What Causes Hepatitis In General
- Virus and other infections
- An acute illness caused by the hepatitis A virus .
- Transmitted through food and water contaminated by feces of infected people.
What is hepatitis D?Hepatitis D is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus. Only people infected with the hepatitis B virus can get hepatitis D. They can become infected with both viruses at the same time or get hepatitis D after first being infected with hepatitis B virus . Hepatitis D can cause severe symptoms and serious illness that can lead to life-long liver damage and even death.
Read Also: Hepatitis B And Hpv Vaccine Together
Finding Help For Hepatitis
If youve been diagnosed with viral hepatitis, there are a variety of resources that are available to help you. Lets explore a few of them below:
- Your doctor. Your doctor is a great first point of contact for questions and concerns. They can help you to better understand the type of hepatitis you have, as well as how it will be treated.
- American Liver Foundation . ALF is dedicated to ending liver disease through education, research, and advocacy. Their site has educational material about viral hepatitis, as well as ways to find doctors, support groups, and clinical trials in your area.
- Patient assistance programs. If you have hepatitis C, the cost of antiviral drugs can be high. The good news is that many drug manufacturers have patient assistance programs that can help you pay for these medications.
The chart below is an at-a-glance summary of some of the key differences between hepatitis A, B, and C.
| Hepatitis A |
|---|
Recommended Reading: Genotype Test For Hepatitis C
Causes And Risk Factors Of Hepatitis D
The primary route of transmission for hepatitis D is contact with infected blood or other bodily fluids. This can happen through sharing needles or drug materials with an infected person or having unprotected sex with an infected person.
Although it is rare, hepatitis D can be passed from mother to child during birth.
People cant get hepatitis D through everyday close contact that doesnt involve blood or bodily fluids.
Read Also: Hepatitis Vaccine For Adults Schedule
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
Initial symptoms may include:
- not having energy for everyday tasks
- feeling sick, like you may vomit
These initial symptoms may lead to jaundice and the ongoing symptoms of tiredness and sickness.
Infection generally causes severe liver inflammation and may lead to chronic hepatitis D infection. Individuals with chronic hepatitis D can develop:
- cirrhosis of the liver
- fulminant hepatitis
Some people do not develop any symptoms for the next 5 to 10 years, until their liver has been damaged. This is why it is important to take precautions against hepatitis D.
What Impact Does Hep C Have On Pregnancy And Expectant Mothers
There is a 4-7% chance of transmission from HCV-positive mother to child during childbirth. Women who have been exposed or are at high risk of HCV should be tested and treated during pregnancy. There are no prophylactic measures that can be taken to prevent transmission during birth. If a child is suspected of being infected they should be tested after 18 months .
HCV is transmitted through blood only, so infected mothers are able to breastfeed if they choose. These women should use caution if they have dry or cracked nipples that could expose the infant to contaminated blood. Read more about STDs and pregnancy here.
You May Like: Dating Someone With Hepatitis B
What Should Be Done After A Person Is Exposed To Hcv
- Follow-up of occupational HCV exposures:
- Perform anti-HCV testing of source patient.
- For the person exposed to an HCV-positive source:
- Perform baseline testing for anti-HCV, ALT activity, with follow-up testing at 4-6 months .
- Confirm all positive anti-HCV results obtained by enzyme immunoassay using HCV RNA testing.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis D
Coinfection with hepatitis D usually makes the hepatitis B infection more severe.
Coinfection with hepatitis B and D can lead to fulminant hepatitis Symptoms . Fulminant hepatitis can progress very quickly. Toxic substances normally removed by the liver build up in the blood and reach the brain, causing hepatic encephalopathy Hepatic Encephalopathy Hepatic encephalopathy is deterioration of brain function that occurs in people with severe liver disease because toxic substances normally removed by the liver build up in the blood and reach… read more . People may lapse into a coma within days to weeks. Fulminant hepatitis may be fatal, especially in adults.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Titer Labcorp Cost
What Are The 5 Types Of Viral Hepatitis
Viral infections of the liver that are classified as hepatitis include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. A different virus handles each type of virally transmitted hepatitis.
Hepatitis A is always an acute, short-term disease, while hepatitis B, C, and D are most likely to become ongoing and chronic. Hepatitis E is usually acute but can be dangerous in pregnant women.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Hepatitis D only occurs in patients with hepatitis B. Thus, healthcare workers, including the nurse practitioner should consider serological testing for HDV in patients with hepatitis B. This can be obtained by detection of total anti-HDV antibody followed by confirmatory staining for HDAg in liver tissues and/or measurement of serum HDV RNA. As HBV replication is suppressed in chronic HDV infection, hepatitis B e-antibodies are typically present.
As HDV depends on HBV, prevention can be achieved with hepatitis B vaccination. If the host is immune to HBV, they are subsequently protected against HDV. Patients who are at risk of contracting HDV infection should be encouraged to receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
At the moment there is no specific treatment for hepatitis D but unlike hepatitis B, the former is a benign infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C From Drug Use
Should You Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Since you can live with hep C for decades without knowing itit can take 10 to 40 years for hep C to progress from mild disease to cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancerthe Centers For Disease Control and Prevention recommends a one-time blood screening test for anyone born between 1945 and 1965. This population is more at risk of having received a tainted blood transfusion.
Hepatitis C can only be diagnosed through a simple blood test called an HCV antibody test. True to its name, it looks for antibodies, proteins released into the bloodstream, that show up in someone infected with the hep C virus. If you have a positive HCV antibody test, youll then be given a follow-up HCV RNA test to learn whether you have an active infection.
How Hepatitis D Is Spread
Hepatitis D is spread when infectious body fluids come into contact with body tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes . In Australia most infections are associated with:
- immigration from a country where hepatitis D is relatively common
- sharing injecting equipment
- mother-to-baby transmission of hepatitis D virus at or around the time of birth can occur, although this is uncommon.
Don’t Miss: Where To Get Hepatitis Vaccine
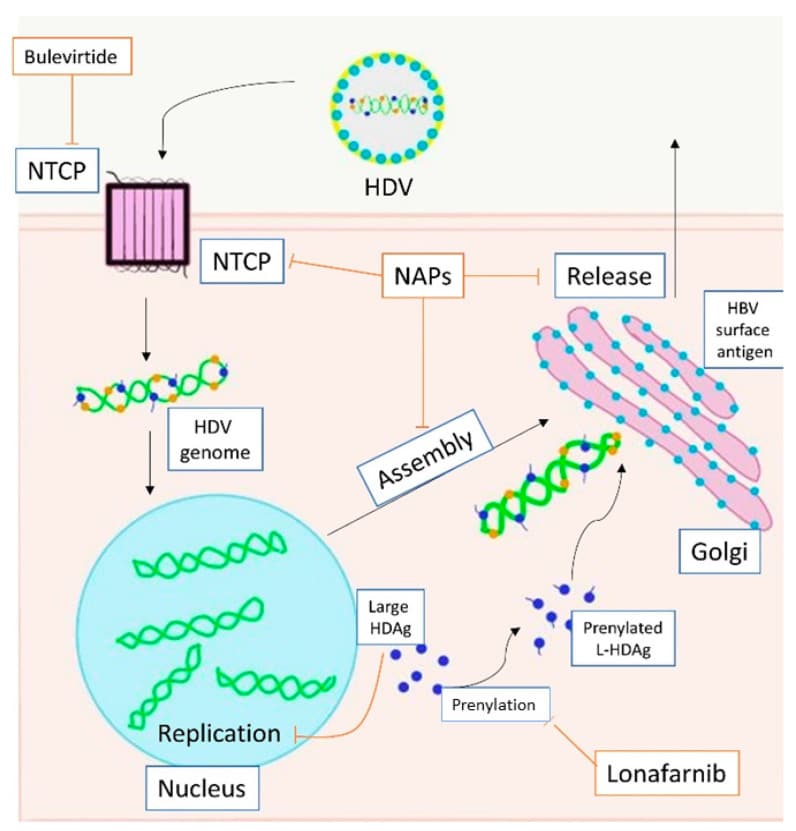
Viral Structure And Life Cycle
Hepatitis D virus viral life cycle and sites of drug target. 1. Hepatitis D virus virion attaches to the hepatocyte via interaction between hepatitis B surface antigen proteins and the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide , a multiple transmembrane transporter. 2. HDV ribonucleoprotein is translocated to nucleus mediated by the hepatitis D antigen . 3. HDV genome replication occurs via a rolling-circle mechanism. 4. HDV antigenome is transported out of the nucleus to the endoplasmic reticulum . 5. HDV antigenome is translated in the ER into small HDAg and large HDAg . 6. L-HDAg undergoes prenylation prior to assembly. 7. S-HDAg is transported back to the nucleus where it supports HDV replication. 8. New HDAg molecules are associated with new transcripts of genomic RNA to form new RNPs that are exported to the cytoplasm. 9. New HDV RNP associates with hepatitis B virus envelop proteins and assembled into HDV virions. 10. Completed HDV virions are released from the hepatocyte via the trans-Golgi network.
Finally, once the RNP interacts with the envelop protein of HBV and the HDV is assembled, the HDV virion is now ready for release. The HDV virion is released via the trans-Golgi network, where it can go on to infect other hepatocytes. However, the exact mechanism of HDV-virion release remains unknown .
Also Check: Can You Recover From Hepatitis B
Where Is Hepatitis D High Prevalence Of Hepatitis B/d Coinfection In Central Africa
By Sierra Pellechio, Hepatitis Delta Connect Coordinator
While hepatitis B is known to be highly endemic to sub-Saharan Africa and is estimated to affect 5-20% of the general population, the burden of hepatitis D, a dangerous coinfection of hepatitis B, has largely been left undescribed. Since the viruss discovery 40 years ago, Africa has faced structural barriers that have contributed to the ongoing prevalence of the virus in this region. Widespread instability, under-resourced health systems, and poor surveillance have contributed to inadequate research and a lack of understanding about the health burden of hepatitis D on hepatitis B patients, particularly in Central Africa.
As an increasing number of studies continue to describe the widespread endemicity of hepatitis B/D coinfection and its public health burden, researchers and the Hepatitis Delta International Network are calling on the World Health Organization to declare hepatitis D a threat in this region in order to promote increased priority and awareness. Addressing hepatitis B/D coinfection prevention and management will be complex and require a multi-pronged approach through methods such as government prioritization, increased funding for health systems, hepatitis B vaccination awareness programs, birth dose prioritization, better sterilization techniques in hospitals, clinics, and barbers, and public awareness of the disease.
Also Check: How Do They Check For Hepatitis C
Reasons For Reduced Prevalence Rate Of Hdv/hbv Chronic Infection
The impact of risk factors for acquiring HBV infection has changed over the past five decades around the world. Vertical transmission is no longer a risk factor for the transmission of HBV infection, due to the introduction of mass passive/active immunization of newborn babies. Furthermore, the impact of risk factors for HBV transmission through household contacts with HBsAg infected subjects has dropped in Western countries with the application of universal HBV vaccination and the reduction in family size. The epidemiological impact of other risk factors, such as the use of improperly sterilized medical and surgical instruments, transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products, the use of glass syringes and for men shaving at a barbers shop have dramatically decreased worldwide. IVDU and sexual transmission of HBV infection plays a major role in HBV transmission nowadays due to the exchange between drug addicts of syringes or other objects used for the preparation of drugs and to the infrequent or incorrect use of condoms in unsafe sexual activity. A marginal role is still played by cosmetic treatment with percutaneous exposure and dental treatment.
Drug use remains a major risk factor, as seen by a study performed in Baltimore showing 50% HBV/HDV co-infection in IV drug users.
The reports on the epidemiology of HDV infection are numerous, but at the same time are inadequate to have a complete overview of the spread of the Delta infection around the world.
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Also Check: How Many Kinds Of Hepatitis Are There
Don’t Miss: What Is The Sign Of Hepatitis C
Immune Response To Hdv
Mechanisms of HDV-specific CD8+ Tcell failure. HDV-specific CD8+ T cells targeting viral epitopes with wild-type sequence display a chronically activated phenotype and are functionally partially exhausted , HDV-specific CD8+ T cells targeting viral epitopes with sequence variations do not recognise the antigen anymore and display a memory-like phenotype . HDV, hepatitis D virus.
Prognosis Of Hepatitis D
Your health outlook depends on whether you were coinfected or superinfected with hepatitis D the prognosis is better for people who were coinfected.
The vast majority of coinfected people experience only the acute phase of the disease most of these people will get better over two to three weeks. Liver enzyme levels typically return to normal within four months.
About 10 percent of people infected with hepatitis D develop a chronic liver infection.
Chronic hepatitis D leads to cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver, in about 70 to 80 percent of cases. Once a person has cirrhosis, the disease may remain stable for as long as 10 years, although a high percentage of people with chronic hepatitis D and cirrhosis eventually die of acute liver failure or liver cancer unless they get a liver transplant.
The overall mortality rate of hepatitis D is unclear, with estimates placing it between 2 and 20 percent. As with most forms of hepatitis, prevention is the best strategy.
People at increased risk for severe disease from hepatitis A infection
- People with chronic liver disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C
- People with HIV
Other people recommended for vaccination
- Pregnant women at risk for hepatitis A or risk for severe outcome from hepatitis A infection
Any person who requests vaccination
There is no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hepatitis A B C
Common Symptoms Of Hepatitis
If you are living with a chronic form of hepatitis, like hepatitis B and C, you may not show symptoms until the damage affects liver function. By contrast, people with acute hepatitis may present with symptoms shortly after contracting a hepatitis virus.
Common symptoms of infectious hepatitis include:
It is crucial to understand what is causing hepatitis in order to treat it correctly. Doctors will progress through a series of tests to accurately diagnose your condition.
Molecular Biology And The Burden Of Hdv Infection
HDV genotypes and endemic hotspots
Due to the sequence variations found in HDV isolates, eight clades, termed genotypes 18, have been classified. They show remarkable differences in their replication efficacies. Genotype 1 is globally scattered while HDV genotypes 28 can be attributed to distinct geographic regions in the world. While the HDV median prevalence in HBsAg carriers is estimated to about 5%, it typically manifests in hotspots like Mongolia, the Middle East, Usbekistan or parts of South America where up to 80% of HBsAg carriers also display markers of an HDV infection. Due to the large gaps of knowledge on reliable epidemiological data HDV prevalence may be profoundly underestimated and needs more attention in the future.
HDV genome structure
HDV replication and envelopment of HDV ribonucleoproteins into HBsAg
Also Check: Can You Catch Hepatitis C
Hepatitis D: Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Hepatitis D, also called the delta agent, affects about 15 million people worldwide. It originates in those who suffer from hepatitis B, whether they are carriers or it has been manifested. It is usually the result of having unprotected sex with infected people, using drugs, or receiving blood transfusions with the virus. It is a severe disease, so the earlier the medical diagnosis, the more effective its treatment will be. At FastlyHealwe, explain what hepatitis D consists of, its causes, symptoms, and treatment.
Dont Miss: How Can You Transmit Hepatitis C