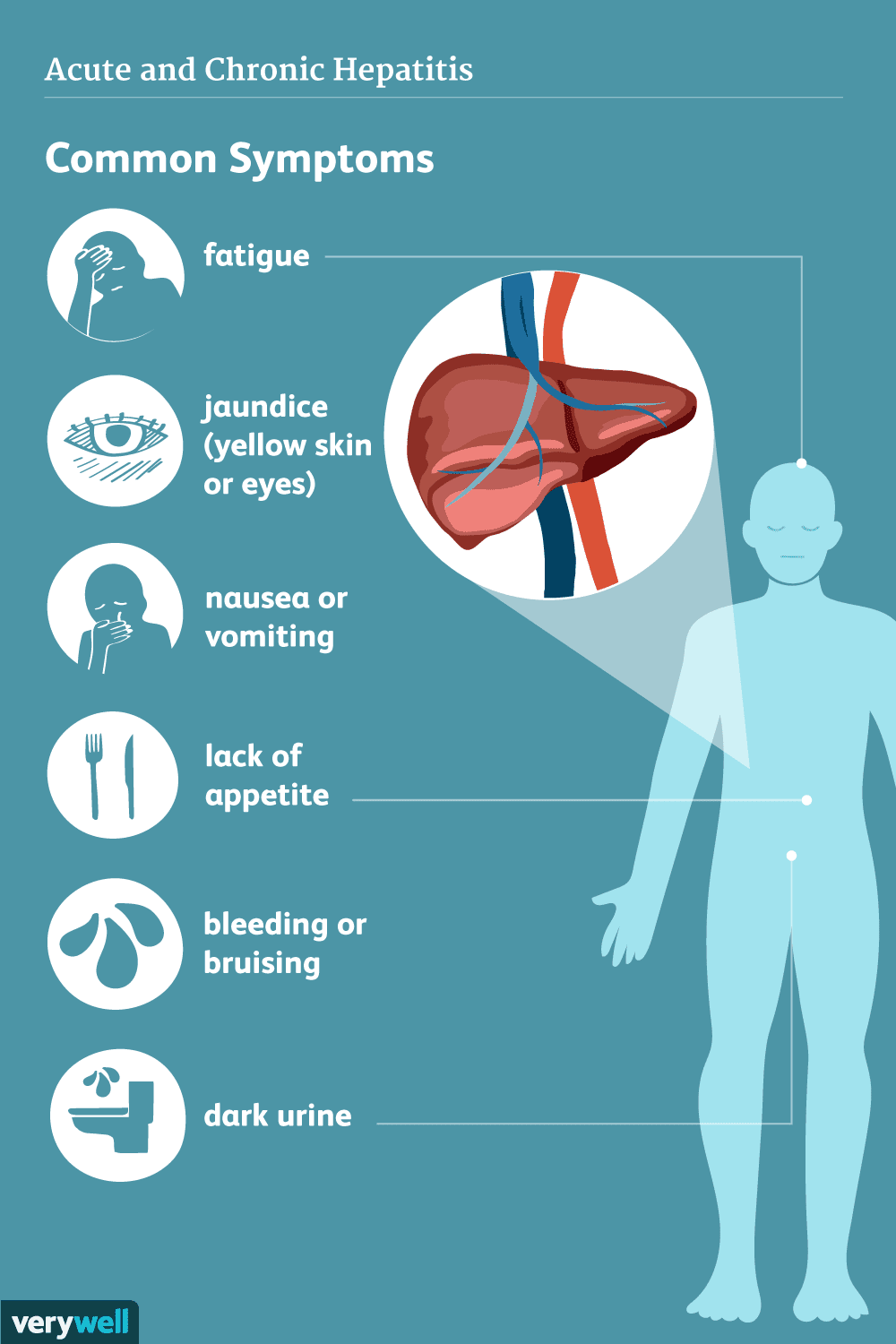
You may have hepatitis C and not have any signs or symptoms.
For those who do have symptoms, you may experience:
- fever
- nausea and vomiting
- jaundice
Hepatitis C can lead to liver damage, as it causes swelling . This swelling causes scarring of the liver, which affects how the organ functions.
Liver scarring can worsen . This increases your chances of getting liver cancer.
How quickly your liver undergoes damage will depend on if you:
- use alcohol
- have a human immunodeficiency virus co-infection
About 60% to 70% of people with hepatitis C do not develop symptoms until their liver has already been damaged.
Also Check: What Happens When You Have Hepatitis B
Don’t Miss: Can You Live A Normal Life With Hepatitis C
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis B
Doctors typically dont treat hepatitis B unless it becomes chronic. Doctors may treat chronic hepatitis B with antiviral medicines that attack the virus.
Not everyone with chronic hepatitis B needs treatment. If blood tests show that hepatitis B could be damaging a persons liver, a doctor may prescribe antiviral medicines to lower the chances of liver damage and complications.
Medicines that you take by mouth include
A medicine that doctors can give as a shot is peginterferon alfa-2a .
The length of treatment varies. Hepatitis B medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Tell your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, you also should talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Reduce Your Chance Of Infection
You can reduce your chance of hepatitis B infection by
- not sharing drug needles or other drug materials
- wearing gloves if you have to touch another persons blood or open sores
- making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools
- not sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers
- using a latex or polyurethane condom during sex
Also Check: How Do You Diagnose Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A B And C: What Is The Difference
A, B, C D and E.
Aside from the letters associated with it, how much do you know about hepatitis? Whats the difference between the types? And if you get a vaccination for hepatitis, which are you protected from?
We spoke with Moises Ilan Nevah, MD, a transplant hepatologist/gastroenterologist and medical director of the Liver Transplant Program at Banner University Medical Center Phoenix, to help better understand the similarities and differences between the various types of hepatitis, who is at risk and when to get vaccinated.
Can Hepatitis Be Prevented
There are different ways to prevent or lower your risk for hepatitis, depending on the type of hepatitis. For example, not drinking too much alcohol can prevent alcoholic hepatitis. There are vaccines to prevent hepatitis A and B. Autoimmune hepatitis cannot be prevented.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Read Also: Tenofovir Alafenamide Vs Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate Hepatitis B
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Ab Immunity
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis B
The goal of treating chronic hepatitis B is to control the virus and keep it from damaging the liver. This begins with regular monitoring for signs of liver disease. Antiviral medications may help, but not everyone can take them or needs to be on medication. Be sure to discuss the risks and benefits of antiviral therapy with your doctor.
What Do You Do If You Become Ill
Talk to your health care provider about getting tested if you think you:
- are at risk
- may have hepatitis C
If you have hepatitis C, tell those who may have been exposed to your blood or bodily fluids. They should get tested and be treated if necessary. Bodily fluids, like semen and vaginal fluid, are a concern because they could be carrying small amounts of infected blood.
Some adults with hepatitis C will recover from the disease on their own within 6 months. Until your health care provider confirms your recovery status, you are still contagious and can spread the disease.
After recovery, you are no longer contagious because you will not have the disease anymore. But you can get hepatitis C again.
Unfortunately, most adults with hepatitis C:
- cannot recover on their own
- develop a more serious form of the disease if they are sick for longer than 6 months
Read Also: How Many Genotypes Of Hepatitis C Are There
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis has many different types. HBV and the hepatitis C virus have both acute and chronic forms.
The main difference between HBV and HCV is how they spread from person to person. Although HCV is transmissible via sexual activity, this is rare. HCV usually spreads when blood that carries the virus comes into contact with blood that does not.
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.
Recommended Reading: Cost Of Medicine For Hepatitis C
What Makes Yale Medicine’s Approach To Treating Hepatitis B And C Unique
The Viral Hepatitis Program at Yale Medicine represents one of the leading viral hepatitis treatment programs in the country and is engaged in innovative research focused on advancing the care of patients with chronic hepatitis B, C and D infections.
A multidisciplinary team of faculty physicians and mid-level providers offer a coordinated approach to preparing patients for success with antiviral therapy, including comprehensive laboratory testing services to characterize your infection, non-invasive liver fibrosis testing with techniques such as FibroScan liver elastography, structured hepatitis patient education classes, mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques , a formal physician-guided weight-loss program and access to clinical trials evaluating current and new therapies that are not available in routine clinical practice. Our program is a core member of several national and international observational cohort studies which contributes to the advancement of science of hepatitis treatment around the world.
How Many People Have Hepatitis B
In the United States, an estimated 862,000 people were chronically infected with HBV in 2016. New cases of HBV infection in the United States had been decreasing until 2012. Since that time, reported cases of acute hepatitis B have been fluctuating around 3,000 cases per year. In 2019, 3,192 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported however, because of low case detection and reporting, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there were 20,700 acute hepatitis B infections. New HBV infections are likely linked to the ongoing opioid crisis in the United States.
Globally, HBV is the most common blood-borne infection with an estimated 296 million people infected according to the World Health Organization .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Catch Hepatitis C