What Is The Purpose Of A Hepatitis B Test
Hepatitis B test is performed to detect, classify, and treat hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B blood tests involve the measurement of several HBV-specific antigens and antibodies. In addition, HBV blood tests also include liver enzymes and liver function tests to assess and monitor the condition of the liver and provide appropriate treatment.
The HBV specific tests include the following:
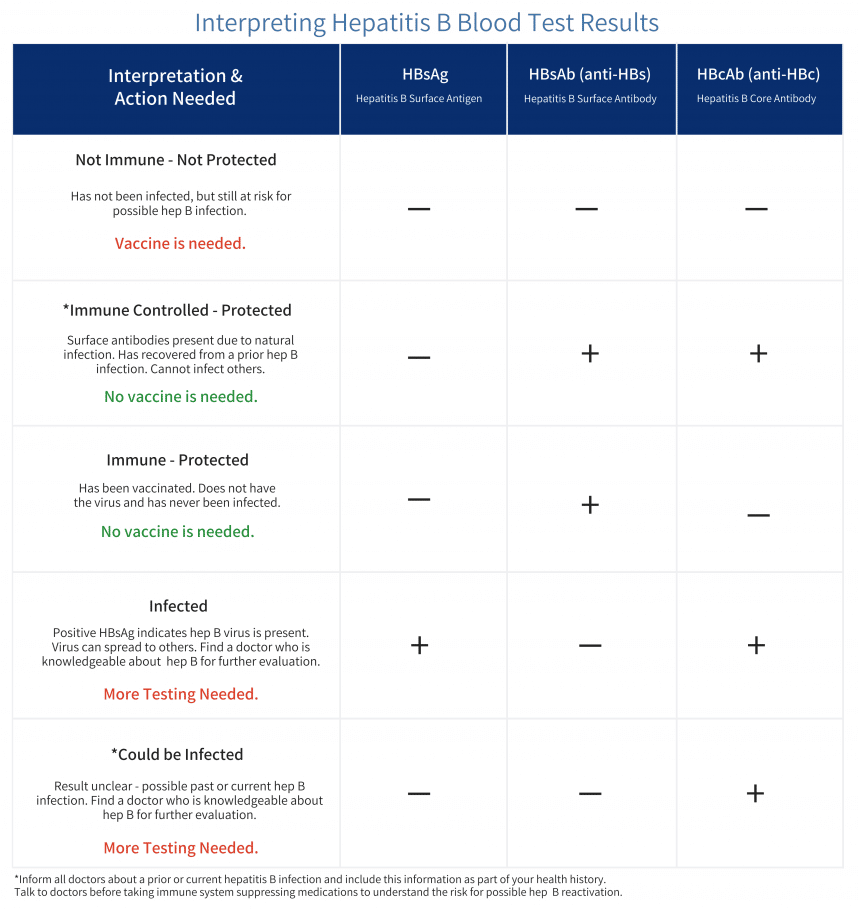
- HBsAg: HBsAg is an antigen found on the surface of hepatitis B virus. HBsAg may be detected in the blood any time after 1 week post-exposure to HB virus, but usually appears after 4 weeks.
- Anti-HBs: Anti-HBs are antibodies produced by the bodys immune system to fight HBsAg. Anti-HBs from a prior infection or vaccination provides immunity against further infection.
- Hepatitis B core antigen : HBcAg is an antigen found in the core layer which covers the hepatitis B viral DNA.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : Anti-HBc is the antibody that fights HBcAg. Anti-HBc is the first detectable antibody after HBV infection. There are two kinds of Anti-HBc:
- Immunoglobulin M hepatitis B core antibody : IgM anti-HBc indicates acute or reactivated recent infection within the previous 6 months.
- Immunoglobulin G hepatitis B core antibody : IgG anti-HBc may indicate previous or chronic infection. Once present, IgG anti-HBc persists for a lifetime.
What Is The Difference Between Hepatitis B Surface Antibody And Antigen
An antigen is a substance that induces antibody production. Hepatitis B surface antigen is a protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus.
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the bodys immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.
Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Qualitative
Test Code: 499
Methodology: Immunoassay
Clinical Significance: The detection of anti-HBs is indicative of a prior immunologic exposure to the antigen or vaccine. To determine immune status as 10 mIU/mL as per CDC guidelines, please order Hepatitis B Surface Antibody, Quantitative.
Alternative Name: Anti-HBS Anti-HBS Qual Anti-HBSAG Australian Antibody HB Surface Ab
Supply: T01 â Red/Gray SST 8.5mL
Preferred Specimen: Serum
Transport Container: Serum Separator Tube
Transport Temperature: Room Temperature
Specimen Stability: Room Temperature: 5 days
Rejection Criteria: Gross Hemolysis, Gross Lipemia
For additional supply or collection device information, please contact DLOâs Customer Service at 891-2917, option 2.
The information contained here on the Diagnostic Laboratory of Oklahoma website is not to be construed as medical recommendations or professional advice. Neither DLO nor its affiliates, agents or any other party involved in the preparation or publication of the works presented is responsible for any errors or omissions in information from the use of such information. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information contained herein with other reliable sources and to direct any questions concerning personal health care to licensed physicians or other appropriate health care professionals.
Also Check: Where To Get Hepatitis A Vaccine
Read Also: Types Of Hepatitis And How They Are Transmitted
Important Information About Vaccine And Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin Shot Administration
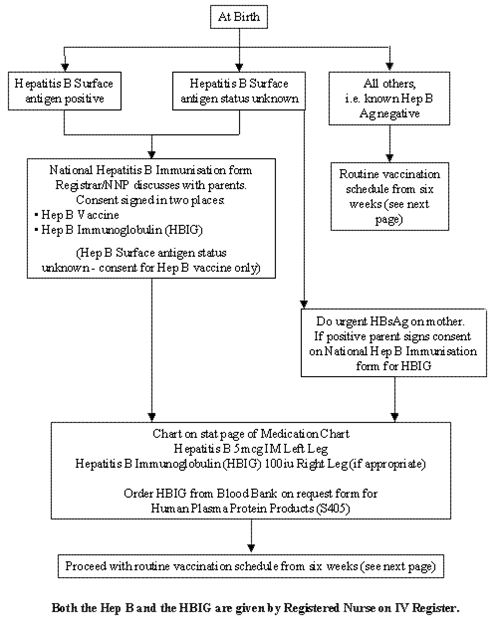
Where available, the hepatitis B birth-dose and HBIG should be administered within 24 hours of birth in order to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B from mother to child. It is very important that the shots be given in opposite limbs, to ensure the highest effectiveness. Please see chart above for more information.
Hepatitis B Immunization And Postimmunizationserology
Michael John, MB, Ch.B., FRCP
Before the introduction of avaccine, hepatitis B virus was a major occupational risk to health care workers.Some of the highest infection rates were found in dentists and surgeons.1Infected health care workers have a 5-10% risk of developing chronic hepatitis B. A numberof clusters of dentist-to-patient HBV transmissions have been reported over the years,although these have decreased since the introduction of universal precautions.2Recent guidelines from Health Canada recommend restriction of practice of health careworkers who test positive for hepatitis B e antigen.3
The development of hepatitis vaccines in the 1980s has substantially decreased dentalworkers risk of acquiring HBV. A recent survey4 of dentists in Canadashowed that more than 90% had completed an immunization series and an additional 3% hadnatural immunity. However, rates of immunization among dental assistants and hygienistswas found to be much lower.
Hepatitis B Vaccines
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle, as glutealinjection may result in decreased response rates. Response to vaccine following a 3-doseseries is typically greater than 95% in young, healthy people, although it decreases withage . Other factors such assmoking, obesity and chronic disease decrease vaccine efficacy and may be used to predictrisk of nonresponse.6 Adverse events are minimal, although mild injection-sitereactions may occur in 20% of recipients.
References
Recommended Reading: Is Hepatitis A Vaccine A Live Virus
Preparation Prior To Transport
Label the specimen container with the patients full name, date of collection and one other unique identifier such as the patients date of birth or Health Card Number. Failure to provide this information may result in rejection or testing delay.
Centrifuge if using SST. Place specimen in biohazard bag and seal. Specimens should be stored at 2-8°C following collection.
Specimens more than the following number of days post collection will not be tested:
- > 6 days for Hepatitis B surface antigen
- > 7 days for Hepatitis B e Antigen and Hepatitis B e Antibody
- > 10 days for Hepatitis B core Antigen and Hepatitis B surface Antibody
What Are My Next Steps Once I Get My Results
It can be difficult to understand what the results of your test mean. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your results and decide whether you need to take further action:
- If your results suggest that youre already immune to hepatitis B and arent contagious, you likely wont need to do anything.
- If your results suggest that youre not immune, a doctor may recommend vaccination, especially if youre somebody whos at a high risk of infection.
You may also need additional testing if more information is needed to interpret your results.
Don’t Miss: How Is Hepatitis B Contracted
Response To Booster Dose
Because study participants in group 3 received a booster vaccine dose 8 years earlier , they did not receive a booster dose at 30 years. Study participants in groups 1 and 2 with anti-HBs levels < 10 mIU/mL received booster doses however, because group 2 participants had anti-HBs levels 10 mIU/mL at 22 years, we chose to focus on group 1 for booster dose response. In group 1, among 118 eligible participants, 96 who had anti-HBs levels < 10 mIU/mL received a booster dose of hepatitis B vaccine. The median age of the 85 persons from whom serum was obtained after the booster dose was 40 years 47 were male. Among these 85 persons tested 30 days after the booster dose, 75 responded with anti-HBs levels 10 mIU/mL the GMC was 150.4 mIU/mL .
Level of Anti-HBs After Hepatitis B Vaccine Booster Dose in Persons Who Responded to the Primary Series, Had Not Received Subsequent Doses, and Had a 30-Year Anti-HBs Level < 10 mIU/mLAlaska, 20112012
| Characteristic . |
|---|
Who Should Get The Hbv Vaccine
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends that all children and adults up to age 59 should receive the hepatitis B vaccine.
Infants should get their first hepatitis B vaccine within 24 hours of birth and complete their doses by age 6 to 18 months.
All unvaccinated children and adults through age 59 should receive the vaccine. Also, unvaccinated adults over the age 60 who are at risk of hepatitis B should get the vaccine.
Adults over age 60 who are not at risk of hepatitis B may also choose to get the shot.
Several types of the HBV vaccine are also safe to administer to pregnant women.
- people who have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months
- men who have sex with men
- people seeking treatment for a sexually transmitted infection
- people whose partners or household members have hepatitis B
- people who inject drugs
- people who live or work in care facilities
- people who are on dialysis
- travelers to countries where hepatitis B is common
- people with chronic liver disease, HIV, or hepatitis C
- people who are in jail or prison
People who have diabetes should talk with a healthcare professional about their risk for contracting hepatitis B.
Also Check: Natural Treatment For Hepatitis C
Concurrent Administration Of Vaccines
HB-containing vaccines may be administered concomitantly with other vaccines or with HBIg. Different injection sites and separate needles and syringes must be used for concurrent parenteral injections.
Refer to Timing of Vaccine Administration in Part 1 for additional information about concurrent administration of vaccines.
Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
Doctors must closely monitor pregnant people who have HBV.
There is a risk that the virus can pass from parent to child during delivery without the correct treatment. Therefore, all people should receive hepatitis B testing during pregnancy. A person with chronic hepatitis B should talk with a doctor about the risks and benefits of antiviral treatment while pregnant.
According to the Hepatitis B Foundation, if someone has HBV, their newborn must immediately receive the first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immune globulin within 12 hours of birth. The infant should then receive the second and third doses of the vaccine according to the standard childhood immunization schedule.
Pregnant people unsure of their vaccination status can receive the hepatitis B vaccine during pregnancy and breastfeeding or chestfeeding.
However, there is currently not enough safety information about Heplisav-B and PreHevbrio, so pregnant people
You May Like: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody Interpretation
Whats The Procedure For A Hepatitis B Titer Test
A hepatitis titer test requires a healthcare professional to draw a small amount of blood for testing.
No special preparation is needed beforehand. If needles or the sight of blood make you anxious, you may want to arrange a drive ahead of time in case you feel faint.
Heres what will typically happen during this test:
Home tests that require a fingerpick are also available. The results of your tests are generally available within 3 days.
Hepatitis B Vaccine Side Effects
The hepatitis B vaccine is considered a very safe and effective vaccine. Its made with an inactivated virus, so most types of the vaccine are even safe for pregnant people.
The hepatitis B vaccine may cause some mild side effects. The most common symptom is redness, swelling, or soreness where the injection was given. Some people also experience headache or fever. These effects usually last a day or two .
Rarely, some people have a serious and potentially life threatening allergic reaction to the vaccine. Call 911 or get to a hospital immediately if you experience any of the following symptoms after vaccination:
Also Check: What Is Hepatitis B From
When And How To Perform Post
Which test to use: If testing is needed following vaccination, use quantitated HBsAb only
- Post-vaccination testing is needed for certain groups who are at especially high risk for HBV infection
- The purpose of post-vaccination testing is to confirm if patients have achieved adequate immune response as measured by hepatitis B surface antibody
- Perform testing 1-2 months after final dose of the HBV vaccine series
- Persons with HBsAb concentrations of > 10 mIU/ml are considered immune
- Post-vaccination testing is recommended for some patients:
- Infants born to HBsAg+ women
- Infants born to women whose HBSAg status remains unknown
- Health care personnel and public safety workers at risk for blood or body fluid exposure
- Hemodialysis patients
- Other immunocompromised persons such as hematopoietic stem-cell transplant patients or persons receiving chemotherapy
- Sex partners of HBSAg+ persons
Cases And Clusters Of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis B data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis B that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation based on the degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
- People of childbearing age who are or have the potential to become pregnant, indicating the potential for perinatal transmission
- Children 24 months of age to detect perinatal transmission
- People in age and demographic groups for whom infection may be acute due to recent transmission, including those
- 70 years of age
You May Like: How To Test For Autoimmune Hepatitis
When Should You Have The Test
Anyone who has symptoms of hepatitis B may benefit from having the test. Other people who may consider undergoing the hepatitis B panel test are those with known risk factors. These people include individuals born in places with a high incidence of HBV infection and those who use needles to inject drugs.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Effects On Liver
Thawing And Resting Of Pbmc
PBMC were thawed at 37°C using CTL Anti-Aggregate Wash 20x Solution Europe, Bonn, Germany) diluted in RPMI-1640 medium . Cells were counted with an automated cell counter in CTL-Test Medium Europe, Bonn, Germany). The median cell recovery after thawing was 4.4 x 106 PBMC per vial with a median viability of 92%. For a standard resting procedure PBMC were incubated for 18 h at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere at 5% CO2 in a concentration of 2 x 106 PBMC/mL CTL-Test medium supplemented with 10% FCS and 1% penicillinstreptomycin RPMI-10. The median cell recovery after resting was 4.2 x 106 PBMC per vial with a median viability of 94%.
Also Check: Hepatitis B Cure Latest News 2020
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
How Do Doctors Test For Hepatitis B Immunity
Doctors may order a panel of blood tests to check if someone has HBV:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen : This test looks for the presence of HBV in the blood by looking for antigens found on the virus. A positive result means that a person has HBV.
- Hepatitis B surface antibody : This test can show if a person is immune and protected against HBV. A positive result indicates that the person has overcome a past HBV infection or it is the result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine.
- Hepatitis B core antibody : This test looks for another antibody in the HBV, but this one does not provide protection. A positive result indicates that a person had a past infection or currently has HBV.
Some people with certain risk factors for hepatitis B infection, such as those who inject drugs, pregnant people, and other populations, may require testing postvaccination to check their immunity.
Also Check: What Type Of Hepatitis Is Contagious
Are Hepatitis B Virus Infections Easily Avoided
Large quantities of hepatitis B virus are present in the blood of people with hepatitis B in fact, as many as one billion infectious viruses can be found in a milliliter of blood from an infected individual. Therefore, hepatitis B virus is transmitted in the blood of infected individuals during activities that could result in exposure to blood, such as intravenous drug use, tattooing, or sex with people who are infected. However, it is also possible to catch hepatitis B virus through more casual contact, such as sharing washcloths, toothbrushes or razors. In each of these cases, unseen amounts of blood can contain enough viral particles to cause infection. In addition, because many people who are infected don’t know that they are infected, it is very hard to avoid the chance of getting infected with hepatitis B virus.
Baseline Characteristics Of Enrolled Participants
Between 1997 and 1999, 2436 newborns who received a full course of primary vaccination were initially recruited in the study cohort, and 1551 participants were followed in 2017. Of the 1551 individuals, 199 individuals with a history of booster vaccination were excluded, and 1352 participants were included in the final analysis. Of the 1352 participants, 616 were male, and the average age of the enrolled participants was 19.3years . All participants completed primary vaccination at day 187.2 after birth, resulting in an average of 18.8 follow-up years.
You May Like: Antiviral Medications For Hepatitis C