Being Tested For Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The hepatitis B core antibody test is part of a screening panel for hepatitis B, which also will include hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B surface antibody . These three tests look for acute and chronic infections.
Tests may be ordered if you have symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice , fever, fatigue, pale stools, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In this case, the hepatitis B core antibody IgM test may be used, as it shows an early stage of infection.
This test may be ordered if you are being screened for hepatitis B because you are donating blood or wish to become an organ donor. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood or through organ transplants, so donors are tested to prevent infecting recipients. Its possible to have had the infection with only mild symptoms, so many people dont realize they have had hepatitis B.
People who are part of populations at risk for hepatitis B infection will be screened. Screening is also often done for pregnant people, infants, people sharing a home with hepatitis B patients, people who may have been exposed by needlestick injuries or body fluids, and for people with HIV .
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Signs And Symptoms
When Should I Get This Test
Using hepatitis B tests to screen for HBV is recommended for certain groups at an increased risk of infection. You may benefit from hepatitis B screening if you:
- Were born in parts of the world where the disease is more common, including Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, South America, and parts of the Middle East
- Didnât receive a hepatitis B vaccine
- Are HIV-positive
- Use injectable drugs
- Are at risk of HBV infection due to sexual exposure
A doctor may order hepatitis testing based on your symptoms, medical and family history, and a physical exam. If you develop symptoms without recent exposure to HBV, doctors may recommend an acute viral hepatitis panel that looks for hepatitis A, B, and C in one sample of blood.
Hepatitis tests may also be performed as follow-up tests when other tests of liver health are abnormal.
Testing is common in those that show symptoms that could be caused by hepatitis B. Symptoms of hepatitis B include:
- Loss of appetite, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain in the joints or abdomen
- Yellowish skin and eyes
Using hepatitis B testing to assess immunity to HBV may take place before or after vaccination. Pre-vaccination testing is not always needed but may be performed if there is a chance that you have previously been infected with HBV or have already been vaccinated. Post-vaccination testing is used in certain groups of people at an especially elevated risk for HBV infection, including infants born to mothers with a hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: Efficacy Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Sequence Following An Initial Negative Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Titer
As you obtain documentation, please submit documentation of each step to CastleBranch
- Initial Hepatitis B titer negative for immunity
- Receive Hepatitis B challenge dose/booster
- Repeat Hepatitis B titer 4-6 weeks after challenge/booster vaccine
Donât Miss: Can Hepatitis B Virus Be Cured
Surrogate Outcome For Nucleoside Analogs
Hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion is much less durable for nucleoside analogs than peginterferon therapy, particularly among Asian patients for whom the infection has persisted since early childhood. Up to 50% of patients may experience hepatitis relapse after HBeAg seroconversion within 3 years posttreatment.92 Therefore HBeAg seroconversion is not an ideal surrogate marker of response for nucleoside analogs, particularly if the posttreatment follow-up is not long enough. As HBsAg clearance is rarely observed with nucleotide analogs, evaluation of predictors for HBsAg clearance may be difficult and less clinically useful.
Milan J. Sonneveld, Suzanne van Meer, in, 2021
You May Like: What Is Treatment For Hepatitis C
Summary Of Information Contained In This Naci Statement
The following table highlights key information for immunization providers. Please refer to the remainder of the Statement for details
1. What
Hepatitis B virus causes liver infection. Although the majority of individuals will spontaneously clear the infection, the risk of becoming a chronic carrier in unvaccinated individuals varies with age at which the infection occurs: up to 95% of infants, 50% of children less than 5 years of age and 10% of adolescents and adults will develop chronic infection.
Infant and adolescent immunization programs have been successfully implemented in all Canadian provinces and territories since 1990s. Duration of protection following a completed primary schedule is believed to be long lasting and no routine booster doses are currently indicated for immunocompetent individuals.
2. Who
This Statement addresses whether there is a need for HB re-immunization of adolescents who have received routine immunization in infancy, risk of HB infection in people with diabetes and timing of re-vaccination of people with immunocompromising conditions.
3. How
Although decline of antibody levels may be observed over time, long-term protection and prevention of chronic infection is dependent on the presence of T- and B-cell memory. Anamnestic response to a HB vaccine challenge dose is considered to be a reliable measure of preserved immunologic memory and a correlate of protection in previously immunized individuals.
4. Why
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Positive
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Options
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
Quick Links:
bolt
What Is the Difference Between a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test and a Hepatitis B Antibody Test?
The hepatitis B surface antigen test can detect current hepatitis B infection, while the hepatitis B antibody test checks for the antibodies that are presumed to provide immunity to hepatitis B.
expand_less
When Should Someone Get a Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test?
If someone is suspected to have hepatitis B, this test is intended to identify a chronic or current infection.
expand_less
What Does a Positive Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test Mean?
A positive test means the person is currently infected or has a chronic infection of hepatitis B. This means that the person has the hepatitis B virus in their blood and can be contagious.
expand_less
About Our Other Services
For industries that require specific occupational health testing, such as healthcare, construction, and manufacturing, Health Street offers quick and easy scheduling. Simply enter your ZIP code and choose the location nearest to you or the person being tested. When the registration process has been completed, we will email you the registration barcode to and a map to the facility.
Why Choose Health Street
Related Services
You May Like: Hepatitis C Ab W/reflex To Hcv Rna Qn Pcr
Hbeag Chronic Hepatitis B
HBeAg chronic hepatitis B occurs as a result of the selection of HBV mutants that are unable to secrete the pre-core protein . It has become the most prevalent form of disease presentation in many parts of the world, particularly in Asian and Mediterranean countries. The most common of several mutations that can cause HBeAg negativity is a guanine to adenine transition at nucleotide position 1896 , which creates a TAG stop codon at codon 28 of the pre-core protein. The phase of HBeAg chronic hepatitis B appears to be associated with rapid disease progression, resulting in cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Monica A. Konerman, Anna S. Lok, in, 2018
Question 1 What Is The Clinical Indication For Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Quantitation
Hepatitis B surface antibody quantitation is used to determine hepatitis B immune status, ie, to determine if the patient has developed immunity against the hepatitis B virus. Such immunity may develop following exposure to the hepatitis B virus or its vaccine.
Patients at higher risk of exposure to the virus include:
- Infants born to infected mothers
- Sex partners of infected persons
- People with more than 1 sex partner in the last 6 months
- People with a history of sexually transmitted infection
- Men who have sex with men
- Injection drug users
- Household contacts of an infected person
- Healthcare and safety workers who have contact with blood and body fluids
- People who have lived or traveled in an area in which hepatitis B is common
- People who live or work in a prison
Testing is not recommended routinely following vaccination. It is advised only for people whose subsequent clinical management depends on knowledge of their immune status. These people include:
- Chronic hemodialysis patients
- Immunocompromised people, including those with HIV infection, hematopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients, and people receiving chemotherapy
- Infants born to women who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Sex partners of people who test positive for the hepatitis B surface antigen
- Healthcare and public safety workers who have contact with blood or body fluids
You May Like: Injection For Hepatitis B Treatment
What Is Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A, also called hep A, is a contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus. Some people have only a mild illness that lasts a few weeks. Others have more severe problems that can last months. You usually get the disease when you eat or drink something contaminated by poop from a person who has the virus.
The hepatitis A virus usually isnât dangerous. Almost everyone who has it gets better. But because it can take a while to go away, youâll need to take care of yourself in the meantime.
Is Hepatitis B Contagious
Hepatitis B is highly contagious. Its transmitted through contact with blood and certain other bodily fluids. Although the virus can be found in saliva, its not transmitted through sharing utensils or kissing. Its also not transmitted through sneezing, coughing, or breastfeeding.
Symptoms of hepatitis B may not appear for 3 months after exposure. Symptoms can last for several weeks.
But even without symptoms, you can still transmit the infection to others. The virus can live outside the body and remains infectious for at least
Hepatitis B is a highly contagious condition. Its associated with many serious complications, some of which can be life threatening.
But there are many treatment options available and multiple ways you can prevent infection, including getting vaccinated.
If you suspect you may have been exposed to hepatitis B, its important to talk with a doctor to prevent infection and determine the best course of treatment for you.
Recommended Reading: What Is Mild Hepatic Steatosis
Does Hepatitis B Show Up In Routine Blood Tests
Routine blood tests do not detect hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatitis B tests are specifically done if blood tests show abnormal liver function results, or if a person experiences symptoms or falls into the high-risk category for HBV infection.
A panel of HBV-specific blood tests are required to detect HBV infection.
Scientific Tools And Resources
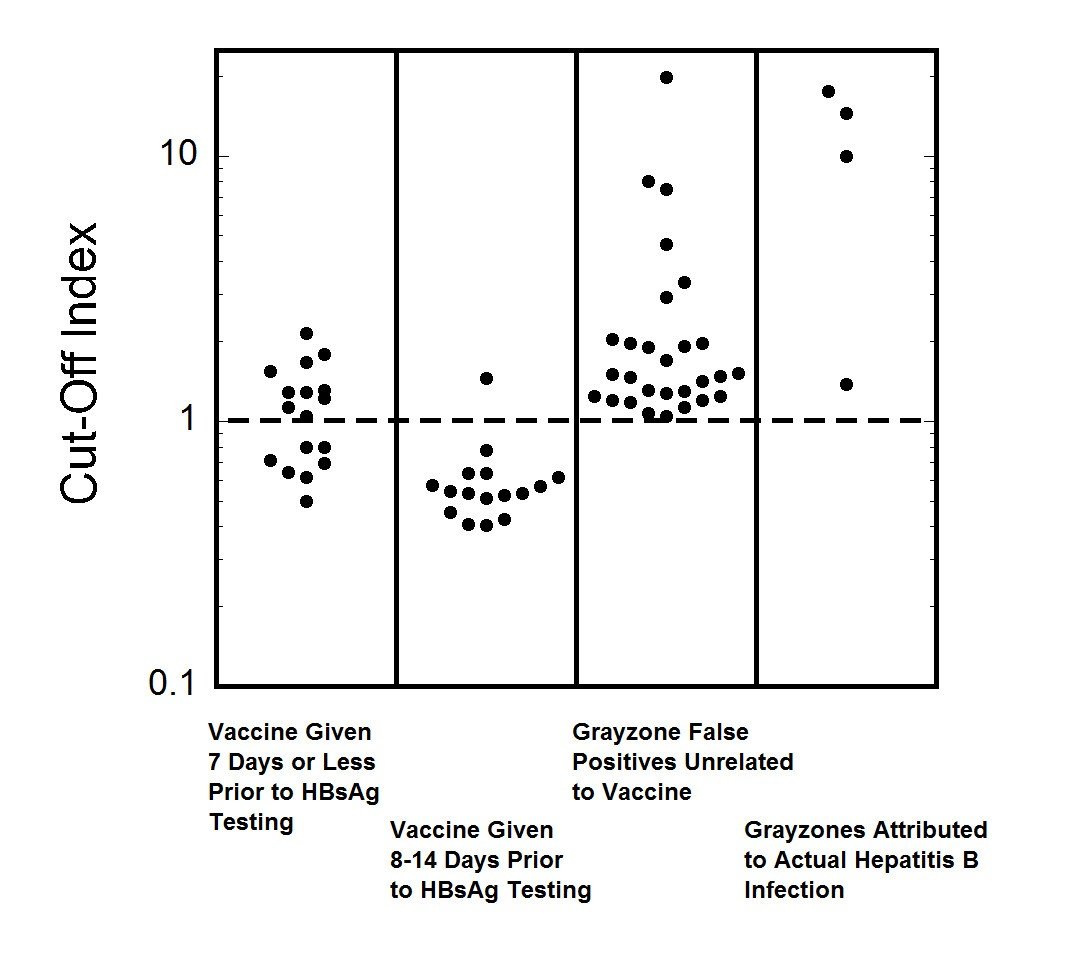
Interpretation of Hepatitis B Serologic Test Results
One page Summary Table describes the four most common tests used in hepatitis B serologic testing and provides guidance to interpret different patterns of test results.
Screening and Referral Algorithm for Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Pregnant Women
This is a clinical algorithm for screening and referral of pregnant women who are HBsAg-positive.
N/A=not available
*This CPT code corresponds only to the HBsAg screening component additional CPT codes might be associated with other component tests.
Notes: CDC recommends healthcare providers use prenatal HBsAg tests for pregnant women, which allows for reporting of positive results along with pregnancy status to public health jurisdictions. Refer all HBsAg positive pregnant women to Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program coordinators for case management of mother and infant: .
Laboratories reserve the right to add, modify, or stop performing tests at any time providers should review any test notifications from laboratories for changes.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Treatment
Is Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Enough Alone As A Screening Test Before Immunosuppressive Therapies
| The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators. Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the U.S. Federal Government. Read our disclaimer for details. |
| Verified June 2017 by Sherief Abd-Elsalam, Tanta University. Recruitment status was: RecruitingFirst Posted : June 14, 2016Last Update Posted : June 20, 2017 |
Hepatitis B virus infection is a challenging health problem. According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 240 million individuals suffered from chronic HBV infection worldwide.
After acute hepatitis B virus infection, the disappearance of hepatitis B surface antigen had generally been believed to signify viral elimination. However, it now becomes clear that those subjects may have occult HBV infection which is defined as the presence of HBV DNA in the liver in the absence of HBsAg in the serum. Occult HBV infection usually accompanies antibody against hepatitis B core antigen and/or antibody against HBsAg , but some cases might not have these serological markers .
Hepatitis B E Antigen And Hepatitis B E Antibody
Hepatitis B e antigen is a secretory protein processed from the precore protein. It is a marker of HBV replication and infectivity. Its presence is usually associated with high levels of HBV DNA. During acute HBV infection, HBeAg appears shortly after the appearance of HBsAg. In persons who recover from HBV infection, HBeAg to hepatitis B e antibody seroconversion precedes that of HBsAg to anti-HBs seroconversion. Anti-HBe may persist for many years after the resolution of acute HBV infection. In persons with chronic infection, HBeAg may persist for years to decades. Seroconversion from HBeAg to anti-HBe is usually associated with a marked decrease in serum HBV DNA levels and remission of liver disease, but some patients with anti-HBe continue to have high serum HBV DNA levels and associated active liver disease. The latter patients often have precore or core promoter HBV variants that prevent or decrease the production of HBeAg.37,38
Henry Lik-Yuen Chan, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, in, 2012
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis A And B
What Does The Test Measure
Hepatitis B testing looks for antigens, antibodies, or the genetic material of the hepatitis B virus. HBV antigens are substances from the virus that cause a patients body to produce an immune response. Antibodies are substances made by the immune system in response to the hepatitis B virus.
Initial tests for hepatitis B measure antibodies and antigens related to HBV including:
If a patient is diagnosed with hepatitis B based on these initial tests, additional hepatitis B testing may be used to monitor the disease, guide treatment, and determine if a person can spread hepatitis B to others. These additional tests may include:
- Hepatitis B e antigen : Hepatitis B e antigen is a protein from the hepatitis B virus found in some patients who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen. Measuring this antigen can help doctors understand infectivity, which describes a persons ability to spread HBV to others.
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. The symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same. So this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus and what stage of infection you may have.
Your healthcare provider may also order a series of blood tests called a hepatitis B monitoring panel to see if your infection is getting better.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Ql Reactive Means
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens And Antibodies
The Structure of Hepatitis B Virus
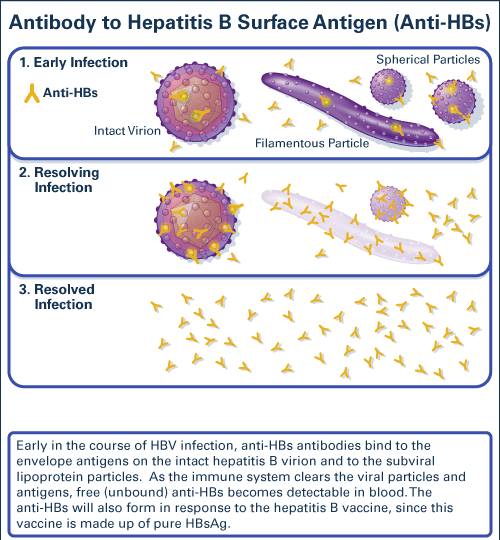
The hepatitis B virus is a small DNA virus with unusual features similar to retroviruses, which is a prototype virus of the Hepadnaviridae family. HBV causes acute and chronic hepatitis in humans. The hepatitis B virus consists of an outer lipid envelope and an icosahedral nucleocapsid core composed of protein. The virus is one of the smallest enveloped animal viruses with a virion diameter of 42 nm, and also named Dane particles. Dane particles contains both envelope and core.
The outer envelope contains embedded proteins which are involved in viral binding of susceptible cells. There are three types of proteins: small hepatitis surface proteins, middle hepatitis surface proteins and large hepatitis surface proteins, they are totally composed of hepatitis B surface proteins. The nucleocapsid encloses the viral DNA and a DNA polymerase that has reverse transcriptase activity.
There are three types of Hepatitis B Virus particles in infectious serum by electron microscopy, Dane particles, filamentous particles and spherical particles. Except for Dane particles , there also exist pleomorphic forms, as filamentous particles and spherical particles .
Hepatitis B Virus Antigens
Hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg
Hepatitis B core antigen-HBcAg
Hepatitis B e antigen-HBeAg
The X gene codes for HBxAg. The product of the X gene is hepatitis B x antigen . It may be involved in carcinogenesis.
Hepatitis B Virus Antibodies
Referrence