What Is Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
Viruses invade normal cells in your body. Many viruses cause infections that can be spread from person to person. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood.
Hepatitis C can cause an acute or chronic infection.
Although no vaccine for hepatitis C is available, you can take steps to protect yourself from hepatitis C. If you have hepatitis C, talk with your doctor about treatment. Medicines can cure most cases of hepatitis C.
Side Effects Not Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Some side effects of hepatitis a adult vaccine may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
- change in the amount of bleeding during periods
- change in the pattern of monthly periods
- lack or loss of strength
- tenderness or warmth at the injection site
- unusual stopping of menstrual bleeding
Rare
Incidence not known
- Bleeding, blistering, burning, coldness, discoloration of the skin, feeling of pressure, hives, infection, inflammation, itching, lumps, numbness, pain, rash, redness, scarring, soreness, stinging, swelling, tenderness, tingling, ulceration, or warmth at the injection site
- sleepiness or unusual drowsiness
Donât Miss: Natural Cure For Hepatitis A
Who Is More Likely To Get Hepatitis A
People more likely to get hepatitis A are those who
- travel to developing countries
- have sex with an infected person
- are men who have sex with men
- use illegal drugs, including drugs that are not injected
- experience unstable housing or homelessness
- live with or care for someone who has hepatitis A
- live with or care for a child recently adopted from a country where hepatitis A is common
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
Impact On The Integumentary System
Hepatitis C is associated with a wide variety of skin problems. Some common conditions include easy bruising, loss of skin pigment, rashes, and itching.
Bilirubin is an important substance that comes from the breakdown of hemoglobin. When the liver cant do its job, bilirubin can build up and cause jaundice, or the yellowing of your skin and the whites of your eyes.
Poor liver function can also lead to poor nutrition. This leads to inadequate growth of hair and nails as well.
Skin conditions that may occur include:
- porphyria cutanea tarda, which is a kind of photosensitivity leading to skin blistering
- lichen planus, which are purple, itchy papules than can appear on the skin and in the mouth
- leukocytic vasculitis, which is inflammation of the small blood vessels
The endocrine system regulates hormones. As part of the endocrine system, the thyroid gland delivers hormones into the bloodstream.
Sometimes HCV can cause the immune system to mistakenly attack or damage thyroid tissue. This
How Does Hepatitis C Cause Stomach Troubles
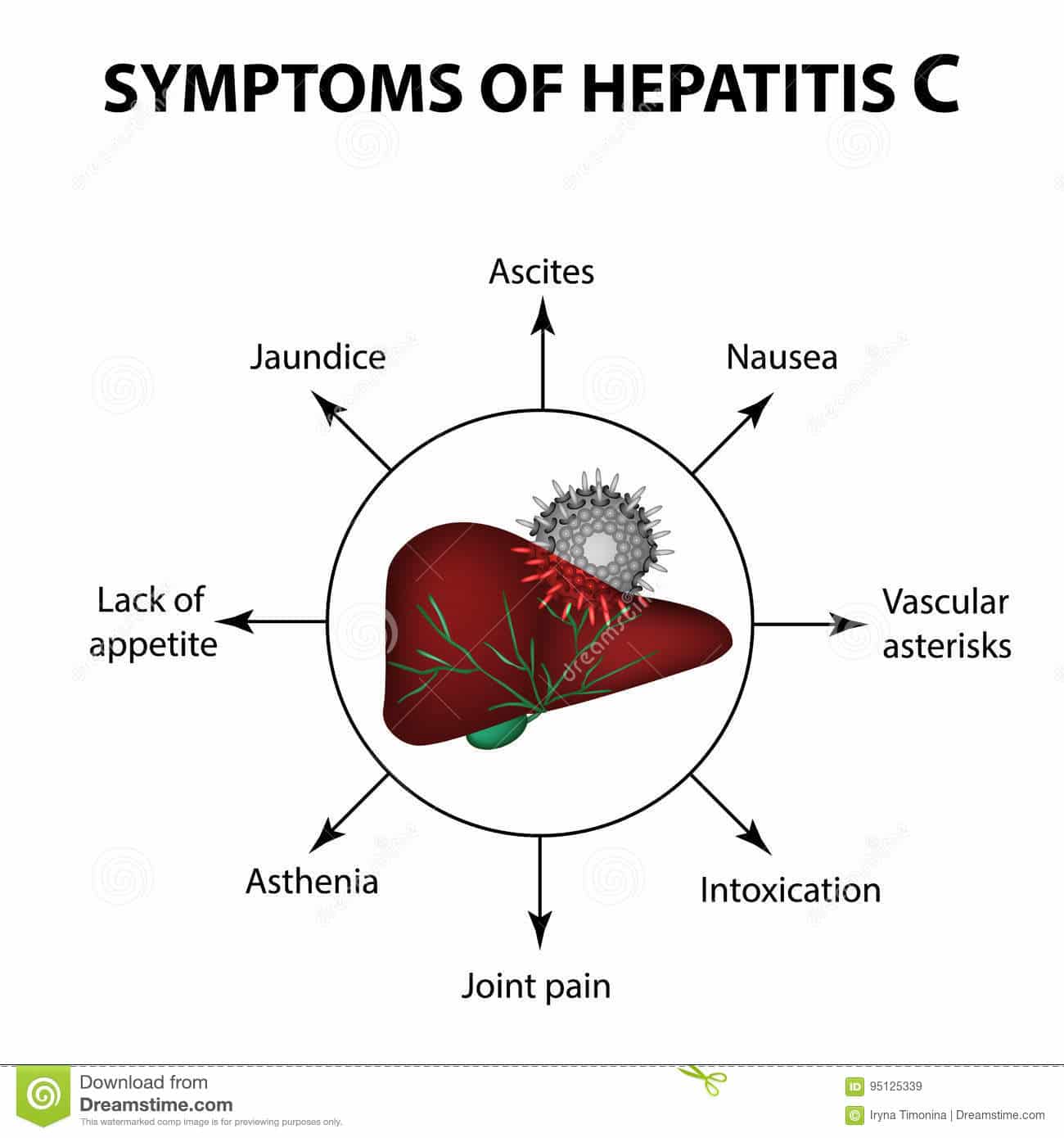
Its important to understand what a healthy liver is tasked with doing to understand precisely how hepatitis C causes or aggravates intestinal symptoms. In response to the virus, the liver swells and gradually stops doing its very important jobs, which include processing nutrients, filtering your blood, and staving off infections. Bilea greenish-brown fluid produced by the liveraids in these tasks. Hepatitis C can cause any of the following intestinal problems.
Don’t Miss: How Can You Tell If You Have Hepatitis
Deterrence And Patient Education
Vaccinations for both hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus have been available since the 1990s and have significantly decreased the incidence of these infections. Hepatitis A virus gets transferred by fecal-oral contamination, and improved food handling, water purification, and improved hygiene will reduce the risk of spreading infection. The risk of contracting hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection can be decreased by avoiding IV drug use and safe sex practices.
Accidently toxic ingestion of acetaminophen by children can be reduced with safe storage practices out of reach from children and utilizing packaging that utilize childproof safety precautions. Also, in adults, unintentional toxic ingestion can be reduced with education about the many non-prescription products which contain acetaminophen.
For stable minimally symptomatic patients, if an etiology for acute hepatitis is not determined initially, then they need follow-up to monitor for the normalization of the liver tests or further evaluation if the abnormal test results continue.
Also Check: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Stages Of Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus affects people in different ways and has several stages:
- Incubation period. This is the time between first exposure to the start of the disease. It can last anywhere from 14 to 80 days, but the average is 45
- Acute hepatitis C. This is a short-term illness that lasts for the first 6 months after the virus enters your body. After that, some people who have it will get rid of, or clear, the virus on their own.
- Chronic hepatitis C. For most people who get hepatitis C — up to 85% — the illness moves into a long-lasting stage . This is called a chronic hepatitis C infection and can lead to serious health problems like liver cancer or cirrhosis.
- Cirrhosis. This disease leads to inflammation that, over time, replaces your healthy liver cells with scar tissue. It usually takes about 20 to 30 years for this to happen, though it can be faster if you drink alcohol or have HIV.
- Liver cancer. Cirrhosis makes liver cancer more likely. Your doctor will make sure you get regular tests because there are usually no symptoms in the early stages.
Learn more about the stages and progression of hepatitis C.
Also Check: How To Diagnose Autoimmune Hepatitis
Acute Hepatitis C Vs Chronic Hepatitis C
Acute and chronic hepatitis C are caused by the same virus.
Acute hepatitis C develops after initial infection with the HCV. This stage can last up to 6 months. Many people have no symptoms during the acute stage and never find out that they have the infection.
According to the CDC, of people with acute hepatitis C develop chronic hepatitis C.
The World Health Organization states that 15 to 45 percent of people with acute hepatitis C spontaneously clear the virus within 6 months. This means that the virus goes away even though it hasnt been treated.
The 55 to 85 percent of people who dont clear the virus will develop a chronic HCV infection.
Chronic hepatitis C can be managed with medications and even cured, but its still a serious condition. According to the CDC,
Who Is At Risk Of Getting Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is usually spread from person to person, making it highly contagious. However, certain factors can increase your risk of contracting it, including:
- living in an area where hepatitis A is common, including most countries with low sanitation standards or a lack of safe water
- injecting or using illegal drugs
- living in the same household as someone who is hepatitis A-positive
- having sexual activity with someone who is hepatitis A-positive
- being HIV-positive
Read Also: Hepato Liver Support For Dogs
When To Seek Medical Advice
See your GP if you persistently have any of the later symptoms listed, or if they keep returning. They may recommend having a blood test that can check for hepatitis C.
Read more about diagnosing hepatitis C
None of these symptoms mean you definitely have hepatitis C, but it’s important to get them checked out.
You should also speak to your GP about getting tested if there’s a risk you’re infected, even if you don’t have any symptoms. This particularly includes people who inject drugs or have done so in the past.
Read about the causes of hepatitis C for more information about who’s at risk of having the infection.
Page last reviewed: 27 October 2021 Next review due: 27 October 2024
Is Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Contagious
Hepatitis C can be passed from person to person. Most people with HCV get it through direct contact with blood containing the virus.
People with hepatitis C can pass on the virus to others by sharing needles and syringes. Hepatitis C is easily transmitted among people who use intravenous drugs.
Its also possible, but much less common, to acquire the HCV by:
- sharing a razor with a person who has the virus
- sharing a toothbrush with a person who has the virus at the same time that you have bleeding gums
- having sexual contact with a person who has the virus
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Ab Test
Stool Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
**When you think about hepatitis, the first thing that comes to mind is probably your liver.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
** But infection with the hepatitis C virus can lead to stool symptoms as well. Diarrhea can occur in the early or late stages of hepatitis C infection, or it may be a side effect of medications used to treat the virus. Severe liver disease may also cause pale, oily, bloody or tar-like stools. If you have hepatitis C, it is important to be aware of stool symptoms, as they are often an indicator of disease severity, and some require prompt medical care.
Cirrhosis Of The Liver
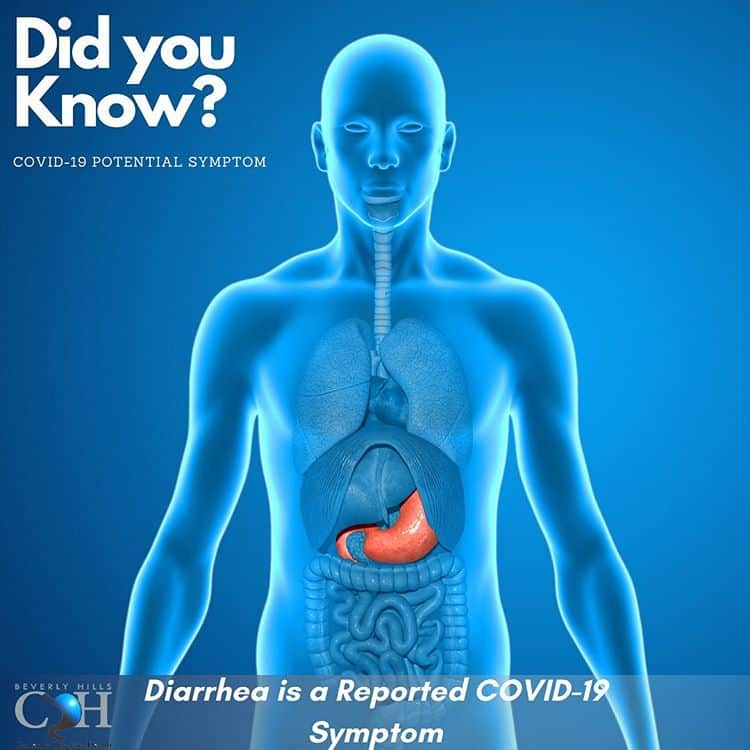
When permanent scar tissue replaces healthy liver cells and your liver loses the ability to function, its called cirrhosis. In this condition, your liver can no longer heal itself. This can cause a variety of health concerns, including a buildup of fluid in your abdomen and bleeding from veins in the esophagus.
When the liver fails to filter toxins, they can build up in your bloodstream and impair brain function. Cirrhosis of the liver can sometimes develop into liver cancer. This risk is greater in people who drink excess alcohol. Treatment of cirrhosis depends on the progression of the condition.
Chronic hepatitis C can cause serious long-term health consequences when it leads to liver scarring. End-stage hepatitis C occurs when the liver is severely damaged and can no longer function properly.
Symptoms may include:
- abdominal swelling
- muddled thinking
People with cirrhosis may also experience bleeding in the esophagus, as well as brain and nervous system damage.
A liver transplant is the only treatment for end-stage liver disease. Those whove had hepatitis C and received a liver transplant almost always see a return of the infection. Because the disease recurs, treatment of the viral infection usually follows transplant surgery.
Because alcohol is processed in the liver, consumption of excess alcohol can hasten liver damage, so its important to not drink it. Damage also progresses faster in people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV.
You May Like: Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta Agent Definition
What Causes Hepatitis C
The hepatitis C virus causes hepatitis C. The hepatitis C virus spreads through contact with an infected persons blood. Contact can occur by
- sharing drug needles or other drug materials with an infected person
- getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on an infected person
- being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not kept sterilefree from all viruses and other microorganismsand were used on an infected person before they were used on you
- having contact with the blood or open sores of an infected person
- using an infected persons razor, toothbrush, or nail clippers
- being born to a mother with hepatitis C
- having unprotected sex with an infected person
You cant get hepatitis C from
- being coughed or sneezed on by an infected person
- drinking water or eating food
- hugging an infected person
- shaking hands or holding hands with an infected person
- sharing spoons, forks, and other eating utensils
- sitting next to an infected person
A baby cant get hepatitis C from breast milk.18
Hepatitis C Testing And Diagnosis
Doctors will start by checking your blood for:
Anti-HCV antibodies: These are proteins your body makes when it finds the hep C virus in your blood. They usually show up about 12 weeks after infection.
It usually takes a few days to a week to get results, though a rapid test is available in some places.
The results can be:
- Nonreactive, or negative:
- That may mean you donât have hep C.
- If youâve been exposed in the last 6 months, youâll need to be retested.
If your antibody test is positive, youâll get this test:
HCV RNA: It measures the number of viral RNA particles in your blood. They usually show up 1-2 weeks after youâre infected.
- The results can be:
- Negative: You donât have hep C.
- Positive: You currently have hep C.
You might also get:
Liver function tests: They measure proteins and enzyme levels, which usually rise 7 to 8 weeks after youâre infected. As your liver gets damaged, enzymes leak into your bloodstream. But you can have normal enzyme levels and still have hepatitis C. Learn the reasons why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis B Vaccine For Newborns Pros And Cons
Does Hepatitis A Always Cause Symptoms
Thereâs a lot of variety in how people feel when they have the disease. Itâs possible you might not have any symptoms. But people often feel and look sick. You might even need to go to the hospital.
Symptoms and complications are more common as you get older. Most children under age 6 with hep A donât have any.
Read Also: What Is Hepatitis A And B
What Is Chronic Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. In chronic hepatitis, liver inflammation continues for at least six months. This condition may be mild, causing relatively little damage, or more serious, causing many liver cells to be destroyed. Some cases lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis from infection is most often caused by these viruses:
- Hepatitis B and C. Often the person infected is unaware of any initial symptoms. Or the symptoms were so mild that the person did not seek medical attention. This is especially true for chronic hepatitis C. Over time, perhaps a decade or more, both types may lead to the serious complication of cirrhosis due to ongoing destruction of liver cells and resultant scarring. A minority of patients with cirrhosis develop liver cancer over time.
- Hepatitis D. Hepatitis D infects only patients already infected with hepatitis B, and it generally results in a flare of active hepatitis.
This information helps to determine the best treatment and to assess your risk of developing cirrhosis and liver failure. A liver biopsy also can help to check for other disorders, such as alcoholic liver injury or fatty liver.
Also Check: Liver Transplant With Hepatitis C
How You Can Get Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is most widespread in parts of the world where standards of sanitation and food hygiene are generally poor, such as parts of Africa, the Indian subcontinent, the Far East, the Middle East, and Central and South America.
You can get the infection from:
- eating food prepared by someone with the infection who hasnât washed their hands properly or washed them in water contaminated with sewage
- drinking contaminated water
- eating raw or undercooked shellfish from contaminated water
- close contact with someone who has hepatitis A
- less commonly, having sex with someone who has the infection or injecting drugs using contaminated equipment
Someone with hepatitis A is most infectious from around two weeks before their symptoms appear until about a week after the symptoms first develop.
You May Like: Hep Forte Hepatic Lipotropic Nutritional Support
Is Hepatitis A Contagious
Hepatitis A Transmission
Hepatitis A is a type of liver infection caused by a virus termed hepatitis A . Symptoms, if they occur, start about 2 to 6 weeks after exposure to HAV. About 80% of adults have symptoms while children seldom show symptoms. Symptoms of hepatitis A may include the following:
- Nausea and/or vomiting
Read Also: Hepatitis B Core Total Antibody Positive
Abdominal Pain Nausea Vomiting And Diarrhea
Digestive issues and abdominal pain may come along with HCV. Talking with your doctor when these symptoms arise can be helpful. They can determine if these are related to your HCV or another health issue. They may be able to recommend anti-nausea or anti-diarrhea drugs, depending on your symptoms.3,4
In some cases, it may be necessary to change your diet. This includes the foods you eat as well as the amount eaten. For example, some people may feel better eating smaller meals more often rather than a few large meals each day.3,4
A dietitian is a professional who specializes in creating a personalized diet plan. Your doctor may be able to recommend a dietitian to help address your needs.
What Is Acute Fulminant Hepatitis
Rarely, individuals with acute infections with HAV and HBV develop severe inflammation, and the liver fails . These patients are extremely ill with the symptoms of acute hepatitis already described and the additional problems of confusion or coma , as well as bruising or bleeding . In fact, up to 80% of people with acute fulminant hepatitis can die within days to weeks therefore, it is fortunate that acute fulminant hepatitis is rare. For example, less than 0.5% of adults with acute infection with HBV will develop acute fulminant hepatitis. This is even less common with HCV alone, although it becomes more frequent when both HBV and HCV are present together.
Don’t Miss: When Does Hepatitis C Show Up