Who Should Receive Hepatitis B Vaccination
- All newborns before hospital discharge. Infants born to hepatitis B-positive women need hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG within 12 hours of birth.
- All children and adolescents not previously vaccinated.
- Children born in the U.S. to individuals born in a country with high hepatitis B endemicity.
- All individuals at risk of hepatitis B infection:
- Sex partners of hepatitis B-positive persons.
- Sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship .
- Persons seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually-transmitted disease.
- Men who have sex with men.
- Persons who inject drugs.
- Household contacts of hepatitis B-positive persons.
- Persons born in countries where hepatitis B infection is endemic should be tested and vaccinated if susceptible.
- International travelers to regions with high or intermediate rates of endemic hepatitis B infection.
- Health care and public safety workers that may be exposed to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids.
- Residents and staff of facilities for developmentally disabled persons, corrections facilities, and other facilities that serve adults at risk for hepatitis B infection.
- Persons with end-stage renal disease, including pre-dialysis, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients.
- Persons with chronic liver disease.
- Persons to age 60 years with diabetes.
- Persons with HIV infection.
Hepatitis B Vaccine New Recommendations For Vaccinating Infants
The American Academy of Pediatrics is now recommending that infants receive their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth. This recommendation is in line with the guidance of the CDC.
Hepatitis B is a serious disease that is easily preventible with the vaccine. Yet, the hepatitis B vaccine is one of the most vilified of the vaccines by the anti-vaccine crowd.
This article will take a look at hepatitis B, the vaccine, and some of the nonsensical claims of the anti-vaccine world.
Contents
Does Your Child Need A Pediatrician Or Primary Care Provider
All Harbor Health community health centers are welcoming new patients! Our family medicine providers see patients ages 2 and older and our pediatrics practice at Daniel Driscoll Neponset Health Center sees patients newborn to age 21.
Find a health center located near you and call to make an appointment!
You May Like: Which Hepatitis Is The Most Contagious
International Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedules
*Please note that the first dose should be given as soon as possible. Additional doses require minimum time intervals between doses in order for the vaccine to be effective.
The hepatitis B vaccine is an injection that is generally given in the arm and as a three-dose series. The World Health Organization recommends a 0, 1, and 6-month vaccine schedule, though schedules may vary based on a countrys national immunization program. Completing the hepatitis B vaccine series, preferably beginning at birth, will ensure protection against hepatitis B, hepatitis delta and lower the lifetime risk of liver cancer. Greater than 90% of babies and up to 50% of young children who are not vaccinated and are infected with hepatitis B will have lifelong infection, which makes the birth dose essential to their protection. Please note that the vaccine brand name, manufacturer and associated schedules for adults, children and infants may be unique to different countries, though there is a list of WHO prequalified vaccines.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Infants
The World Health Organization recommends all infants receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and to complete the vaccine series with additional shots at 1 month and 6 months of age. Beginning the hepatitis B vaccine at birth will ensure protection against hepatitis B for life.
3-Dose Vaccine Series for Children and Adults
4-Dose Combination Vaccine Series for Infants
Additional Resource Links:
Cdc Recommends Universal Hepatitis B Vaccinations For Adults
The guidelines replace risk-based reccomendations for adults between 19-59 years.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released new guidelines for hepatitis B virus vaccination, calling for universal HBV vaccination for all adults aged 19-59 years in the US.
The CDC said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that the decision is based on 4 decades of safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy data on the HBV vaccine, but with suboptimal coverage in the US.
Read Also: How Many Genotypes Of Hepatitis C Are There
What Can Travelers Do To Prevent Disease
The best way to protect yourself against hepatitis B is by getting vaccinated. Hepatitis B vaccine is a routine vaccination that infants in the United States receive at birth. The hepatitis B vaccine is over 90% effective and has been routinely recommended for infants since 1991. The vaccine is given in 2, 3, or 4 shots, and the series of shots is usually completed by 6 months of age.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all unvaccinated travelers under 60 years old and is also recommended for travelers 60 years and older going to a country where hepatitis B virus infection is common. The vaccine is given in 2 or 3 doses. To find the hepatitis B vaccine recommendations for your destination check CDC’s destination pages.
It usually takes 6 months to be fully vaccinated against hepatitis B so if youll be traveling internationally within 6 months talk to your doctor about accelerated vaccination options including the 2-dose series and accelerated dosing of the combination hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine.
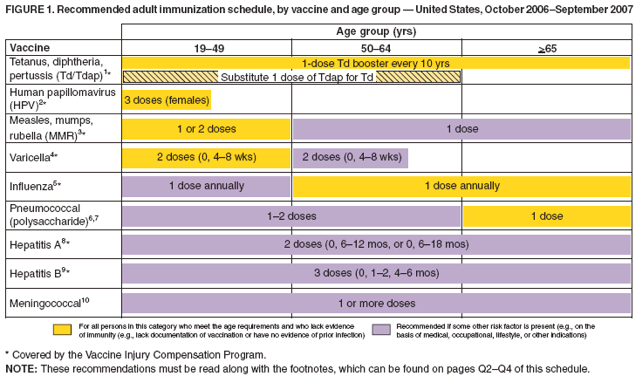
Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Adults
Hepatitis B is a vaccine-preventable viral disease that involves inflammation of the liver.
The hepatitis B virus usually leads to a short-term infection known as acute hepatitis B. If their infection is left untreated, some people develop chronic hepatitis B. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious, permanent condition that can cause organ damage, cirrhosis , liver cancer, liver failure, and even death.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , all people should be vaccinated against hepatitis B starting at birth. Adults who are at risk of developing hepatitis B should also receive the vaccine, which is highly effective in preventing infection.
Read on to learn more about the hepatitis B vaccine for adults, including who should receive it, the details of the dosage schedule, side effects, and more.
Prasit photo / Getty Images
Recommended Reading: What Is The Cause Of Hepatitis B
Indications For Hepatitis B Vaccine
HepB vaccine is a routine childhood vaccination .
HepB vaccine also is indicated for all adults aged 19 through 59 years who have not been previously vaccinated.
HepB vaccine also is indicated for adults aged 60 years and older who have not been previously vaccinated and who have any of the following:
-
A desire for protection from hepatitis B
-
A sexually active lifestyle in people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship
-
Need for evaluation or treatment of a sexually transmitted infection
-
Current or recent use of illicit injection drugs
-
Sex between men
-
Employment in which workers may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious body fluids
-
Diabetes in people < 60 years and sometimes in those 60 years
-
End-stage renal disease
-
A chronic liver disorder
-
Household contact and/or sexual contact with people who are positive for hepatitis B surface antigen
-
Travel to endemic areas
-
Time spent in correctional facilities or in facilities that provide sexually transmitted infection treatment, HIV testing and treatment, drug abuse treatment and prevention services, services to injection-drug users or men who have sex with men, or care for patients with developmental disabilities or with end-stage renal disease
The combination HepA and HepB vaccine can be used in people 18 years who have indications for either hepatitis A or hepatitis B vaccine and who have not been previously vaccinated with one of the vaccine components.
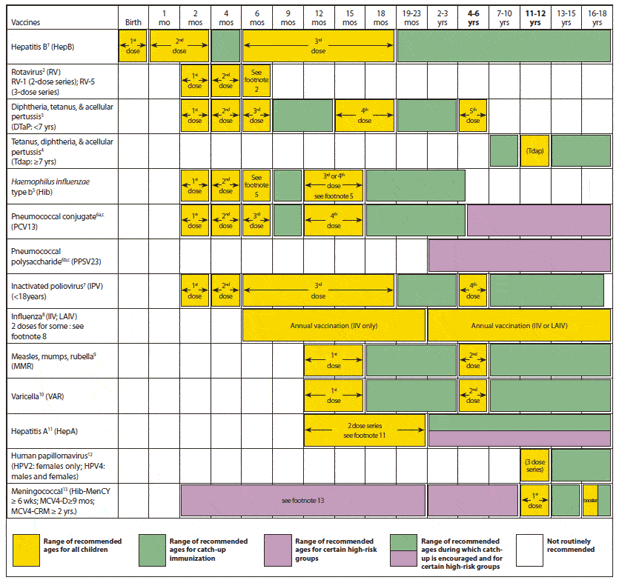
Learn About The Recommended Vaccines Children Infant To Age 18
Staying on track with vaccinations for your child helps keep them healthy and safe!
Recommendations about when to have your child vaccinated change from time to time. Please see the 2020 recommended schedule from the American Academy of Family Physicians and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention below.
Also Check: What Does Hepatitis Do To Your Body
Committee Also Passed New Recommendations On Vaccines Against Ebola Orthopoxviruses
byMolly Walker, Deputy Managing Editor, MedPage Today November 3, 2021
Adults ages 59 and younger, and adults ages 60 and up who have risk factors for hepatitis B virus , are recommended to be vaccinated against HBV, the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices said in a unanimous vote Wednesday.
ACIP voted 15-0 to recommend this split philosophy for HBV vaccination, and also voted to recommend expanded use of vaccines against Ebola and orthopoxviruses, and approved the 2022 adult and childhood immunization schedules.
HBV Vaccine
The initial recommendation from CDC staff was universal HBV vaccination for all adults ages 18 and up, but an amendment to separate out the age groups, and retain the risk-based recommendation for older age groups, passed 8-7 earlier in the day.
The current risk-based recommendation applies to:
- People at risk for infection by sexual exposure or percutaneous or mucosal exposure, such as injection-drug users
- Other risk groups, such as international travelers with high or intermediate levels of endemic HBV infection
- People with chronic liver disease
- Incarcerated people
- People living with HIV
This would be consistent with the current immunization schedule, with CDC staff adding that any adult who wishes to receive protection may receive the vaccine, meaning all adults ages 60 and up who do not have any HBV risk factors.
The cost is high for people over 60, added Beth Bell, MD, of the University of Washington in Seattle.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Don’t Miss: What Is Hepatic Cirrhosis Of The Liver
Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule For Children And Infants
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that babies and children receive three 0.5 milliliter doses of either Engerix-B or Recombivax HB, starting just after birth.
The current recommended hepatitis B vaccine schedule for children and infants is as follows:
| Hepatitis B Vaccination Schedule for Infants and Children | |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis B Vaccine Dose | |
| 3 | 618 months old |
If your child is undergoing hemodialysis, your healthcare provider may recommend that they receive additional doses of the HBV vaccine.
Why Should I Vaccinate My Newborn Child If I Know That I Am Not Infected With Hepatitis B Virus
Before the hepatitis B vaccine, every year in the United States about 18,000 children were infected with hepatitis B virus by the time they were 10 years old. This statistic is especially important because people are much more likely to develop liver cancer or cirrhosis if they are infected early in life, rather than later in life .
About 9,000 of the 18,000 children infected in the first 10 years of life caught the virus from their mother during birth. However, many young children didn’t catch the disease from their mother. They caught it from either another family member or someone else who came in contact with the child. Because hepatitis B can be transmitted by relatively casual contact with items contaminated with the blood of an infected person, and because many people who are infected with hepatitis B virus don’t know that they have it, it is virtually impossible to be “careful enough” to avoid this infection.
For these reasons, all young children are recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccine. The best time to receive the first dose is right after birth. This will ensure that the child will be protected as early as possible from catching hepatitis B from people who dont know that they are infected with the virus.
Listen to Dr. Offit explain why newborns get the hepatitis B vaccine by watching this short video, part of the series Talking About Vaccines with Dr. Paul Offit.
Read Also: Direct Acting Antivirals Hepatitis C
New Hepatitis B Vaccination Recommendations Praised Amid Low Awareness
Nancy A. Melville
An updated recommendation from the Centers for Disease Control and Preventions Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices calling for universal hepatitis B vaccination of all adults aged 59 and younger has boosted the call to improve clinicians awareness of the increasing infection and low vaccination rates and raise the issue with patients.
Dr Rita Kaur Kuwahara
This new recommendation from ACIP will be instrumental raising adult hepatitis B vaccination rates in the US to levels that will allow us to finally eliminate hepatitis B in this country, said Rita K. Kuwahara, MD, a primary care internal medicine physician and health policy fellow at Georgetown University, in Washington, DC, in addressing the issue at the US Conference on HIV/AIDS this month.
We have the tools to prevent hepatitis B, and since we have such safe and highly effective vaccines to protect against community , we should not have a single new infection in our nation, she asserted.
The unanimously approved updated ACIP recommendation was issued in November and still requires adoption by the CDC director. The ACIP specifically recommends that adults aged 19 to 59 and those 60 years and older with risk factors for infection should receive the hepatitis B vaccine, and it further stipulates that those 60 years and older without known risk factors for hepatitis B may receive the vaccine.
Is It Okay To Get An Extra Dose Of Hepatitis B Vaccine
Yes. Although extra doses of vaccine are not recommended, you can think of the extra dose as another chance for the immune system to see the hepatitis B virus. A vaccine is not the only time the immune system will see the virus or bacteria contained in it. People may be exposed to the virus or bacteria at school or the store or when visiting family or friends. An extra dose of vaccine is like one more exposure, except the difference is that the virus or bacteria in any vaccine has been made safe, so it wont make you ill.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Is More Infectious Than Hiv
What Is The Recommended Vaccine Schedule For Hepatitis B
The recommended vaccine schedule for PreHevbrio includes three doses over the course of 6 months. The first dose is at 0 months, the second dose is at 1 month, and the third and final dose is at 6 months.
Heplisav-B is also approved for adults 18 years of age and older. It requires two doses administered 1 month apart.
Engerix-B and Recombivax HB are approved starting at birth, and for pediatric and adult populations. Administration varies between 2 to 3 doses depending on age but generally follows a schedule of 6 months.
Depending on the number of doses, these vaccines are typically administered at 0, 12, and 46 months following the start of the vaccination process.
Sbp Adjuvant For Hepatitis B Vaccine
Wang and colleagues stated that although adjuvants are a common component of many vaccines, there are few adjuvants licensed for use in humans due to concerns about their toxic effects. There is a need to develop new and safe adjuvants, because some existing vaccines have low immunogenicity among certain patient groups. In this study, SBP, a hepatitis B surface antigen binding protein that was discovered through screening a human liver cDNA expression library, was introduced into hepatitis B vaccine. A good laboratory practice, non-clinical safety evaluation was performed to identify the side effects of both SBP and SBP-adjuvanted hepatitis B vaccine. The results indicated that SBP could enhance the HBsAg-specific immune response, thus increasing the protection provided by the hepatitis B vaccine. The authors concluded that given the encouraging safety data obtained in this study, further evaluation of SBP as a vaccine adjuvant for human use is warranted. They stated that this research has the potential to accelerate adjuvant development for HBV vaccine and for other vaccine types in the future.
Code Code Description
You May Like: Cost Of Medication For Hepatitis C
Advisory Committee On Immunization Practices Recommendations
In February 2018, ACIP approved recommendations for Heplisav-B vaccine as an option for previously unvaccinated or incompletely vaccinated persons, including:
- Adults 18 years of age and older who have a specific risk, or lack a risk factor but want protection. See ACIP Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults for risk factors.
The Hepatitis B Vaccine And Immunosuppressants
If you are taking or about to start taking a medication that suppresses your immune response, let your healthcare provider know. Immunosuppressants may make certain vaccines less effective. Your healthcare provider may recommend that you get the hepatitis B vaccine at a particular time during your course of medication.
Also Check: What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis Ab And C
Potential Challenges With Implementing Updated Hepatitis B Vaccination Guidelines
Potential challenges with implementing the updated CDC ACIP guidelines for hepatitis B vaccination are summarized in Table 2. Ensuring effective HBV screening is essential for expanding hepatitis B vaccine coverage. Although current HBV screening guidance remains risk-based,5 cost-effectiveness models have found that universal one-time testing of adults 18 to 69 years old with hepatitis B surface antigen, compared with current practice, would prevent an additional 7 cases of compensated cirrhosis, 3 cases of decompensated cirrhosis, 5 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma, 2 liver transplants, and 10 HBV-related deaths, with a savings of $263,000 per 100,000 adults screened.24 Although universal one-time testing with hepatitis B surface antigen may be effective in identifying cases of chronic HBV,24 the additional tests of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen and immunoglobulin G antibody to the hepatitis B core antigen will identify individuals who may benefit from receiving the hepatitis B vaccine, require additional testing to determine whether they are infected, or may need education regarding potential risk for HBV reactivation in the future.25
Dont Miss: Hepatitis B Antibody Test Cost