What Will My Doctor Need To Know To Treat Me
If you want to be assessed for treatment, you need to make an appointment with a doctor. They will be mostly interested in the condition of your liver. Your doctor will organise, if possible, for you to have a Fibroscan examination. If Fibroscan is not available, your doctor will probably use an APRI test. This is an online calculator that estimates the health of your liver. It involves a blood test called a liver function test.
Dont forget, its very important to get a PCR test 12 weeks after finishing treatment this will mean the doctor can make sure you are cured.
Whats The Outlook For Hep C Thats Developed Into Cirrhosis Or Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis, especially if left untreated. Without treatment, cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
Treating cirrhosis and liver cancer typically requires a liver transplant. A transplant can cure both cancer and liver function impairment. But a transplant is only available for a small number of people.
Whats The Optimal Hcv Screening Strategy
Using a simulation model, Barocas, Tasillo, Eftekhari Yazdi, et al. compared the clinical costs, outcomes, and cost-effectiveness of four HCV testing strategies: the existing one one-time testing for adults aged 40 or higher, 30 or higher, or 18 or higher. All strategies included targeted testing of people at higher risk, such as those who inject drugs. As shown below, expanded age-based strategies increased identification and lifetime cure rates.
Figure 3. HCV continuum of care over a lifetime, by strategy
The authors estimate that the existing strategy would identify 71% of all HCV-infected people, and 44% of them would be cured over a lifetime. Compared to existing screening, a strategy of age 18 or older would result in 256,000 additional people identified, 28,000 additional cures, and 4,400 fewer cases of hepatocellular liver cancer over the lifetime of this age group. For people born outside the baby boomer cohort, case detection rates would increase from 74% to 85%, and cure rates would increase from 49% to 61%. Overall, this would represent a 21% reduction in liver-attributable mortality, and an increase in life expectancy from 67.2 to 68.2 years among the affected population.
Read Also: How Do You Contract Hepatitis C
Are There Ways To Cure Hepatitis C Other Than With Medications
Patients sometimes ask whether there are ways to treat hepatitis C other than taking medicines. Currently, there are no vaccines to prevent hepatitis C. Once a person is infected, the only way to treat it is with prescribed antiviral medications.
Some patients worry that having hepatitis C means they will need a liver transplant. Only a very small fraction of people with hepatitis C require a liver transplant. By far, most people with hepatitis C never need a liver transplant. A transplant is performedonlywhen damage to the liver is extremely advanced and the liver is unable to perform its basic functions. A transplant provides a new working liver, but a transplant does not get rid of the hepatitis C virus in the patient. Patients with a liver transplant still need antiviral medication to cure their virus.
What Drugs Cure Hepatitis C Infection
Most hepatitis C is currently treated with all-oral medical regimens of “direct-acting antivirals” or DAAs. DAAs is a term used to distinguish these hepatitis C drugs from an older generation of injected medicines that act indirectly on the immune response to the hepatitis C virus. DAAs act directly on the virus to block different steps in its life cycle. There are several DAAs that are used in combinations that have been scientifically proven to cure hepatitis C. They are not interchangeable, and some are only available combined in one pill or dose pack as a specific combination. DAAs are not used as single-drug therapy because of the high risk of the virus developing resistance and because they work best in combinations. The choice of which regimen to use depends upon the genotype of the virus, the level of liver fibrosis , and any drug resistance that may be present .
Examples of combination DAAs with cure rates between 91%-100% include:
- Harvoni
- Zepatier
- Mavyret
Genotype 1a and 1b are the commonest genotypes in the United States. Of all the genotypes, genotype 3 has been the most difficult to treat with DAAs alone and required the use of ribavirin, which has significant side effects. All genotypes can now be treated with oral DAAs without ribavirin. Some genotypes may still require the use of injected pegylated interferon and/or ribavirin if there is no response to DAAs.
Read Also: Is There An Immunization For Hepatitis C
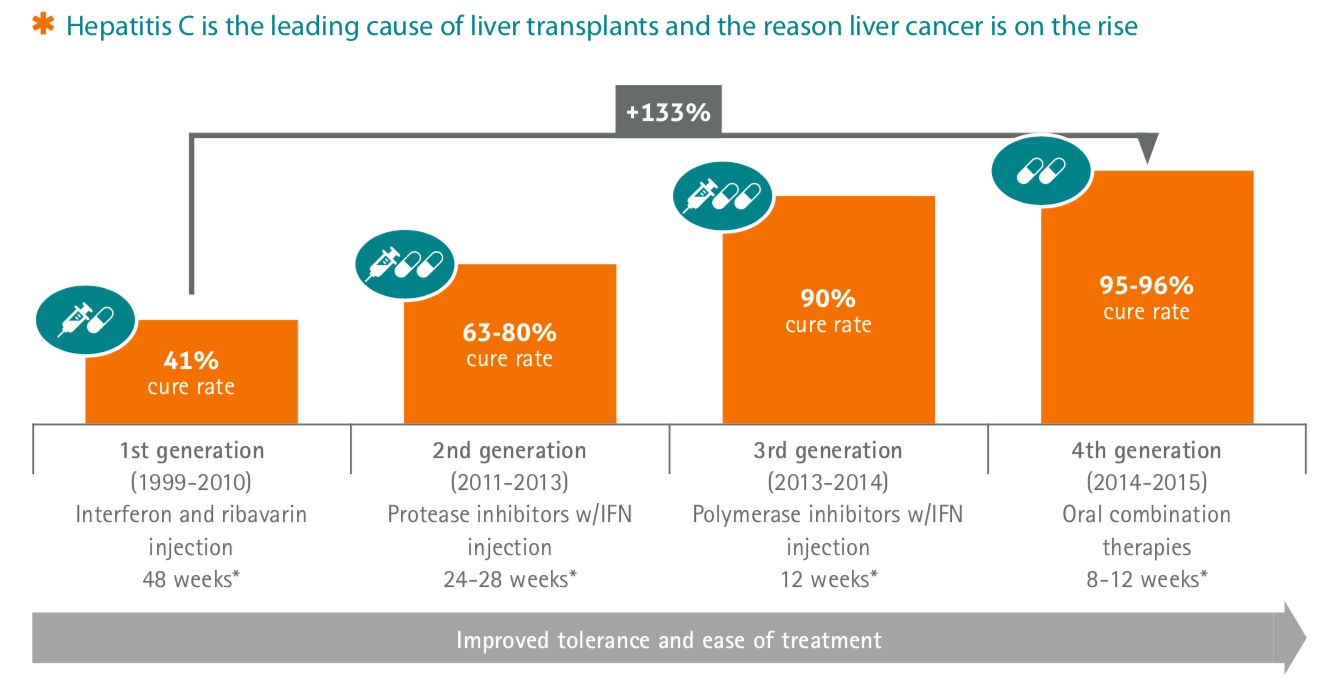
Discovery To Cure In 25 Years
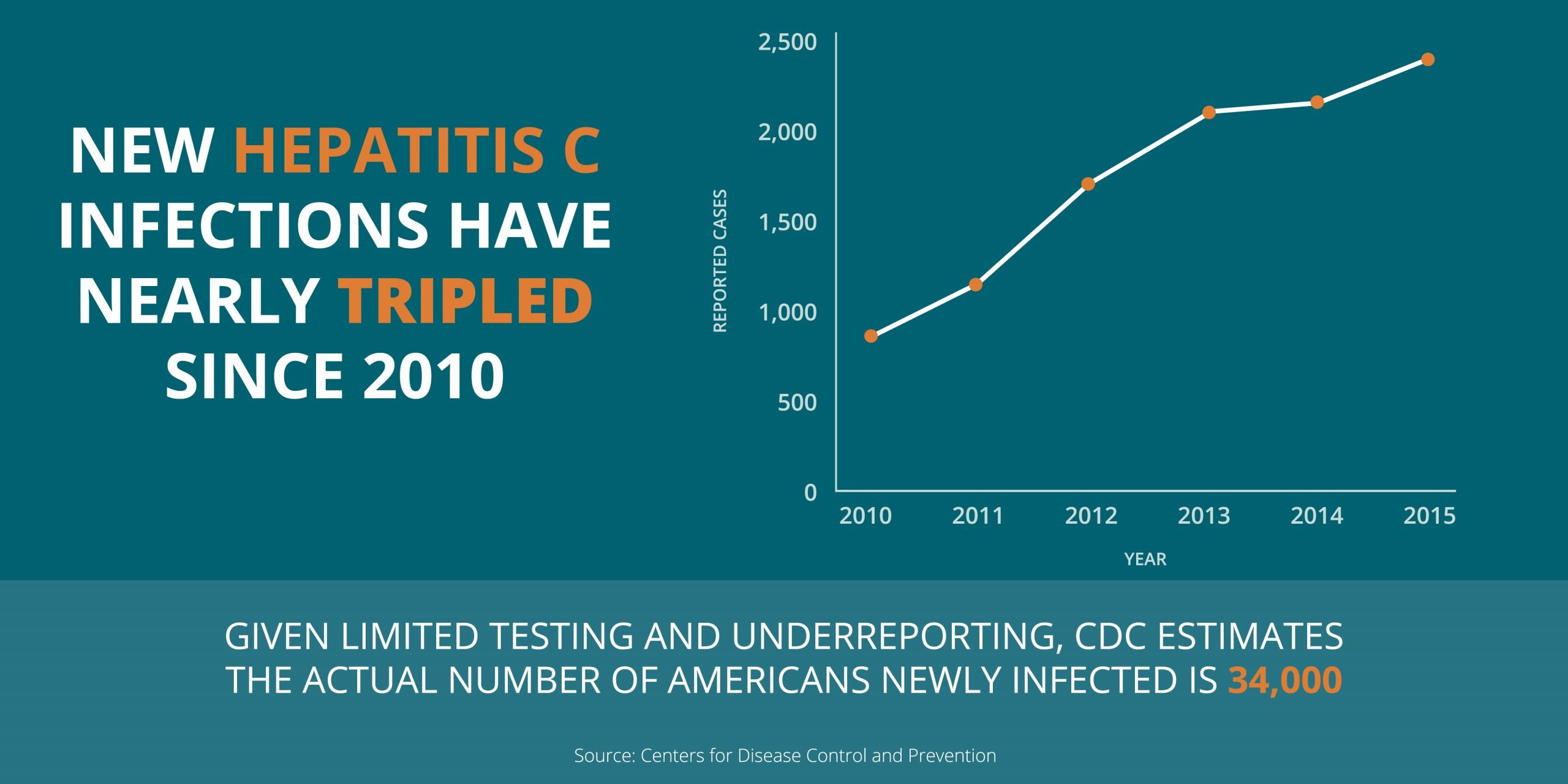
Hepatitis C is a viral, blood-borne disease that progresses slowly over time. If left untreated, it can cause life-threatening damage to the liver. An estimated 71 million people have chronic hepatitis C infection with almost 400,000 deaths each year. The hepatitis C virus is the leading cause of liver cancer and the main reason for liver transplantation.
Prior to the identification of HCV in 1989, so little was known about the virus that it was simply called non-A, non-B hepatitis. Since identification, effective treatments have been relatively rapidly developed. Compared to the first-ever HCV treatment approved in 1991, in which a patient faced cure rates of around 6%, drugs today have more than a 95% success rate over short treatment courses. That makes HCV the fastest viral disease ever to be identified and cured. It remains the only chronic viral illness that can be completely cured, allowing millions of people to regain their health and live full and productive lives.
Will Community Pharmacies Be Able To Dispense These New Hepatitis C Drugs
Community pharmacists will be able to dispense the drugs. However, because these are new drugs, it may take time for pharmacies to order in sufficient stock to meet demand.
This means that patients may need to wait a couple of days after providing their script for the drugs to be available from their local pharmacy.
Recommended Reading: The Cost Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Can You Die From Hepatitis C
Complications from untreated hepatitis C, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, can be fatal, though HCV itself is rarely fatal.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , people who develop cirrhosis from HCV have a
more than half of people with an HCV infection will develop chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C is long term and can lead to permanent cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C usually has no symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis C may not even know they have it. But once symptoms appear, it means that damage to the liver has already begun.
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Considerable progress has been made by past clinical trials in the medical treatment of hepatitis C. The rate of cure has increased with the development of direct-acting, all-oral antiviral regimens, and the length of therapy is much shorter. Treatment recommendations continue to change as new medicines become available. Treatment helps to reduce progression of liver damage to cirrhosis, may prevent liver cancer, and may prevent spread of the infection to other people.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Hepatitis C In Males
What Health Professionals Need To Know About Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus is transmitted primarily through parenteral exposure to infectious blood or body fluids containing infectious blood. Hepatitis C is not a vaccine-preventable infection.
Hepatitis C infection is reportable by laboratories and clinicians to local public health authorities in all provinces and territories.
Consult the national case definition for additional information.
In Canada, screening of the blood supply was implemented in 1992. This has virtually eliminated the risk of HCV transmission via transfusion. Prior to this, thousands of people contracted HCV through receiving blood or blood products.
How Do You Get Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C spreads when blood or body fluids contaminated with the hepatitis C virus get into your bloodstream through contact with an infected person.
You can be exposed to the virus from:
- Sharing injection drugs and needles
- Having sex, especially if you have HIV, another STD, several partners, or have rough sex
- Being stuck by infected needles
- Birth — a mother can pass it to a child
- Sharing personal care items like toothbrushes, razor blades, and nail clippers
- Getting a tattoo or piercing with unclean equipment
You canât catch hepatitis C through:
- Breastfeeding
- Casual contact
- Have been on long-term kidney dialysis
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Have HIV
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
Since July 1992, all blood and organ donations in the U.S. are tested for the hepatitis C virus. The CDC says it is now rare that someone getting blood products or an organ would get hepatitis C. That said, The CDC recommends that anyone over the age of 18 get tested for Hepatitis C. If you haven’t been screened, you should consider having it done.
Learn more about the risk factors for hepatitis C.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A Virus
How Much Will It Cost Patients To Access The New Drugs
The Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme listing means that hepatitis C patients will only pay the normal co-payment for the new drugs. The co-payment is currently worth $6.20 for patients with concessional healthcare cards and $38.30 for general patients without concessional healthcare cards, per drug, per month. For some patients needing three drugs, for example, the co-payment will therefore be $114.90 per month, or $18.60 per month concession.
Also Check: How Do You Get Infected With Hepatitis C
Helpful Tips While Taking Hepatitis C Medications
- Always follow your health care providers’ advice, particularly the instructions on taking your medicine.
- If you have to cancel an appointment, call your provider and schedule a new one as soon as possible.
- Take good care of yourself. Eat well, drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day, and try to get a full night’s sleep.
- Learn about the hepatitis C medications you are taking. This includes special risks and warnings.
- If taking ribavirin, use sunscreen, wear long sleeves and a hat, and limit sun exposure.
- Write down your doctor’s name and phone number. Carry this information with you at all times.
- Write the names and amounts of the medicines you are taking. Carry this information with you at all times.
Recommended Reading: Drug Therapy For Hepatitis C
Treatment Of Patients With Impaired Renal Function/dialysis
Renal excretion is the main elimination pathway of the NS5B polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir and its metabolites. For patients with mild to moderate renal impairment administration of sofosbuvir is safe. Since patients with severe renal dysfunction or hemodialysis have not been included during the initial phase III study trials, drug safety of sofosbuvir in these patients has not been studied in detail, and therefore sofosbuvir treatment is not recommended by the FDA and EMA label. Nevertheless, some real-world studies and preliminary data of a prospective multicenter trial show high efficacy and safety during full dose sofosbuvir treatment for patients with severe kidney dysfunc nt-related discontinuations or treatment-related serious adverse events . However, in some studies these patients also experience higher rates of anemia and worsening of kidney dysfunction . Therefore, sofosbuvir-free treatment options should be preferred if possible. Since the introduction of the pangenotypic combination of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir, a highly effective treatment of GT 2 and 3 is available, and safety and efficacy for patients with renal impairment and hemodialysis have been shown successfully . Alternatively, grazoprevir/elbasvir can be safely administered in patients with GT 1 or 4 infection and severe renal dysfunction .
Do Antiviral Treatments Cure Liver Damage Too
Antiviral treatment can clear the hepatitis C virus from your body. This will stop the virus from causing more damage to your liver. But it wont reverse any liver damage that youve already experienced.
If youve developed liver scarring from hepatitis C, ask your doctor how you can manage it. They may encourage you to undergo regular ultrasound exams or other tests to monitor the health of your liver, even after the infection has been cured.
If needed, your doctor may prescribe lifestyle changes, medications, or other treatments to help address symptoms or complications of liver damage. In some cases, you might be a candidate for liver transplantation.
Read Also: How Do You Test For Hepatitis C
Can You Drink Alcohol If You Have Hepatitis C
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis C viral infection causes this inflammation. There are several risk factors for contracting HCV infection due to the hepatitis C virus. One serious risk factor is drinking alcohol with HCV infection. The combination of HCV and alcohol can cause complications, and may result in more severe and serious liver injury including chronic cirrhosis . It also increases your chances of developing liver cancer having an alcohol induced increase in viral replication and rapid mutation of the hep C virus,which creates complications like:
- Greater viral capacity
Hepatitis refers to any cause of liver inflammation, with or without scarring of the liver . It is contagious, and is spread from person-to-person by blood-to-blood contact. Other viral causes of hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, and E. Other types of noninfectious causes of hepatitis include:
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Medications such as some prescription medications or even acetaminophen, for example, Tylenol liver damage and drug induced liver disease.
- Bacteria and viruses other than the hepatitis viruses
How are hepatitis A, B, and E spread?
- Transmission of hepatitis A and E: These forms of the virus are acquired from improper hygiene during food or drink preparation by someone who’s infected.
- Transmission of hepatitis B: This form is spread by blood-to-blood or sexual contact.
Why Does The Genotype Of The Virus Matter
If youve been diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C, your doctor will order blood tests to learn which subtype of virus is causing the infection.
There are six main genotypes of hepatitis C. These genotypes differ from one another at a genetic level. Some genotypes of the virus are more resistant to certain types of medication, compared to others. The virus can also mutate in ways that make it more resistant to treatment.
Your recommended treatment plan will depend in part on the specific strain of hepatitis C thats causing your condition. Your doctor can explain how it might affect your treatment options and long-term outlook.
Don’t Miss: Non Reactive Hepatitis C Antibody
Hepatitis C Treatment Time
This page explains how the length of treatment time for Hepatitis C effects Hep C treatment outcomes and cure rates
What is the best option for you when considering the length of time for Hepatitis C treatment? In a nutshell the truth is simple: The longer the treatment time the higher the cure rate.
When Is Someone Considered Cured Of Hepatitis C
If youre treated for hepatitis C, your doctor will order blood tests during and after your treatment to learn how the medication has affected you.
If the virus is no longer detectable in your blood 12 weeks after your last dose of antiviral medication, you will be considered cured of hepatitis C. This is also known as a sustained virologic response . About 99 percent of people who achieve SVR remain free of hepatitis C for the rest of their lives.
Don’t Miss: Signs And Symptoms Of Hepatitis C Virus
Hcv Treatment Provides Good Value
Despite its cost, HCV treatment provides good value for the money, as expressed in terms of cost-effectiveness. In a recent review, Linas and Nolen note that most studies in the past five years find that HCV treatment falls within the generally accepted value of $100,000 per quality-adjusted life year . They note that these studies do not reflect price decreases that have occurred in the past 1-2 yearsbut the substantial cost burden remains. A critical question is not whether to treat patients with HCV, but when, because of the significant lag time between infection and disease. Facing costs that could overwhelm fixed budgets, many payers have restricted treatments to those with advanced disease or those who are alcohol- or drug-free.
There is some evidence that public payers are relaxing their eligibility restrictions for hepatitis C treatment. Kapadia, Jeng, Schackman, and Bao looked at Medicaid drug utilization data from 2014 to 2016, and found that states that loosened their restrictions had a more rapid increase in prescriptions of direct-acting antivirals than states maintaining their restrictions. The 31 states that implemented Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act saw much more of an increase in utilization than states that did not.
What About Patients With Hepatitis C Who Also Have Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B virus can flare in patients who are co-infected with hepatitis B and hepatitis C and are taking medication for hepatitis C. This has been reported as a potential risk for patients who are taking hepatitis C treatment and have underlying hepatitis B as well. The flare usually occurs within a few weeks after the patient starts taking medication for hepatitis C. Therefore, patients who have both hepatitis B and hepatitis C should be seen by a hepatitis expertbeforestarting treatment of the hepatitis C they may need to start taking hepatitis B treatment to avoid a hepatitis B flare.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitative Titer
Hiv And Hepatitis C Coinfection
HCV infection is common among people with HIV who also inject drugs. Nearly 75% of people living with HIV who report a history of injection drug use are co-infected with HCV. All people who are diagnosed with HIV are recommended to be tested for HCV at least once. People living with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HCV infection. Fortunately, direct acting antivirals that are used to treat HCV work equally well in people with and without HIV infection. For more information about HIV and HCV coinfection, visit the HIV.govs pages about hepatitis C and HIV coinfection.