Factors That Trigger The Risk Of Hepatitis B
Moreover, between 20 and 50 percent of children and less than 10 percent of matured children in age progress from acute to chronic hepatitis B infection.
People that are at risk of contacting the virus are
What Are Signs Of Hepatitis B
When you first get hepatitis B, it is called acutehepatitis B. Most adults who have hepatitis B willrecover on their own. However, children and someadults can develop chronic hepatitis B.
Acute hepatitis B: Signs of acute hepatitis B canappear within 3 months after you get the virus.These signs may last from several weeks to 6 months.Up to 50% of adults have signs of acute hepatitis Bvirus infection. Many young children do not show anysigns. Signs include:
- Yellow skin or eyes
- A longer than normal amount of time for bleedingto stop
How Hepatitis B Is Formed
At the initial stage, after the hepatitis B virus has been contracted, it passes through an incubation period which can be within 45 days to 6 months.
At this period, there are no clear symptoms.
If the immune system is unable to fight it at the initial period, it further develops into the acute hepatitis B which usually comes with noticeable viral signs and symptoms. Symptoms can be moderate discomfort, fulminant liver failure.
After the acute stage of hepatitis B, if the immune system is not still able to get rid of the virus it will further develop into Chronic hepatitis B.
Also Check: Hepatitis C Genotype 2 Treatment Guidelines
Chronic Hepatitis B Complications
Chronic hepatitis B can lead to
- cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue and prevents your liver from working normally. Scar tissue also partly blocks the flow of blood through the liver. As cirrhosis gets worse, the liver begins to fail.
- liver failure, in which your liver is badly damaged and stops working. Liver failure is also called end-stage liver disease. People with liver failure may require a liver transplant.
- liver cancer. Your doctor may suggest blood tests and an ultrasound or another type of imaging test to check for liver cancer. Finding cancer at an early stage improves the chance of curing the cancer.
You May Like: Does Biktarvy Treat Hepatitis B
Antiviral Medication For Hepatitis B
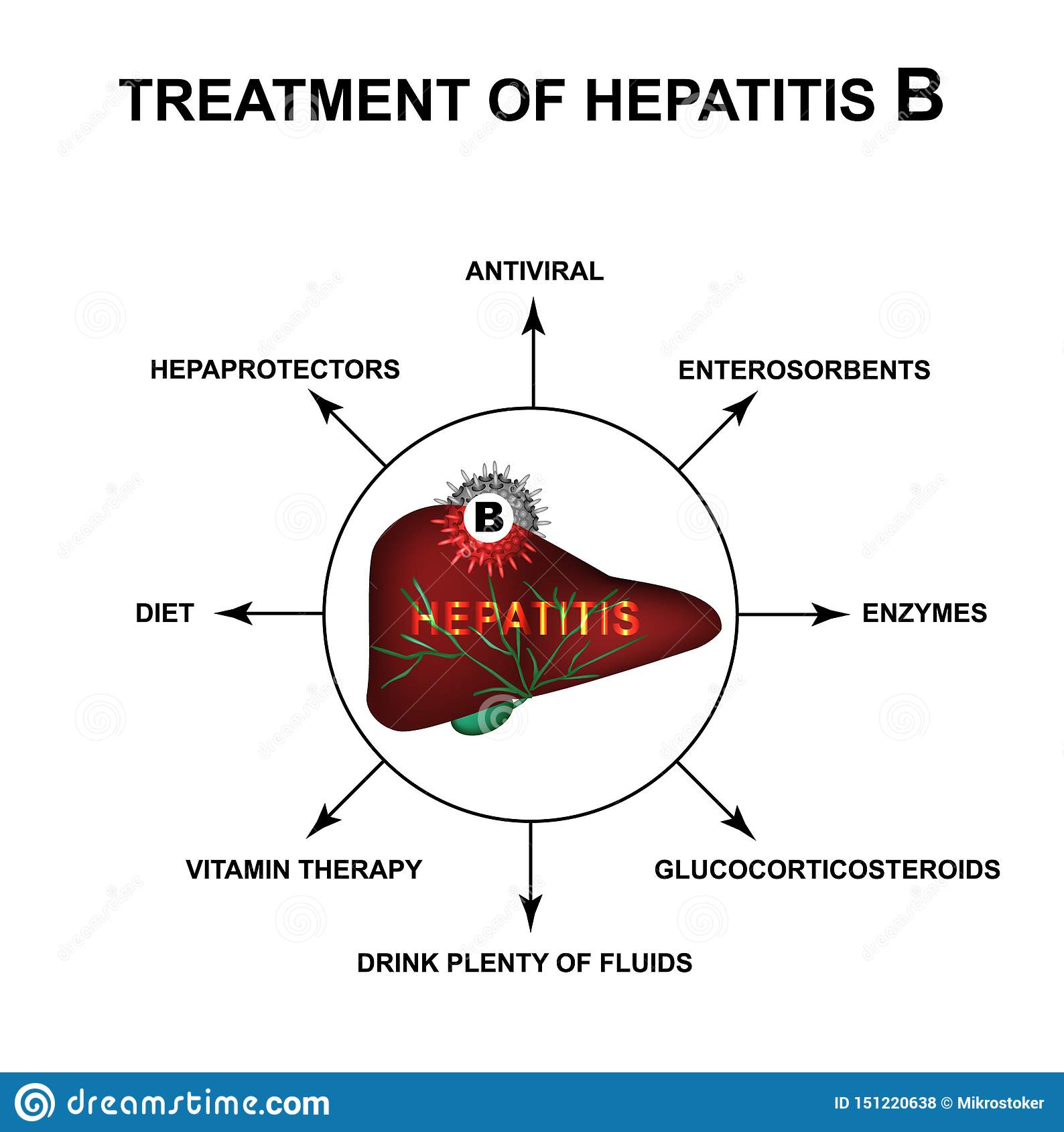
Doctors may recommend antiviral medication for people with chronic hepatitis B, which occurs when the virus stays in your body for more than six months.
Antiviral medication prevents the virus from replicating, or creating copies of itself, and may prevent progressive liver damage. Currently available medications can treat hepatitis B with a low risk of serious side effects.
NYU Langone hepatologists and infectious disease specialists prescribe medication when they have determined that without treatment, the hepatitis B virus is very likely to damage the liver over time. People with chronic hepatitis B may need to take antiviral medication for the rest of their lives to prevent liver damage.
There are many different types of antiviral medications available, and your doctor recommends the right type for you based on your symptoms, your overall health, and the results of diagnostic tests. A doctor may take a wait-and-see approach with a person who has a healthy liver and whose blood tests indicate a low viral load, the number of copies of the hepatitis B virus in your bloodstream.
Someone with HIV infection or AIDS may have a weakened immune system and is therefore more likely to develop liver damage. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention strongly recommends that people with HIV infection who are diagnosed with hepatitis B immediately begin treatment with antiviral medication.
Don’t Miss: Common Treatment For Hepatitis C
Hiv And Hbv Coinfection
About 2% of people with HIV in the United States are coinfected with HBV both infections have similar routes of transmission. People with HIV are at greater risk for complications and death from HBV infection. All people with HIV are recommended to be tested for HBV, and if susceptible, are further recommended to receive the hepatitis B vaccination or, if chronically infected, evaluated for treatment to prevent liver disease and liver cancer. For more information about HIV and HBV coinfection, visit HIV.govâs pages about hepatitis B and HIV coinfection.
How Is It Spread
Hepatitis B virus is spread by contact with body fluidsthat carry the virus, such as:
Hepatitis B is spread by contact with infected body fluids, mostly by:
- Sexual contact:
- Sharing unclean sex toys
- During illegal drug or drug equipment use
- Open sores of an infected person
- Sharing items such as razors or toothbrushes with an infected person
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools that were not properly cleaned
- Hepatitis B can spread to babies during pregnancy and birth.
Infected motherscan pass hepatitisB to their babiesduring childbirth.
Hepatitis B is rarely spread from a blood transfusion because:
- Hepatitis B tests are done on all donated blood.
- Blood and blood products that test positive for hepatitis B are safely destroyed. None are used for transfusions.
- There is no risk of getting hepatitis B when donating or giving blood.
Read Also: How Much Is Hepatitis A Vaccine
Recommendations For Adult Correctional Facilities
— Cases of hepatitis A should be reported to the appropriate public health authority . — Identification of a case of hepatitis A in a correctional facility should prompt an epidemiologic investigation by correctional officials, in collaboration with the appropriate health authorities, to identify the source of infection and contacts that might have been exposed . — Unvaccinated or known susceptible close contacts of a confirmed case of hepatitis A should be administered postexposure prophylaxis with a single dose of IG as soon as possible, but not > 2 weeks after the last exposure . Strongly recommended.
Transmission Of Hepatitis B
The hepatitis B virus is transmitted through blood and sexual fluids. This can most commonly occur in the following ways:
Direct contact with infected blood
From an infected pregnant person to their newborn during pregnancy and childbirth
Needles and other medical/dental equipments or procedures that are contaminated or not sterile
Unprotected sex
Use of illegal or street drugs
Body piercing, tattooing, acupuncture and even nail salons are other potential routes of infection unless sterile needles and equipment are used. In addition, sharing sharp instruments such as razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, earrings and body jewelry can be a source of infection.
Hepatitis B is NOT transmitted casually. It cannot be spread through toilet seats, doorknobs, sneezing, coughing, hugging or eating meals with someone who is infected with hepatitis B.
Read Also: What Is Autoimmune Hepatitis And How Is It Treated
How Is It Treated
Acute hepatitis B: There are no drugs to treat acutehepatitis B. Doctors usually suggest rest, goodnutrition, and fluids. Some people may need to be inthe hospital.
Chronic hepatitis B: People with chronic hepatitis Bvirus infection should receive care from a provider whohas experience treating hepatitis B. These providerscan be:
- Some internists or family medicine providers
- Infection specialists
- Gastroenterologists
If you have chronic hepatitis B, get checked regularlyfor signs of liver disease. Discuss treatment with yourhealth care provider. Not every person with chronichepatitis B needs treatment. If you show no signs ofliver damage, your provider will continue to check youfor liver disease.
Causes Of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is spread through contact with blood that contains the hepatitis B virus. If infected blood or body fluids enter another persons bloodstream, that person may become infected.
The time from exposure to the hepatitis B virus to the appearance of the illness is 45 to 180 days.
Risky activities that can cause infection include:
- Sharing unsterile or unclean equipment for injecting drugs.
- Piercing the skin with equipment that is not properly cleaned, disinfected and sterilised.
- Sharing razor blades or toothbrushes.
- Coming into contact with infected blood through open cuts or the mucous membranes of another person.
- Having unprotected sex , especially if there is blood present.
Mothers who have hepatitis B can pass the virus to their babies or children at the time of birth or after birth. If the newborn baby is quickly immunised with 2 vaccines, they can be protected from getting hepatitis B.
All blood and blood products produced for medical purposes in Australia are carefully screened for hepatitis B and other blood-borne viruses. The risk of getting infected with hepatitis B from a blood transfusion is extremely low .
Read Also: Can You Get Hepatitis From Your Own Blood
What Are The Risk Factors For Hepatitis B And C
Hepatitis B: Although most commonly acquired early in life, adults can also contract it. Hepatitis B is largely transmitted through bodily fluids. It can be passed at birth from a hepatitis B-infected mother or through exposure in early childhood to body fluids, blood or contaminated medical instruments. Hepatitis B can also be transmitted through intranasal and injection drug use as well as infected tools used during tattooing and body piercing.
Hepatitis C: The key risk factors are also intranasal and injection drug use, tattoos and body piercings, high-risk sexual contact, blood transfusions before 1992 and organ transplantation.
Another key risk factor for hepatitis C is being born from 1945 to 1965, during the baby-boom years. Eighty percent of all people who currently have hepatitis C in the United States were born in that timeframe.
Although the reasons that baby boomers are more likely to have hepatitis C than others arent entirely understood, its believed that most were infected in the 1970s and 1980s, when rates of hepatitis C were at their peak.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommend that all U.S. adults born from 1945 to 1965 undergo a one-time screening test for hepatitis C. Connecticut is one of several states that has written this recommendation into law. In Connecticut ,the law requires that primary care clinicians screen all adults born within those years.
How Are Hepatitis B And C Diagnosed

Hepatitis B is diagnosed by a series of blood tests. The test may show an ongoing infection or antibodies that indicate that the patient is protected against hepatitis B. In patients who have a positive screening test that suggests the possibility of ongoing infection, further testing is done to determine the levels of the virus in the bloodstream.
Hepatitis C is diagnosed via a blood test called a Hepatitis C Antibody Test. A positive result means that hepatitis C antibodies are present in the blood. But a positive antibody test doesnt necessarily mean a person has hepatitis C. A further blood test is needed to confirm the diagnosis. This second blood test quantifies the amount of the virus or the viral load in the liver and the bloodstream.
Don’t Miss: Justfoodfordogs Vet Support Diets Hepatic Support
How Do People Get The Hbv Virus
Hepatitis B virus is found in the blood of people with HBV infection. It enters the body through blood-to-blood contact.
Reliable blood tests for HBV were developed many years ago. Since blood donors and blood products are tested for HBV, this is no longer the typical means of infection.
In many parts of the world, hepatitis B virus infects more than 8% of the population. HBV-infected women pass the infection to their babies during the birth process. People can also get hepatitis B by sharing needles for injection drug use, through sexual contact with an infected person, by an accidental needlestick with a contaminated needle, or from improperly sterilized medical, acupuncture, piercing, or tattooing equipment.
How Can You Prevent Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B: Vaccination is the best way to prevent all the ways that hepatitis B is transmitted. People with HIV who do not have active HBV infection should be vaccinated against it. The hepatitis B vaccine is now recommended for all infants, children and adults ages 19-59, as well as adults ages 60+ at high risk for infection. There is a 3-dose series of hepatitis B vaccine given over 6 months, and a 2-dose series given over 1 month. Additionally, there is a 2-dose combination vaccine that protects against both hepatitis A and hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C: No vaccine exists for HCV and no effective pre- or post-exposure prophylaxis is available. Injection drug use is one of the risk factors for hepatitis C. For people who inject drugs, the best way to prevent hepatitis C infection is to always use new, sterile needles or syringes, and never reuse or share needles or syringes, water, or other drug preparation equipment. Community-based prevention programs, such as medication-assisted treatment and syringe services programs provide support and services aimed at preventing and reducing the transmission of HCV. Although the risk of sexual transmission of HCV is considered to be low, avoiding unprotected sexual exposure by using condoms has been shown to reduce the chance of sexually transmitted infections.
Recommended Reading: How You Get Hepatitis B
Duration Of Protection After Hbv Immunization In Infancy
Anti-HBs titers gradually decline with age in children immunized in infancy with hepatitis B vaccine, which is also seen in those who received a booster dose during childhood . In a prospective long-term follow-up study of 1200 HBV vaccinees in the general population , the annual new anti-HBc seropositive rate was low , and no new chronic HBV infection was detected. The decay rate of anti-HBs titer during age 716 yr was 20% of the titer of the previous year. Among the uninfected children who had anti-HBs < 10 mIU/mL, the boosted and nonboosted children developed new anti-HBc positivity at a similar rate, indicating that a vaccine booster at this age is not necessary .
Check If You Have Hepatitis B
Symptoms of hepatitis B infection include:
- a high temperature
- pain in your upper tummy
- feeling sick or being sick
- patches of raised skin that may be itchy
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
The infection usually lasts for 1 to 3 months and most people either have no symptoms or mild symptoms. If the infection lasts longer than 6 months it is called chronic hepatitis B.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis Rash Look Like
Combination Of Passive And Active Immunization
A pilot clinical trial combining active and passive immunization with injection of HBIG within 24 h after birth followed by three doses of HBV vaccine further reduced the HBsAg carrier rate to 3% in infants. The results of early clinical trials for HBV immunization conducted in Taiwan established the ground for the universal HBV immunization strategies and programs used currently.
Global View Of Hbv Immunization
In 2009, the World Health Organization recommended that all infants receive the hepatitis B vaccine as soon as possible after birth, preferably within 24 h. The birth dose should be followed by two or three doses to complete the primary series. In 1992, the World Health Assembly passed a resolution to recommend global vaccination against hepatitis B. Furthermore, as of July 2011, 93 member states have introduced the hepatitis B birth dose . WHO recommended that high-risk groups should be vaccinated. They include people who frequently require blood and/or blood products, dialysis patients, recipients of solid organ transplantations people interned in prisons IV drug users household and sexual contacts of people with chronic HBV infection people with multiple sexual partners, health-care workers, and others who are exposed to blood or blood products through work and travelers who have not completed their hepatitis B vaccination series before leaving for endemic areas.
The global hepatitis B vaccine coverage rate was estimated at 75%, and was as high as 91% in the Western Pacific and 89% in the Americas. Coverage in Southeast Asia reached 52% in 2010. In 2011, 180 countries had introduced infant HBV vaccination, and the global HBV vaccination coverage rate for the third dose was estimated to be 78%.
Read Also: Hepatitis B Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Who Should Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine
All newborn babies should get vaccinated. You should also get the shot if you:
- Come in contact with infected blood or body fluids of friends or family members
- Use needles to take recreational drugs
- Have sex with more than one person
- Are a health care worker
- Work in a day-care center, school, or jail
How Do You Get Hepatitis B
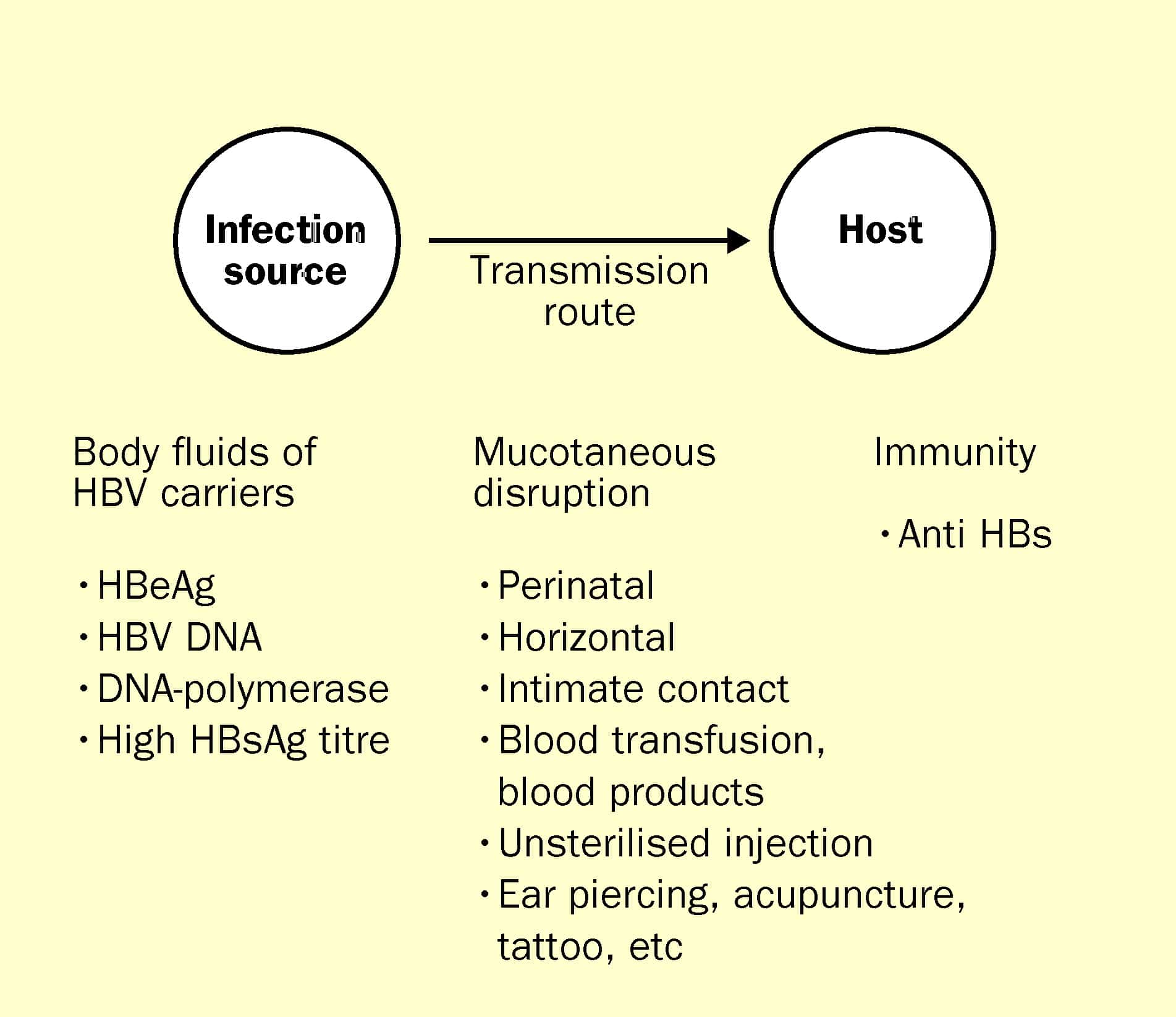
-
sharing toothbrushes and razors
-
sharing needles for shooting drugs, piercings, tattoos, etc.
-
getting stuck with a needle that has the Hep B virus on it.
Hepatitis B can also be passed to babies during birth if their mother has it.
Hepatitis B isnt spread through saliva , so you CANT get hepatitis B from sharing food or drinks or using the same fork or spoon. Hepatitis B is also not spread through kissing, hugging, holding hands, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding.
Recommended Reading: Hepatitis B And C How Do You Get It
Also Check: How To Find Out If You Have Hepatitis