Starting Hepatitis C Treatment
If you are diagnosed with HCV, several antiviral medications can be prescribed for treatment. The newest medications available are in pill form. Current medications are successful at treating and curing over 90% of HCV infections.
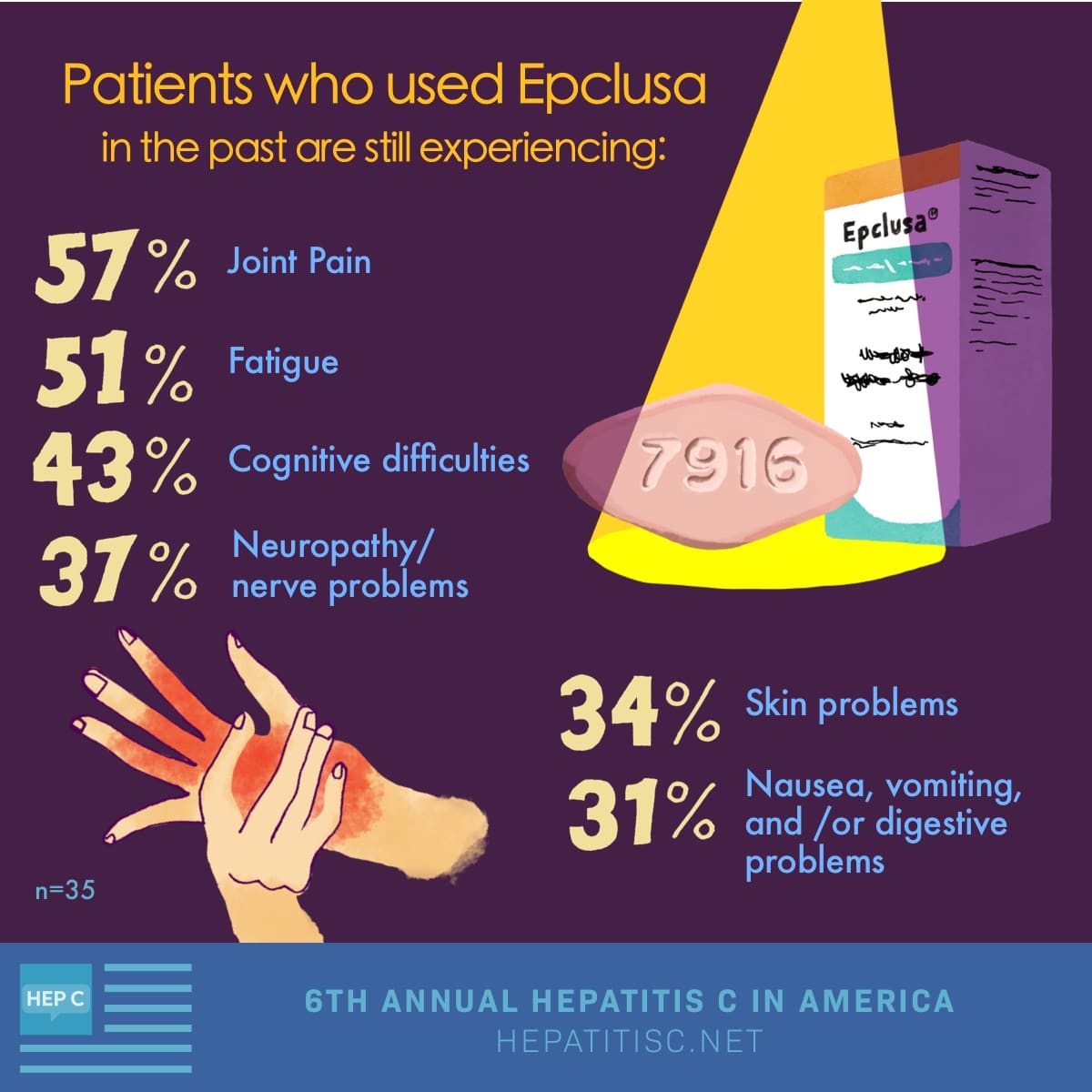
Many people have mild or no side effects from the medication. Some people report:
A significant drop in your HCV viral load may occur within the first two weeks of treatment. After four weeks of treatment, undetectable viral loads are possible, though it may be longer for others.
A healthcare provider will use blood tests and check-in to determine how you are tolerating the treatment periodically throughout and afterward.
But Even If You’ve Been Cured It Can Have Lifelong Health Implications
“Hepatitis C is a lot more than just a liver disease,” Reau says. “It has been associated with many medical conditions, such as an increased risk of developing diabetes, kidney disease and cancer.”
While curing hepatitis C significantly reduces the risk of serious complications, like liver failure, liver cancer and the need for transplantation, it doesn’t completely eliminate the health risks associated with the disease.
“Hep C is linked to scarring of the liver or cirrhosis and the more scar tissue that develops, the greater the likelihood of complications,” Reau says. “If there is a lot of scarring, you will need lifelong monitoring.”
Reau also recommends leading a healthy lifestyle to help prevent re-infection and further liver damage: Limit alcohol consumption, control your weight, avoid high-risk activities and manage diabetes if you have it.
The Acute Phase Of Hepatitis C
The term Acute Phase can be confusing. This is because it only refers to the 6 month period of time after the virus has first entered your body. It bears no relation to the acuteness of the symptoms or the severity of the disease.Antibodies to the virus are produced by your immune system when it reacts to the presence of the virus and are detectable in the blood from between 3 to 12 weeks after initial infection. Depending on how long it takes for the virus to take hold in the body, different immune systems will take different amounts of time to create antibodies. This is called the window period. Because it can take up to 3 months for the antibodies to show up in a blood test, if you suspect you have recently been infected, it is important to wait this long before having a test. If the antibody test is positive you will be offered a PCR or RNA test.
Symptoms during the Acute Phase
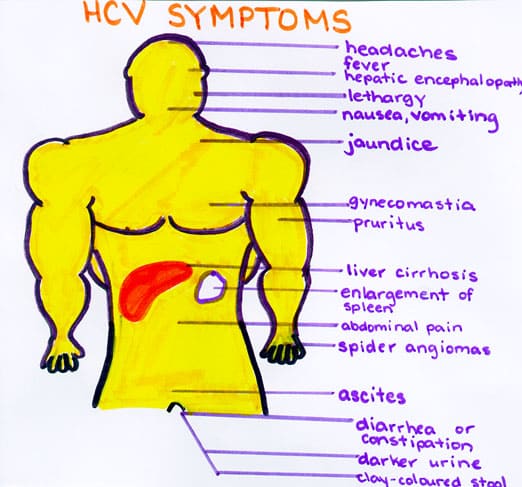
During the acute phase most people do not seem to experience any noticeable symptoms. For the 25-35% of people who do, the symptoms are normally vague and non-specific. They can include low-grade fever, fatigue, appetite loss, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. About 20% of the people who develop symptoms contract jaundice. This can be seen in the yellowing of the skin and eyes. This is a sign of the livers functions being affected as bilirubin begins to build up in the body. Jaundice is a recognised sign of liver problems and may lead to a test for hepatitis C being suggested.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C Viral Load Labcorp
Public Health Significance And Occurrence Of Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C occurs worldwide. Current estimates suggest that more than 250,000 Australians have been infected with this virus. An estimated 9,700 new cases of HCV occurred in 2005 however, only 354 cases were determined to be newly acquired, as most cases are subclinical, go unnoticed and are incidentally found.
Three-quarters of people infected with HCV become chronically infected with the virus. Of these, approximately 1020 per cent will develop liver cirrhosis over a period of 1540 years, and an estimated 5 per cent will develop hepatocellular carcinoma after 40 years of infection. This risk can be exacerbated by liver injury, especially concurrent alcohol use. Five per cent of infants born to HCV-infected women develop HCV infection. Breastfeeding is not an additional risk factor for transmission unless the nipples are cracked, or the baby has cuts on or inside the mouth.
There are at least six major genotypes of HCV. At present, the main genotypes found in the Australian population are 1 , 3 and 2 . It is important to determine the genotype because this guides therapy.
Prevention Of Hepatitis C
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C.
The best way to avoid getting hepatitis C is to reduce your risk factors, such as by:
- Not using intravenous drugs
- Using only sterile injection equipment if you do inject drugs, and not reusing or sharing your equipment
- Not sharing personal care items that might have blood on them, including razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers
- Safely handling needles and other sharp equipment if you are a healthcare worker
- Not getting a tattoo, body piercing, or acupuncture treatment from an unlicensed practitioner
- Practicing safe sex
You May Like: What Is Chronic Hepatitis B
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HA vaccine may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with Ig. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
If concurrently providing HA-containing vaccine and Ig, separate anatomic injection sites should be used for each injection.
Passive immunization with human Ig preparations can interfere with the immune response to measles-mumps-rubella , measles-mumps-rubella-varicella and univalent varicella vaccines . These vaccines should be given at least 14 days prior to administration of a human Ig preparation, or delayed until the antibodies in the Ig preparation have degraded. Refer to Blood Products, Human Immunoglobulin and Timing of Immunization in Part 1 for additional information.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
What Are The Types Of Hepatitis C Infection
There are two types of hepatitis C infection:
- Acute: a short-term infection that occurs within 6 months after a person is exposed to the virus. However, about 75 to 85 percent of people with the acute form go on to develop the chronic form.
- Chronic: a long-term illness that can continue throughout a persons life. It can lead to cirrhosis of the liver and other serious problems, such as liver failure or cancer. About 15,000 people a year die from liver disease associated with hepatitis C.
Don’t Miss: How Long Is The Hepatitis A Vaccine Good For
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
How Can The Spread Of Hepatitis C Be Prevented
People who have had hepatitis C should remain aware that their blood is potentially infectious.
- Do not shoot drugs if you shoot drugs, stop and get into a treatment program if you cant stop, never share needles, syringes, water or works, and get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
- Do not share personal care items that might have blood on them .
- If you are a health care or public safety worker, always follow routine barrier precautions and safely handle needles and other sharps get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Consider the risks if you are thinking about getting a tattoo or body piercing. You might get infected if the tools have someone elses blood on them or if the artist or piercer does not follow good health practices.
- HCV can be spread by sex, but this is rare. If you are having sex with more than one steady sex partner, use latex condoms correctly and every time to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted diseases. You should also get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- If you are infected with HCV, do not donate blood, organs or tissue.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis C And Baby Boomers
Should I Be Screened For Hepatitis C
Doctors usually recommend one-time screening of all adults ages 18 to 79 for hepatitis C. Screening is testing for a disease in people who have no symptoms. Doctors use blood tests to screen for hepatitis C. Many people who have hepatitis C dont have symptoms and dont know they have hepatitis C. Screening tests can help doctors diagnose and treat hepatitis C before it causes serious health problems.
All Adults Pregnant Women And People With Risk Factors Should Get Tested For Hepatitis C
Most people who get infected with hepatitis C virus develop a chronic, or lifelong, infection. Left untreated, chronic hepatitis C can cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and even death. People can live without symptoms or feeling sick, so testing is the only way to know if you have hepatitis C. Getting tested is important to find out if you are infected so you can get lifesaving treatment that can cure hepatitis C.
Read Also: Hepatitis C And Liver Disease
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
How Do Doctors Treat Hepatitis C
Doctors treat hepatitis C with antiviral medicines that attack the virus and can cure the disease in most cases.
Several newer medicines, called direct-acting antiviral medicines, have been approved to treat hepatitis C since 2013. Studies show that these medicines can cure chronic hepatitis C in most people with this disease. These medicines can also cure acute hepatitis C. In some cases, doctors recommend waiting to see if an acute infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
Your doctor may prescribe one or more of these newer, direct-acting antiviral medicines to treat hepatitis C:
You may need to take medicines for 8 to 24 weeks to cure hepatitis C. Your doctor will prescribe medicines and recommend a length of treatment based on
- which hepatitis C genotype you have
- how much liver damage you have
- whether you have been treated for hepatitis C in the past
Your doctor may order blood tests during and after your treatment. Blood tests can show whether the treatment is working. Hepatitis C medicines cure the infection in most people who complete treatment.
Hepatitis C medicines may cause side effects. Talk with your doctor about the side effects of treatment. Check with your doctor before taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medicines.
For safety reasons, talk with your doctor before using dietary supplements, such as vitamins, or any complementary or alternative medicines or medical practices.
Don’t Miss: New Hepatitis B Vaccine Recommendations
Complications Of Chronic Hepatitis C
Unless successfully treated with medication, chronic Hepatitis C infection can cause other serious health problems, such as cirrhosis, liver cancer and liver failure. However, with recent advances in Hepatitis C treatment we now have higher cure rates, shorter treatment times, and all-oral treatment regimens for most people. If youre at risk for Hepatitis C, speak to your healthcare provider today about getting tested.
Tests To Diagnose Hepatitis C
How is Hepatitis C diagnosed?
There are two main blood tests typically used to diagnose Hepatitis C. First, youll have a screening test that shows if youve ever had Hepatitis C at some point in your life. If this test is positive, youll have a second test to see if you have Hepatitis C now. These blood tests are described below:
Hepatitis C antibody test
This is the screening test used by doctors to show whether or not you have ever been exposed to Hepatitis C at some time in your life, by detecting antibodies in your blood. Antibodies are substances your body makes to fight off all kinds of infections. If you were ever infected with Hepatitis C, your body would have made antibodies to fight the virus.
If the test result is:
- Negative, it means you have not been exposed to Hepatitis C and further testing is usually not needed.
- Positive, you have had Hepatitis C at some point. However, it does not tell you whether you have it now. Youll need to see your doctor for another test the Hepatitis C RNA test to determine if the virus is still active and present in your blood.
Hepatitis C RNA Qualitative Test
This test will determine whether or not you are currently infected with Hepatitis C. It is often called the PCR test because of the process used . It looks for the genetic material of the Hepatitis C virus in your blood.
If the test result is:
Hepatitis C RNA Quantitative Test
You May Like: What Does Hepatitis B Come From
Read Also: Is Hepatitis B Worse Than Hepatitis C
Common And Local Adverse Events
HA vaccine
HA vaccine is well tolerated. Reactions are generally mild and transient, and are usually limited to soreness and redness at the injection site. Other less frequent reactions include headache, irritability, malaise, fever, fatigue and gastrointestinal symptoms. Injection site reactions occur less frequently in children than in adults as do mild, systemic events . No significant difference in reactions is evident between initial and subsequent doses of vaccine or in the presence of pre-existing immunity.
HAHB vaccine
Refer to Hepatitis B Vaccine in Part 4 for information about HAHB vaccine.
Ig
Injection site reactions following receipt of standard human Ig include tenderness, erythema and stiffness of local muscles, which may persist for several hours. Mild fever or malaise may occasionally occur.
Getting Tested Is The Only Way To Know If You Have Hepatitis C
A blood test called a hepatitis C antibody test can tell if you have been infected with the hepatitis C viruseither recently or in the past. If you have a positive antibody test, another blood test is needed to tell if you are still infected or if you were infected in the past and cleared the virus on your own.
- Are 18 years of age and older
- Currently inject drugs
- Have ever injected drugs, even if it was just once or many years ago
- Have abnormal liver tests or liver disease
- Are on hemodialysis
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose Newborn
Will You Test Positive For Hcv During The Incubation Period
Not always. If you are newly infected, it’s possible that a test may not detect an infection right away. On average, it may take your body eight weeks to 11 weeks to produce enough antibodies to be detected on an HCV test.
That said, there’s also a wider range of timebetween two weeks and six monthswhen it’s possible that the test could pick up enough antibodies. This varies from person to person.
Some people may not produce enough antibodies to be detected on a typical HCV test due to a lowered immune response. In those cases, it may be necessary to have other types of tests done.
Symptoms Of An Acute Infection
Few people show symptoms during acute infection . These symptoms can include: fatigue tenderness or an aching feeling on the right side of the abdomen decreased appetite perhaps with weight loss flu-like symptoms nausea tendency to bruise or bleed easily jaundice rash dark-coloured urine and light or clay-coloured stools. These symptoms often go away after a short time.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B Virus Dna Quantitative
What Occupations Have Increased Risk Of Hepatitis C
The risk of acquiring hepatitis C from the workplace depends on the amount of exposure to human blood or blood products and needlestick injuries. In general, occupational groups with increased risk include workers such as healthcare workers, dentists, and laboratory personnel who are repeatedly exposed to human blood and who are at risk of needlestick injuries.
When Should You See A Doctor Or Other Healthcare Professional

Since so many people dont experience any symptoms, healthcare professionals recommend getting screened for hepatitis C at least once in your adult life. They may recommend more frequent screenings if you have a higher risk of contracting the virus.
Hepatitis C doesnt always become severe, but the chronic form can increase your risk for liver damage, liver cancer, and liver failure.
If you have any symptoms that suggest hepatitis C, especially if theres a chance youve been exposed, connect with a doctor or another healthcare professional as soon as possible to discuss your options for testing and treatment.
With a prompt diagnosis, you can get treatment earlier, which may help prevent damage to your liver.
Recommended Reading: How Many Hepatitis Are There
You May Like: Screening Test For Hepatitis C
Who Is Most At Risk Of Contracting Hepatitis C
You have a high risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- use or have used injection drugs even if it was just once or many years ago
- have received blood or blood products or an organ transplant before July 1990 in Canada
- have been in jail or
- have been injected or scratched during vaccination, surgery, blood transfusion or a religious/ceremonial ritual in regions where hepatitis C is common.
You have a high moderate risk of contracting hepatitis C if you:
- have tattoos or body piercing
- have multiple sexual partners
- have a sexually transmitted infection , including HIV or lymphogranuloma venereum
- have experienced traumatic sex or rough sex or have used sex toys or fisting that can tear body tissue
- have vaginal sex during menstruation
- have received a kidney treatment
- have received an accidental injury from a needle or syringe
- have another infectious disease
- were born to a hepatitis C infected mother or
- have a sexual partner infected with hepatitis C.
Hepatitis C is NOT passed from person to person by:
- coughing, sneezing
- breastfeeding unless your nipples are cracked and bleeding or
- oral sex, unless blood is present.
Recommended Reading: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Hepatitis A