How Can I Be Sure That The Patient Has Hepatitis B Virus Infection
HBV infection presents with nonspecific features. Infection with HBV has a wide spectrum of manifestations, including subclinical hepatitis, anicteric hepatitis, icteric hepatitis, and fulminant hepatitis during the acute phase and the asymptomatic carrier state. HBV infection includes chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma during the chronic phase.
Approximately 70% of patients with acute HBV infection have subclinical hepatitis or anicteric hepatitis, whereas 30% become icteric. Acute liver failure develops in approximately 0.1% to 0.5% of patients. The incubation period lasts 1 to 4 months. A serum sickness-like syndrome may develop during the prodromal period. This is followed by constitutional symptoms such as low-grade fever, malaise, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, and right upper quadrant or midepigastric pain. Jaundice usually appears as the constitutional symptoms begin to subside. Clinical symptoms and jaundice generally disappear after 1 to 3 months, but some patients may have prolonged fatigue, even after normalization of aminotransferase levels.
The Icd Code B16 Is Used To Code Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications result in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.
| Specialty: |
Hepatitis B: Diagnosis And Treatment
THAD WILKINS, MD DAVE ZIMMERMAN, MD and ROBERT R. SCHADE, MD, Medical College of Georgia, Augusta, Georgia
Am Fam Physician. 2010 Apr 15 81:965-972.
Patient information: See related handout on hepatitis B.
Globally, an estimated 350 million persons are chronically infected with hepatitis B virus , resulting in 600,000 deaths annually from cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma.1,2 Approximately 88 percent of the world’s population live in regions where the prevalence of chronic HBV infection among adults is more than 2 percent.3 The prevalence of HBV infection in the United States is 0.4 percent, with an estimated 0.8 to 1.4 million persons chronically infected.3,4 With the implementation of vaccination programs in 1991, the incidence of new infections in the United States has declined from 11.5 cases per 100,000 persons in 1985 to 1.6 cases per 100,000 persons in 2006.3,4
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
High-risk populations should be screened for HBV infection.
HBV = hepatitis B virus.
A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. For information about the SORT evidence rating system, go to .
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
High-risk populations should be screened for HBV infection.
HBV = hepatitis B virus.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Virus Is Spread Through The Contact Of
Acute Hepatitis B Infection
An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months and infected persons are able to pass the virus to others during this time. A simple blood test can let a person know if the hepatitis B virus is in their blood or if they have successfully gotten rid of the virus. Until your health care provider confirms that the blood test shows that there is no more hepatitis B virus in your blood, it is important to protect others from a possible infection.
It is also important to have your sexual partner and family members get tested for hepatitis B. If they have not been infected and have not received the hepatitis B vaccine then they should also start the hepatitis B vaccine series.
Symptoms of an acute infection may include loss of appetite, joint and muscle pain, low-grade fever, and possible stomach pain. Although most people do not experience symptoms, they can appear 60-150 days after infection, with the average being 90 days or 3 months. Some people may experience more severe symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, jaundice , or a bloated stomach that may cause them to see a health care provider.
If treatment for an acute hepatitis B infection is required, a person may be hospitalized for general support. Rest and managing symptoms are the primary goals of this medical care. A rare, life-threatening condition called fulminant hepatitis can occur with a new acute infection and requires immediate, urgent medical attention since a person can go into sudden liver failure.
What Is The Right Therapy For The Patient With Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Treatment with antiviral therapy is recommended in patients with chronic hepatitis B in the immune active phase with elevated HBV DNA levels and ALT greater than 2x the ULN. Patients with cirrhosis and HBV DNA > 2,000 IU/mL should be treated regardless of ALT levels. If patients do not meet these cutoff criteria, antiviral therapy should still be considered if older age, positive family history, presence of extrahepatic manifestations, or prior treatment).
Treatment with antiviral therapy is generally not recommended for patients with immune tolerant chronic hepatitis B. However, patients should have labs checked every 6 months to look for evidence of activation. Additionally, in spite of normal ALT levels, patients should be treated with antiviral therapy if there is evidence of necroinflammation or fibrosis.
What treatment options are effective?
Several agents are currently approved for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: interferon alpha , pegylated interferon alfa 2a, lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir, telbivudine, and tenofovir. Each agent has inherent limitations.
With the drugs currently available, the physician may consider two different concepts for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: the first concept is that of sustained response obtained after a limited duration of therapy with pegylated interferon the second concept is that of maintained response obtained during prolonged administration of therapy with analogues.
You May Like: What Type Of Hepatitis Is Curable
Hcc Incidence Among Linked
Among the 553,085 study population, 354,499 subjects did not have any history of malignancy at baseline and they were included in the incident HCC analysis. During the follow-up period , 71,765 patients developed new HCC over a mean follow-up of 14.5 years . Cumulative incidence for HCC development at 15 years was significantly higher in male . . By age, the 40s age group had the highest proportion of patients who developed HCC while linked-to-care , followed by the 30s group , with also higher rates among males .
Cumulative incidence rate and survival rates of patients who newly developed HCC during LTC. Cumulative incidence of HCC development according to sex. The distribution of age group who developed HCC during LTC. Kaplan-Meier plots for survival estimates after HCC development by sex. Kaplan-Meier plots for survival estimates after HCC development by age. All the p-values were less than 0.0001 in the comparison between 20s vs. 30s, 20s vs. 40s, 20s vs. 50s, 30s vs. 40s, 30s vs. 50s, and 40s vs. 50s. Kaplan-Meier plots for survival estimates after HCC development by income levels.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not spread through sharing utensils or kissing. It also doesnt spread through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding. Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure and can last for 212 weeks. However, you are still contagious, even
To screen for hepatitis B, your doctor will perform a series of blood tests.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis C With Hepatic Coma
Drg Mapping Rules For B181
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patient’s primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient’s primary diagnostic code is B18.1, look in the list below to see which MDC’s “Assignment of Diagnosis Codes” is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patient’s discharge date.
A Listing Of A Subset Of Second
There are currently six medications approved for use in the United States. Choice of antiviral agent is driven by side effect profile, co-morbidities, prior therapy exposure, HBV genotype, costs, and pregnancy state.
Peg-IFN-2a: dose of 180 mcg weekly. Side effects include flu-like symptoms, mood disturbances, cytopenias, autoimmune disorders. Monitoring should include a CBC and TSH every 3 months, monitoring for infection, autoimmune disorders, neuropsychiatric complications, and infections. Pregnancy category C.
Entecavir: dose of 0.5 or 1.0 mg daily. Side effects include lactic acidosis. Pregnancy category C.
Tenofovir: dose of 300mg daily. Side effects include nephropathy, Fanconi-like syndrome, osteomalacia, lactic acidosis. Monitoring should include yearly creatinine clearance, serum phosphate, urine glucose and protein annually, as well as bone density scan if at risk. Pregnancy category B.
Lamivudine: dose of 100mg daily. Side effects include pancreatitis, lactic acidosis. Monitoring should include creatinine kinase and lactic acid if clinical concerns. Pregnancy category C.
Telbivudine: dose of 600mg daily. Side effects include creatine kinase elevations, myopathy, peripheral neuropathy, and lactic acidosis. Monitor creatinine kinase if symptoms. Pregnancy category B.
Don’t Miss: Hepatic Steatosis Versus Hepatocellular Disease
A Tabular Or Chart Listing Of Features And Signs And Symptoms
HBV or HDV infection does not have any pathognomonic or characteristic features.
Some less common clinical presentations
Extrahepatic manifestations occur in approximately 10% of patients with chronic HBV infection. Mediated by circulating immune complexes, acute hepatitis may be heralded by a serum sickness-like syndrome manifested as fever, skin rashes, arthralgia, and arthritis, which usually subside with the onset of jaundice.
Hepatitis B virus-related glomerulonephritis, most commonly membranous glomerulonephritis, is another manifestation.
Other extrahepatic manifestations include rarely essential mixed cryoglobulinemia and aplastic anemia.
Other diseases and conditions that might mimic the signs, symptoms, or clinical features of HBV infection
Other viral hepatitis , perform HCV antibodies, and HCV RNA.
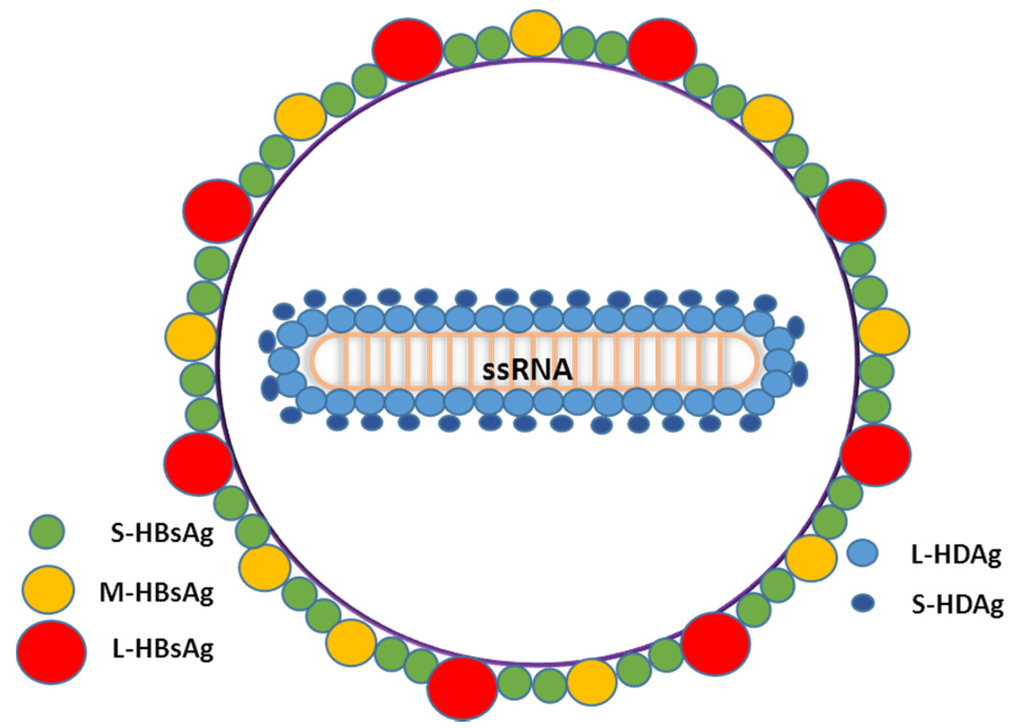
What Is Hepatitis Delta
Hepatitis delta, also known as hepatitis D or HDV, is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis delta virus that results in the most severe form of viral hepatitis known to humans. Only those already infected with hepatitis B can acquire hepatitis delta, however, as it is dependent on the hepatitis B virus to reproduce.
Worldwide, more than 296 million people live with hepatitis B and of this number, an estimated 15-20 million are also infected with hepatitis delta. Coinfections lead to more serious liver disease than hepatitis B infection alone. They are associated with faster progression to liver fibrosis, increased risk of liver cancer, and early decompensated cirrhosis and liver failure.
Types of Infection
Hepatitis delta can be acquired either through coinfection or superinfection . A coinfection generally resolves spontaneously after about 6 months, but it can sometimes result in life-threatening or fatal liver failure.
A superinfection is the most common form of hepatitis delta and leads to a more severe liver disease than a chronic hepatitis B infection alone. Up to 90% of superinfected individuals will develop chronic infections of both hepatitis B and delta, of which approximately 70% will progress to cirrhosis , compared to 15-30% of those infected only with the hepatitis B virus.
Prevention
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Hepatitis C Take To Show Up
Genetics Of Infection With Hepatitis B
Several genes, many having to do with the host immune response, have been implicated in the susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B infection. The TNFSF9 gene encodes the CD137L protein, and its expression was found to be significantly higher in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection than in healthy controls. Its expression was also found to be higher in patients who had chronic hepatitis B with cirrhosis, in contrast to those without cirrhosis.
Research done in West Africa, where 90% of the population is infected with hepatitis B, shows that certain human leukocyte antigen class II haplotypes influence the likelihood of chronic infection. For reasons that are not completely clear, persons in the study who were heterozygous for the HLA-DRA and HLA-DQA1 genes were found to be less likely to develop a chronic infection.
IFNGR1 gene
Several additional genes are associated with susceptibility to hepatitis B infection. The IFNGR1 gene is located at 6q23.3 and encodes the interferon gamma receptor 1, which has an important role in cell-to-cell communications and can be activated in response to infection, but it is not specific to hepatitis B. Patients with significant dysfunction in this gene have a particular immune deficiency that leaves them extremely susceptible to mycobacterial infections.
IFNAR2 gene
IL1OR2 gene
Variations in vaccine response
What Is Chronic Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. In chronic hepatitis, liver inflammation continues for at least six months. This condition may be mild, causing relatively little damage, or more serious, causing many liver cells to be destroyed. Some cases lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Chronic hepatitis from infection is most often caused by these viruses:
- Hepatitis B and C. Often the person infected is unaware of any initial symptoms. Or the symptoms were so mild that the person did not seek medical attention. This is especially true for chronic hepatitis C. Over time, perhaps a decade or more, both types may lead to the serious complication of cirrhosis due to ongoing destruction of liver cells and resultant scarring. A minority of patients with cirrhosis develop liver cancer over time.
- Hepatitis D. Hepatitis D infects only patients already infected with hepatitis B, and it generally results in a flare of active hepatitis.
This information helps to determine the best treatment and to assess your risk of developing cirrhosis and liver failure. A liver biopsy also can help to check for other disorders, such as alcoholic liver injury or fatty liver.
Don’t Miss: Hepatitis C Can You Catch It From Saliva
B181chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta
Rare males and females disease from the section “”. Causes not a significant loss of workdays. Not mortally.
2 641 141 people were diagnosed with Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent
44 867 died with a diagnosis of Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent
0.02 % disease mortality Chronic viral hepatitis B without delta-agent
Chronic Viral Hepatitis B Without Delta
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- B18.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B18.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B18.1 – other international versions of ICD-10 B18.1 may differ.
- Carrier of viral hepatitis B
- Chronic hepatitis B
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: Hepatitis B Homeopathy Treatment In Hindi
How Should I Monitor The Patient With Hepatitis B Virus Infection
Prevention through universal vaccination has effectively decreased the incidence of liver cancer, and new therapeutic agents may delay or avoid the establishment of cirrhosis. All patients with cirrhosis should be screened for HCC with ultrasound every 6-12 months. Additionally, some high risk populations with chronic hepatitis B should be screened even in the absence of cirrhosis. These populations include Asian men over 40 years old, Asian women over 50 years old, African men and women over 20 years old, persistent ALT elevation, HBV DNA level > 2,000 IU/mL, and patients with a family history of HCC.
The only chance for long-term survival after HCC diagnosis is to achieve early detection through regular surveillance by ultrasound and AFP determination. This will allow the indication of effective therapy such as surgical resection, liver transplantation or percutaneous ablation.
Certain Infectious And Parasitic Diseasesincludes
- certain localized infections – see body system-related chapters
- carrier or suspected carrier of infectious disease
- infectious and parasitic diseases complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
- infectious and parasitic diseases specific to the perinatal period
- influenza and other acute respiratory infections
- code to identify resistance to antimicrobial drugs
- herpesviral hepatitis
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Includes
- Chronic hepatitis b with hepatic coma
- Chronic type b viral hepatitis
- Hepatitis b, chronic
- Hepatitis b, chronic, with hepatic coma
- Inflammation of the liver in humans caused by hepatitis b virus lasting six months or more. It is primarily transmitted by parenteral exposure, such as transfusion of contaminated blood or blood products, but can also be transmitted via sexual or intimate personal contact.
- 441 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with mcc
- 442 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis with cc
- 443 Disorders of liver except malignancy, cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis without cc/mcc
- 791 Prematurity with major problems
- 793 Full term neonate with major problems
- : New code
- 2017
You May Like: Hepatitis A How Is It Spread
Listing Of Usual Initial Therapeutic Options Including Guidelines For Use Along With Expected Result Of Therapy
Goals of antiviral therapy are HBeAg seroconversion , HBsAg loss, and suppression of HBV DNA. All patients with cirrhosis should continue treatment indefinitely. Patients without cirrhosis can consider discontinuation after 12 months of achieving above mentioned goal. However, the risk for seroconversion or recurrent viremia persists and patients need to be monitored every 3 months for at least one year after discontinuation of antiviral therapy.
Treatment Indications And Phases Of Chronic Hbv Infection
Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
| Phase | |
|---|---|
| HBV DNA | Inflammation |
|
May or may not be indicated |
|
|
Immune tolerant |
HBV = hepatitis B virus + = detectable = undetectable +/= may or may not be detectable.
Information from reference 22.
Phases of Chronic HBV Infection
| Phase | |
|---|---|
| HBV DNA | Inflammation |
|
May or may not be indicated |
|
|
Immune tolerant |
HBV = hepatitis B virus + = detectable = undetectable +/= may or may not be detectable.
Information from reference 22.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults