Chemotherapy With Hepatic Arterial Infusion
A new chemotherapy technique called HAI, in combination with traditional chemotherapy, has been shown to dramatically increase survival for patients with liver cancer, including those with recurrent disease. HAI involves delivering a high dose of chemotherapy drugs directly to the liver through a tiny pump implanted under the skin in the lower abdomen. Additional chemotherapy medicine is injected into the pump, as needed, on an outpatient basis. HAI therapy may be used to shrink tumors before surgery, or after surgery to prevent recurrence.
Hepatic Artery Infusion Therapy
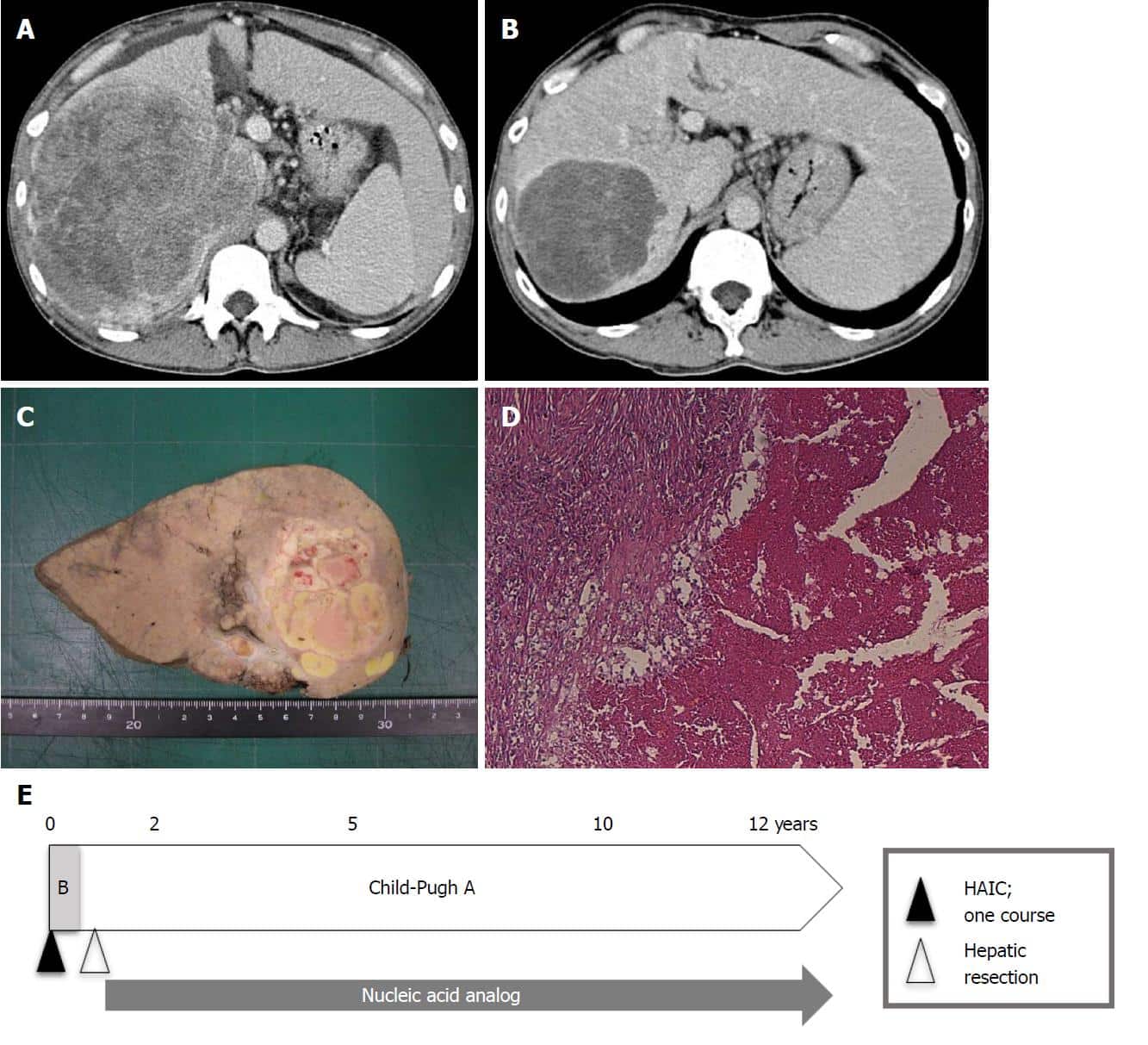
Hepatic infusion tube placement was performed according to the Seldinger method in order to insert a catheter with a side hole via the right femoral artery the tip was placed at the gastroduodenal artery, and the drug was administered into the hepatic artery via the catheter side hole. A coiling procedure was performed to prevent drug influx into the gastroduodenal artery . Angiography was performed to allow drug influx into the hepatic artery. The chemotherapy regimen comprised once weekly 5-FU and LV . Four 6-week courses were administered. The efficacy was evaluated using computed tomography after four courses the efficacy was evaluated in accordance with the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, and adverse reactions were assessed according to assessed on the basis of RECIST criteria and National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0 .
Hepatic artery infusion therapy. Hepatic infusion tube placement was performed according to the Seldinger method. The tip was placed at the gastroduodenal artery, and the drug was administered into the hepatic artery via the catheter side hole. A coiling procedure was performed to prevent drug influx into the gastroduodenal artery
Rationale For Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy
There are approximately 150,000 new cases of colorectal carcinoma diagnosed annually in the United States . Approximately 25% of patients present with metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis and over 50% will develop metastasis to the liver at some point in their lifetime . Five-year overall survival in metastatic colorectal cancer confined to the liver is approximately 20%, although complete resection can increase 5-year survival to over 50% in selected series .
Liver resection provides the only chance for cure in patients with colorectal liver metastases , however, only 1520% of patients with CRC metastases confined to the liver are deemed resection candidates at presentation. Most patients with CRC die from metastatic disease, and two-thirds of CRC deaths are due to liver metastases .
HAI therapy has evolved in the last three decades with improved surgical techniques and discovery of new systemic agents. It is now an acceptable first line option in the United States for unresectable CRLM and a treatment option in the adjuvant setting however, it remains infrequently used. Reasons for this include lack of widespread expertise with HAI therapy, requirement of a multidisciplinary team to manage therapy, and more widespread use of systemic chemotherapy in first-line settings .
Don’t Miss: How Can I Tell If I Have Hepatitis
First Visit Out Patient
Apollo Cancer Centre prides itself in setting newer standards of excellence every day be it in technology, advances in treatment or patient satisfaction. Outpatient Care is medical care provided on an outpatient basis. This includes diagnosis, observation, consultation, treatment, intervention and rehabilitation services.
Registration Process
A patient coming in for the first-time will need to register at the registration counter to help create a Unique Hospital Identification number . UHID helps keep an electronic repository of your medical history and medical records.
Registration is a one-time process.
Registration is done after verification and submission of:
- Copy of Aadhaar card For National Patients.
- Copy of Passport For International Patients.
To facilitate a hassle-free registration experience, please bring the following with you: Registration is done after verification and submission of:
- Aadhaar Card for the Registration Process.
- Previous medical records.
- Letter of credit .
- Referral Letter .
After registration, the patient is guided to the consultation room.
It is advisable to fix appointments in advance to avoid delays.
To book an Appointment for a consultation, you may.
- Call us on 18002031066
- Email us at apollocancercentres@apollohospitals.com
To book an appointment for Diagnostic Services, please call us at +9144 61151111
Risk Factors For Liver Cancer
There are several factors that might increase the chance of developing liver cancer. These risk factors include:
Gender: Hepatocellular carcinoma is more common in men than in women.
Race: Of all racial groups in the United States, Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders have the highest incidence rates of liver cancer.
Chronic viral hepatitis: Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus or hepatitis C virus is the most common risk factor for liver cancer.
Cirrhosis: An irreversible condition that causes damage to liver cells and creates scar tissue. Cirrhosis is a progressive disease that increases the chances of developing liver cancer.
Weight: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is common among obese people. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, a subtype of this disease can cause cirrhosis and lead to an increased risk of liver cancer.
Inherited liver diseases: Hereditary hemochromatosis and Wilsons disease can increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Diabetes: People with diabetes have a greater risk of liver cancer than other people.
Excessive alcohol use: Alcohol abuse over many years can lead to irreversible liver damage linked with an increased risk of liver cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Hepatitis B
The Role Of Hepatic Artery Infusion
When colorectal cancer spreads, it frequently results in metastatic tumors in the liver. When possible, the liver tumors are surgically removed, and chemotherapy destroys the remaining cancer cells. Sometimes the tumors cant be removed because of their location or size, or the available treatments simply cant slow the disease. At this point, some people are told by their doctors that chemotherapy is their only option. Or worse, that nothing more can be done.
However, there is another option. It just hasnt been widely available because it requires specialized training in surgical and medical oncology.
Hepatic arterial infusion delivers chemotherapy through a pump thats implanted in the abdominal wall. We then use a catheter to deliver high doses of chemotherapy through the hepatic artery, which directly feeds metastatic tumors in the liver, said Peter Allen, MD, a Duke surgical oncologist. Even though the HAI pump delivers chemotherapy directly to the liver at concentrations that are hundreds of times higher than whole-body chemotherapy, it does not increase the side effects beyond those associated with whole-body chemotherapy.
If the liver tumors can be removed — doctors use the term resected — the pump may be implanted at the time of surgery and used to delay or prevent recurrence of cancer. If the liver tumors cannot be removed, the pump may be inserted to help control the tumor or, even better, shrink its size so it can be surgically removed in the future.
Information For Patients Interested In This Treatment With Haip
Thank you for your interest. Many people have tumours that have spread to the liver. Presently at Sunnybrook Odette Cancer Centre, HAIP is only being used in patients with colorectal cancer that has spread to the liver, cannot be removed surgically, and has not spread to anywhere else in the body. If you believe you may benefit from this therapy and would like to learn more about our clinical trial due to resources only open to residents of Ontario, your medical oncologist or surgeon may fax a referral to 416-480-6179.
– Paul Karanicolas MD, FRCSC and Yoo-Joung Ko MD, FRCPC
Recommended Reading: Chronic Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent
Hepatic Arterial Infusion With Systemic Chemotherapy
When combined with systemic chemotherapy, hepatic arterial infusion leads to higher response rates compared to systemic chemotherapy alone. There are several major benefits to including HAIP chemotherapy in late-stage cancer treatment plans:
- Higher resection rates of previously unresectable tumors
- Lower recurrence rates
How Does Hepatic Arterial Infusion Work
The surgical team places a wireless pump about the size of a hockey puck under the skin of your abdomen. They connect the pump to a tube that feeds into the hepatic artery. The pump delivers chemotherapy to the liver for two weeks. Then the pump is recharged and the cycle repeats.
After surgery, patients usually stay in the hospital for four to six days to recover. Patients return for office visits every two weeks so the team can check progress and refill the pump.
The pump stays in place as long as needed to kill the cancer cells and to help keep cancer from coming back. Patients may have it anywhere from six months to six years.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Sexually Transmitted Disease
Symptoms Of Liver Cancer
Most people diagnosed with liver cancer develop symptoms in the later stages of the disease. Signs and symptoms of liver cancer include:
Unexplained weight loss: Many people who develop liver cancer notice unplanned weight loss due to loss of appetite.
Feeling full after a small meal: This is caused by an enlarged liver or spleen pushing against the stomach.
Nausea/vomiting: This can also include coughing up blood.
Pain or swelling in the abdomen: This is caused by swelling of the spleen or liver or fluid accumulation in the abdomen.
Jaundice: Also known as yellowing of the skin or eyes.
Outcomes Of Hai Chemotherapy For Unresectable Disease
Conversion to resection is the goal of HAI and systemic chemotherapy, as resection is independently associated with prolonged OS . However, resectability of liver metastasis is surgeon and institution dependent, and therefore, reports of conversion to resection rates in available studies are difficult to interpret.
Available treatment options for unresectable CRLM limited to the liver were initially limited to systemic chemotherapy, with low conversion rates and poor OS. The first systemic chemotherapy used for metastatic CRC was systemic 5-FU, with a response rate of only about 20%, and average survival of approximately 11 months . Irinotecan and oxaliplatin were later developed and had a higher response rate and a slightly longer median survival of 1519.5 months . In a single institution study from 1988 to 1999, the conversion rate with chemotherapy was 12.5% . In more recent studies using modern combination therapy and targeted therapy, response rates of up to 81% and conversion rates up to 60% are reported with combination FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab . Modern systemic chemotherapy has increased survival in metastatic CRC patients to 1830 months however, disease progression and eventual death secondary to liver failure remain the biggest clinical challenges. Thus, there is a continued interest in HAI and other locoregional therapies including radiofrequency ablation, stereotactic body radiation, and chemoembolization as methods to stave off hepatic disease progression .
You May Like: Drug Therapy For Hepatitis C
Hai Therapy Vs Systemic Chemotherapy For Unresectable Disease
HAI alone was initially compared to available systemic chemotherapies for first-line use for unresectable CRLM. Multiple prospective clinical trials published in the late 1980s to early 1990s comparing HAI with systemic chemotherapy demonstrated superior response rates of HAI therapy but did not show consistent improvements in OS . To add to the skepticism towards HAI therapy, a 2006 meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing HAI and systemic chemotherapy in unresectable disease showed that there was no survival advantage to HAI alone . This analysis, however, had several limitations including, small number of patients from single institutions, old HAI chemotherapy, and allowance for cross over to HAI in patients who had initially failed systemic chemotherapy. To overcome these limitations, a multi-institutional prospective randomized clinical trial, Cancer And Leukemia Group B 9481, investigated response rate in patients receiving HAI FUDR compared to systemic 5-FU only, demonstrating significantly improved survival . In that study, 4070% of patients with unresectable hepatic liver metastases who underwent HAI therapy later developed extrahepatic disease thus, systemic chemotherapy combined with HAI was considered as a practical approach to control both intrahepatic and extrahepatic metastases .
Table 2Table 3
Chemotherapy For Liver Cancer
Chemotherapy is a treatment that uses drugs that travel through the bloodstream to reach cancer cells in most parts of the body. Unfortunately, chemo has not shown to have a great impact on liver cancer and is rarely used except in rare forms of liver cancer.
The University of Colorado Cancer Center partners with UCHealth, Childrens Hospital Colorado, and Rocky Mountain Regional VA to provide clinical care. Please make an appointment with one of our clinical partners to be seen by a CU Cancer Center doctor.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Acute Or Chronic
Patient Who Received Implanted Chemotherapy Infusion Pump In July Now Cancer
One of the first patients in the region to undergo a targeted cancer therapy directed at the liver through a pump implanted under the skin has been declared cancer-free. UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center Cancer is the first in Northern California, including the Bay Area, to start what is called a hepatic artery infusion program.
Peter Romero, 63, said the procedure was a real game-changer and whats remarkable is that he was able to keep exercising. He walked up to eight miles a day and cycled, during the entire three months of treatment.
Hepatic artery infusion delivers chemotherapy directly to the liver through a pump the size of a hockey puck. The pump is implanted under the skin between the ribs and the pelvis. It is connected by a small catheter to the circulatory system that feeds the hepatic artery supplying blood to the liver. A powerful chemotherapy drug is deposited into the pump and refilled every couple of weeks.
For patients with metastatic colon cancer that has spread to the liver, it can be transformative. It was for Romero, who said, If the amount of chemotherapy that went directly into my liver was given to me through a port and into my whole body, it would have killed me. Instead, the pump fed targeted chemotherapy straight into my liver, destroying those stubborn cancer cells.
I love my doctor. She not only provided for my physical care, but my mental care as well.Peter Romero, cancer patient
UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center
The State Of Hepatic Artery Infusion Chemotherapy In The Management Of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer To The Liver
University of California Davis Cancer Center , , USA
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: None Collection and assembly of data: None Data analysis and interpretation: None Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy is a locoregional therapy for colorectal cancer liver metastasis that has been available since the 1980s. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of HAI with higher response rates compared to systemic chemotherapy alone. Clinical trials have shown the benefit of using HAI as a bridge to conversion to resection at a higher rate than systemic chemotherapy alone with rates as high as 60% in heavily pretreated patients. HAI in combination with systemic chemotherapy has also been associated with prolonged recurrence free survival and overall survival in the adjuvant setting. Specifically, the addition of HAI continues to show a benefit in prolonging overall survival, despite increased effectiveness of modern systemic chemotherapy . Lower recurrence and improved survival rates associated with HAI and systemic chemotherapy persist regardless of RAS mutational status.
Keywords: Biological tumor markers locoregional liver therapy cancer chemotherapy agents colorectal cancer metastasis
Submitted Jul 18, 2019. Accepted for publication Aug 22, 2019.
Read Also: What Type Of Cirrhosis Is Caused By Hepatitis C
Our Experts Are Leaders In Hepatic Arterial Infusion Pump Therapy
Washington University specialists at Siteman have made incredible strides in research and implementing hepatic arterial infusion pump chemotherapy into certain advanced cancer treatment plans. Our multidisciplinary team consists of exceptional surgical, medical and radiation oncologists who work together to deliver HAI care.
What is hepatic arterial infusion?
Hepatic arterial infusion is a type of cancer treatment in which surgeons implant a special pump to deliver specialized chemotherapy drugs directly to metastatic tumors in the liver. Via the pump, a catheter is connected to the hepatic artery, which supplies blood to tumors within the liver. Because the chemotherapy is delivered directly to the liver, high doses that are effective against tumors can be used without causing damage to the rest of the body. This reduces side effects and makes HAIP chemotherapy very effective in treating advanced tumors in the liver.
The HAI pump, which is about the size and shape of a hockey puck, will likely need to be refilled every 2 to 4 weeks. The pump releases chemotherapy at a set rate and delivers a constant dose of chemotherapy to the liver, which also increases the effectiveness of the treatment.
Surgery For Liver Cancer
Full resection or removal of a liver tumor with a small portion of health tissue offers the most favorable outlook. A tumors resectability depends on the size and location in the liver, how well the liver functions, and the patients overall health.
Partial hepatectomy is a procedure during which part of the liver is removed if the patient has good liver function and is healthy enough for surgery, usually stage I or stage II.
Liver transplant is an option for a small percentage of patients with tumors that cannot be removed surgically. During a liver transplant, the diseased liver is removed and replaced with a healthy donor liver.
Our experts are among the nations leaders in minimally invasive techniques for the surgical treatment of liver cancer. The minimally invasive approach involves inserting a camera and delicate surgical instruments into the body through multiple small incisions instead of one large opening. Sometimes a surgical robot may be utilized to allow for more precision and flexibility than would be feasible with conventional surgical instruments. Recovery is typically faster and less painful than with conventional surgery.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Get Hepatitis C
Objectives And Endpoints Of The Phase Ii Study
Our main objective is to investigate the efficacy, in term of CRR , of treatment intensification in patients with liver-only CRLM not amenable to curative-intent resection after at least 2 months of induction sys-CT. Patients will receive either HAI oxaliplatin plus systemic FOLFIRI plus targeted therapy or conventional sys-CT plus targeted therapy . Secondary objectives are to compare: progression-free survival, overall survival, objective response rate, depth of response, feasibility of delivering HAI oxaliplatin including HAI catheter-related complications, and toxicity .