Detection Of Antiviral Resistance
Lamivudine monotherapy has been reported to be associated with the rapid emergence of antiviral resistance in 15% to 60% of treated individuals . Resistant HBV genomes have mutations in codon 552 within the YMDD motif of the reverse transcriptase/polymerase where a valine or isoleucine replaces the methionine. Resistance is typically clinically manifested by significant elevations in ALT after an initial decline in response to treatment. Prolonged treatment after development of the YMDD mutant is controversial, although improvement in liver pathology with decreased fibrosis may occur with continuation of treatment. Concerns about disease flares after stopping lamivudine have been raised . The development of genotypic resistance can be documented by molecular sequencing or by the INNO-LiPA HBV DR assay , which involves hybridization of amplified HBV-DNA fragments onto specific nucleotide probes that have been immobilized on nitrocellulose strips .
Why It Is Done
You may need testing if:
- You have symptoms of hepatitis.
- You may have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus. You are more likely to have been exposed to the virus if you inject drugs, have many sex partners, or are likely to be exposed to body fluids .
- You’ve had other tests that show you have liver problems.
- You are pregnant.
- You or your doctor wants to know if you are protected from getting the disease.
The tests also are done to help your doctor decide about your treatment and see how well it’s working.
Recommended Tests To Investigate Chronic Hbv Infection And The Interpretation Of Results
Chronic HBV infection is defined by the continued presence of HBsAg in the blood for longer than six months. Figure Figure11 and Table Table22 outline the tests used to diagnose most cases of chronic HBV. Test selection should be based on the person’s risk factors, vaccination history and findings from previous tests .
Diagnostic tests for acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection . ALT Alanine aminotransferase Anti-HAV-IgM Immunoglobulin M class antibody to HAV Anti-HCV Antibody to HCV antigens HBsAg Hepatitis B surface antigen
Don’t Miss: Acute Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Blood Test
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Blood Test earliest indicator of the presence of acute infection.
Test Code: 006510
CPT Code: 87340
Also Known As: Anti-HBs Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg Hepatitis-associated Antigen Hepatitis B Acute Exposure
Methodology: Immunochemiluminometric assay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
Test Code: 498
CPT Code: 87340
Also Known As: Anti-HBs Antibody to Hepatitis B Surface Antigen HBsAg Hepatitis-associated Antigen Hepatitis B Acute Exposure
Methodology: Immunoassay
Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results: 2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
What Happens During A Hepatitis Panel
A health care professional will take a blood sample from a vein in your arm, using a small needle. After the needle is inserted, a small amount of blood will be collected into a test tube or vial. You may feel a little sting when the needle goes in or out. This usually takes less than five minutes.
At-home testing kits are available for hepatitis B and C. Usually the test kit will include a sharp device, to prick your finger so you can collect a drop of blood to send to a lab for testing. For more information on at-home testing for hepatitis, talk to your provider.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Screening For Hepatocellular Carcinoma
The most important risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma is prolonged chronic HBV infection for decades, particularly in patients with active disease based on elevated ALT levels . The development of cirrhosis in chronic carriers increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, although in the case of HBV, the latter may occur in the absence of cirrhosis. Although the cost benefit remains to be established, screening for hepatocellular carcinoma is suggested in patients 30 years of age or older with one or more of the following risk factors : infection at birth being male a duration of infection for several decades a family history of hepatocellular carcinoma the presence of HCV co-infection and finally, specific at-high-risk populations . Suggested screening consists of an abdominal ultrasound and serum alpha-fetoprotein at approximately six-month intervals .
Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel
A Hepatitis B Blood Test Panel includes a Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total , Hepatitis B Surface Antigen , Hepatitis B Surface Antibody .
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
CPT Code: See Individual Tests
Also Known As:
No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
Test Results:
2-3 days. May take longer based on weather, holiday or lab delays.
You May Like: Hepatitis B And Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Demographic Characteristics And Clinical Status
The analytic samples drawn from 294 patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus at baseline, comprised 23 cases and 311 matched controls Table shows their demographic and clinical characteristics. Mean age and rheumatic disease types were similar between case and control groups. No patients with HBsAg/anti-HBs+serostatus had detectable HBV DNA at enrolment. Compared with controls, cases had lower baseline serum anti-HBs titers, more prevalent comorbidities , and relatively higher accumulated doses of sulfasalazine, leflunomide, and prednisolone. Most people in both groups used anti-TNF agents . No study subjects were kidney transplant recipients.
Table 1 Baseline characteristics of cases and controls treated with biologic DMARDs
No cases had clinical HBV reactivation during follow-up , and no cases developed alanine transaminase elevation, or received any anti-viral treatment during median follow-up of 30months after anti-HBs loss. Only one of the 16/23 cases whose serum HBV DNA was monitored after anti-HBs loss ever had a detectable viral load , which was observed only once, with no recurrence as of August 2020.
How Do I Know If I Have Hepatitis B
Like all STDs, the only way to know for sure if you have hepatitis B is to get tested whether or not you have symptoms.
If youre showing any signs of hepatitis B, you should get tested. Its also a good idea to get a test if you had unprotected sex or shared a needle, razor, or toothbrush with someone who has hepatitis B .
Your nurse or doctor will take a quick blood sample to test you for hepatitis B. It may take up to two months after infection for the test to be accurate but if youre not feeling well, dont wait to see a doctor or nurse.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Can Be Cured
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis B
Anyone can contract hepatitis B. However, certain groups are at greater risk. According to the CDC, the following groups are at highest risk for contracting hepatitis B:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- People who inject drugs or share needles
- Sexual partners of people infected with hepatitis B
- Men who have sex with men
- People living in close proximity to a person with hepatitis B
- Health care workers or others exposed to blood in their work environments
- Hemodialysis patients
Explainer: Lab Results And Their Interpretation
Before posting your lab results, please read through and abide by the best practices thread first
We all know that its important to have blood tests to know your current Hep B status or to know if youre protected against it. There are a lot of different tests in a panel for Hep B and these can be confusing. Here are short explanations for some of the common ones:
Use this thread to get help if you dont understand your results.
Hi Everich,
You need to be a bit more specific about what the exact test was. What is all the information you have about the test? We cannot answer your question without that information.
Thomas
Hi Everich, there are basically 3 blood tests that are required for a new vs. a chronic hepatitis B infection. Below is a simple summary of these tests. If you could let us know which blood test was indeterminate that would be very helpful.
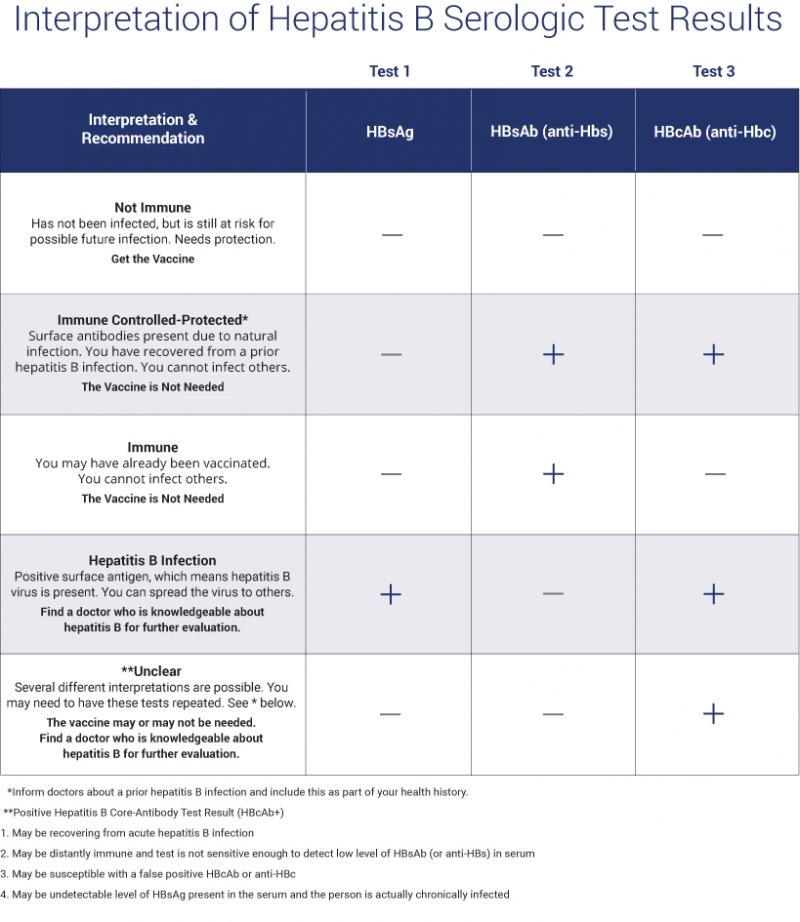
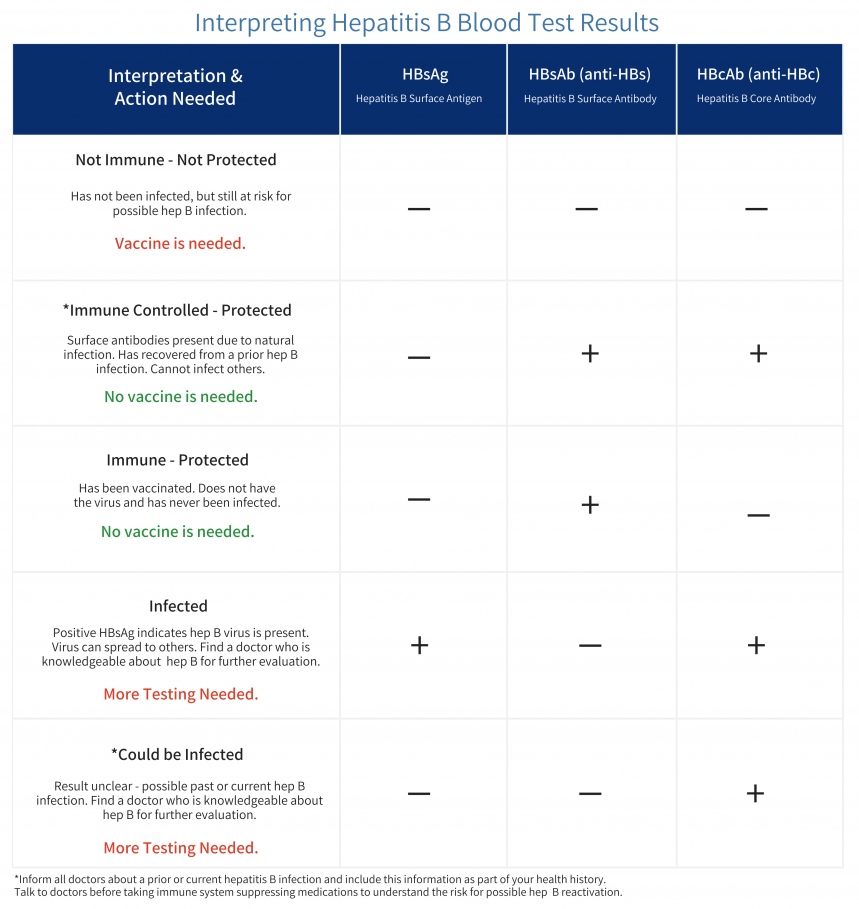
Hepatitis B surface antigen â If or means the hep b virus is present. This could mean a new infection or a chronic infection . If this test is or , then the hep b virus is not present in the blood.
Hepatitis B surface antibody â this tests for a protective antibody against the hep b virus. This can occur through getting the hep b vaccine or recovery from an exposure to the virus. If or , then it means a person has been protected against the hep b virus either through vaccination or recovery from an infection. Generally, the above test will be or .
Her report says HBV VIRAL LOAD < 34. IU/ml
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis Do To The Body
Who Is Getting Tested *
Currently you can only purchase testing for one person in one cart checkout. Or product cannot be purchased because you do not meet the age, gender, or location requirements to purchase the test.
Because of this, you cannot buy this test unless you update your cart or account setting.
This product contains duplicate test components to items in your cart. You are already covered by a test that you have in the cart.
Additionally, COVID-19 tests cannot be combined with other tests at this time.
Please update your cart before you try again.
Based on your response, this test is not right for you or not available.
This test is unavailable for your age and/or gender.
Please update your address
Quest does not currently support lab testing at your location, please update to a valid address to purchase this test.
Visit Account Settings to change your address.
Please select who is getting tested.
Must be 18+ years of age to purchase
Orders not permitted in: AK, HI, AZ
Blood
Hbv Dna Hbv Genotype And Hbv Drug Resistance Assays
Specimen: Serum or plasma
Container: Red-top tube, yellow-top tube , gel-barrier tube, plasma preparation tube, or lavender tube
Collection method: Routine venipuncture
The specimen should be transfused to separate plasma/serum from cells within 6 hours and kept frozen when testing cannot be done promptly.
The tests use PCR amplification, DNA probe hybridization, and sequencing method.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Virus Caused By
Ask A Laboratory Scientist
This form enables patients to ask specific questions about lab tests. Your questions will be answered by a laboratory scientist as part of a voluntary service provided by one of our partners, American Society for Clinical Laboratory Science. Please allow 2-3 business days for an email response from one of the volunteers on the Consumer Information Response Team.
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Donât Miss: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
Also Check: Hepatitis C How Is It Contracted
Time For Processing Hcv Ab Test Results
The turnaround time for 3rd-generation EIAs is at least 1 day. Many labs do not perform the tests on site and must send specimens to another lab for processing, which may further increase the turnaround time.
A point-of-care test is also available. The OraQuick® HCV Rapid Antibody Test is an FDA-approved test that can be performed with a fingerstick . It is also a CLIA-waived test and therefore can be used in clinic offices and outreach facilities. Results are reported as reactive or nonreactive within 20 minutes. Just as for the standard HCV Ab test done in the lab, a positive OraQuick® test must be confirmed by an HCV RNA test. The sensitivity and specificity of the test is similar to that of the laboratory-based assays.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Vaccine Cost Cvs
Enzyme Immunoassays For Detection Of Hepatitis C Antibody
The HCV Ab test is used for initial screening for hepatitis C. The test is performed by enzyme immunoassays , which detect the presence of hepatitis C antibodies in serum. The result of the test is reported as positive or negative. Third-generation EIAs have a sensitivity/specificity of approximately 99%. However, the presence of HCV Ab does not indicate whether the infection is acute, chronic, or resolved. A positive antibody test result should be followed up with an HCV RNA test to confirm that viremia is present.
You May Like: The Spread Of Hiv And Hepatitis In The Healthcare Setting
To Order The Following Combination Of Tests
Tests that will be performed:
- HbsAg HbcAb Total
- *HBeAg and/or HBeAb
Note: Indicate HBeAg and/or HBeAb in Section 3 Test Requestedof the General Test Requisition, in addition to completion of the Hepatitis Serology Box.*Testing for HBeAg and/or HBeAb will only be performed if HBsAg is reactive.
How Much Does The Test Cost
The cost of hepatitis B testing depends on the tests that are performed, where the test is conducted, and a patientâs health insurance coverage. When testing is ordered by a doctor, patients with health insurance may find it helpful to discuss the cost of testing with their health insurance company as they may be responsible for testing costs as well as other out-of-pocket costs such as copays and deductibles.
For patients without health insurance or for whom insurance doesnât cover the cost of testing, it may be helpful to discuss the cost of hepatitis B testing with a doctor or hospital administrator.
The cost of at-home hepatitis B testing starts around $45. At-home test kits may also test for additional types of viral hepatitis in the same sample. The cost of test panels that look for more than one type of viral hepatitis start around $80.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And How Do You Catch It
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. The symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same. So this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus and what stage of infection you may have.
Your healthcare provider may also order a series of blood tests called a hepatitis B monitoring panel to see if your infection is getting better.
When Should I Get Hepatitis B Testing
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups that are at an increased risk of infection. Groups that may benefit from hepatitis B screening include:
- Pregnant people
- People born in parts of the world where hepatitis B is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- People who didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- HIV-positive people
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may be used before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that a patient has previously been infected with HBV or has already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people who are at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Antibody Rflx Hcv Rna Pcr
Evaluation Of Individuals Suspected Of Having An Hbv Infection
Given the perinatal and childhood vaccination programs already in place in North America, most HBV-infected individuals will likely present with chronic infection. Such individuals are likely to have risk factors that include immigration from high endemicity regions, injection drug use or sexual contact with an infected person 1) . Therefore, the present guideline will provide diagnostic recommendations first for individuals suspected of having chronic HBV infection and, subsequently, for those with acute infection. The diagnosis of HBV infection in any individual has important management implications, including appropriate counselling, monitoring and/or treating and vaccinating family or at-risk contacts.
How It Is Done
The health professional taking a sample of your blood will:
- Wrap an elastic band around your upper arm to stop the flow of blood. This makes the veins below the band larger so it is easier to put a needle into the vein.
- Clean the needle site with alcohol.
- Put the needle into the vein. More than one needle stick may be needed.
- Attach a tube to the needle to fill it with blood.
- Remove the band from your arm when enough blood is collected.
- Apply a gauze pad or cotton ball over the needle site as the needle is removed.
- Put pressure on the site and then put on a bandage.
You May Like: How Does Someone Contract Hepatitis
How Is It Used
The main uses for hepatitis B virus tests include:
Some of the secondary reasons to perform testing include: to screen for hepatitis B infection in at-risk populations or in blood donors, to determine if someone is a carrier, to detect a resolved infection, and to determine if immunity has developed due to vaccination.
Generally, one set of tests is used as an initial panel of tests to detect HBV infection or to determine the cause of acute symptoms while another set of tests may be used after a diagnosis is made to monitor possible progression of the disease, to detect chronic infection, and/or to determine carrier status.
The following table summarizes the set of tests typically used for initial testing:
The following table summarizes tests that may be used as follow-up after initial tests detect an HBV infection: