Taking A Hepatitis B Test
Testing for hepatitis B is performed on a sample of blood. A doctor, nurse, or other health care provider can obtain a blood sample using a small needle to draw blood from a vein.
At-home hepatitis B testing requires that users carefully follow instructions provided in the test kit to collect a small sample of blood, package the sample, and mail it to a lab for testing.
What Does It Mean If Your Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Is Negative
Your test results may not mean you have a problem. Ask your healthcare provider what your test results mean for you. Normal results are negative or nonreactive, meaning that no hepatitis B surface antigen was found. If your test is positive or reactive, it may mean you are actively infected with HBV.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Being Tested For Hepatitis B Core Antibody
The hepatitis B core antibody test is part of a screening panel for hepatitis B, which also will include hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B surface antibody . These three tests look for acute and chronic infections.
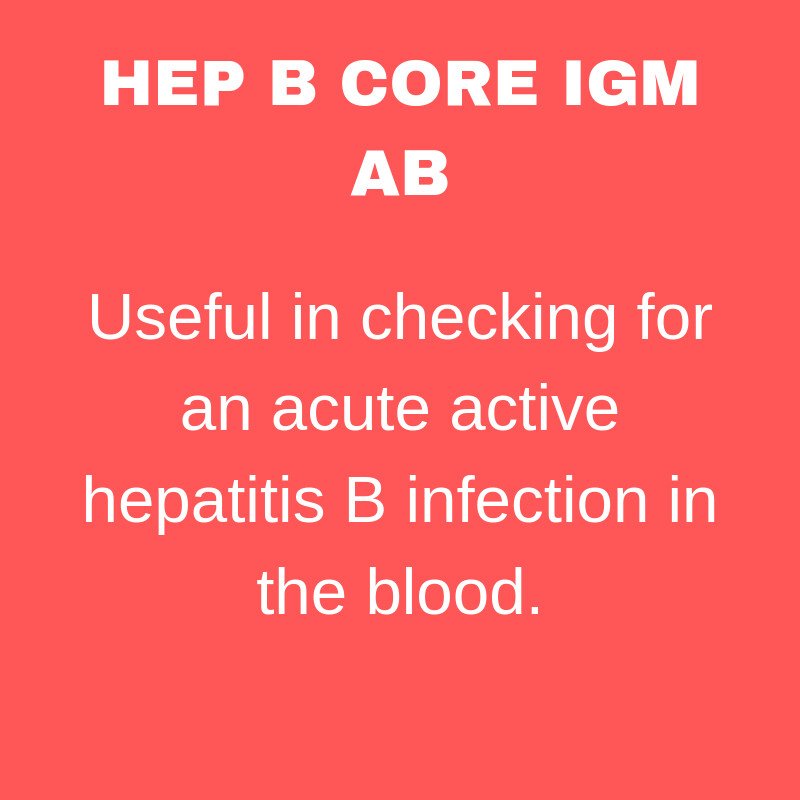
Tests may be ordered if you have symptoms of hepatitis, such as jaundice , fever, fatigue, pale stools, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. In this case, the hepatitis B core antibody IgM test may be used, as it shows an early stage of infection.
This test may be ordered if you are being screened for hepatitis B because you are donating blood or wish to become an organ donor. Hepatitis B can be transmitted by blood or through organ transplants, so donors are tested to prevent infecting recipients. It’s possible to have had the infection with only mild symptoms, so many people don’t realize they have had hepatitis B.
People who are part of populations at risk for hepatitis B infection will be screened. Screening is also often done for pregnant people, infants, people sharing a home with hepatitis B patients, people who may have been exposed by needlestick injuries or body fluids, and for people with HIV .
Read Also: How Can You Get Hepatitis B
How Long Do Hep B Antibodies Last
How long does protection from hepatitis B vaccine last? Studies indicate that immunologic memory remains intact for at least 30 years among healthy people who initiated hepatitis B vaccination at > 6 months of age. The vaccine confers long-term protection against clinical illness and chronic hepatitis B virus infection.
How To Get Tested
Hepatitis B testing is typically prescribed by a doctor and performed in a hospital, lab, or other medical setting. Taking a hepatitis B test requires a blood sample, which can be collected by a health care professional.
For laboratory-based testing, blood is drawn from a patients vein. After blood is collected, the sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
You May Like: What Are The First Symptoms Of Hepatitis C
Recommended Reading: Does Hepatitis Affect The Liver
What Other Tests Might I Have Along With This Test
Your healthcare provider may order other blood tests to look for HBV. These tests can look for antigens on the surface, envelope, and core of the virus, as well as the antibodies to these antigens. Because the symptoms of all 5 hepatitis infections are much the same, this blood test is often done along with other hepatitis blood tests to tell your provider which type of virus you may have.
Hepatitis B Core Igm Antibody
Hepatitis B Core Antibody
| Synonym: | Enzyme Immunoassay for the Detection of Antibodies to Hepatitis B Core IgM in Human Serum Specimens |
| Requisition Form | G-2A |
| Test Description | An enzyme immunoassay for the qualitative detection of IgM Antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen in human serum |
| Pre-Approval Needed | |
| Performed on Specimens from | Human |
| 500 µL | |
| Storage/Preservation Prior to Shipping | Serum may separated from the clot may be stored at 2°C to 8°C up to 48 hours, but then must be frozen at -20°C or colder till tested. |
| Transport Medium | N/A |
| Specimen Labeling |
|
| Shipping and Specimen Handling Requirements |
|
Also Check: Is Hepatitis C Sexually Transmitted
Hbcab Or The Hepatitis B Core Antibody Test
The hepatitis B core antibody is produced by your immune system after infection by the hepatitis B virus, and it can persist for life. It is a sign that you either have an new, active hepatitis B infection or that you acquired hepatitis B in the past.
HBcAb is an immune system response to a protein in the core of the virus, and it is only present if you have been infected, rather than immunized against the virus. It is part of a routine screening panel of tests for hepatitis B. If your rest results turn out to be positive, your healthcare provider will order further tests to determine the stage of the infection: acute or chronic .
Also Known As: anti-HBc, HBcAb
Results Of The Hbcab Test
There are two variations of antibodies. The IgM antibody is the largest antibody and the first produced in an infection. It shows that you may have a current, active infection. Sometimes it persists for years, but it usually drops to undetectable levels.
The HBcAb IgG variant is produced later in the course of the infection, and it’s likely that you will have a positive HBcAb IgG test the rest of your life.
The screening panel usually has a test that is for total HBcAb, which includes both IgM and IgG. The IgM test may be ordered to help determine if you have an acute infection.
A positive HBcAb test must be interpreted along with the results of the other tests. You may have an active or chronic infection, or you may be immune to hepatitis B due to past infection. Discuss the results with your healthcare provider. In any case, a positive HBcAb test means your blood or organs cannot be donated to a recipient.
Also Check: Hepatomegaly With Diffuse Hepatic Steatosis
What Is This Test
This test looks for antibodies called IgM in your blood. The test is used to find out whether you are actively infected with the hepatitis B virus .
HBV has a central core and a surrounding envelope. Your immune system makes IgM antibodies for the core of HBV during the active stage of infection. Hepatitis B core IgM antibodies begin to appear in your blood several weeks after you are first infected with HBV. People who have had the hepatitis B vaccine will not have the core antibody in their blood.
HBV is 1 of 5 hepatitis viruses. The others are hepatitis A, C, D, and E. Most hepatitis infections are caused by these 5 viruses. HBV is spread through blood, seminal fluid, and vaginal secretions. It can take 60 to 150 days to develop symptoms of hepatitis B after you become infected. The virus causes an infection in the liver. In most cases, this virus clears up on its own within 6 months. But in a small portion of adults and a larger portion of children, the virus does not go away. This is especially true for newborns. This is called having a chronic infection. It may lead to liver cell damage, scarring, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
How Is The Hbcab Test Done
This is a blood test. A clinician will fill a tube with blood taken from a vein in your arm through which a needle is inserted. If you are giving blood, a sample will be taken from the blood you’re donating. The blood is sent to a lab, where it is tested. Sometimes HBcAb will be added on to lab orders when results from other tests indicate there may be a hepatitis B infection.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatitis Ab And C
How Is My Privacy Protected When I Take A Sti Test Online
We guarantee complete discretion, we wonât disclose your results to your GP, employer or insurers under any circumstances.
Your data security is hugely important to us. We take strict measures to ensure result integrity with the minimum of data sharing. We only share the essential details need to conduct testing with our laboratory provider.
We donât believe in selling your data, individually or in aggregate. And you can request to wipe your account data at any time.
All samples are disposed of following analysis.
You May Like: Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen

An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Read Also: Cdc Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule
Hepatitis B And Your Liver
The liver is such an important organ that we can survive only one or two days if it completely shuts down â if the liver fails, your body will fail, too. Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 80% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to regenerate â or create â itself from healthy liver cells that still exist.
If your body were an automobile, your liver would be considered the engine. It does hundreds of vital things to make sure everything runs smoothly:
- Stores vitamins, sugar and iron to help give your body energy
- Controls the production and removal of cholesterol
- Clears your blood of waste products, drugs and other poisonous substances
- Makes clotting factors to stop excessive bleeding after cuts or injuries
- Produces immune factors and removes bacteria from the bloodstream to combat infection
- Releases a substance called âbileâ to help digest food and absorb important nutrients
The word hepatitis actually means inflammation of the liver. Thus, hepatitis B refers to inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus. With early detection and appropriate follow-up medical care, people living with a chronic hepatitis B infection can expect to enjoy a long and healthy life.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
- Sharing needles
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Sharing personal care items like razors or toothbrushes
- Birth to an infected mother
- Sharing a household with a chronically infected individual
- Human bites from a hepatitis B-infected person
- Needle sticks exposures of healthcare workers
HBV can survive for at least seven days outside of the body and still be able to cause infection.
Recommended Reading: Can You Catch Hepatitis C From Kissing
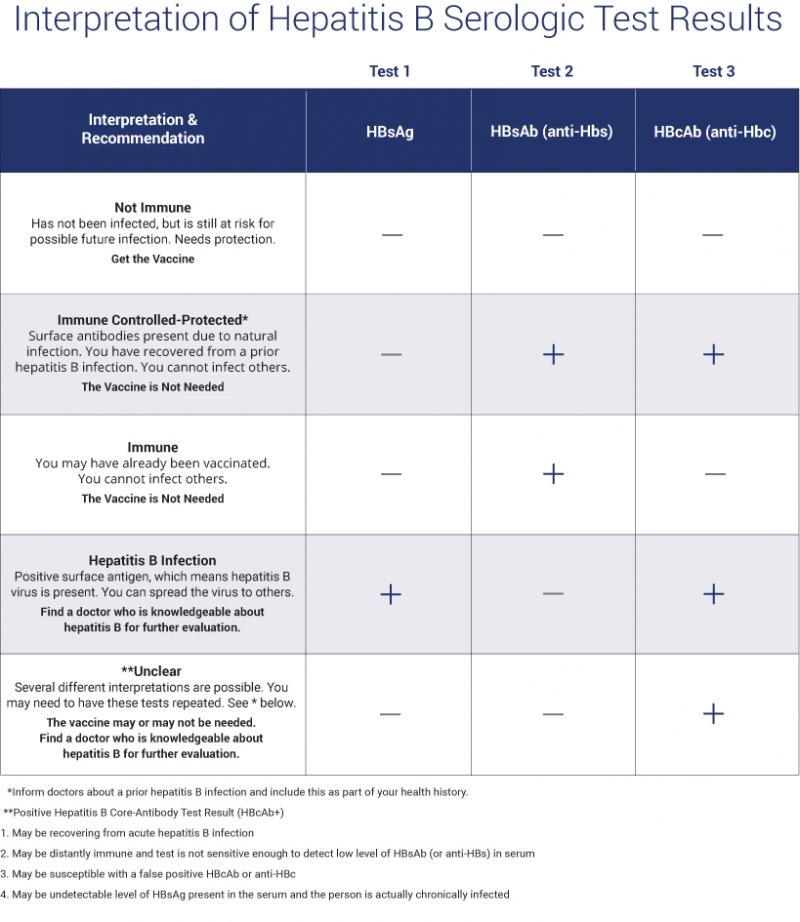
Understanding Your Test Results
Understanding your hepatitis B blood tests can be confusing. It is important to talk to your health care provider so you understand your test results and your hepatitis B status. Are you infected? Protected? Or at risk? The Hepatitis B Panel of blood tests includes 3 tests and all three results must be known in order to confirm your status.
Below is a chart with the most common explanation of the test results, but unusual test results can occur. Please note that this chart is not intended as medical advice, so be sure to talk to your health care provider for a full explanation and obtain a printed copy of your test results. In some cases, a person could be referred to a liver specialist for further evaluation.
More Detailed Information About Hepatitis B Blood Tests
An acute hepatitis B infection follows a relatively long incubation period – from 60 to 150 days with an average of 90 days. It can take up to six months, however, for a person to get rid of the hepatitis B virus. And it can take up to six months for a hepatitis B blood test to show whether as person has recovered from an acute infection or has become chronically infected .
The following graphic from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention represents the typical course of an acute hepatitis B infection from first exposure to recovery.
According to the CDC, a hepatitis B blood test result varies depending on whether the infection is a new acute infection or a chronic infection.
What Does Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positive Mean
Hepatitis B is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus. Signs of hepatitis include tiredness or fatigue, fevers, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, headache, itchy skin, muscle soreness , jaundice , dark urine, and light stools.Here are some hepatitis B facts:
1. HBV infections will occur in one out of every 20 people at some time in the United States
2. Your risk of HBV is greater if you have sex with someone who has HBV.
3. Your risk is greater if you have a job that places you in contact with human blood.
4. Your risk is greater if you travel to areas where HBV is common.
Some people who donate blood get a letter from the blood bank saying that they are hepatitis B core antibody positive. Dont panic. This does not mean that you have hepatitis B, but you should get a more thorough screening. There are three blood tests that are used to diagnose hepatitis B: hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B surface antibody, and hepatitis B core antibody positive. If your blood tests show that you are hepatitis B core body positive, it means that you either have a present infection or that you were infected in the past. There is a possibility of having a false hepatitis B core antibody positive. Blood banks only screen for hepatitis B core antibody positive and not for surface antigens or antibodies.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis C Spread Through Saliva
Read Also: Newborn Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose
Mutant Viruses And Chronic Infection
Anti-HBe-positive patients in the reactivated phase of the disease are also referred to as the HBeAg-negative viremic group. Genomic analyses has revealed that such patients carry natural mutants of the virus that have either reduced levels or complete abrogation of HBeAg production. These variants are selected at the time of, or soon after, seroconversion, and become dominant during the reactivation phase. The most common precore mutation is the G1896A substitution, which creates a premature stop codon in the precursor protein from which HBeAg is elaborated. This mutation affects the stem of the encapsidation signal, but leads to stronger base pairing with the A1896 change in genotypes with a T at position 1858 of the precore region, such as B, C, D, and E. The double mutation affecting the core promoter region is thought to result in decreased transcription of the precore mRNA, with a knockon effect on HBeAg production, while pgRNA production remains the same or is even upregulated. It is now apparent that additional mutations in this region may contribute to this phenotype.
Geoffrey M. Dusheiko, in, 2003
Hep B Core Antibody Igm Blood Test
This test looks for the presence of Hepatitis B Core IgM Antibodies. Hep B is a viral liver infection that is spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. It is the most common cause of acute viral Hepatitis. Core antibodies are produced by the body’s immune system in response to the inner core of the hepatitis B virus. IgM antibodies develop shortly after infection and fade away after a short period of time. The presence of HBc IgM antibodies typically indicates that a person has an acute or current infection. People with a chronic hepatitis B infection may begin to develop IgM antibodies if the virus becomes active. Results of this test are qualitative and provide a positive or negative result.
Anti-HBc, IgM is not typically ordered by itself. Because IgM antibodies are only detectable for a short period of time, a negative IgM result is not enough to determine that a person has not been exposed to Hep B. Other tests such as the Hep B Surface Antigen and Hepatitis B Surface Antibody. are often ordered at the same time. Together, these tests can help to determine if a person has hepatitis B, whether they have an acute or chronic infection, or if they have immunity due to vaccination or natural recovery. Request A Test offers a Hepatitis B Panel which includes all 3 tests at a discounted price.
Turnaround for this test is typically 1-2 business days.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms For Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Core Antibody
CPT Code: 86705
Methodology: Immunoassay
Clinical Significance: Hepatitis B core-specific IgM class antibody has been detected in most acute infections and is a reliable marker for acute disease. In some cases, hepatitis B core IgM antibody may be the only specific marker for the diagnosis of acute infection with hepatitis B virus.
Alternative Name: Anti-HBc, IgM
Supply: T01 – Red/Gray SST 8.5mL
Preferred Specimen: Serum
Transport Container: Serum Separator Tube
Transport Temperature: Room Temperature
Specimen Stability: Room Temperature: 7 days
Rejection Criteria: Gross Hemolysis, Gross Lipemia
For additional supply or collection device information, please contact DLO’s Customer Service at 891-2917, option 2.
The CPT codes provided are based on AMA guidelines and are for informational purposes only. CPT coding is the sole responsibility of the billing party. Please direct any questions regarding coding to the Payor being billed.
Interpreting Hepatitis B Laboratory Results
Many jurisdictions have regulations requiring laboratories to report all positive HBsAg, HBV DNA, and anti-HBc IgM laboratory results to the HD while a subset might also routinely receive positive total anti-HBc and anti-HBs results.
Additionally, some HDs might receive negative hepatitis B laboratory results, which are useful for determining false-positive results and monitoring patients through their infection and recovery. Table 3-1 shows how to interpret the combinations of laboratory results frequently available in hepatitis B test panels, following the biomarker changes over the course of disease as shown in Figure 3-1.
Table 3-1. Interpretation of hepatitis B laboratory results
| HBsAg |
|---|
- Concurrent ALT and total bilirubin result
- Other hepatitis serological results
- Negative HBsAg and/or negative/undetectable HBV DNA results
Total anti-HBc is detectable, on average, approximately 5 weeks post-HBV exposure, remains detectable indefinitely following exposure, and indicates past or current infection. In the presence of total anti-HBc, a positive HBsAg, HBeAg, or anti-HBc IgM result is a more reliable indication of recent or current infection. Jurisdictions that receive total anti-HBc laboratory results can use these results to clarify a persons HBV infection status.
Don’t Miss: Life Expectancy Of Someone With Hepatitis C