Living With Hepatitis B Or C
Taking care of yourself
Its important to take care of yourself if you have hepatitis B or C. Hepatitis stops the liver from working properly and there are things you can do to reduce the amount of work your liver has to do:
- cut back on alcohol
Talk to your doctor or nurse for advice.
Telling others
You do not have to tell others if you have hepatitis B or C. But you do need to do everything you can to prevent spreading the disease to others see below for more information. Letting your sexual and household contacts know that you the disease means they can get tested to see if they have caught it. They can also be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B Titer Test Panelmost Popular
The Hepatitis B Titer Test Panel panel contains 3 tests with 4 biomarkers.
Hepatitis B Titer Test
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Reflex Confirmation
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Immunity, Quantitative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total
The Hepatitis B Titer Test is ordered when a person needs proof of immunity to Hepatitis B or just want to check their immune status.
The Hepatitis Titer Test includes immunity testing for Hepatitis B. Hepatitis is a viral disease which affects the liver. Vaccinations for Hepatitis B can provide protective antibodies which immunize a person from catching the virus. Additionally, a person who has been affected by Hepatitis B and recovers can develop natural immunity. Titer testing looks for the antibodies which typically indicate that a person is immune to a particular virus or infection.
Hepatitis B Immunity
Not Immune and no active or prior infection may be a good candidate for vaccine
- Hepatitis B Surface Antigen = Negative
- Hepatitis B Surface Antibody = Negative
- Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total = Negative
Immunity due to vaccination
What Do Doctors Do
A doctor who thinks someone may have hepatitis may ask questions like these:
- Has the person been around anyone who works in health care or childcare?
- Did the person stick himself or herself with a dirty needle or get a tattoo with a dirty needle?
- Did the person have contact with the bodily fluids of someone who has hepatitis?
- Did the person have a blood transfusion as a baby?
- Have any of the person’s family members had hepatitis?
- Could the person have eaten food that was contaminated with hepatitis A?
The doctor can order a blood test to see if someone has hepatitis and which type, then help the person get the right care.
Also Check: Is Hepatitis B A Virus
For Patients With Chronic Hbv
Reducing the risk of liver damage
- Have liver enzymes monitored every 6-12 months.
- Reduce or eliminate alcohol.
- Stop smoking, as it increases the risk of liver cancer.
- You may drink coffee 3 or more cups per day may reduce the risk of liver cancer.Endnote 21
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis A if you are not already immune â talk to your HCP or contact your local public health department.
- Stick to your medication schedule and your regular lab testing and follow-up visits.
- Tell your HCP before starting any immunosuppressive therapy.
About medications for patients with cirrhosis
- Avoid aminoglycosides , benzodiazepines, and narcotics including codeine .
- Whenever possible, avoid ASA or NSAIDs. Acetaminophen, oral contraceptive pills, and statins are safe to use.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- If you require surgery, discuss it with your specialist first.
- If you have black stools, call your specialist immediately or go to the ER.
- Tell your HCP about any complementary/alternative therapies or over the counter supplements including herbal remedies that you are taking.
- Follow your HCPâs advice on how frequently you require abdominal ultrasounds.
Living well with HBV
Read Also: How Soon Can You Test For Hepatitis C
Hepatitis A: What Happens

Hepatitis A is highly contagious and can spread from person to person in many different settings. It typically causes only a mild illness, and many people who are infected may never realize they’re sick at all. The virus almost always goes away on its own and does not cause long-term liver damage.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Hepatitis Ab And C
How Does It Affect The Body
The incubation period for hepatitis B can range from . However, not everyone who has acute hepatitis B will experience symptoms.
About 95 percent of adults completely recover from hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B can also become chronic.
The risk of chronic hepatitis B is greatest in those who were exposed to HBV as young children. Many people with chronic hepatitis B dont have symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
In some people whove had hepatitis B, the virus can reactivate later on. When this happens, symptoms and liver damage may occur. People with a weakened immune system and those being treated for hepatitis C are at a higher risk for HBV reactivation.
Are You At Risk
Take this survey to find out if you are at risk of becoming infected with one of the hepatitis viruses.
Check your risk of hepatitis A
If you answered yes to any of the questions, you are at risk and should see your doctor if you desire testing.
Check your risk of hepatitis B
Check your risk of hepatitis C
References
You May Like: How To Treat Hepatic Encephalopathy
Preventing Hepatitis B Or C
There are vaccines available to prevent hepatitis B. The vaccines are free for babies and children under 18 years, and some adults. Talk with your doctor or nurse to find out more.
There is no vaccine against hepatitis C. To prevent spreading or catching hepatitis B or C:
- Always use condoms during sex.
- Cover cuts and scratches.
- Do not share toothbrushes, razors or other personal items.
- Do not share needles, syringes or other injecting equipment, including those used for skin piercing and tattooing.
- Be careful about blood contact, for example, when playing a contact sport.
- Get advice from your doctor if you are likely to have contact with blood or body fluids at work.
- Do not donate blood if you have hepatitis B or C.
How Are Hepatitis B And C Treated
Hepatitis B: Not all patients with chronic hepatitis B infection require treatment. At Yale Medicine, specialists decide on an individual basis whether a patient is an appropriate candidate for treatment. Generally, patients require treatment when their hepatitis B virus level is high, and when laboratory tests demonstrate significant inflammation or injury to the liver.
There are currently seven approved drugs for hepatitis B, two of which are considered to be first-line treatments. These drugs are oral pills taken once daily, and while they’re very effective at suppressing the virus to very low or undetectable levels over the long term, they are not considered curative.
Therefore, the goal of treatment is to control the virus long-term and decrease the risk of hepatitis B related complications such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C: For the greater part of the last 20 years, treatment of hepatitis C required the use of a chemotherapy-like injection drug called interferon, which has been associated with serious side effects and a low cure rate. Fortunately, advances in hepatitis C treatments within the last three years now allow for the use of oral medications that are significant improvements in terms of safety and effectiveness.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
What Are Clinical Trials For Hepatitis B
Clinical trialsand other types of clinical studiesare part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Researchers are studying many aspects of hepatitis B, such as
- progression of hepatitis B and long-term outcomes
- new treatments for hepatitis B
- prevention of reactivated or worsening hepatitis B in people receiving cancer treatment
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis A is spread when a person ingests fecal mattereven in microscopic amountsfrom contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by feces or stool from an infected person.
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sex with an infected person
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles, syringes, and even medical equipment, such as glucose monitors
- Sharing personal items such as toothbrushes or razors
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
Hepatitis C is spread when blood from a person infected with the Hepatitis C virus even in microscopic amounts enters the body of someone who is not infected. The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from:
- Sharing equipment that has been contaminated with blood from an infected person, such as needles and syringes
- Receiving a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Poor infection control has resulted in outbreaks in health care facilities
- Birth to an infected mother
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Be Contracted Sexually
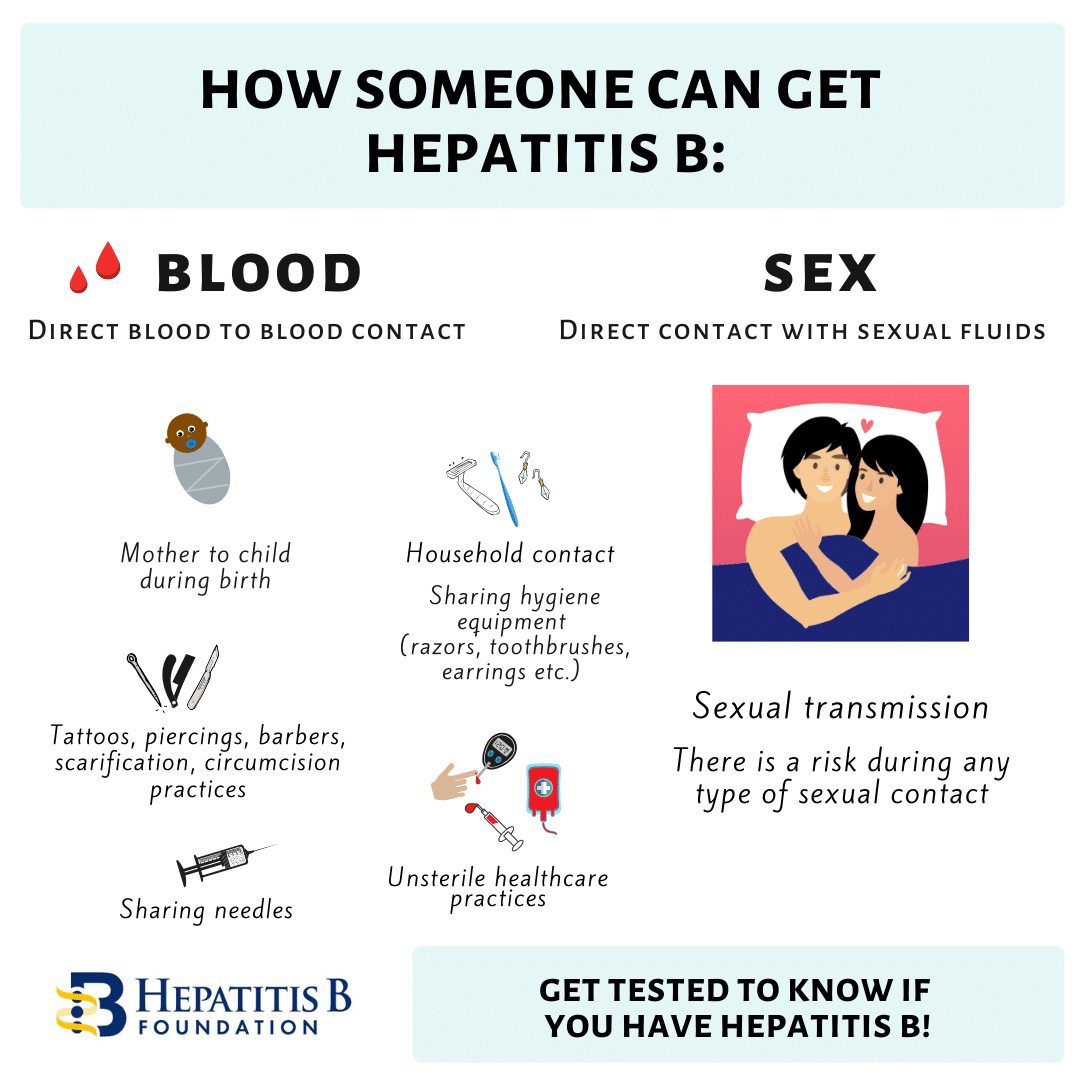
Hepatitis B: How Does It Spread
You can get it through contact with the blood or body fluids of an infected person. In the U.S., it’s most often spread through unprotected sex. It’s also possible to get hepatitis B by sharing an infected person’s needles, razors, or toothbrush. And an infected mother can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Hepatitis B is not spread by hugging, sharing food, or coughing.
What Is The Relationship Between Drug Use And Viral Hepatitis
Drug and alcohol use places people at particular risk for contracting viral hepatitis. Engaging in risky sexual behavior that often accompanies drug use increases the risk of contracting HBV and, less frequently, HCV. People who inject drugs are at high risk for contracting HBV and HCV from shared needles and other drug preparation equipment, which exposes them to bodily fluids from other infected people. Because drug use often impairs judgement, PWID repeatedly engage in these unsafe behaviors, which can increase their risk of contracting viral hepatitis. One study reported that each person who injects drugs infected with HCV is likely to infect about 20 others, and that this rapid transmission of the disease occurs within the first 3 years of initial infection.4 Drug and alcohol use can also directly damage the liver, increasing risk for chronic liver disease and cancer among those infected with hepatitis. This underscores that early detection and treatment of hepatitis infections in PWID and other people who use drugs is paramount to protecting both the health of the person and that of the community.
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis C Weaken Your Immune System
What Is Hepatitis B Surface Antibody
When you are exposed to HBV, your body mounts an immune defense to specifically target and neutralize the invader. Unlike innate immunity which mounts a generalized defense against all invaders, this type of immunity is disease-specific.
This immune response occurs whether you are exposed to HBV through blood or sexual contact, or if you are vaccinated with the hepatitis B vaccine.
The virus has proteins on its surface, called antigens, that serve as unique identification tags. When HBV enters the body, the immune system âencodesâ antibodies specific to these antigens so that it can recognize and attack the virus should it appear again.
There are two types of antibodies produced in response to the virus:
- Immunoglobulin M is the antibody that mounts the initial attack but eventually fades away.
- Immunoglobulin G is the antibody that provides long-lasting immune protection against HBV. The immunity can last for many years, but it gradually wanes over time.
You May Like: What Kinds Of Hepatitis Are There
Who Is Most Affected
In the United States, rates of new HBV infections are highest among adults aged 30-59 years, reflecting low hepatitis B vaccination coverage among adults at risk. The most common risk factor among people with new HBV infections is injecting drugs, related to the opioid crisis.
The highest rates of chronic hepatitis B infection in the United States occur among foreign-born individuals, especially people born in Asia, the Pacific Islands, and Africa. Approximately 70% of cases in the United States are among people who were born outside of the United States. CDC developed this map of the geographic distribution of hepatitis B around the world – PDF. Other groups who have higher rates of chronic HBV infection include people who inject drugs and men who have sex with men.
Also Check: How Is Hepatitis B Transmitted
Testing Treating And Reducing Risk Of Hepatitis
If you think youre at risk for hepatitis infection, talk to your healthcare provider about getting tested. A blood test is usually done to see if you have been exposed to the virus. Women who are pregnant or trying to become pregnant should get tested for hepatitis.
Get treated for hepatitis infection
There are treatments for hepatitis. Treating long-lasting hepatitis B or C infection can reduce the amount of the virus in a person, which may lower the risk of liver cancer.
India Hepatitis Knowledge Index
We used ten hepatitis survey questions adapted from the NHANES follow-up questionnaire for hepatitis C to create the India Hepatitis Knowledge Index . These ten questions assessed patient knowledge of hepatitis disease transmission, natural history, treatment, and prevention options. HBV and HCV patients were only asked about knowledge regarding their specific hepatitis type.
We conducted a factor analysis by hepatitis type to assess whether items on the knowledge scale hold together as one or more constructs or measures of knowledge. Only one distinct factor of knowledge was identified in factor analysis. For each hepatitis type, a Cronbachs alpha for the reliability of our ten scale items to assess the adequacy of scale reliability was performed. We created IHKI by hepatitis B or C patients. The index score was the number of correct questions .
Read Also: What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis B
Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis B. Many people who have hepatitis B dont have symptoms and dont know they are infected with hepatitis B. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis B, which can lower your chances of developing serious health problems.
Your doctor may recommend screening for hepatitis B if you9,14
- were born in an area of the world where 2 percent or more of the population has hepatitis B infection, which includes Africa, Asia, and parts of the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South America
- didnt receive the hepatitis B vaccine as an infant and have parents who were born in an area where 8 percent or more of the population had hepatitis B infection, which includes sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia
- are HIV-positive
- are a man who has sex with men
- have lived with or had sex with a person who has hepatitis B
- have an increased chance of infection due to other factors
Screening For Hepatitis B & C
NYU Langone doctors provide screening for hepatitis B and hepatitis C, two forms of hepatitis that can become chronic and lead to serious liver damage without treatment.
Hepatologists, or liver specialists, and infectious disease specialists at NYU Langone recommend screening for some people who may be at increased risk of becoming infected.
Even though hepatitis B and C may cause no symptoms for years or even decades after infection, the viruses still may damage the liver. For this reason, screening is an important tool for early detection and treatment. It can prevent serious illness, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, and hinder the spread of infection.
Vaccination for hepatitisis also an important prevention tool.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Sexuality Activity
Treatment: Chronic Hepatitis C
The latest drug to be approved by the FDA is glecaprevir and pibrentasvir . This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with all types of HCV who donât have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated. The length of treatment is longer for those who are in a different disease stage. The prescribed dosage for this medicine is 3 tablets daily.
There are several other combination drugs available, as well as some single drugs that may be used in combination. Your doctor will choose the right one for you depending on the type of hepatitis C you have, how well your liver is functioning and any other medical problems you may have. Also be sure to discuss your insurance coverage since these medications are expensive.