Is Alcoholic Hepatitis Dangerous
Yes. It may be fatal, especially if you have had previous liver damage.
Those who have had nutritional deficiencies because of heavy drinking may have other ailments. These medical complications may affect almost every system in the body.
It’s important to recognize and treat alcoholic hepatitis early, to help prevent these life-threatening consequences.
What Are The Complications Of Alcohol
Complications from alcohol-related liver disease usually occur after years of heavy drinking. These complications can be serious.
They may include liver related conditions that are a consequence of portal hypertension:
- build up of fluid in the abdomen
- bleeding from veins in the esophagus or stomach
- enlarged spleen
Search for a Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are research studies that test how well new medical approaches work in people. Before an experimental treatment can be tested on human subjects in a clinical trial, it must have shown benefit in laboratory testing or animal research studies. The most promising treatments are then moved into clinical trials, with the goal of identifying new ways to safely and effectively prevent, screen for, diagnose, or treat a disease.
Speak with your doctor about the ongoing progress and results of these trials to get the most up-to-date information on new treatments. Participating in a clinical trial is a great way to contribute to curing, preventing and treating liver disease and its complications.
Start your search here to find clinical trials that need people like you.
How Much Drinking Can Lead To Alcoholic Hepatitis
Excessive drinking is a major risk factor for alcoholic hepatitis. However, how much alcohol drinking puts you at risk of the condition is still unclear. Studies have reported that most people with alcoholic hepatitis have a history of drinking more than 3.5 ounces of alcohol daily for at least 20 years, which is equal to drinking seven glasses of wine, seven beers or seven shots of spirits.
However, this does not mean that moderate drinking cannot cause the condition. People who drink moderately have also developed it, making the connection between drinking and alcoholic hepatitis complex.
Also Check: How Do You Hepatitis B
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Drinking a large amount of alcohol, even for just a few days, can lead to a build-up of fats in the liver.
This is called alcoholic fatty liver disease, and is the first stage of ARLD.
Fatty liver disease rarely causes any symptoms, but it’s an important warning sign that you’re drinking at a harmful level.
Fatty liver disease is reversible. If you stop drinking alcohol for 2 weeks, your liver should return to normal.
Who To Treat: Stratification Of Patients By Disease Severity
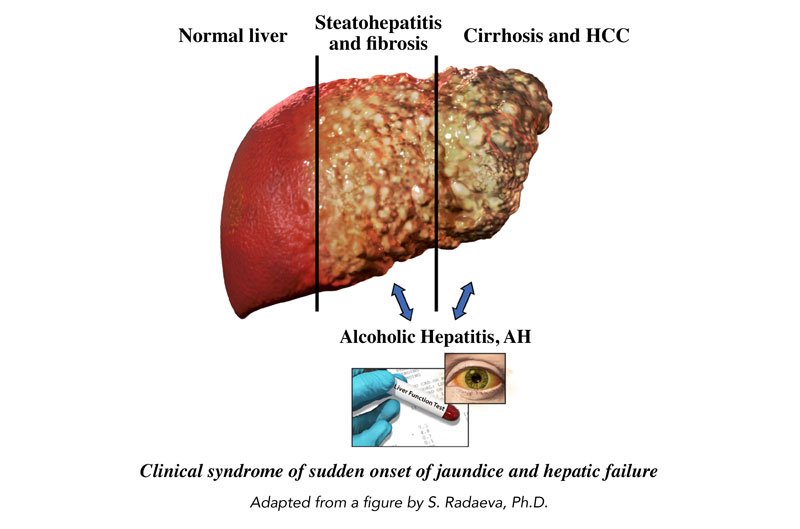
Encephalopathy, renal failure, coagulopathy , and serum levels of bilirubin have served as independent prognostic factors for AH since the early 1970s.5,9,10 However, Maddrey et al2 used discriminant analysis to produce a scoring system that reliably defined individuals at highest risk for death in the short term. In the original study describing the DF, a cut-off value of 93 was used to identify patients who died. Subsequently, the scoring system was changed a cut-off value of 32, which corresponded to the old cut-off value of 93, was used to identify patients with severe AH. By using the DF, large variations in mortality were observed between patients with DF values of 32 or more compared with patients with lower DF values.9 Most trials conducted since that time have used this threshold to identify patients who might benefit from treatment. Most trials conducted before 2000 enrolled relatively small numbers of patients, which would make it difficult to detect a statistically significant difference in mortality rate in patients with a low mortality rate.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Autoimmune Hepatitis
Oral Intake Vs Parenteral/enteral Hyperalimentation
Some studies have suggested that improved energy and protein intake may improve the survival rate in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. However, complications associated with parenteral hyperalimentation or enteral hyperalimentation may outweigh the benefits of these approaches. Thus, if patients are able to take food orally, this is the route of choice, and formal nutritional support can be reserved for those instances in which patients are unable to ingest enough by mouth to meet their needs. Energy intake should be carefully measured to ensure adequate consumption. The use of nutritional supplements and appetite stimulants may be appropriate.
The 2010 AASLD ALD guideline states that patients with advanced disease should receive aggressive enteral nutritional therapy. Patients with mild to moderate alcoholic hepatitis that improves during the first week of hospitalization and who are treated with nutritional therapy and abstinence will probably neither need nor benefit from other interventions, but these individuals should be monitored closely.
Is There A Safe Level Of Drinking
For most people, moderate drinking will not lead to alcohol-related liver disease. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, moderate drinking is one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men. Each of these alcoholic beverages, in the following amounts, is considered one drink and contains the same amount of alcohol:
- One 12-ounce bottle of beer
- One 4-ounce glass of wine
- One 1-ounce shot of hard liquor.
However, if you have chronic liver disease, even small amounts of alcohol can make your liver disease worse. People with alcohol-related liver disease and those with cirrhosis from any cause should abstain from alcohol completely.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Hepatitis C Naturally
Natural Compounds That Regulate Programmed Cell Death
Corosolic acid, also known as 2α-hydroxyursolic acid, is the main active ingredient found in banaba leaves. Corosolic acid has attracted considerable attention due to its anti-diabetic effect and was called âPhyto-insulinâ . As a potential activator of AMPK, corosolic acid can restore ethanol-suppressed autophagy via AMPK activation in vivo and in vitro .
Gastrodin is one of the main bioactive components of Gastrodia elata, an ancient Chinese medicinal plant, geranium. Zhang et al. showed that gastrodin significantly inhibited caspase-3 activation and apoptosis from ethanol-induced toxicity in vivo and in vitro .
Ursolic acid is a pentacyclic terpenoid carboxylic acid with many health functions, such as anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and hepato-protective activities . Ma et al. directly confirmed that ursolic acid reduced hepatocellular apoptosis and alleviated alcohol-induced liver injury via inhibition of CASP3 in vivo and in vitro .
How Can You Prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis
The best way to prevent alcoholic hepatitis is to avoid alcohol or drink only in moderation. Moderate drinking is defined as less than two drinks per day for men and less than one drink per day for women.
You can also reduce your risk by taking steps to protect yourself from hepatitis B and hepatitis C. The bloodborne viruses that cause these conditions can be transmitted in several ways, including shared needles or razors and through body fluids during sex. Currently, vaccines are available for hepatitis B, but not for hepatitis C.
Your healthcare team may also recommend certain lifestyle changes based on your specific symptoms and health needs.
For example:
Read Also: Hepatitis A How Is It Spread
Potential New Avenues Of Research And Therapies In Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis
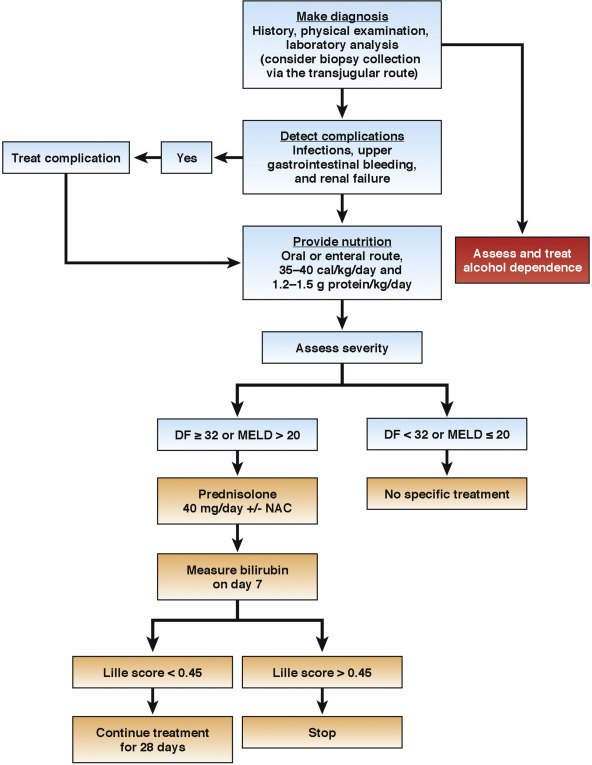
Prednisolone is the treatment of choice in the management of sub group of severe alcoholic hepatitis without any active infections or active UGI bleeding or renal impairment. Prednisolone is conventionally given at a dose of 40 mg per day for 4 wk followed by tapering over next 2 wk, with close monitoring for infections and other side effects of steroids. Despite the best standard of care and steroids, many patients either do not respond to steroids or are not eligible for steroids. Large majority of steroid intolerant, ineligible, unresponsive alcoholic hepatitis patients are thus left with no specific available treatment options. Better understanding of the pathogenesis of alcoholic hepatitis and advances in the basic sciences are opening new avenues for alcoholic hepatitis, as described below .
Natural Compounds That Improve Lipid Metabolism
Curcumin, the main active ingredient in turmeric, has been shown to reduce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes and subsequent steatosis by regulating the NF-E2ârelated factor 2 -farnesoid X receptor pathway . Some scholars also found that treatment with curcumin could suppress oxidative stress in ALD mice by reducing the generation of ROS .
Dihydroquercetin, one of the most common dihydroflavonoids, is widely found in milk thistles and onions. Zhang et al. proposed that dihydroquercetin improves alcoholic liver steatosis by regulating the activation of the SIRT1-AMPK pathway . Dihydroquercetin increased the activity of AMPK, thereby reducing the expression of SREBP1 in ethanol-treated HepG2 cells. Dihydroquercetin shows the ability to inhibit lipid formation and protect the liver, suggesting that dihydroquercetin has the potential as a treatment for ALD.
Tanshinone IIA is superabundant in the root of Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE. Yin et al. found that tanshinone IIA can inhibit the synthesis of FAs and stimulate the oxidation of FAs, improving ALD . Tanshinone IIA has a lipid-modulating effect and attenuates lipid accumulation by regulating LXRα/SREBP1 pathway in HepG2 Cells .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know When You Have Hepatitis
How Can Prevent Alcoholic Hepatitis
The best treatment is to stop drinking.
Treatment also may include:
- Hereditary defects in iron or copper metabolism
- Prolonged exposure to toxins
In children, the most frequent causes are biliary atresia â a disease that damages the bile ducts â and neonatal hepatitis. Children with these diseases often receive liver transplants.
Many adult patients who require liver transplants suffer from primary biliary cirrhosis. We do not yet know what causes this illness, but it is not in any way related to alcohol consumption.
Treating Alcoholic Liver Disease
The most important part of treating alcoholic liver disease is to permanently stop all alcohol consumption. Your health care team can help you find programs to support you on this critical undertaking, including both inpatient and outpatient treatment programs at UChicago Medicine. Additionally, treatment for alcoholic liver disease may involve:
- Taking medications to prevent your craving for alcohol
- Eating healthy, well-balanced meals
Don’t Miss: Can Hepatitis B Lead To Liver Cancer
Hepatitis C Alcohol And Alcoholic Hepatitis
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver. Several things can lead to the condition one major cause is hepatitis C, which can result from a viral infection. Another is alcohol consumption, which can cause alcoholic hepatitis.
These two types of hepatitis are separate conditions. However, alcohol consumption and the hepatitis C virus also have associations with one another.
According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism , HCV infection appears to be more prevalent among people with alcohol abuse disorder. Consuming alcohol also worsens HCV and can interfere with its treatment.
Keep reading to learn more about the association between hepatitis C and alcohol, as well as symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of alcoholic hepatitis.
No, it is not possible to get hepatitis C from alcohol. This condition results from a viral infection, which a person can only contract if they have exposure to blood containing HCV.
However, excessive alcohol consumption may raise the risk of acquiring HCV. According to the NIAAA , research from the 1990s found that people with alcohol abuse disorder had higher rates of HCV than the control group. This was true even for individuals with no other HCV risk factors.
Scientists are not sure why HCV is more common in those who consume excess alcohol. However, some believe alcohol makes it easier for the virus to enter and remain inside the body.
Alcohol Related Liver Disease
Alcohol related liver disease is the result of drinking more alcohol than the liver can process, which damages the organ. The liver, responsible for performing many functions in the body, processes what the body needs, discarding what it doesnt. As the liver breaks down the alcohol, the chemical reaction releases a toxin, which damages liver cells. If too much alcohol is ingested repeatedly over time, even without getting drunk, liver damage begins. When too much liver damage occurs, it impacts the whole body. ALD is both preventable and can be fatal.
More than 21,000 people die annually in the United States from ALD. Nearly 70 percent of those deaths are men, yet women develop the disease after less exposure to alcohol than men.
Recommended Reading: Royal Canin Hepatic Dog Food Side Effects
Can Hepatitis C And Alcoholic Hepatitis Coexist
Hepatitis due to both HCV and alcohol abuse can coexist. According to a 2018 article, it is common for the two conditions to occur simultaneously.
Excessive alcohol consumption can accelerate and multiply the damage due to HCV, worsening liver cirrhosis. However, even small amounts of alcohol can exacerbate HCV. It may also interfere with HCV treatment by causing the virus to become resistant to medication.
Although both conditions are responsible for liver inflammation, there are differences in the symptoms of HCV and alcoholic hepatitis.
According to the World Health Organization , around of people with HCV show no symptoms after contracting the initial infection. They may not realize they have the virus until later if it becomes chronic and causes liver damage.
Individuals who do experience hepatitis C symptoms may develop:
- tenderness in the liver
- systemic inflammatory response syndrome, which involves fever, fast heart rate, and fast breathing
It is important to note that HCV is contagious. If a person is unsure if they have contracted the infection, they should take safety precautions to prevent others from coming into contact with their blood.
Study Finds Admissions For Alcoholic Hepatitis Rose 50 Percent In Early Months Of The Pandemic
In new research published in Liver International, researchers at Henry Ford Health System have found that people hospitalized for alcoholic hepatitisa life threatening liver disease fueled by alcohol useincreased a staggering 50 percent in the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Researchers said the role of gender and race had no meaningful impact on the spike in admissions.
The findings add to the growing body of research and surveys that have shown more people were turning to alcohol to cope with the stresses of the pandemic and the health implications that followed. A 54 percent surge in national alcohol sales were reported during the first week of pandemic alone.
Humberto Gonzalez, M.D., a Henry Ford transplant hepatologist in the Department of Gastroenterology and the study’s lead author, described the findings as alarming.
“This is an eye opener for how much the increase in alcohol use has affected us as a community,” Dr. Gonzalez said. “Being hospitalized for alcoholic hepatitis changes the severity of the problem. We need to work on coping strategies for this never-ending health crisis.”
Alcoholic hepatitis, or AH, often occurs after years of regular, heavy alcohol use. It has also been associated with bouts of binge drinking. More than 120,000 people are hospitalized with AH each year and the average 28-day mortality rate is 26 percent. The condition leads to early liver and kidney failure and rapid multi-organ failure.
Read Also: How Bad Is Hepatitis B
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Diagnosis Of Alcoholic Hepatitis
Diagnosis of AH should always be considered in a patient with chronic alcohol use presenting with liver disease. As the clinical profile of AH may mimic sepsis or cholangitis, detailed wotk up including chest X-ray, blood cultures, ascitic fluid examination, urinalysis and culture, and abdominal imaging should be obtained. Decompensation of alcoholic liver disease from causes other than AH and other liver diseases should also be considered. Atypical features for AH include jaundice for over 3 months, transaminases over 400 IU/l, and last alcohol use more than 4 weeks prior to presentation. White blood cell count and platelet count may help to determine the clinical diagnosis of AH. However, 2530% of AH patients may require liver biopsy for accurate diagnosis especially when the clinical diagnosis remains uncertain.
Assessment of disease severity
Don’t Miss: Does Hepatitis C Have Symptoms
How Is Alcoholic Hepatitis Diagnosed
Diagnosing alcoholic hepatitis is not always simple. Alcoholic hepatitis can vary widely in presentation and can sometimes mimic bacterial infections. Maintaining a thorough history remains one of the best ways to diagnose alcoholic hepatitis. A thorough history may consist of a robust medical history, an evaluation of alcoholic hepatitis related symptoms, and a comprehensive physical examination. Physicians may also conduct labs that will provide clues to a diagnosis of AH. Physicians may also conduct liver scans, liver biopsies, nutritional assessments, and more.10