Who Is At Risk
Your risk of infection with HCV is increased if you:
- Had tattoos or body piercings in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment
- Worked in a place where you came in contact with infected blood or needles, for example, healthcare workers
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Received a blood product for clotting problems made before 1987
- Needed to have your blood filtered by a machine for a long period of time because your kidneys werent working
- Were born to a mother with HCV
- Had unprotected sex with multiple partners
- Have or had a sexually transmitted disease
New Cdc Data Reveal Less Than A Third Of People Diagnosed With Hepatitis C Receive Timely Treatment
An issue of CDCâs Vital Signs provided new research on low rates of timely treatment initiation among insured adults diagnosed with hepatitis C, even though hepatitis C is largely curable. The report finds that large gaps in hepatitis C treatment persist nearly a decade after a highly effective cure for this deadly infection was approved. The report notes that only 1 in 3 individuals with insurance receive direct-acting antiviral treatment for hepatitis C within a year of diagnosis. Cost, insurance treatment restrictions, and few primary care providers treating hepatitis C are some of the many barriers to timely treatment. Treatment is even lower among people who are Medicaid or Medicare recipients, those living in states with Medicaid treatment restrictions as well as racial and ethnic minority populations, and among adults under the age of 40. Read the August 2022 MMWR article, Vital Signs:â¯Hepatitis C Treatment Among Insured Adults â United States, 2019â2020.
Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Hepatitis C can be passed from person to person. Most people with HCV get it through direct contact with blood containing the virus.
People with hepatitis C can pass on the virus to others by sharing needles and syringes. Hepatitis C is easily transmitted among people who use intravenous drugs.
Its also possible, but much less common, to acquire the HCV by:
- sharing a razor with a person who has the virus
- sharing a toothbrush with a person who has the virus at the same time that you have bleeding gums
- having sexual contact with a person who has the virus
Read Also: How Can Someone Get Hepatitis B
Can Hepatitis C Be Cured
Unlike Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, a vaccine for Hepatitis C is not available.
However, treatment options are available and Hepatitis C may be cured .
Learn more about your treatment options and speak to your healthcare provider today.
The Hepatitis C virus is considered cured if the virus is not detected in your blood when measured with a blood test 3 months after treatment is completed. This is called a sustained virologic response and data suggest that you will stay virus free indefinitely.
Try to keep yourself as healthy as possible, keep your medical appointments and get regular check-ups. Remember that you could become re-infected if you expose yourself to high-risk situations such as injection drug use, and so do everything possible to avoid these situations. Speak with a substance abuse counselor if needed.
Reactive Or Positive Hepatitis C Antibody Test
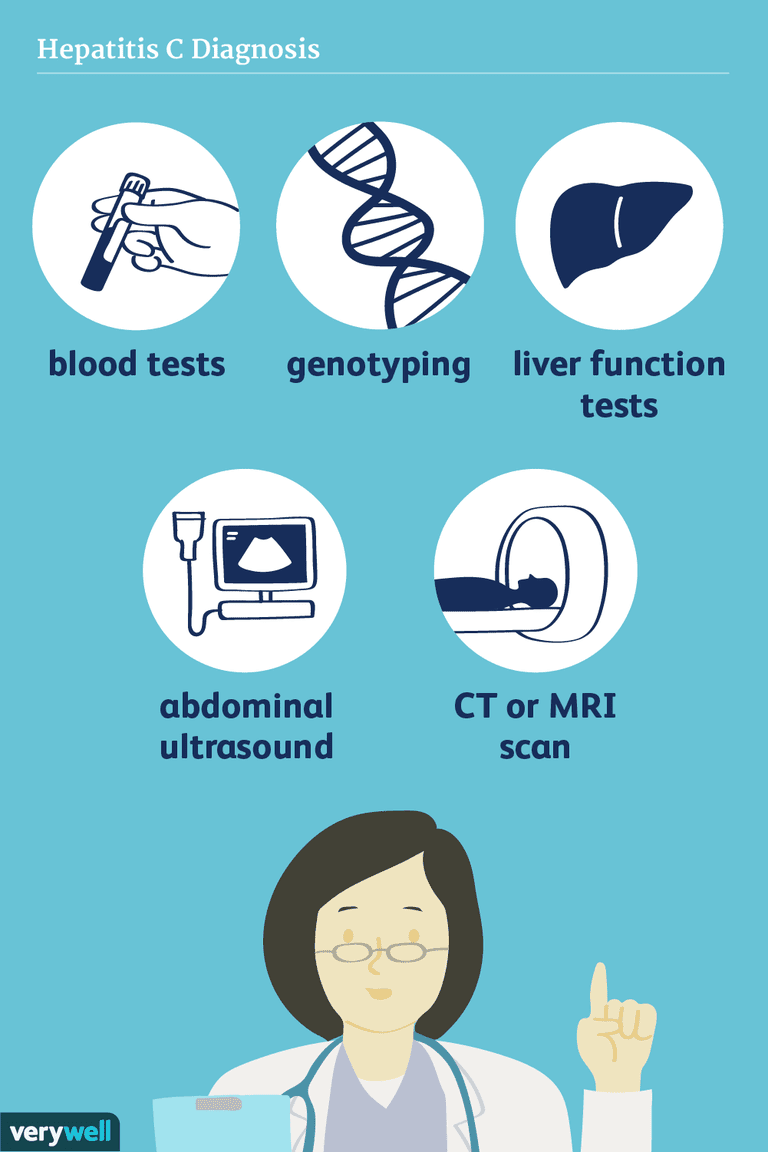
- A reactive or positive antibody test means that Hepatitis C antibodies were found in the blood and a person has been infected with the Hepatitis C virus at some point in time.
- Once people have been infected, they will always have antibodies in their blood. This is true even if they have cleared the Hepatitis C virus.
- A reactive antibody test does not necessarily mean that you have Hepatitis C. A person will need an additional, follow-up test.
Persons for Whom HCV Testing Is Recommended
- Adults born from 1945 through 1965 should be tested once
- Ever injected drugs, including those who injected once or a few times many years ago
- Have certain medical conditions, including persons:
- who received clotting factor concentrates produced before 1987
- who were ever on long-term hemodialysis
- with persistently abnormal alanine aminotransferase levels
- who have HIV infection
You May Like: Can You Donate Plasma With Hepatitis C
Hcv Antibody Blood Tests
When hepatitis C viruses infect your liver cells, your immune system responds by using antibodies to mark the viruses as harmful intruders. The antibodies are specific for HCV, so their presence indicates that you have had HCV at some time in your life. Antibody tests cannot distinguish between past or current infection, so clinical information such as medical history, signs, symptoms, or other tests can determine whether you have an active infection or a previous infection.
Who Is At Risk For Hepatitis C
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
You May Like: How To Live With Hepatitis B
What Are The Treatments For Hepatitis C
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your health care provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Eliminating Viral Hepatitis C Is In Sight Now Lets Leave No One Behind
Sometimes it takes a stark reminder of the devastating impact an illness can have to show us just how important it is to diagnose, treat and if possible cure those affected. This is exactly the case with hepatitis C virus
In the 1970s and 1980s, over 4,000 people with haemophilia and other bleeding disorders were infected with HIV or HCV as part of contaminated blood transfusions. Many sadly passed away as a result and their story and fight for justice continues to shock people around the UK today.
The media attention around this story has served to highlight the injustice faced by those affected. But it has also had another impact: to remind us of the very real danger of HCV, and why it is vital that we continue to strive to eliminate this virus leaving no one behind.
What is HCV?HCV is a virus. It infects the liver and, if left untreated, can cause serious and life-threatening damage, including cirrhosis and even liver cancer1. In many cases, there are few symptoms in its early stages, meaning a person may go undiagnosed for years.
Contracting HCV is typically the result of contact with infected blood. This is commonly through sharing contaminated needles. However, it is far from the only route. Today, HCV poses a real health concern, which is felt by some of the most marginalised people in society: people who inject drugs migrants prisoners people who are homeless or communities in which HCV is stigmatised, such as amongst first-generation South Asians.
You May Like: New Treatments For Hepatitis B
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Clinical Scenarios That Suggest Acute Hcv Infection
Symptomatic Presentation
Individuals with acute HCV infection can develop significant symptoms and may present with the new onset of jaundice, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, and malaise. More often, however, these individuals have no obvious symptoms or only have limited symptoms, such as slight malaise.
History of a Recent HCV Exposure but Without Symptoms
Since acute HCV is usually asymptomatic, clinicians should test person for HCV if they suspect a new exposure to HCV could have taken place, regardless of clinical symptoms. The most common exposures include recent injection drug use that involved needle sharing, a needlestick injury, and sexual contact with a partner who has known HCV infection. For persons with acute or recent HCV acquisition, HCV testing soon after the exposure can make the diagnosis of a new infection and distinguish acute from chronic infection. Recent injection drug use with shared needles or equipment would be considered the highest risk exposure, especially if the needle-sharing partner is known to have HCV. Although the exact risk of acquiring HCV through sexual contact is controversial, sexual transmission appears to be highest among men who have sex with men, particularly if this involves persons with HIV who have engaged in physically traumatic or rough sex.
You May Like: How Is Hepatitis A Transmitted
Remember That Personal Hygiene Products Are Well Personal
In other words, only use intimate grooming items that belong to you, and avoid letting other people use yours.
This advice isnt as obvious as it might sound. One 2019 survey from the Oral Health Foundation and Philips, for example, found that 26% of British respondents were willing to share their toothbrushes with someone else.
Theres a small but present risk of getting hepatitis C by sharing toothbrushes, says Ton.
If one of you has a cut in your mouth from flossing, brushing aggressively, or a violent tortilla chip the blood residue on the brush can transmit the virus, she says.
Jennifer Veltman, an infectious disease specialist affiliated with Loma Linda University Medical Center, adds that clippers, trimmers, and other tools can also be a source of contamination.
That means your besties blade is off-limits, no matter how frustrating that missed patch of hair may be.
Recommended Laboratory Evaluation Prior To Referral
All persons referred for further evaluation and management of HCV infection should have a confirmed positive HCV RNA level, preferably a quantitative HCV RNA level and not a qualitative HCV RNA level. It is ideal, but not imperative, that the clinician who makes the diagnosis of HCV infection can perform some preliminary tests to provide advanced information in anticipation of the initial referral visit. These initial preliminary tests include an HCV genotype, tests of synthetic liver function , hepatic inflammation , and assays to detect relevant coinfection . For primary care providers taking on a more comprehensive role for the initial evaluation and management, see Module 2, Lesson 1 for a detailed discussion in the Core Concept Initial Evaluation of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B What You Need To Know
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis C
People more likely to get hepatitis C are those who
- have injected drugs
- had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- have been on kidney dialysis
- have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- have had tattoos or body piercings
- have worked or lived in a prison
- were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- are infected with HIV
- have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months or have a history of sexually transmitted disease
- are men who have or had sex with men
In the United States, injecting drugs is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.13
Gap In Linkage To Care
Unfortunately, many individuals diagnosed with HCV infection do not get linked to appropriate care for their HCV infection. Multiple reasons for the gap in linkage to care have been cited, including failure of the medical provider to make the referral, lack of medical insurance, and substance use or mental health disorders that interfere with making or keeping the referral appointment. Linkage to care rates have been lower among racial and ethnic minorities. Failure to link to care negatively impacts health outcomes in persons living with HCV infection. With highly effective HCV treatment now available for all HCV genotypes, referral for evaluation and management of HCV has taken on even greater importance.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Viral Hepatitis C
Staying Healthy With Hepatitis
Not everyone needs treatment right away, but its important to be monitored regularly by an experienced doctor and discuss treatment options of the best way to keep you healthy.
- Get vaccinated against Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B
- Avoid alcohol and drugs
- Eat a healthy & balanced diet. Include a lot of vegetables and fruits try to stay away from too much salt, sugar and fat.
- Exercise regularly. Walking is one of the best exercises, and it helps to make you feel less tired.
- Check with a health professional before taking any prescription pills, supplements, or over-the-counter medications.
- Do not share razors, nail clippers, needles or other items that come in contact with blood with other people.
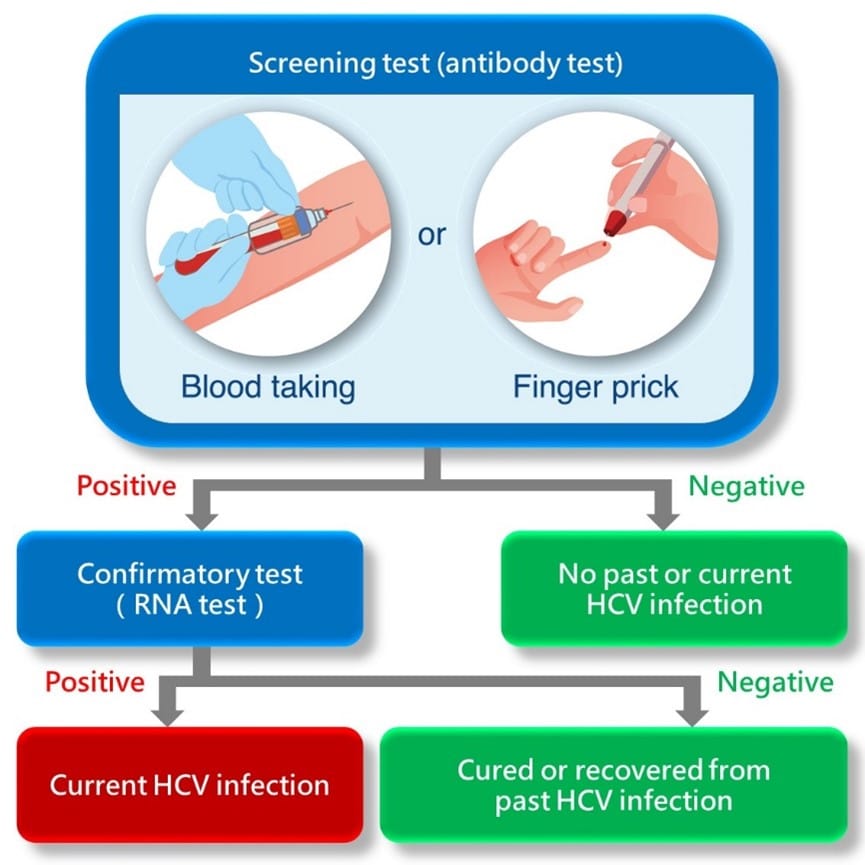
Using Elisa And Hcv Rna Tests Together:
- Negative ELISA = No hepatitis C antibodies found in blood. You are probably not infected with HCV.
- Positive ELISA = You may have HCV infection. However, it is possible this is a false-positive. More testing is required.
- Negative HCV RNA = No active HCV infection.
- Positive HCV RNA = Active HCV infection.
You May Like: Latest News On Hepatitis B
Medications For Hepatitis C
Many different medications can treat hepatitis C. Treatments most often include antivirals, with Riboviria sometimes prescribed if previous treatments were ineffective.
Medications called direct-acting antivirals work to fully remove the hepatitis C virus from your body while helping prevent liver damage at the same time.
A few brand names of these medications include:
6 different genotypes , or strains, of hepatitis C.
Once your doctor or other healthcare professional knows your genotype, theyll have a better idea of which medication will work best for you. Some strains have developed a resistance to some medications, so your genotype can affect your treatment options.
Effective Treatments Are Available For Hepatitis C
New medication to treat for HCV have been approved in recent years. These treatments are much better than the previously available treatment because they have few side effects and do not need to be injected. There are several direct-acting antiviral HCV treatments that cure more than 95% of people who take them in 8 to 12 weeks. HCV treatment dramatically reduces deaths among people with HCV infection, and people who are cured of HCV are much less likely to develop cirrhosis or liver cancer.
Take Action! CDCs National Prevention Information Network Service Locator helps consumers locate hepatitis B and hepatitis C prevention, care, and treatment services.
Also Check: What Hepatitis Vaccines Are Available
How Is Hepatitis C Spread
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes
- Being born to a mother with HCV
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Relationship Of Symptoms And Spontaneous Clearance
Overall, when combining data from multiple historical studies, approximately 25 to 35% of person with acute HCV infection have spontaneous clearance of HCV. The rates of spontaneous clearance are significantly lower in persons who are Black and in those individuals who have HIV coinfection. In contrast, rates of spontaneous clear are higher in females and in persons who acquired HCV in childhood. It has also been demonstrated that patients who present with symptomatic acute HCV infection and jaundice have higher rates of spontaneous clearance of HCV, in the range of 35 to 50%. The presence of jaundice is believed to reflect hepatic inflammation caused by a more robust initial immune response against HCV.
You May Like: Can Hiv Lead To Hepatitis