How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while theyre very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Discussing Screening Results With Clients
The medical personnel who ordered or arranged the screening test, not counselors, usually explain the results. Hepatitis screening should be part of the intake physical examination in an opioid treatment program, and medical personnel may report the results. However, the client may want to discuss the results with the counselor or ask the counselor questions.
Anxiety might interfere with some clients ability to comprehend or retain information, which might need to be repeated.
Suggestions for conversations with clients when the test results are negative include the following:
- Explain results clearly and simply: So the HCV screening result was negative? This means that, as of 6 months ago, you did not have .
- Emphasize that a negative result to an HCV test does not indicate to and that the client should take precautions to avoid . If a relapse to drug use occurs, advise clients to avoid sharing any drug paraphernalia or equipment. Specify that this includes cookers, cotton, water, needles, syringes, pipes, and straws.
- Emphasize the importance of getting HAV and HBV vaccinations. Provide information about the availability of low- or no-cost vaccinations.
Clients whose screening test results are positive for will need additional tests and examinationsusually with doctors who specialize in diseases of the liver to get accurate diagnoses and to determine their health status and the extent of liver damage. These tests are described in .
When Should I Get This Test
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups at an increased risk of infection. You may benefit from hepatitis B screening if you:
- Were born in parts of the world where the disease is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- Didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- Are HIV-positive
- Use injectable drugs
- Are at risk of HBV infection due to sexual exposure
A doctor may order hepatitis testing based on your symptoms, medical and family history, and a physical exam. If you develop symptoms without recent exposure to HBV, doctors may recommend an acute viral hepatitis panel that looks for hepatitis A, B, and C in one sample of blood.
Hepatitis tests may also be performed as follow-up tests when other tests of liver health are abnormal.
Testing is common in those that show symptoms that could be caused by hepatitis B. Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may take place before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that you have previously been infected with HBV or have already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
You May Like: Most Common Cause Of Hepatitis C
What Do The Results Mean
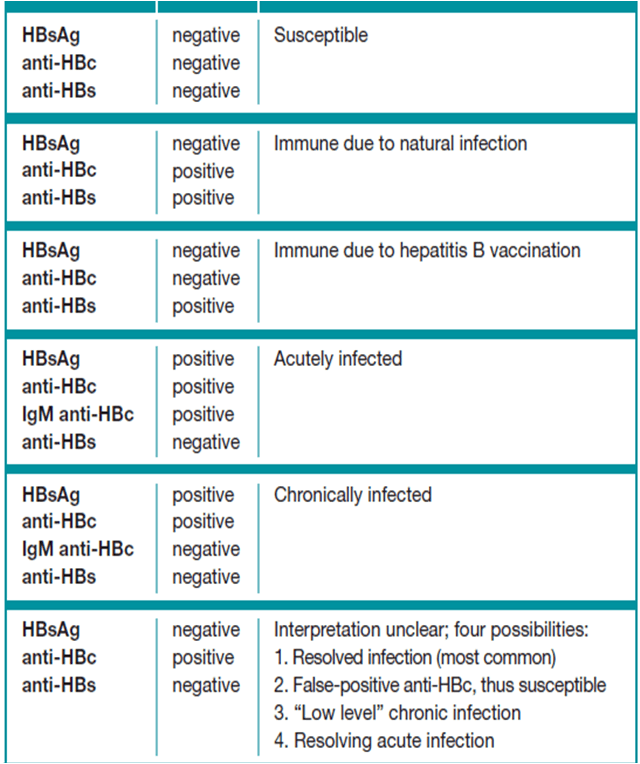
A hepatitis B blood panel consists of three tests that can be done with just one blood sample:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen . A positive test indicates that youre infected with hepatitis B and that you can spread it to other people. Further tests are needed to see if you have an acute or chronic infection.
- Hepatitis B core antibody . A positive result can indicate a past or current hepatitis B infection, but doesnt mean youre immune. A positive result needs to be interpreted by a doctor by examining the results of the other two tests.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody . A positive test indicates that youre protected from hepatitis B either through previous infection or vaccination .
The combination of these tests can indicate your hepatitis B status and whether you need to be vaccinated. Your test will give a negative or positive result for each category depending on whether your results are above or below the cutoff value.
Most peoples test results fall into the following categories. But its possible to have a result that doesnt fall into one of these groups. If youre reading your results yourself, be careful not to confuse HBsAb with HBcAb.
| HBsAG |
is associated with hepatitis B immunity after vaccination. But research has found that anti-HBs decline over time.
A found that more than 95 percent of people had anti-HBs levels greater than 10IU/L two years after vaccination. But this rate decreased to 70 percent after eight years.
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test
A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Read Also: Hepatic Steatosis Treatment Step By Step
Don’t Miss: Can You Cure Hepatitis A
Clinical Information Discusses Physiology Pathophysiology And General Clinical Aspects As They Relate To A Laboratory Test
Hepatitis B e antigen is a small polypeptide that exists in a free form in the serum of individuals during the early phase of hepatitis B infection, soon after hepatitis B surface antigen becomes detectable. Serum levels of both HBeAg and HBsAg rise rapidly during the period of viral replication. The presence of HBeAg in serum correlates with hepatitis B virus infectivity, the number of infectious virions, and the presence of HBV core antigen in the infected hepatocytes.
During recovery from acute hepatitis B, HBeAg level declines and becomes undetectable in the serum, while hepatitis B e antibody appears and becomes detectable in the serum. Anti-HBe usually remains detectable for many years after recovery from acute HBV infection.
In HBV carriers and patients with chronic hepatitis B, positive HBeAg results usually indicate presence of active HBV replication and high infectivity. A negative HBeAg result indicates very minimal or no HBV replication. Positive anti-HBe results usually indicate inactivity of the virus and low infectivity. Positive anti-HBe results in the presence of detectable HBV DNA in serum also indicate active viral replication in these patients.
Educating Clients About Viral Hepatitis
Clients may believe they know about viral , but their understanding of the disease may not be accurate. It is easy to confuse the three main types of viral , B, and C. Clients may have formed impressions based on limited or incorrect information. Counselors should briefly describe hepatitis A, B, and C, including their prevalence, , and relationship to drug use, as well as to other infections, such as HIV and sexually transmitted diseases. Specific strategies for speaking with clients include:
- Speak clearly and keep the message simple, focused, and brief.
- Use language, examples, and concepts that the client understands.
- Use appropriate visual aids.
- Frame numerical statements in terms that are easy to visualize. Say 5 out of 100 people rather than 5 percent of the population say more than half instead of the majority.
- Repeat the information at different times in different ways. The average client retains only approximately one-third of what he or she is told. Summarize essential points.
- Pay attention to a clients response to the information. For example, if a client stiffens his or her posture, consider saying, I notice that this topic seems to make you uncomfortable. It does for a lot of people. Please tell me what youre feeling right now. Id really like to help you with this.
- Use the opportunity to describe the potential detrimental effects of alcohol and other substance use on the liver of a person who is infected with HCV.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
How Long Can You Live With Hepatitis B
Most people who contract hepatitis B during adulthood fully recover within 1 to 3 months.
People with chronic hepatitis B may have a higher risk of developing long-term liver problems, like cirrhosis or liver cancer, which require treatment and may be life threatening.
Keep in mind that the risk of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for babies and children, especially if they have not been vaccinated against the virus.
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
Ethical approval with a referenced protocol number LHREC/2020/07 to conduct the study was granted by Lubaga hospital research ethical review committee following thorough review to ensure adherence to safety and protection of the rights of human subjects. All the study methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations . The aim, benefits and risks of the study were explained to the participants before requesting them to participate which they had to consent . Informed consent was obtained from each participant employed for the study.
Recommended Reading: New Drugs For Hepatitis C
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
Addressing Hepatitis For The First Time
It is crucial that a treatment counselor or health professional use a nonjudgmental and compassionate tone. Clients need to feel comfortable disclosing information about their health and risky behaviors. The following strategies can help initiate the conversation:
- Display posters, literature, or other -related items that could help prompt the client to ask questions about hepatitis. .
- Assess clients ability to discuss , based on their degree of openness in the counseling session, the amount of detail they provide in their responses, and the length of the therapeutic relationship.
- Raise the subject in a way that avoids making clients feel defensive or afraid. Consider introducing the subject by making parallels with other conditions that have been discussed. Say, for example, You said you were tested for HIV several times. Were you ever tested for viral ? or You mentioned that your friend is sick with HIV. Have you been tested for HCV or HIV? Tell me about those tests.
- Be patient and allow time for multiple, short conversations about the subject. This might ease feelings of fear, anxiety, or shame.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis
Preparing Clients For Screening
Once clients are comfortable talking about viral , they might be more willing to undergo screening. However, clients might be anxious about the test itself a reassurance that testing is a simple procedure can help allay these concerns. Many substance use treatment facilities do not offer screening, and clients might need to be referred elsewhere. The following strategies can enhance the discussion of the hepatitis screening process and hepatitis prevention:
How Is Hepatitis B Diagnosed
Your health care provider will ask about your medical history and symptoms. Especially important is your history of Hepatitis B risk factors such as IV drug abuse.Your provider will examine your skin and eyes for signs of Hepatitis B. Your provider will check your abdomen to see if the liver is enlarged or tender.You will have blood tests. If blood tests show that your liver is not working normally, your provider will do tests to see if you are infected with the Hepatitis B virus.
Questions about online blood testing or how to order a lab test?
Recommended Reading: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis
Is Hepatitis B Curable
Theres currently no known cure for hepatitis B, but there are many ways you can prevent infection and avoid transmitting the virus to others.
The most effective and safe way to prevent hepatitis B is to get vaccinated. You can also use barrier methods, like condoms, when having sex and avoid sharing needles.
Diagnosing Hepatitis A B & C
At NYU Langone, hepatologists, or liver specialists, and infectious disease specialists use blood tests to diagnose hepatitis A, B, and C. These viral infections cause inflammation of the liver.
If the results of a blood test confirm a diagnosis of viral hepatitis, your doctor may recommend imaging tests or a liver biopsy to determine the extent of liver disease.
Donât Miss: How Soon Do Hepatitis C Symptoms Appear
Recommended Reading: Can You Heal From Hepatitis B
Counseling Practices That Educate Support And Motivate Clients Undergoing Screening
Clients might need help deciding whether to get screened, understanding the test results, and determining their next steps. Even when services offered through the substance abuse treatment program are limited, discussing testing with clients presents an opportunity for counselors to motivate clients for change by confronting substance use and by making choices that improve their overall health. However, this may also be true when services are offered on-site through substance abuse treatment programs. A study at one methadone clinic that offered hepatitis screening and vaccination revealed that although the majority of clients completed screening , only 54.7 percent of clients who lacked for hepatitis A received vaccinations and only 2.9 percent of clients who lacked immunity for received vaccinations .
The Consensus Panel makes the following general recommendations while recognizing that, in some programs, the counselors role may be limited:
Recommended Reading: Can You Give Hepatitis C To Yourself
Management Of Pregnant Hbv Carriers
Pregnant HBV carrier mothers present a unique opportunity to prevent transmission of HBV to their neonates. All infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers should receive hepatitis B immune globulin and a full course of HBV vaccination . Vaccine failure in the neonate is rare but does occur , and may be accounted for by transplacental transmission before birth. Follow-up testing of the neonate should be performed to confirm vaccination effectiveness. Testing should be performed for HBsAg to detect vaccine failures, anti-HBs to confirm a successful vaccine response and anti-HBc-Total to determine if the anti-HBs response was due to vaccination or resolution of natural infection. While testing for these markers is recommended one to two months after completion of the vaccine series, testing at approximately 18 months would ensure that the anti-HBc-Total test does not represent maternal antibody. This may be important because vaccination failures have occasionally been associated with HBV vaccine escape mutants that may only demonstrate a positive anti-HBc-Total as the sole marker of infection. These mutations occur in the open reading frame of the HBsAg, may not be recognized by antibodies induced by current HBV vaccine, and may not be detected by currently available HBsAg enzyme immunoassays . Clearly, surveillance systems need to be in place to ensure that HBV vaccines remain effective and vaccine escape mutants do not replace current HBV strains.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Screen For Hepatitis C
Prosedur Tes Anti Hbs Kuantitatif
Untuk tes anti-HBS kuantitatif, dokter akan mengumpulkan darah dari pasien dan mengirimkannya ke laboratorium untuk dianalisis dan dievaluasi bersama dengan hasil tes hepatitis.
Bila hasil tes positif, hal itu menunjukkan bahwa orang tersebut memiliki kekebalan terhadap virus hepatitis B. Kekebalan tersebut bisa didapat dari vaksinasi atau karena infeksi. Nilai anti-HBS yang lebih tinggi dari 5 mIU/ml dinilai sebagai positif. Meski begitu, nilai antara 5 hingga 12 mIU/ml setelah vaksinasi menunjukkan bahwa vaksin tidak bertahan. Nilai di atas 12 mIU/ml menunjukkan bahwa vaksin bertahan dan menandakan sudah diimunisasi lengkap.
Sedangkan nilai negatif yang diperoleh tingkat anti-HBS pada 5,0 mIU/ml ke bawah menunjukkan bahwa tubuh tidak menghasilkan antibodi terhadap antigen yang diidentifikasi sebagai HBsAG pada permukaan virus Hepatitis B.
Direkomendasikan agar orang tersebut divaksinasi jika nilai anti-HBS negatif, yang merupakan indikasi bahwa orang tersebut belum pernah terkena virus hepatitis B atau belum pernah divaksinasi sebelumnya.
Selain itu, hasil Anti-HBS negatif juga bukan berarti bahwa orang tersebut tidak mengidap hepatitis B dan tidak terkena infeksi. Untuk memastikan kondisi tersebut, tingkat HBsAg yang dikenal sebagai tes antigen permukaan Hepatitis B harus diperiksa.
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Also Check: Can Hepatitis Cause Kidney Problems