For Adults And Children
This vaccine schedule involves three doses within 2 months, followed by a booster dose at 1 year.
The initial accelerated doses provide immediate protection from HBV, and the booster dose helps provide long-term protection.
Below is the accelerated vaccination schedule approved for both adults and children:
| Vaccine series | |
|---|---|
| 2 months after the first dose | 1 year after the first dose |
What To Do If You Miss A Scheduled Dose
The recommended schedule for the HBV vaccine follows a three-dose pattern, with all doses complete within 6 months. The good news is that if you miss a dose, you dont need to start the series of shots all over.
If you missed getting the second dose 1 month after the first, make an appointment as soon as possible. If you miss the third dose, you should also try to get it as quickly as possible. Keep in mind that the second and third doses
When To Delay Or Avoid Hepb Immunization
Doctors delay giving the vaccine to babies who weigh less than 4 pounds, 7 ounces at birth whose mothers do not have the virus in their blood. The baby will get the first dose at 1 month of age or when the baby is discharged from the hospital.
The vaccine is not recommended if your child:
- is currently sick, although simple colds or other minor illnesses should not prevent immunization
- had a serious allergic reaction after an earlier dose of the vaccine or is allergic to baker’s yeast
Don’t Miss: Low Protein Diet For Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatitis B Vaccine On The Nhs
A hepatitis B-containing vaccine is provided for all babies born in the UK on or after 1 August 2017. This is given as part of the 6-in-1 vaccine.
Hospitals, GP surgeries and sexual health or GUM clinics usually provide the hepatitis B vaccination free of charge for anyone at risk of infection.
GPs are not obliged to provide the hepatitis B vaccine on the NHS if you’re not thought to be at risk.
GPs may charge for the hepatitis B vaccine if you want it as a travel vaccine, or they may refer you to a travel clinic for a private vaccination. The current cost of the vaccine is around £50 a dose.
How Do You Catch Hepatitis B Virus
Blood from a person infected with hepatitis B virus is heavily contaminated with the virus. As a result, contact with blood is the most likely way to catch hepatitis B. Even casual contact with the blood of someone who is infected can cause infection.
Healthcare workers are at high risk of catching the disease, as are intravenous drug users and newborns of mothers infected with the virus. Sexual contact can also expose people to infection. The virus is also present in low levels in saliva.
Also Check: What Are The Side Effects Of Hepatitis C Treatment
Babies And Children Can Develop Chronic Hbv
You may be wondering why the recommendations for the HBV vaccine start on the first day of life.
Adults who contract HBV will likely not experience long-term complications from hepatitis B. But the same is not the case for babies. As many as of babies who contract an HBV infection at birth from their mothers become chronically infected with HBV.
Children between the ages of 1 and 5 who get an HBV infection have a 25 percent of people who become chronically infected during childhood will develop liver cancer or cirrhosis. Thats why pediatricians want children to have immunity from HBV from the earliest possible age. Many babies and children exposed to HBV receive post-exposure prophylaxis, which decreases chance of infection.
If youre pregnant, youll most likely have a blood test to see if youre positive for hepatitis B. This allows doctors to find out if theres a chance that you could pass on the virus. These tests are highly sensitive and have a good accuracy rate, but they arent perfect. Additionally, a pregnant person may become infected between the time of the test and giving birth. The first dose of the vaccine given at birth lowers the risk of a newborn baby contracting hepatitis B.
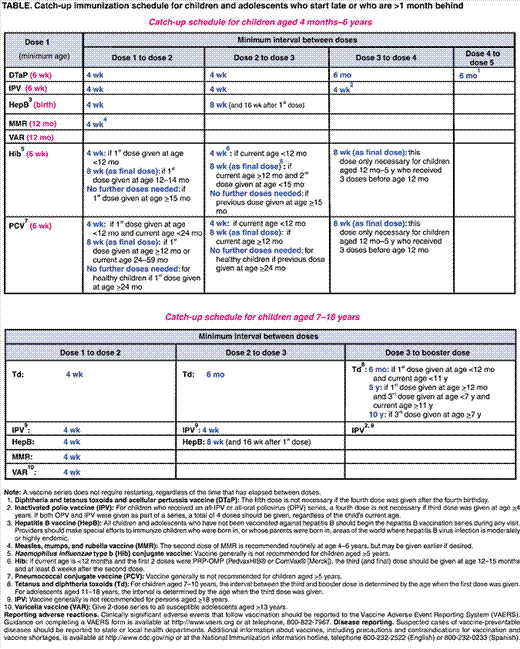
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C And Is It Curable
Who Should Be Given The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Besides newborns, others who should take the vaccine are:
-
Unvaccinated people under the age of 19
-
Anyone with a sexual partner with hepatitis B
-
Sexually active people outside of a long-term monogamous relationship
-
People being examined for STDs
-
Men having sexual intercourse with other men
-
People who share drug-injecting equipment
-
Anyone sharing living space with an infected person
-
Anyone whose job puts them in contact with infected persons, or blood and bodily fluids
-
People with end stage renal disease or chronic liver disease
-
Workers at facilities for the developmentally disabled
-
Anyone who has travelled to a region with significant rates of the infection
-
People with HIV infections
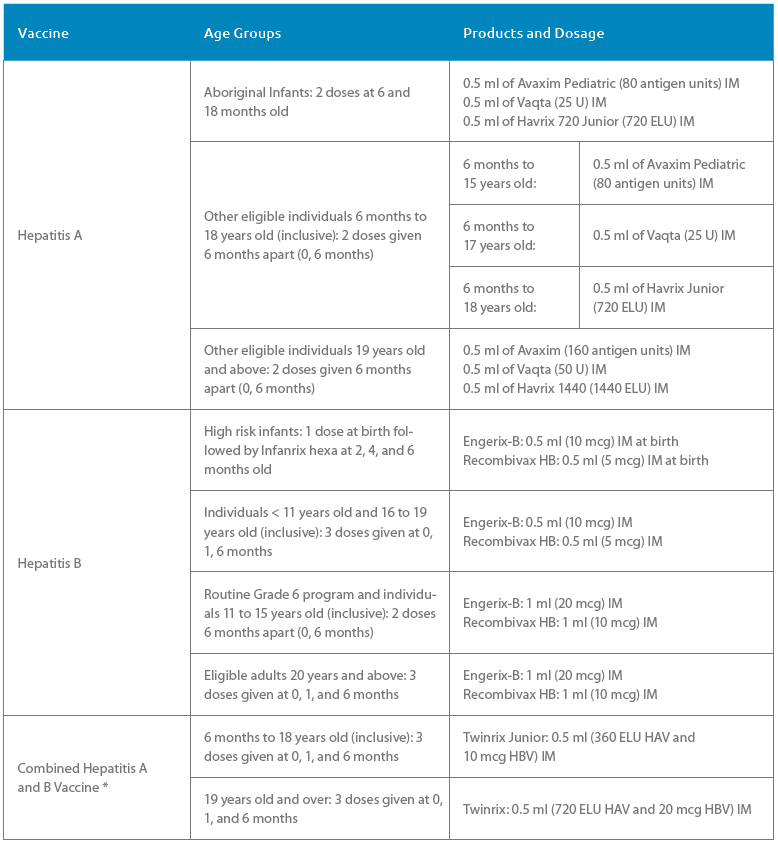
Recommended Adult Dosing Volume Of Monovalent Hepatitis B Vaccine
- Age 19 years and younger: Use 0.5 mL per dose .
- Age 20 years and older: 1.0 mL per dose .
For a one-page sheet reviewing the hepatitis B dosing schedule for children and adults, consult IACs Hepatitis A and B Vaccines: Be Sure Your Patients Get the Correct Dose. For complete dosing information, consult the ACIP hepatitis B vaccine recommendations for adults.
Don’t Miss: Is Hepatitis C Contagious Through Saliva
Does The Hepatitis B Vaccine Have Side Effects
Some children will develop pain or soreness in the local area of the shot, and low-grade fever.
There is one extremely rare, but serious, side effect. About 1 out of every 600,000 doses of the hepatitis B vaccine will cause a severe allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, with symptoms including swelling of the mouth, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure or shock. Anaphylaxis usually occurs within 15 minutes of receiving the vaccine. Although anaphylaxis can be treated, it is quite frightening. People should remain at the doctors office for about 15 minutes after getting the vaccine.
Although the hepatitis B vaccine is made in yeast cells, no one has ever been shown to be allergic to the yeast proteins contained in the hepatitis B vaccine .
How Is The Hepatitis B Vaccine Made
People are protected against hepatitis B virus infection by making an immune response to a protein that sits on the surface of the virus. When hepatitis B virus grows in the liver, an excess amount of this surface protein is made. The hepatitis B vaccine is made by taking the part of the virus that makes surface protein and putting it into yeast cells. The yeast cells then produce many copies of the protein that are subsequently used to make the vaccine. When the surface protein is given to children in the vaccine, their immune systems make an immune response that provides protection against infection with the hepatitis B virus.
The first hepatitis B vaccine was made in the 1980s by taking blood from people infected with hepatitis B virus and separating or purifying the surface protein from the infectious virus. Because blood was used, there was a risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses that might be found in blood, such as HIV. Although contamination with HIV was a theoretical risk of the early, blood-derived hepatitis B vaccine, no one ever got HIV from the hepatitis B vaccine. That is because the blood used to make vaccine was submitted to a series of chemical treatments that inactivated any possible contaminating viruses. Today, there is no risk of contaminating the vaccine with other viruses because the surface protein is manufactured in the laboratory.
You May Like: Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive
Difference Between Hep A And Hep B Vaccines
In the United States, the hep A shot is administered routinely to very young children. It may be given in one or two doses. If the child is getting two doses, the first one should be no later than 12 months of age. There is some flexibility in the interval between shots, but six to 18 months is common.
The hep B vaccine should be given to all babies as soon as possible after birth. After the first dose, two or three doses follow with an interval of at least four weeks. Unvaccinated adults get three doses spanning six months. If you are at least 18 years old, you have the option to get a combination vaccine. The dual vaccine is given in three shots over six months.
Adults traveling to areas with a high rate of HAV would benefit from getting the hep A shot. Talk to your physician about your risk for hep A and hep B to determine if you should receive the vaccines. You can schedule your hepatitis vaccine with your primary care physician or one of your local pharmacies, such as CVS and Walgreens.
Dosage Forms & Strengths
Contraindicated
- belimumab
belimumab decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by immunosuppressive effects risk of infection. Contraindicated. Do not administer live vaccines 30 days before or concurrently with belimumab.
Serious – Use Alternative
Monitor Closely
Minor
-
chloroquine decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Minor/Significance Unknown.
- ozanimod
ozanimod decreases effects of hepatitis b vaccine by immunosuppressive effects risk of infection. Minor/Significance Unknown. No clinical data are available on the efficacy and safety of vaccinations in patients taking ozanimod. Vaccinations may be less effective if coadministered with ozanimod.
You May Like: What Is The Best Treatment For Autoimmune Hepatitis
Emergency Hepatitis B Vaccination
If you have been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and have not been vaccinated before, you should get immediate medical advice, as you may benefit from having the hepatitis B vaccine.
In some situations, you may also need to have an injection of antibodies, called specific hepatitis B immunoglobulin , along with the hepatitis B vaccine.
HBIG should ideally be given within 48 hours, but you can still have it up to a week after exposure.
Who Should Not Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B is a safe vaccine that does not contain a live virus.
However, there are some circumstances in which doctors advise against getting the HBV vaccine.
You should not receive the hepatitis B vaccine if:
- youve had a serious allergic reaction to a previous dose of the hepatitis B vaccine
- you have a history of hypersensitivity to yeast or any other HBV vaccine components
Recommended Reading: When Was Hepatitis B Discovered
What Is The Treatment For Hepatitis B
Prevention is recommended by receiving a vaccine for HBV.
Receiving an injection of the hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of coming in contact with the virus may help prevent the development of the disease.
At present, there is no specific treatment for patients with acute hepatitis B. Acute infection is usually short and will often resolve on its own. Your health care provider may recommend rest, and adequate nutrition and fluids to help your body fight the infection. Hospitalization may be required for patients who suffer from severe vomiting and who are unable to maintain adequate nutritional levels. It may also be required to prevent the development of complications.
While chronic infection cannot be cured, there are two standard treatments in Canada that may control the virus and prevent further damage to the liver.
- Antiviral medications can fight the virus and slow damage to the liver.
- Interferon which may be given for short periods and if effective, results in suppression of the virus.
Read Also: How To Catch Hepatitis B And C
Infants Born To Mothers Who Have Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
Protecting Your Baby
Infants born to women with hepatitis B must receive accurate doses of hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin to ensure complete protection. In order to protect these infants, medications should be given immediately after birth in the delivery room or within the first 12-24 hours of life*.
* See Testing and Treatment During Pregnancy section for details. Please note that testing of all pregnant women for hepatitis B is a global recommendation.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends that infants born to hepatitis B positive mothers receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth, and ideally a dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin . These shots must be followed by the additional vaccine doses given on the recommended schedule. In the U.S., infants should follow a 1 month and 6-month schedule for the additional two doses.
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Recommended Reading: How Do I Catch Hepatitis B
Preparations Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is produced using recombinant DNA technology. A plasmid containing the gene for hepatitis B surface antigen is inserted into common bakers yeast, which then produces HBsAg. The HBsAg is harvested and purified. This vaccine cannot cause hepatitis B virus infection because no potentially infectious viral DNA or complete viral particles are produced during this process.
Single-antigen and a combination formulation that combines hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines are available. Two single-antigen vaccines, Engerix-B® and Recombivax HB®, are conjugated with aluminum. A newer formulation, HepB-CpG , uses the immune-stimulating adjuvant, cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide .
Tips For Protecting Yourself Against Hepatitis
The hepatitis A virus spreads through ingestion of the virus through sexual contact, caregiving, sharing drugs and consuming contaminated food or water. The virus can contaminate food at any time between when it is grown and cooked.
HAV is more common in environments with unsanitary conditions, poor sewage systems and no potable water. To reduce your risk, be vigilant about hand hygiene by washing your hands thoroughly before you leave the bathroom, after you change diapers, and any time you touch food.
Don’t Miss: Chronic Hepatitis C Without Hepatic Coma Hcc
Why Should My Baby Get The Hepatitis B Shot
- Protects your child from against hepatitis B, a potentially serious disease.
- Protects other people from the disease because children with hepatitis B usually dont have symptoms, but they may pass the disease to others without anyone knowing they were infected.
- Prevents your child from developing liver disease and cancer from hepatitis B.
- Keeps your child from missing school or child care and you from missing work.
Why Is The Hepb Vaccine Recommended
People who dont know they’re infected can spread the hepatitis B virus. So it cant be avoided just by being careful. That’s why health experts recommend that all babies get the vaccine right from birth.
The HepB injection usually creates long-term immunity. Most infants who get the HepB series are protected from hepatitis B infection beyond childhood, into their adult years.
Eliminating the risk of infection also decreases risk for cirrhosis of the liver, chronic liver disease, and liver cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Hepatitis A
I Am A Healthcare Worker Who Did Not Develop Hepatitis B Antibodies After Immunization What Should I Do
Two versions of hepatitis B vaccine are available. One, called Heplisav-B, contains a novel adjuvant that was not present in previous versions used by adults . Some people did not respond to the older version hepatitis B vaccine. In fact, in a group of adults younger than 40 years of age who received two doses of the older version vaccine 75 of 100 were protected. Following the third dose, this number increased to 90 of 100. However, people older than 40 years of age were less likely to respond to the vaccine with increasing age. On the other hand, 90 to 100 of 100 adults 18 years of age and older respond to Heplisav-B, which was approved for use in 2018.
About 5-10 of every 100 children and adults younger than 40 years of age do not respond to the third dose of the hepatitis B vaccine. Some of these people will be recommended to get vaccinated again. About 5 of 100 people will still not respond after getting all recommended doses of both series. Note that children younger than 18 years of age cannot get Heplisav-B.
If the people who do not respond to vaccination are determined not to have chronic hepatitis B, they will be reliant on taking precautions to reduce the chance of exposure and relying on those around them for protection. In other words, these people will be reliant on herd immunity.
Hepatitis B Vaccination In Pregnancy
Hepatitis B infection in pregnant women may result in severe disease for the mother and chronic infection for the baby.
This is why the hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for pregnant women who are in a high-risk category.
There’s no evidence of any risk from vaccinating pregnant or breastfeeding women against hepatitis B.
And, as it’s an inactivated vaccine, the risk to the unborn baby is likely to be negligible .
Read Also: How Can You Get Rid Of Hepatitis B
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.