Positive Hcv Antibody And Positive Hcv Rna
Individuals with a positive HCV EIA and positive HCV RNA should be told they have evidence of active hepatitis C infection and they should clearly understand they need medical follow-up evaluation and potential treatment of liver disease. A single positive HCV RNA value indicates infection, but must be interpreted in the context of clinical history to determine whether the individual has acute or chronic infection. For persons with a positive HCV EIA and positive HCV RNA, the CDC has generated counseling messages that focus on four areas: contacting a health care provider for further evaluation and management of their HCV infection, protecting their liver from further harm, addressing weight management in overweight and obese persons, and minimizing transmission of their HCV to others . In addition, the CDC recommends performing alcohol screening and brief intervention, which consists of screening for excessive alcohol consumption, brief counseling for individuals who screen positive, and referral to a specialized alcohol treatment program for individuals with possible alcohol dependence.
How Did I Get Hepatitis C If I Dont Do Drugs
Because the hepatitis C virus is spread through contact with infected blood, this disease is often associated with intravenous drug use or sharing needles with someone with HCV. But there are other ways to contract hep C.
They include:
- Coming in contact with needles used by someone with HCV in other ways, such as during your work as a police officer, first responder, or healthcare provider
- Sharing personal items with someone who has hepatitis C, or being exposed to the virus through any open sores they may have
- Getting a tattoo or piercing at a facility that does not use sterile equipment, potentially exposing you to the virus from a previous client infected with HCV
- Not using protection when engaging in sexual actions with someone who has hepatitis C
Women who are pregnant can also pass HCV onto their unborn child. This method of disease transference is increasing dramatically, largely due to the opioid epidemic, resulting in a higher rate of children between the ages of 2 and 3 being identified as having the virus.
Hepatitis C Antibody Test
Certain foreign substances that enter your body trigger your immune system to make antibodies. Antibodies are specifically programmed to only target the foreign substance they were made to fight.
If youve ever had a hepatitis C infection, your body will make hepatitis C antibodies as part of its immune response.
Your body only makes these antibodies if you have hepatitis C or had it in the past. So the hepatitis C antibody test can confirm whether you have the virus by testing for these specific antibodies.
It may take 2 to 3 months after exposure for the test to detect antibodies. If needed, your healthcare professional may order an HCV RNA test, which can detect the virus after just 1 or 2 weeks.
If the antibody test is positive, an HCV RNA test can show whether the infection is current.
While people of any gender experience the same hepatitis C symptoms, 2014 research suggested some effects of the virus may differ, depending on the sex you were assigned at birth.
Researchers noted that:
- women have a higher chance of clearing the virus without treatment
- liver disease may progress more rapidly in men
- men have a higher chance of developing cirrhosis
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis B Antibody
Sharing Toothbrushes Scissors And Razors
There’s a potential risk that hepatitis C may be passed on through sharing items such as toothbrushes, razors and scissors, as they can become contaminated with infected blood.
Equipment used by hairdressers, such as scissors and clippers, can pose a risk if it has been contaminated with infected blood and not been sterilised or cleaned between customers. However, most salons operate to high standards, so this risk is low.
New Cdc Data Reveal Less Than A Third Of People Diagnosed With Hepatitis C Receive Timely Treatment
An issue of CDCâs Vital Signs provided new research on low rates of timely treatment initiation among insured adults diagnosed with hepatitis C, even though hepatitis C is largely curable. The report finds that large gaps in hepatitis C treatment persist nearly a decade after a highly effective cure for this deadly infection was approved. The report notes that only 1 in 3 individuals with insurance receive direct-acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C within a year of diagnosis. Cost, insurance treatment restrictions, and few primary care providers treating hepatitis C are some of the many barriers to timely treatment. Treatment is even lower among people who are Medicaid or Medicare recipients, those living in states with Medicaid treatment restrictions as well as racial and ethnic minority populations, and among adults under the age of 40. Read the August 2022 MMWR article, Vital Signs:â¯Hepatitis C Treatment Among Insured Adults â United States, 2019â2020.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Tested For Hepatitis C
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C Infection
There are two types of hepatitis C infection:
- Acute: a short-term infection that occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to the virus. However, about 75 to 85 percent of people with the acute form go on to develop the chronic form.
- Chronic: a long-term illness that can continue throughout a persons life. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and other serious problems, such as liver failure or cancer. About 15,000 people a year die from liver disease associated with hepatitis C.
Whats The Outlook For Hep C Thats Developed Into Cirrhosis Or Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis, especially if left untreated. Without treatment, cirrhosis can lead to liver cancer and liver failure.
Treating cirrhosis and liver cancer typically requires a liver transplant. A transplant can cure both cancer and liver function impairment. But a transplant is only available for a small number of people.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Quant Rna Pcr
Who Is At Risk
Your risk of infection with HCV is increased if you:
- Had tattoos or body piercings in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment
- Worked in a place where you came in contact with infected blood or needles, for example, healthcare workers
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Received a blood product for clotting problems made before 1987
- Needed to have your blood filtered by a machine for a long period of time because your kidneys werent working
- Were born to a mother with HCV
- Had unprotected sex with multiple partners
- Have or had a sexually transmitted disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Most people infected with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with an acute hepatitis C infection may have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include
- yellowish eyes and skin, called jaundice
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you most likely will have no symptoms until complications develop, which could be decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
Also Check: Can Autoimmune Hepatitis Be Cured
Can You Die From Hepatitis C
Complications from untreated hepatitis C, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, can be fatal, though HCV itself is rarely fatal.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , people who develop cirrhosis from HCV have a
more than half of people with an HCV infection will develop chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C is long term and can lead to permanent cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Chronic hepatitis C usually has no symptoms. People with chronic hepatitis C may not even know they have it. But once symptoms appear, it means that damage to the liver has already begun.
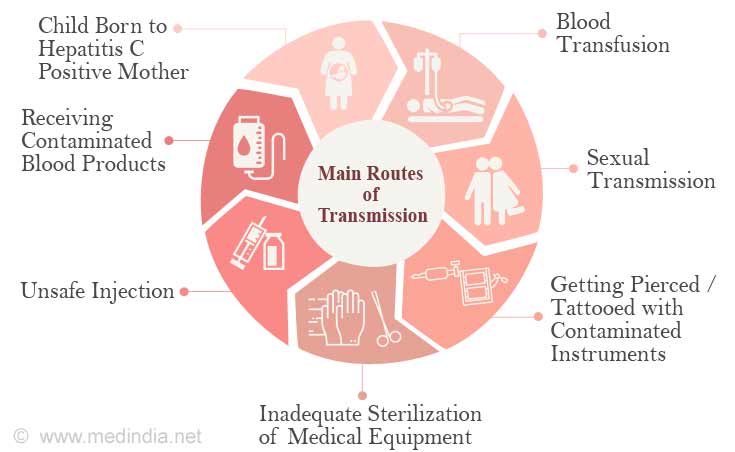
How Is Hepatitis C Transmitted
Because HCV is primarily spread through contact with infected blood, people who inject drugs are at increased risk for HCV infection. HCV can also be transmitted from an infected mother to child at the time of birth, from unregulated tattoos or body piercings, and from sharing personal items that may be contaminated with infected blood, even in amounts too small to see. Much less often, HCV transmission occurs through sexual contact with an HCV-infected partner, especially among people with multiple sex partners and men who have sex with men. Currently in the United States, health care related transmission of HCV is rare, but people can become infected from accidental needle sticks and from breaches in infection control practices in health care facilities.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
Causes And Risk Factors
HCV causes hepatitis C. People contract the virus through blood-to-blood contact with contaminated blood. For transmission to occur, blood containing HCV must enter the body of a person without HCV.
A speck of blood, invisible to the naked eye, can carry hundreds of hepatitis C virus particles, and the virus is not easy to kill.
The report the following risk factors for developing hepatitis C:
- using or having used injectable drugs, which is currently the most common route in the U.S.
- receiving transfusions or organ transplants before 1992, which is before blood screening became available
- having exposure to a needle stick, which is most common in people who work in healthcare
- being born to a mother who has hepatitis C
The CDC offer advice on cleaning syringes if it is not possible to use clean and sterile ones. Although bleach can kill the HCV in syringes, it may not have the same effect on other equipment. Boiling, burning and using alcohol, peroxide, or other common cleaning fluids to wash equipment can reduce the amount of HCV but might not stop a person from contracting the infection.
It is extremely dangerous to inject bleach, disinfectant, or other cleaning products, so people should make sure they rinse the syringe thoroughly. A person should only ever use bleach to clean equipment if new, sterile syringes and equipment are not available.
People who are at risk due to these factors can have screening to rule out HCV.
- peginterferon alfa-2a
How Is Hepatitis C Infection Prevented
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine to prevent hepatitis C. To reduce your risk of getting hepatitis C:
- Injection drug use is the most common way people get hepatitis C. Avoid injecting drugs to reduce your risk. If you do inject drugs, use sterile injection equipment. Avoid reusing or sharing.
- Avoid sharing personal care items that might have blood on them
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, follow universal blood/body fluid precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about tattooing, body piercing, or acupuncture are the instruments properly sterilized?
- If youre having sex with more than one partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases, including hepatitis C.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Symptoms In Men
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
What Is A Hep C Genotype
A genotypeis the genetic variation in the DNA of the virus you have.
There are 6 main genotypes of hep C. In the United States, about 74% of people with hep C have genotype 1. Some treatments work against all hep C genotypes, whereas others only work on some genotypes. If you and your healthcare professional determine that treatment is right for you, your genotype and your degree of liver damage may factor into the treatment decision.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis A Shots At Costco
Who Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
The CDC recommends that you get tested at least once no matter what. Definitely get screened if any of these things apply to you:
- You were born between 1945 and 1965.
- You use or inject drugs.
- You have ever injected drugs — even if it was just once or a long time ago.
- Youâre on kidney dialysis.
- You have abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels .
- You had a blood transfusion, blood components, or an organ transplant before July 1992.
- Youâve ever gotten clotting factor concentrates made before 1987.
- You received blood from a donor who later tested positive for hepatitis C virus.
- Youâre a health care worker, first responder, or have another job that exposes you to HCV-infected needles.
- You were born to a mother with HCV.
Meaning Of Hcv Viral Load
The number of HCV RNA international units per milliliter of blood must be measured before treatment and during the course of treatment, to assess response. Before treatment, however, the HCV viral load is not related to the patient’s liver disease severity or HCV prognosis. This is important for patients and providers to understand.
Note: In hepatitis B, unlike hepatitis C, a higher HBV DNA viral load does correlate with increased disease severity and increased likelihood of outcomes such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
You May Like: Is Fasting Required For Hepatitis C Test
Immunoassays For Hcv Core Antigen
As an HCV diagnostic marker, HCV core antigen has been studied, either alone or as an HCV antibody-HCV antigen combination assay. Some experts have proposed use of an HCV core antigen test as a less expensive option than HCV RNA testing, but there are no HCV antigen assays that are FDA-approved for use in the United States at this time.
Complications Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Unless successfully treated with medication, chronic Hepatitis C infection can cause other serious health problems, such as cirrhosis, liver cancer and liver failure. However, with recent advances in Hepatitis C treatment we now have higher cure rates, shorter treatment times, and all-oral treatment regimens for most people. If youre at risk for Hepatitis C, speak to your healthcare provider today about getting tested.
Don’t Miss: What Is Symptoms Of Hepatitis
Molecular Hcv Rna Tests
Molecular diagnostic tests for hepatitis C specifically detect HCV RNA and the process is commonly referred to as a Nucleic Acid Test or Nucleic Acid Amplification Test . The HCV NAT becomes positive approximately 1 to 2 weeks after initial HCV infection. The NAT test has become the gold standard supplemental test for patients who have a positive HCV EIA screening test. The NAT can determine whether a patient with a positive HCV antibody test has current or resolved HCV infection. In addition, the NAT can be used in combination with other laboratory studies, such as prior antibody test results or hepatic aminotransferase levels, to suggest the possibility of acute HCV infection. The results for the commercially available quantitative HCV RNA assays, which were previously reported as copies/mL, are now given in International Units /mL.
Interpretation Of Hcv Test Results And Recommended Action
Prior to discussing the HCV test results with the individual who has undergone testing, it is important to interpret the test results and have a plan for communicating the test results and your recommended further action . Individuals who engage in activities, such as injection drug use, that place them at higher risk of acquiring HCV should undergo regular screening for HCV infection.
You May Like: How Can I Get Hepatitis C
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
Whos Most At Risk Of Developing Hepatitis C
Injection drug use is still the most common risk factor in both the United States and the United Kingdom.
People who used injection drugs and shared equipment long ago may still develop symptoms of chronic hepatitis C later in life, especially if the virus was never detected and treated.
Others at risk for hepatitis C infection include:
- healthcare workers who experience accidental needle pricks while caring for people with hepatitis C
- infants birthed by a parent with hepatitis C
- people who received transfusions, organ transplants, or other blood products before proper screening was introduced in June 1992
Hepatitis C is transmitted by:
- yellowing of the skin or eyes
It can take anywhere from 2 weeks to 6 months for a hepatitis C infection to develop after exposure to the virus.
In some cases, the body can clear the infection on its own before diagnosis or treatment occurs.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed using an antibody test and a PCR test. Both blood tests offer slightly different insights into the state of infection.
Also Check: What Is Viral Hepatitis B
What Can You Do To Reduce Your Risk Of Hepatitis C
Although theres a vaccine for hepatitis A and hepatitis B, there isnt a vaccine for hepatitis C.
The best way to reduce your risk of contracting the hepatitis C virus or transmitting it to others is to practice harm reduction. This applies to substance use and partnered sexual activity.
If you use intravenous drugs or other substances, this means:
- using sterile syringes, needles, or straws whenever possible
- safe handling and disposal of syringes, needles, and other medical waste
- cleaning the area of injection before and after intravenous drug use
If you engage in partnered sexual activity, this means:
- regularly testing for hepatitis C and other STIs
- asking your partner about their STI status and sharing yours
- using a condom or other barrier method consistently and correctly
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all adults should screen for hepatitis C at least once in their lifetime and that adults who are at an increased risk for hepatitis C screen more regularly.
If youre unsure about your risk for hepatitis C, consult with a doctor or other healthcare professional. They can recommend a screening schedule that best suits your needs.