Why Should People Take Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis C
The purpose of taking antiviral medications for hepatitis C is to:
- remove all the hepatitis C virus from your body permanently
- stop or slow down the damage to your liver
- reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis
- reduce the risk of developing liver cancer
- reduce the risk of liver failure and the need for a liver transplant
Model Structure And Assumptions
In this study, an established Markov model , developed in Microsoft Excel 2013, was used from Chinese payer perspective to estimate the lifetime outcomes of treating a cohort of HCV genotype 1b treatment-naïve patients with two hypothetical regimens, DCV+ASV and PR . The model runs in annual cycles over a lifetime horizon and an annual discount rate of 5% was applied.
How Is It Treated
Hepatitis A is treated using supportive methods. These can include things like rest, fluids, and healthy foods. Medications can also help to ease some symptoms like fever, aches, and pains.
Theres a vaccine available to protect against infection with HAV. This is typically recommended for children as well as for people at an increased risk for contracting the virus.
Also, receiving a single dose of the hepatitis A vaccine may prevent you from becoming ill if youve been exposed to HAV. For it to be effective, the vaccine needs to be given of exposure.
You May Like: Where Can I Get The Hepatitis B Vaccine For Free
Also Check: How To Get Hepatitis D
Is There A Cure For Chronic Hepatitis B
Currently, there is no complete cure for hepatitis B. But when managed properly, those living with the virus can expect to live a normal life. Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding alcoholic beverages and tobacco products are crucial components in managing the disease.
You should also visit a doctor familiar with hepatitis B at least annuallythough twice a year might be best to monitor your liver through blood tests and medical imaging. As with most diseases, detecting it early leads to a better outcome. If youre exposed to the virus, you should get an antibody injection within 12 hours of exposure.
Also Check: How Does One Contact Hepatitis C
Persons Who Inject Drugs
Injection drug use is the most common risk factor for HCV infection in the United States and Europe, with an HCV seroprevalence rate of 10% to 70% . IDU also accounts for the majority of new HCV infections and is the key driving force in the perpetuation of the epidemic. Given these facts and the absence of an effective vaccine against HCV, testing and linkage to care combined with treatment of HCV infection with potent DAAs has the potential to dramatically decrease HCV incidence and prevalence . However, treatment-based strategies to prevent HCV transmission have yet to be studied, including how to integrate hepatitis C treatment with other risk-reduction strategies .
In studies of interferon-based treatments in persons who inject drugs, adherence and efficacy rates are comparable to those of patients who do not use injected drugs. A meta-analysis of treatment with peginterferon, with or without ribavirin, in active or recent injection drug users showed SVR rates of 37% and 67% for genotype 1 or 4, and 2 or 3, respectively . With the introduction of shorter, better-tolerated, and more efficacious interferon-free therapies, these SVR rates are expected to improve. Importantly, the rate of reinfection in this population is lower than that of incident infection in the general population of injection drug users , although reinfection increases with active or ongoing IDU and available data on follow-up duration are limited .
Read Also: How Do People Contract Hepatitis C
Helpful Tips While Taking Hepatitis C Medications
- Always follow your health care providers’ advice, particularly the instructions on taking your medicine.
- If you have to cancel an appointment, call your provider and schedule a new one as soon as possible.
- Take good care of yourself. Eat well, drink 8 to 10 glasses of water each day, and try to get a full night’s sleep.
- Learn about the hepatitis C medications you are taking. This includes special risks and warnings.
- If taking ribavirin, use sunscreen, wear long sleeves and a hat, and limit sun exposure.
- Write down your doctor’s name and phone number. Carry this information with you at all times.
- Write the names and amounts of the medicines you are taking. Carry this information with you at all times.
Environmental Assessment And Support
Environmental support is an important part of patient assessment because treatment may be given for up to one year, and the adverse effects of treatment may incapacitate patients. A patient’s living situation and household income should be addressed prior to treating treatment. Homelessness may be a significant problem, and the need for a support network for such patients should be assessed and arranged before the treatment. In addition, most formulations of pegylated interferon now require refrigeration. Family meetings can be helpful to prepare family members for side effects of treatment. Neuro-psychiatric side effects such as irritability and hostility can strain relationships if unexpected. These issues can be assessed with the collaboration of social services. Family and friends may need to help with activities of daily living including transportation to medical appointments.Home health nurses and case managers may be helpful in providing support at home.
Recommended Reading: What Does Hepatitis C Antibody Mean
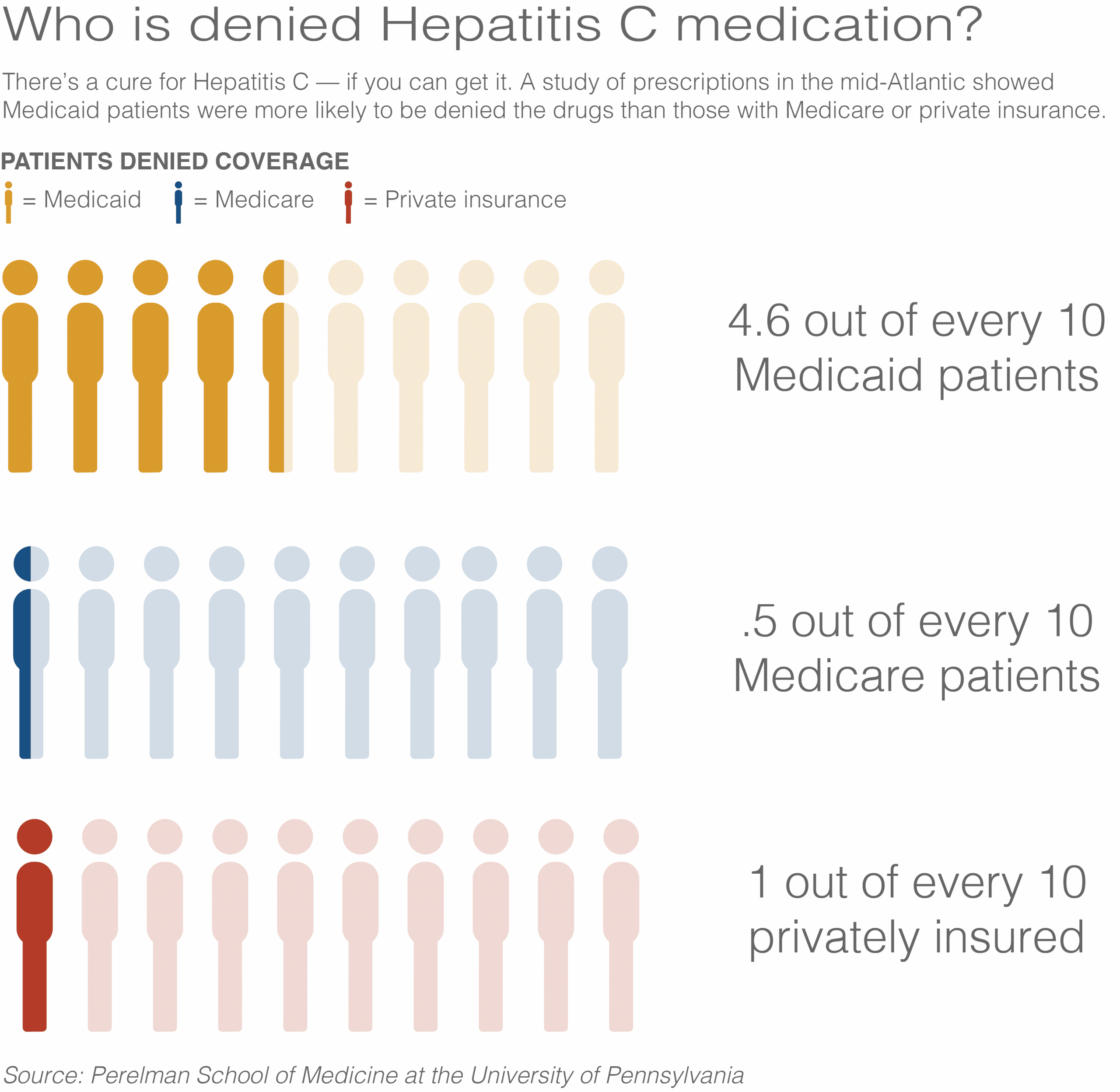
Cost Of Hepatitis C Medicines
The newer direct-acting antiviral medicines for hepatitis C can be costly. Most government and private health insurance prescription drug plans provide some coverage for these medicines. Talk with your doctor about your health insurance coverage for hepatitis C medicines.
Drug companies, nonprofit organizations, and some states offer programs that can help pay for hepatitis C medicines. If you need help paying for medicines, talk with your doctor. Learn more about financial help for hepatitis C medicines.
How Do Doctors Treat The Complications Of Hepatitis C
If hepatitis C leads to cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Doctors can treat the health problems related to cirrhosis with medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If you have cirrhosis, you have an increased chance of liver cancer. Your doctor may order an ultrasound test to check for liver cancer.
If hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Don’t Miss: What’s In Hepatitis B Vaccine
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Hcv
An estimated 240,000 children in the United States have antibodies to hepatitis C. The seroprevalence is 0.2% for children under 12 years of age and 0.4% for those 12 to 19 years of age. Cross-sectional studies indicate that viremia is present in 50% to 75% of children. Children at risk for HCV infection include those born to HCV-infected mothers and those who received blood or blood products prior to 1992. The rate of spontaneous viral clearance varies by age at acquisition and generally occurs within the first year after acute infection. At present, new HCV infections in children are primarily the result of vertical transmission.
Monitoring While On Treatment
Recommendations
Patients who do not achieve virologic suppression or a 2-log decrease in HCV RNA at 12 weeks may have therapy discontinued, although factors such as degree of fibrosis and tolerability of therapy should be considered.
Patients should have a CBC and chemistry evaluations 2 weeks after initiation of treatment to assess for potential toxicities. CBC, chemistry evaluations, and pregnancy tests in women should be done routinely at each follow-up visit and not less often then every 4-6 weeks during treatment.
Patients who achieve an end-of-treatment virological response should have HCV RNA testing performed 24 weeks after stopping treatment to evaluate for a SVR.
Erythropoetin alfa and granulocyte colony stimulating factor may be used to treat anemia and neutropenia, respectively, in order to maintain the patient on full medication doses.
Providers should reference the full discussion of side effects of hepatitis C treatment in Appendix A.
Pegylated interferon and ribavirin have been found to be safe and effective in HCV mono-infection and in co-infection with HIV.2,61 Safety and efficacy has not been established in patients who have received liver or other organ transplants, in patients who have failed other alpha interferon treatments and in patients under the age of 18.56,57
Recommended Reading: Hepatic Porphyrias Diagnosis And Management
How Genotypes Affect Treatment
Medications known as direct acting antivirals, or DAAs, stop the hep C virus from making copies of itself. Some DAAs appear to work well on all hepatitis C genotypes. Others work on only one or some.
Your doctor will probably prescribe some combination of these medications:
Some pills combine two drugs into one pill.
Youll probably take these meds for anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks. But they may not be right for everyone because of things like cost or other illnesses.
Your specific genotype can tell your doctor important things about how to use those medications, what to watch for, and other drugs you might need.
For example, you may have a higher chance for cirrhosis if you have genotype 1.
Genotype 3, the second most common subtype worldwide, may not respond as well to DAAs alone. In addition, this type might suggest that:
- Liver cancer is more likely.
- Insulin resistance might happen. When your body resists or doesnt respond to insulin as well as normal, you have a higher chance of heart disease and diabetes.
- You might need longer, more challenging treatment
Your doctor might adjust or change your DAA treatment if you have:
Show Sources
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: âInitial Treatment of Adults with HCV Infection,â âHCV Guidance: Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C.â
CDC: âHepatitis C Questions and Answers for the Public.â
Infohep.org: âHepatitis C treatment factsheet: Harvoni .â
Will A Specialist Need To Be Involved
In order to prescribe, general practitioners including physicians with expertise in viral hepatitis, will be required to first consult with a gastroenterologist, hepatologist or infectious diseases physician to ensure patients with liver disease or other complex needs are appropriately referred to specialist care. A face to face consult with the specialist is not required and patients with complex needs will likely be referred to specialist care where appropriate.
Patients affected by hepatitis C with severe or advanced liver disease may still need to access the treatments under the care of a specialist – such as a gastroenterologist, hepatologist, or an infectious disease physician with experience in treating chronic hepatitis C infection.
You May Like: Hepatitis C Can You Catch It
Treatment Of Patients After Solid Organ Transplantation
The prevalence of hepatitis C infection in the recipients of solid organ transplants depends on the organ received. Currently, 40% to 50% of liver recipients are infected with HCV, whereas the proportion of cardiac, lung, and kidney transplant recipients with HCV infection is lower. Among recipients of liver allografts, the majority with pretransplantation infection have persistent virus posttransplantation, and persistent infection is often associated with progressive liver disease. Similarly, HCV viremia persists in other organ transplant recipients with pretransplantation infection and may result in rapid progression of liver disease in those with advanced fibrosis. In addition, recipients of heart, lung, or bone marrow transplants with posttransplantation HCV infection may have acquired their infection as a result of infected grafts, blood, or blood products, particularly before 1992, when routine screening for HCV was introduced. Since then, the risk of acquiring HCV during the peritransplant period has been very low.
Adverse events are frequent, particularly ribavirin-associated anemia, most likely as a result of calcineurin inhibitor-induced renal insufficiency. Once patients develop cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation is common. Results of retransplantation for HCV disease are generally poor. Studies using pegylated interferon and ribavirin are ongoing to refine further the appropriate posttransplantation therapies.
Benefits Of Treatment At Early Fibrosis Stages
Initiating therapy in patients with lower-stage fibrosis augments the benefits of SVR. In a long-term follow-up study, 820 patients with biopsy-confirmed Metavir stage F0 or F1 fibrosis were followed for up to 20 years . The 15-year survival rate was significantly better for those who experienced SVR than for those whose treatment failed or those who remained untreated . The study results argue for consideration of earlier initiation of treatment. Several modeling studies also suggest a greater mortality benefit if treatment is initiated at fibrosis stages prior to F3 .
A modeling study based on the Swiss HIV cohort study also demonstrated that waiting to treat HCV infection until Metavir fibrosis stages F3 and F4 resulted in 2- and 5-times higher rates of liver-related mortality, respectively, compared with treating at Metavir stage F2 . A US Veterans Administration dataset analysis that used very limited endpoints of virologic response dating from the interferon-treatment era suggested that early initiation of therapy increased the benefit attained with respect to likelihood of treatment success and mortality reduction, and ultimately decreased the number of patients needed to treat to preserve 1 life by almost 50% .
Also Check: Is There A Cure For Hepatitis C Now
Exacerbation Of Chronic Viral Hepatitis
In the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, HBe seroconversion was sometimes preceded by transient and moderate worsening of serum transaminases, but severe exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection and fatal liver failure can occur. Such fatalities were reported in under 0.5% of patients with hepatitis B . Patients with active cirrhosis or a previous history of decompensated cirrhosis are particularly susceptible to these complications .
Acute exacerbation of hepatitis is an extremely rare complication of chronic hepatitis C treatment. An exaggerated immune response to hepatitis virus was supposedly the cause of acute icteric hepatitis in two patients .
-
A 43-year-old man had a moderate rise in hepatic transaminase activities after 4 weeks of interferon alfa treatment. His liver tests normalized after withdrawal, but the aspartate transaminase activity increased dramatically shortly after treatment was restarted. His condition rapidly deteriorated, with a diagnosis of hepatorenal failure, and he finally required liver transplantation. Histological examination of the liver showed advanced micronodular cirrhosis, a feature not found on pretreatment liver biopsy.
In another study, only four of 11 241 patients treated with interferon alfa died of fulminant liver failure .
Talia B. Baker, Juan Carlos Caicedo, in, 2017
What Are The New Hepatitis C Treatments And When Will They Be Available
Recent advances in antiviral treatment have led to the development of new highly effective drugs for the treatment of all types of hepatitis C.
The new hepatitis C treatments are sofosbuvir with ledipasvir sofosbuvir daclatasvir and ribavirin .
These new treatments will be available on the Pharmaceuticals Benefits Scheme from 1 March 2016.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Difference Between Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Geographic Distribution Of Hcv Genotypes
At least six major genotypes of HCV, each comprising multiple subtypes, have been identified worldwide . Substantial regional differences appear to exist in the distribution of HCV genotypes .2). Although HCV genotypes 1, 2, and 3 appear to have a worldwide distribution, their relative prevalence varies from one geographic area to another .2).
Worldwide geographic distribution of HCV genotypes and subtypes. Others indicate unclassified sequences.
HCV subtypes 1a and 1b are the most common genotypes in the United States 3) . These subtypes also are predominant in Europe . In Japan, subtype 1b is responsible for up to 73% of cases of HCV infection . Although HCV subtypes 2a and 2b are relatively common in North America, Europe, and Japan, subtype 2c is found commonly in northern Italy. HCV genotype 3a is particularly prevalent in intravenous drug abusers in Europe and the United States . HCV genotype 4 appears to be prevalent in North Africa and the Middle East , and genotypes 5 and 6 seem to be confined to South Africa and Hong Kong, respectively . HCV genotypes 7, 8, and 9 have been identified only in Vietnamese patients , and genotypes 10 and 11 were identified in patients from Indonesia . There has been disagreement about the number of genotypes into which HCV isolates should be classified. Investigators have proposed that genotypes 7 through 11 should be regarded as variants of the same group and classified as a single genotype, type 6 .
Genotypes And Hcv Genetic Heterogeneity As Epidemiologic Markers
Because of geographic clustering of distinct HCV genotypes, genotyping may be a useful tool for tracing the source of an HCV outbreak in a given population. Examples include tracing the source of HCV infection in a group of Irish women to contaminated anti-D immunoglobulins . All of these women were infected with HCV genotype 1b, a genotype identical to the isolate obtained from the implicated batch of anti-D immunoglobulin. Hohne et al. used genotyping to trace the sources of outbreaks in Germany . More recently, genotyping and molecular characterization of HCV isolates provided evidence for a patient-to-patient transmission of HCV during colonoscopy . The index case as well as the two other infected patients had HCV genotype 1b. Nucleotide sequencing of the NS3 region showed that the three patients had the same isolate , strongly suggesting a common source of infection.
Although Zein et al. found no association between HCV genotypes and the mode of HCV acquisition in their population, others have provided evidence for such an association . It has been suggested that genotypes 3a and 1a are closely associated with intravenous drug use and that genotype 1b is seen more often in patients who acquired HCV through blood transfusion. This information may be useful in tracing sources of HCV epidemics.
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted More Easily Than Hepatitis
Where Are The Different Hepatitis C Genotypes Found
HCV has evolved over time into 7 distinct genotypes , with at least 67 subtypes. Hepatitis C genotypes are distributed throughout the world, with some genotypes being predominant in certain geographic areas. HCV genotype 1 is the most common genotype in the US and Europe, accounting for 60% to 70% of HCV. HCV genotype 1a is more common than 1b in the US. 3
Hepatitis C genotypes 1 and 3 infection are associated with more aggressive liver disease, with increased risk for cirrhosis and fibrosis, as well as greater risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. After genotype 1, HCV genotype 2 is the next most common HCV genotype in the US, where it accounts for approximately 10% of cases. HCV genotypes 3-6 are more common in Africa, the Middle East, the Far East, India, and Australia. Genotype 7 has only been isolated in a limited number of cases. Genotype 3 is associated with increased risk for development of fatty liver disease . 1,4
Hepatitis C genotypes are substantially different from one another in their genetic make-up, which explains why each genotype responds differently to antiviral treatments.1,4
Also Check: Hepatitis B Vaccine Schedule For Baby