Who Should Be Immunised Against Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B immunisation is recommended and funded for the following groups:
- all children up to their 18th birthday
- babies born to mothers with hepatitis B infection
- people who live in close contact with someone infected with hepatitis B
- anyone undergoing renal dialysis
- people who have hepatitis C infection, or who are HIV positive, or who have had a needle stick injury.
- anyone who has received immunosuppression therapy of at least 28 days or has had solid organ or bone marrow transplant.
Hepatitis B immunisation is also recommended, but not funded, for:
- workers who are likely to come into contact with blood products, or who are at increased risk of needlestick injuries, assault, etc.
- people who change sex partners frequently such as sex workers
- people who regularly receive blood transfusions such as people with haemophilia
- current or recent injecting drug users
- migrants and travellers from or to areas with intermediate or high rates of hepatitis B such as the Asia and Pacific region.
General Information About Vaccination Outside The Us
In developing countries, the pentavalent vaccine, a combination 5-in-one vaccine that protects against five diseases, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Hib and hepatitis B, may be given to babies more than 6 weeks of age, and can be given up to 1 year of age. The first dose is given at 6 weeks, and the second and third doses are given at 10 and 14 weeks of age. The pentavalent vaccine may be made available free of charge with the support of GAVI, the vaccine alliance. Check the GAVI country hub to see the resources and immunizations that may be available:
For babies born to mothers with hepatitis B, waiting for the first dose of the pentavalent vaccine is too late and will NOT protect the baby from vertical or horizontal transmission of hepatitis B. Babies born to a mother with hepatitis B have a greater than 90% chance of developing chronic hepatitis B if they are not properly treated at birth.
WHO recommends the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth for ALL babies. Plan ahead and inquire about the availability and cost of the monovalent , birth dose of the vaccine, as it is not a GAVI provided immunization. This is particularly important to women who are positive for hepatitis B.
If you are unsure of your hepatitis B status, please be sure your doctor tests you for hepatitis B!
*WHO does not recommend a birth dose of HBIG, which may not be available in all countries. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Page updated September 2022.
How Is Hepatitis B Treated
Immunoglobulin, a passive immunisation, can be administered within 12 hours of an at-risk exposure to help prevent HBV infection. Treatment for chronic disease is through the use of antiviral medications and medications containing naturally-occurring proteins. A liver transplant may be necessary in the event of severe liver damage.
A Hepatitis B vaccination schedule is the best way to prevent infection.
Read Also: What Types Of Hepatitis Have Vaccines
Who Should Get Hepatitis Vaccinations
Since the vaccines were first developed, the hepatitis A and B vaccines have become part of the regular childhood immunization schedule. They are not considered a routine adult immunization.
“When we’re talking about adults, I would say yes, get the vaccine if they fit into one of these risk factors” says Poland. “If they don’t fit into the risk factors, their risk is so low that there’s no compelling reason to do it.”
People at risk for hepatitis A include:
- Anyone traveling to or working in areas where hepatitis A is more widespread.
- People whose work puts them in potential contact with hepatitis A, such as those who work with the hepatitis A virus in research labs
- People who are treated with clotting-factor concentrates
- People who have chronic liver disease
- People who use recreational drugs, injected or not
- Men who have sex with men
People at risk for hepatitis B include:
- Anyone traveling to or working in areas where hepatitis B is more widespread.
- Health care workers and other people whose job exposes them to human blood
- People with HIV infection, end-stage kidney disease, or chronic liver disease
- People who live with someone with hepatitis B
- People who inject street drugs
- Sexually active people who have had more than one partner
- Anyone who has had an STD
- Men who have sex with men
- Sex partners of people with hepatitis B
If I Already Have Hepatitis B Can The Vaccine Treat It
No. The hepatitis vaccine prevents hepatitis, but doesnt cure it if you already have it. If you have hepatitis B, there are other treatment options.
However, if you recently got exposed to the hepatitis B virus and you havent had the vaccine yet, tell your doctor right away. The vaccine and possibly other treatment can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis B if you get it within 2 weeks after you came into contact with the virus. The sooner you seek care after being exposed to hepatitis B, the better, so try to get there right away.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Hepatitis B In Females
Medicare Part B Vaccines
These vaccinations are covered under Medicare Part B :
- Pneumococcal pneumonia
In addition, these other vaccinations are covered to treat certain injuries, or if youve been directly exposed to a particular disease or condition:
- Botulin antitoxin
Part B vaccinations are available at no cost! You can get them at your doctors office, or see if your in-network pharmacy carries them.
Note: If you get other services besides the vaccine shot during your doctors visit, a copay may apply for those other services.
If you choose an out-of-network pharmacy, you may have to pay out of pocket and then submit a claim for reimbursement. In some cases, the amount of that reimbursement may be less than what you paid at the pharmacy.
How Hepatitis Is Spread
Hepatitis A: About 20,000 people in the U.S. contract hepatitis A each year. The hepatitis A virus is found in the stool of the infected person. It is spread through contaminated food or water or by certain types of sexual contact.
Children who get hepatitis A often don’t have symptoms, so they can have the virus and not know it. However, they can still spread it easily. Fortunately, children are now routinely vaccinated against hepatitis A.
Most people who get hepatitis A recover completely within two weeks to six months and don’t have any liver damage. In rare cases, hepatitis A can cause liver failure and even death in older adults or people with underlying liver disease.
Hepatitis B: Every year, about 40,000 people in the U.S. become infected with hepatitis B. Acute hepatitis lasts from a few weeks to several months. Many infected people are able to clear the virus and remain virus-free after the acute stage. However, for others, the virus remains in the body, and they develop chronic hepatitis B infection, which is a serious, lifelong condition. About 1.2 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B. Of these, 15% to 25% will develop more serious health problems, such as liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer, and some people die as a result of hepatitis B-related disease.
Hepatitis B cannot be spread by contaminated water, food, cooking, or eating utensils, or by breastfeeding, coughing, sneezing, or close contact such as kissing and hugging.
Read Also: Hey Google What Is Hepatitis B
Before Taking This Medicine
Hepatitis A and B vaccine will not protect you against infection with hepatitis C or E, or other viruses that affect the liver. It will also not protect you from hepatitis A or B if you are already infected with the virus, even if you do not yet show symptoms.
You should not receive this vaccine if you are allergic to yeast or neomycin, or if you have ever had a life-threatening allergic reaction to any vaccine containing hepatitis A or hepatitis B.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
-
an allergy to latex rubber or
-
a weak immune system .
You can still receive a vaccine if you have a minor cold. In the case of a more severe illness with a fever or any type of infection, wait until you get better before receiving this vaccine.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C An Std
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
Which Adults Should Be Vaccinated Against Hepatitis B
According to CDC recommendations, adults in the following groups are recommended to receive hepatitis B vaccine:
General
- All people age 18 years and younger.
- Anyone 19 years and older who wants to be protected from hepatitis B.
People at risk for infection by sexual exposure
- Sex partners of people who are hepatitis B surface antigen -positive.
- Sexually active people who are not in long-term, mutually monogamous relationships.
- People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
People at risk for infection by percutaneous or permucosal exposure to blood or body fluids
- Current or recent illegal injection drug users.
- Household contacts of people who are HBsAg-positive.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally challenged people.
- Healthcare and public safety workers with reasonably anticipated risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- People with end-stage renal disease, including predialysis, hemo-, peritoneal- and home-dialysis patients.
Others
- International travelers to regions with intermediate or high levels of endemic HBV infection.
- People with chronic liver disease.
- People with HIV infection.
- People with diabetes who are age 19 through 59 years. For those age 60 and older, clinicians should make a determination of need for
- vaccination based on their patients’ situation.
In a future issue, we will review the various hepatitis B serologic tests, who needs testing, and when they need it .
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Vaccine Newborn Dosage
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Recommended Reading: Can A Child Get Hepatitis C
A Note About Sex And Gender
Sex and gender exist on spectrums. This article will use the terms male, female, or both to refer to sex assigned at birth. .
It is important that infants who are born to females with hepatitis B receive accurate doses of the hepatitis B vaccine. They may also be required to receive hepatitis B immunoglobulin if it is available.
The WHO also recommends using antiviral prophylaxis to help prevent hepatitis B transmission.
The table below outlines the two recommended hepatitis B vaccine schedules for infants born to those who have hepatitis B:
| Vaccine series |
|---|
What Are The Side Effects
The most common of the hepatitis B vaccine are mild and include:
- Sore arm from the shot.
Prepare for your child’s vaccine visit and learn about how you can:
- Research vaccines and ready your child before the visit
- Comfort your child during the appointment
- Care for your child after the shot
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Cause Urinary Tract Infection
Recommended Doses Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Recommended doses of hepatitis B by vaccine type, age, formulation, dosage and schedule.
Download PDF version formatted for print: Recommended Doses of Hepatitis B Vaccine
|
Vaccine |
|
|
Infants: birth, 1-4, 6-18 monthsOROlder children: 0, 1-2, 4-6 months |
|
|
20 years & older |
|
|
Infants: birth, 1-4, 6-18 monthsOROlder children: 0, 1-2, 4-6 months |
|
|
11-15 years |
|
|
3 doses |
0, 1, 4-6 months |
* The schedule for hepatitis B is flexible, but minimal intervals and minimum ages need to be observed:
- There should be at least 4 weeks between doses 1 and 2, and at least 8 weeks between doses 2 and 3.
- The minimum interval for the overall series from dose 1 to final dose is 4 months .
- Infants, should receive the final dose of hepatitis B vaccine on or after 6 months of age, otherwise long term immunity may be impacted.
Note:
- Adults who are immunocompromised or on dialysis require a larger dose of hepatitis B vaccine.
- The Engerix-B dose required is 40mcg/2.0mL on a scheduled of 0, 1, 2, and 6 months.
- For Recombivax HB, a special formulation is available. The dose is 40mcg/1.0mL given on a schedule of 0, 1, and 6 months
Combination Vaccines:
|
6 weeks thru 6 years |
Hep B as Engerix-B 10 mcg, DTaP as Infanrix, Polio |
0.5 mL |
3 doses |
Give single antigen hep B dose at birth followed by Pediarix at: 2, 4, 6 months |
|
Twinrix |
Hep A as Havrix 720 El.U, Hep B as Engerix-B 20 mcg |
1.0 mL |
0, day 7, day 21-30, 12 months |
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And B Difference
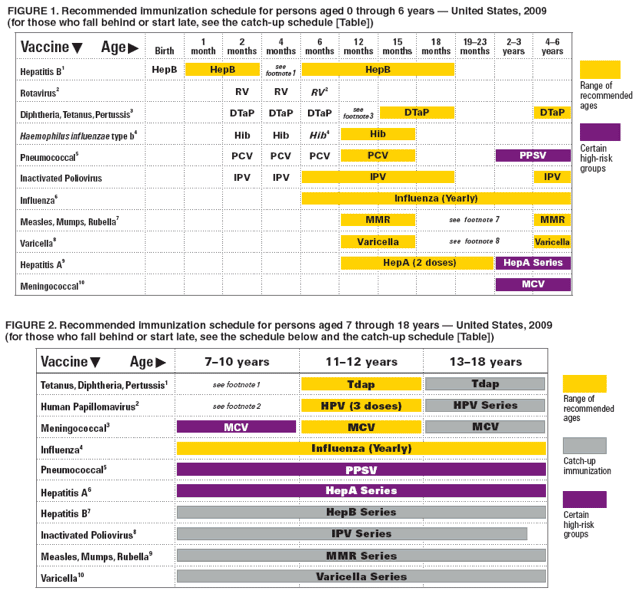
Us Children And Adult Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm as a three-dose series on a 0, 1, and 6-month schedule. Alternative schedules may be considered, noting that a third dose at 6 months, meeting minimum intervals between doses, is needed for maximum, long-term protection. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection.
There are four, 3-dose vaccine brands approved in the U.S.
- PreHevbrio PreHevbrio is only approved for adults age 18 and over.
2-Dose Vaccine Series