How Effective Is Treatment
Direct-acting antivirals cure 9 out of 10 patients with hepatitis C.
Successful treatment does not give you any protection against another hepatitis C infection. You can still catch it again.
There’s no vaccine for hepatitis C.
If treatment does not work, it may be repeated, extended, or a different combination of medicines may be tried.
Your doctor or nurse will be able to advise you.
Its More Important Than Ever To Keep Your Weight In Check
The second biggest contributor to liver damage is fatty liver disease, which can be a result of being overweight, says Massoud. So if hepatitis C has already lead to cirrhosis or damage to your liver, its especially important to keep your weight in check.
Try to eat healthy whenever possible: Fill up on vegetables, while cutting back on sugar and junk food, says Massoud. Eating a balanced diet will not only keep your weight down but can also improve your overall health. If you need help shoring up your diet, ask your primary care doctor or hepatologist to refer you to a nutritionist who has experience working with people who have liver diseases.
Additional reporting by Colleen de Bellefonds
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
There are no special medicines or antibiotics that can be used to treat a person that is acutely infected once the symptoms appear. Generally, bed rest is all that is needed. Interferon is the most effective treatment for chronic HBV infection and is successful in 25 to 50 percent of cases. Chronic carriers of HBV should avoid drinking alcohol or taking medications which are harmful to the liver, as these actions can make the liver disease worse.
Read Also: Where To Get Hepatitis B Vaccine In Nigeria
Recovery After A Fecal Transplant
FMT is regarded as safe and is well-tolerated, even by patients who are ill with C. diff and even by children. Most side effects have to do with the delivery method of the transplant. If you are receiving a stool transplant through the most common method , you might experience temporary side effects such as:
- Bloating and intestinal gas
- Cramping due to air trapped in the colon during the procedure
- Constipation due to anti-diarrhea medication
Serious side effects are rare, but can occur. These include:
- Infection with another bacterium or virus from the donor stool if the donor is not adequately screened and tested.
- Pneumonia from FMT delivered by tube through the nose .
- Standard risks from a colonoscopy or endoscopy, which include infection, bleeding, tear or perforation requiring surgery, and risks of anesthesia.
How Is Acute Hepatitis B Treated
Acute hepatitis B doesnt always require treatment. Most of the time, a doctor or healthcare professional will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body.
While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection. You can also take an over-the-counter pain reliever to help with any abdominal pain you have. Speak with a doctor about which medications can help your symptoms.
See a doctor if your symptoms are severe or seem to be getting worse. You may need to take a prescription antiviral medication to avoid potential liver damage.
Like acute hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B may not require medical treatment to avoid permanent liver damage. For some people, monitoring their symptoms and getting regular liver tests is an appropriate care regimen.
Treatment generally involves antiviral medications, such as:
- peginterferon alfa-2a injections
- antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir
Antiviral medications can help to reduce your symptoms and prevent liver damage, but they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is for you to have the lowest viral load possible. Viral load refers to the amount of a virus in a blood sample.
You can lower your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by:
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Genotype 2b Treatment
What You Need To Know
- Fecal transplantation is also called fecal microbiota transplantation , stool transplant, bacteriotherapy or intestinal microbiota transplant.
- FMT is mainly used to treat persistent infections with C. diff.
- The procedure works by taking healthy bacteria from the feces of a carefully screened donor and transferring them to the colon of the recipient.
- A fecal transplant is typically performed through a colonoscopy however, it can also be performed with upper endoscopy.
Curing A Bacterial Infection
The body reacts to disease-causing bacteria by increasing local blood flow and sending in cells from the immune system to attack and destroy the bacteria. Antibodies produced by the immune system attach to the bacteria and help in their destruction. They may also inactivate toxins produced by particular pathogens, for example tetanus and diphtheria.Serious infections can be treated with antibiotics, which work by disrupting the bacteriums metabolic processes, although antibiotic-resistant strains are starting to emerge. Immunisation is available to prevent many important bacterial diseases such as Hemophilus influenza Type b , tetanus and whooping cough..
You May Like: Hepatic Artery Infusion Liver Cancer
Incomplete Or Failed Response To Treatment
Some people with autoimmune hepatitis have an incomplete response to treatment, meaning that treatment helps but does not lead to remission. If you have an incomplete response to treatment, you may need to take different medicines to help prevent liver damage.
Some people may fail to respond to treatment, meaning that the inflammation and liver damage of autoimmune hepatitis keep getting worse. Your doctor may recommend additional blood tests and higher doses of medicines. If liver damage leads to complications, you may need treatment for complications.
Global Antibiotic Research And Development Partnership
A joint initiative of WHO and Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative , GARDP encourages research and development through public-private partnerships. By 2023, the partnership aims to develop and deliver up to four new treatments, through improvement of existing antibiotics and acceleration of the entry of new antibiotic drugs.
Don’t Miss: Diagnostic Test For Hepatitis B
What Happens During A Fecal Transplant Procedure
The FMT procedures differ depending on the transplant delivery method. For delivery through colonoscopy, the gastroenterologist prepares the transplant by taking the donor stool sample and mixing it with a saltwater solution. The fecal transplant is 100% liquid.
After the procedure, you may return home or to your hospital room, where you should rest for the remainder of the day. Your doctor might have you take anti-diarrhea medication before you leave, to help keep the fecal transplant in your colon so it can do its work.
Pantoea Agglomerans Bacteremia: Is It Dangerous
Ikwinder Preet Kaur
Abstract
Introduction. Pantoea agglomerans, an anaerobic Gram-negative bacillus, is a rare cause of opportunistic infections affecting premature infants to seniors. We present a 34-year-old man who was presented for the management of diabetic ketoacidosis and developed Pantoea agglomerans bacteremia after one week of hospitalization. Case Presentation. A 34-year-old African-American male with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus type I and recurrent skin infections was admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis. He had left upper extremity abscess, preliminary wound cultures were positive for Gram-positive cocci, and an initial set of blood cultures were negative. He was started empirically on vancomycin. One week after admission, he started having chills followed by a recurrent increase in body temperature to 102 degrees Fahrenheit. The wound was healing, without active infection. Chest X-ray and CT scan of abdomen and pelvis to rule out infection were negative. Repeat blood cultures showed P. agglomerans in both the tubes. The patient was successfully treated with intravenous ceftriaxone, and he recovered fully without any complication. Discussion. Pantoea agglomerans is a bacteria associated with plants however, it can infect humans and vertebrate animals. The outcome seems favourable with the institution of appropriate antibiotics even in immunocompromised patients.
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
3. Hospital Course
P. agglomerans
4. Discussion
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Cause Cirrhosis Of The Liver
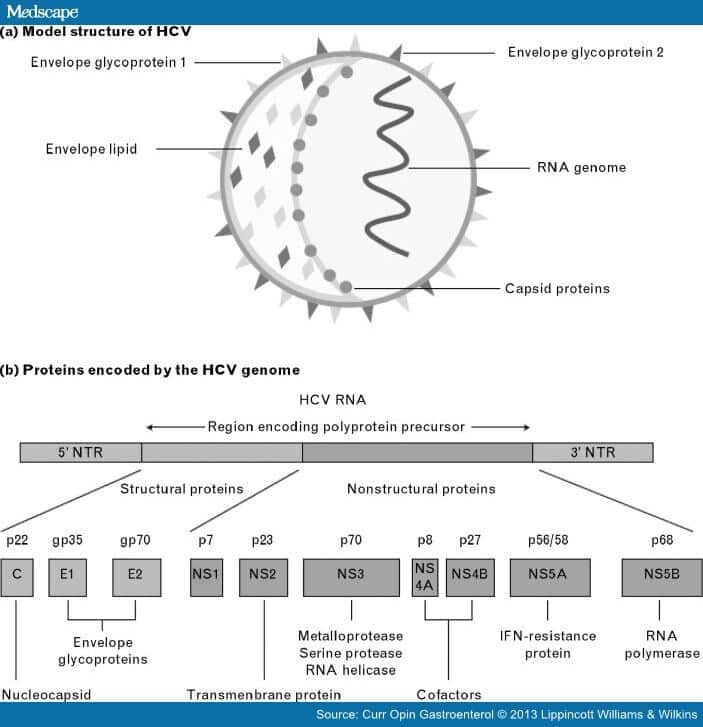
Causes Of Hepatitis C
You can become infected with hepatitis C if you come into contact with the blood of an infected person.
Other bodily fluids can also contain the virus, but blood contains the highest level of it. Just a small trace of blood can cause an infection. At room temperature, it’s thought the virus may be able survive outside the body in patches of dried blood on surfaces for up to several weeks.
The main ways you can become infected with the hepatitis C virus are described below.
You Might Need To Get Vaccinated Against Hepatitis A And B
Hepatitis A, B, and C are three different viruses that all cause inflammation of the liver. If you have hepatitis C and contract one of the other two hepatitis viruses, your symptoms will be even more severe, says Massoud.
If you havent already been vaccinated against hepatitis A and B and also have cirrhosis, the CDC recommends getting the shots after youve finished your hepatitis C treatment, to prevent additional liver damage.
Recommended Reading: Lamivudine Dose In Hepatitis B
Lyme Disease Antibiotic Treatment Research
For early Lyme disease, a short course of oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline or amoxicillin, cures the majority of cases. In more complicated cases, Lyme disease can usually be successfully treated with three to four weeks of antibiotic therapy.
After being treated for Lyme disease, a minority of patients may still report non-specific symptoms, including persistent pain, joint and muscle aches, fatigue, impaired cognitive function, or unexplained numbness. These patients often show no evidence of active infection and may be diagnosed with post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome .
Multiple clinical trials, funded by NIH and others, have shown no benefit to additional IV antibiotic treatment in patients with Lyme disease, although the interpretation of those results have been challenged by some.
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis C
For people with hepatitis C, the goal of treatment with antiviral medication is to prevent the virus from replicating, or copying itself, and to eliminate the virus from the bloodstream. If the hepatitis C virus has been in the body for more than six months, the infection is considered chronic. Without treatment, most people with acute hepatitis C develop the chronic form of the disease.
Your doctor decides which antiviral medicationor combination of medicationsto prescribe based on the results of a blood test called a genotype test. There are six genotypes, or strains, of the hepatitis C virus, and people with certain genotypes respond more quickly to medical treatment.
For many years, the standard treatment for chronic hepatitis C consisted of the antiviral medications pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Ribavirin is taken by mouth every day, and interferon is an injection that you or a caregiver can administer once a week at home.
In 2013 and 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a group of new medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. These medications, which include sofosbuvir, are very effective and have fewer side effects than older medications, particularly interferon.
Recommended Reading: How Bad Is Hepatitis C
You May Have To Stop Drinking
If you have cirrhosis or liver damage even if its mild you should abstain from alcohol until your liver is healed. In this case, there is no safe amount of alcohol to drink, even if the patient is feeling well, Massoud says.
If you dont have liver damage and are cured of hepatitis C, it may be possible to drink in moderation. Talk to your doctor first, though.
Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C often doesn’t have any noticeable symptoms until the liver has been significantly damaged. This means many people have the infection without realising it.
When symptoms do occur, they can be mistaken for another condition. Symptoms can include:
- flu-like symptoms, such as muscle aches and a high temperature
- feeling tired all the time
- loss of appetite
Read more about the complications of hepatitis C.
Also Check: Risk Factors Of Hepatitis B
How Can I Protect Myself Against Viral Hepatitis
There are many ways you can reduce your chances of getting hepatitis:
- Get the vaccines for hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
- Use a condom during sex.
- Don’t share needles to take drugs.
- Practice good personal hygiene such as thorough hand-washing with soap and water.
- Don’t use an infected person’s personal items.
- Take precautions when getting any tattoos or body piercings.
- Take precaution when traveling to areas of the world with poor sanitation.
- Drink bottled water when traveling.
It is very important that you take these preventive measures if you participate in risky behaviors. Take preventive steps, too, if you work in places like a nursing homes, dormitories, daycare centers, or restaurants where there you have extended contact with other people and a risk of coming into contact with the disease.
The Bodys Response To Viral Infection
Viruses pose a considerable challenge to the bodys immune system because they hide inside cells. This makes it difficult for antibodies to reach them. Some special immune system cells, called T-lymphocytes, can recognise and kill cells containing viruses, since the surface of infected cells is changed when the virus begins to multiply. Many viruses, when released from infected cells, will be effectively knocked out by antibodies that have been produced in response to infection or previous immunisation.
Don’t Miss: How Can Hepatitis B And C Be Transmitted
Whats The Difference Between Acute And Chronic Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. If you have acute hepatitis B, you may be asymptomatic or have symptoms and develop icteric hepatitis. It can transition into chronic hepatitis B if the virus doesnt naturally go away after 6 months.
- Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least 6 months. If you have this type of hepatitis, you may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of your life. Its possible to have chronic hepatitis B that started as acute, but many people dont have acute hepatitis B first.
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the infection. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Your risk of developing chronic hepatitis B depends on when you first received your diagnosis of the virus. Children who receive a diagnosis of hepatitis B, especially those under the age of 5 years old, have a higher risk of the infection becoming chronic. Adults are less likely to develop chronic hepatitis B. Around 90 percent of adults who develop it will fully recover.
Keep in mind that hepatitis B can be present for years before you start to show any symptoms.
You May Want To Avoid Supplements
Some supplements, herbs, and over-the-counter drugs can cause liver damage and potentially even liver failure, particularly herbal remedies and bodybuilding supplements, including green tea extract, according to research published in January 2017 in the journal Hepatology. Massoud adds that there are no supplements that can improve the liver, no matter what the claims are.
Nothing can scientifically support, strengthen, or clean the liver, he says, adding that some of them can even be harmful.
Read Also: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Hepatitis A
You May Still Have Liver Damage
Antiviral medication can clear the body of a hepatitis C infection, but it cant treat the permanent liver damage that may have occurred in the meantime. To determine if you have liver damage, your doctor will perform a biopsy or a scan either before or after you start treatment. If theres no scarring, you probably wont need long-term follow-up.
If you have severe liver damage, known as cirrhosis, it can be life threatening, so you will need to continue to see your doctor twice a year to monitor your condition. Currently, theres no treatment for cirrhosis, which is unfortunate, says Massoud. This is why we stress the need for patients to continue to see their doctor.
At each visit, your doctor will assess your symptoms and, if you have any, run blood work to check your liver function and order an ultrasound to look for cancer. The hepatitis C virus causes inflammation in the liver, which can cause scarring and increase the risk for liver cancer.
If you had high levels of liver damage before you started treatment, you may still have an increased risk of liver cancer after the infection has been cured, says Massoud.
If at any time your doctor believes these tests point to a decline in liver function, you may be evaluated for a possible liver transplant.
What Is C Diff
A healthy digestive tract has thousands of bacteria. In most cases, these bacteria are helpful to digestion, or are harmless. However, treatment with antibiotics, which may be required for certain conditions, can kill off many of the good bacteria in the colon. This can allow the bad bacteria, called Clostridium difficile to take over.
C. diff can cause fever, diarrhea and cramping. People can get C. diff after being treated with antibiotics for an infection. In people over age 65 and in those with chronic illness, C. diff infection can be severe even fatal.
Fecal Microbial Transplantation: A Treatment for Clostridium Difficile
Also Check: Can You Give Yourself Hepatitis C
Can A Transplant Cure Hepatitis C
If you develop chronic hepatitis C and it leads to liver cancer or liver failure, you may need a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is one of the most common reasons for a liver transplant.
A liver transplant removes a damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy one. However, theres a high likelihood that the hepatitis C virus will be transmitted to the new liver in time.
The virus lives in your bloodstream, not just your liver. Removing your liver wont cure the disease.
If you have active hepatitis C, continued damage to your new liver is very likely, especially if hepatitis C remains untreated.